
Extreme physical information
Encyclopedia
Extreme physical information (EPI) is a principle, first described and formulated in 1998 by B. Roy Frieden
, Emeritus Professor of Optical Sciences at the University of Arizona
, that states, the precipitation of scientific laws can be derived through Fisher information
, taking the form of differential equation
s and probability distribution function
s.
stated that:
By using Fisher information
, in particular the loss I - J incurred during observation, the EPI principle provides a powerful new approach for deriving laws governing many aspects of nature and human society. EPI can be seen as an extension of information theory
that encompasses much theoretical physics
and chemistry
. Examples include the Schrödinger wave equation and the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law. EPI has been used to derive a number of fundamental laws of physics
, biology
, the biophysics
of cancer
growth,chemistry
, and economics
. EPI can also be seen as a game
against nature, first proposed by Charles Sanders Peirce. The approach does require prior knowledge of an appropriate invariance principle or data.
in the data is , and the Fisher information in the source is
, and the Fisher information in the source is  , the EPI principle states that:
, the EPI principle states that:
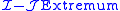
The extremum for most situations is a minimum, meaning that there is a comforting tendency for any observation to describe its source faithfully.
B. Roy Frieden
B. Roy Frieden is an American mathematical physicist.Frieden obtained a Ph.D. in Optics from The Institute of Optics at the University of Rochester. His doctoral thesis advisor was Robert E. Hopkins...
, Emeritus Professor of Optical Sciences at the University of Arizona
University of Arizona
The University of Arizona is a land-grant and space-grant public institution of higher education and research located in Tucson, Arizona, United States. The University of Arizona was the first university in the state of Arizona, founded in 1885...
, that states, the precipitation of scientific laws can be derived through Fisher information
Fisher information
In mathematical statistics and information theory, the Fisher information is the variance of the score. In Bayesian statistics, the asymptotic distribution of the posterior mode depends on the Fisher information and not on the prior...
, taking the form of differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
s and probability distribution function
Probability distribution function
Depending upon which text is consulted, a probability distribution function is any of:* a probability distribution function,* a cumulative distribution function,* a probability mass function, or* a probability density function....
s.
Introduction
Physicist John Archibald WheelerJohn Archibald Wheeler
John Archibald Wheeler was an American theoretical physicist who was largely responsible for reviving interest in general relativity in the United States after World War II. Wheeler also worked with Niels Bohr in explaining the basic principles behind nuclear fission...
stated that:
By using Fisher information
Fisher information
In mathematical statistics and information theory, the Fisher information is the variance of the score. In Bayesian statistics, the asymptotic distribution of the posterior mode depends on the Fisher information and not on the prior...
, in particular the loss I - J incurred during observation, the EPI principle provides a powerful new approach for deriving laws governing many aspects of nature and human society. EPI can be seen as an extension of information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
that encompasses much theoretical physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
. Examples include the Schrödinger wave equation and the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law. EPI has been used to derive a number of fundamental laws of physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, the biophysics
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that uses the methods of physical science to study biological systems. Studies included under the branches of biophysics span all levels of biological organization, from the molecular scale to whole organisms and ecosystems...
of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
growth,chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, and economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
. EPI can also be seen as a game
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
against nature, first proposed by Charles Sanders Peirce. The approach does require prior knowledge of an appropriate invariance principle or data.
EPI principle
The EPI principle builds on the well known idea that the observation of a "source" phenomenon is never completely accurate. That is, information present in the source is inevitably lost when observing the source. Moreover, the random errors that contaminate the observations are presumed to define the probability distribution function of the source phenomenon. That is, "the physics lies in the fluctuations." The information loss is postulated to be an extreme value. Thus, if the Fisher informationFisher information
In mathematical statistics and information theory, the Fisher information is the variance of the score. In Bayesian statistics, the asymptotic distribution of the posterior mode depends on the Fisher information and not on the prior...
in the data is
 , and the Fisher information in the source is
, and the Fisher information in the source is  , the EPI principle states that:
, the EPI principle states that: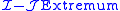
The extremum for most situations is a minimum, meaning that there is a comforting tendency for any observation to describe its source faithfully.
Books
- Frieden, B. Roy - Physics from Fisher Information: A Unification , 1st Ed. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-63167-X, pp328, 1998
- Frieden, B. Roy - Science from Fisher Information: A Unification , 2nd Ed. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-00911-1, pp502, 2004
- Frieden, B.R. & Gatenby, R.A. eds. - Exploratory Data Analysis Using Fisher Information, Springer-Verlag (in press), pp358, 2006
Recent papers using EPI
- Gatenby, Robert A. & Frieden, B. Roy - "Application of Information Theory and Extreme Physical Information to Carcinogenesis",
- Cancer Research 62, 3675-3684, July 1, 2002
- http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/content/full/62/13/3675
- Chimento,L.P. & Pennini, F. & Plastino, A. - “Naudts-like duality and the Extreme Fisher information principle”,
- Phs. Rev. E 62, 7462-7465, 2000
- http://prola.aps.org/abstract/PRE/v62/i5/p7462_1subj: statistical mechanics
- Nagy, A. - “Fisher information in density functional theory,”, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 9401-9405, 2003
- http://scitation.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=JCPSA6000119000018009401000001&idtype=cvips&gifs=yes
- Subj: The Euler equation of density functional theory is derived using EPI.
- Anton, M. & Weisen, H. & Dutch, M.J. - “X-ray tomography on the TCV tokamak”,
- Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 38, 1849-1878, 1996
- http://ej.iop.org/links/q80/fVFo+Bx3KRlwd6qcdU2Saw/p61101.pdf
- Mlynar, J. & Bertalot, L. - “Neutron spectra unfolding with minimum Fisher regularization”
- http://pos.sissa.it/archive/conferences/025/063/FNDA2006_063.pdf
- Subj: Diagnosis of plasma shape within the tokamak fusion machine using reconstructions based upon EPI.
- Venkatesan, Ravi. - “Information encryption using a Fisher-Schrödinger Model”,
- Presented at 6th International Conference on Complex Systems (ICCS) June, 2006
- Boston, MA Full paper is in Frieden and Gatenby, 2006
- http://necsi.edu/community/wiki/index.php/ICCS06/235
- Subj: Encryption, secure transmission using EPI, in particular game aspect.
- Fath B.D. & Cabezas, H. & CW Pawlowski - “Exergy and Fisher information as ecological indices”,
- Ecological Modeling 174, 25-35, 2004 - CW 2003
- http://zp9vv3zm2k.scholar.serialssolutions.com/sid=google&auinit=BD&aulast=Fath&atitle=Exergy+and+Fisher+Information+as+ecological+indices&id=doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2003.12.045
- Subj: monitoring of the environment for species diversity
- Yolles. M.I. - “Knowledge Cybernetics: A New Metaphor for Social Collectives”, 2005
- http://isce.edu/ISCE_Group_Site/web-content/ISCE_Events/Christchurch_2005/Papers/Yolles.pdf
- Subj: Information-based approaches to knowledge management.
- Venkatesan, R.C. - “Invariant Extreme Physical Information and Fuzzy Clustering”, Proc. SPIE Symposium on Defense & Security,
- Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications II, Priddy, K. L. ed, Volume 5421, pp. 48-57, Orlando, FL, 2004
- http://spiedl.aip.org/getpdf/servlet/GetPDFServlet?filetype=pdf&id=PSISDG005421000001000048000001&idtype=cvips&prog=normal
- Ménard, Michel. & Eboueya, Michel. - "Extreme physical information and objective function in fuzzy clustering",
- Fuzzy Sets and Systems 128(3): 285-303, 2002
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6V05-45SR1TJ-1-1&_cdi=5637&_user=56761&_orig=na&_coverDate=06%2F162F2002&_sk=998719996&view=c&wchp=dGLbVlz-zSkWb&md5=4280259595b947a7b560f634f47de5c4&ie=/sdarticle.pdf
- Ménard,Michel. & Dardignac, Pierre-André. & Chibelushi, Claude C. - "Non-extensive thermostatistics and
- extreme physical information for fuzzy clustering (invited paper)", IJCC, 2 (4): 1-63, 2004
- http://www.yangsky.us/ijcc/pdf/ijcc241.pdf
External links
- B. Roy FriedenB. Roy FriedenB. Roy Frieden is an American mathematical physicist.Frieden obtained a Ph.D. in Optics from The Institute of Optics at the University of Rochester. His doctoral thesis advisor was Robert E. Hopkins...
, "Fisher Information, a New Paradigm for Science: Introduction, Uncertainty principles, Wave equations, Ideas of Escher, Kant, Plato and Wheeler." This essay is continually revised in the light of ongoing research using EPI. - The Bactra Review A critical review of the first edition of Science from Fisher Information (2nd ed. listed above), and on EPI in general.
- Unexpected Union - Physics and Fisher Information: An uncritical review of the same book and an introduction to EPI from SIAM News Vol 33 #6; July 17, 2000

