
F
Encyclopedia
F is the sixth letter
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
.
The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic
letter vâv
(or waw) that represented a sound like /v/ or /w/. Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club. It may have been based on a comparable Egyptian hieroglyph, such as that which represented the word mace (transliterated as ḥ(dj)):-T3
The Phoenician form of the letter was adopted into Greek as a vowel, upsilon
(which resembled its descendant, ⟨Y
⟩, but was also ancestor to Roman letters ⟨U
⟩, ⟨V
⟩, and ⟨W
⟩); and with another form, as a consonant, digamma
, which resembled ⟨F⟩, but indicated the pronunciation /w/, as in Phoenician. (After /w/ disappeared from Greek, digamma was used as a numeral only.)
In Etruscan
, ⟨F⟩ probably represented /w/, as in Greek; and the Etruscans formed the digraph
⟨FH⟩ to represent /f/. When the Romans adopted the alphabet, they used ⟨V⟩ (from Greek upsilon) to stand for /w/ as well as /u/, leaving ⟨F⟩ available for /f/. (At that time, the Greek letter phi
⟨Φ⟩ represented an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive
/pʰ/, though in Modern Greek it approximates the sound of /f/.)
The lower case ⟨f⟩ is not related to the visually similar long s
, ⟨ſ⟩. The use of the long s largely died out by the beginning of the 19th century, mostly to prevent confusion with ⟨f⟩.
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
Basic modern Latin alphabet
The International Organization for Standardization basic Latin alphabet consists of the following 26 letters:By the 1960s it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed...
.
History
| Proto-Semitic W | Phoenician waw Waw (letter) Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic .... |
Etruscan V or W | Greek Digamma Digamma Digamma is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet which originally stood for the sound /w/ and later remained in use only as a numeral symbol for the number "6"... |
Roman F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
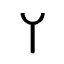 |
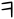 |
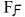 |
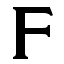 |
The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
letter vâv
Waw (letter)
Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic ....
(or waw) that represented a sound like /v/ or /w/. Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club. It may have been based on a comparable Egyptian hieroglyph, such as that which represented the word mace (transliterated as ḥ(dj)):-
The Phoenician form of the letter was adopted into Greek as a vowel, upsilon
Upsilon
Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or...
(which resembled its descendant, ⟨Y
Y
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
⟩, but was also ancestor to Roman letters ⟨U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
⟩, ⟨V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
⟩, and ⟨W
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
⟩); and with another form, as a consonant, digamma
Digamma
Digamma is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet which originally stood for the sound /w/ and later remained in use only as a numeral symbol for the number "6"...
, which resembled ⟨F⟩, but indicated the pronunciation /w/, as in Phoenician. (After /w/ disappeared from Greek, digamma was used as a numeral only.)
In Etruscan
Etruscan
-Etruscan civilization:*Etruscan alphabet*Etruscan architecture*Etruscan art*Etruscan cities*Etruscan civilization*Etruscan coins*Etruscan language*Etruscan mythology*Etruscan numerals*Etruscan society*Etruscan terracotta warriors*Etruscan warfare...
, ⟨F⟩ probably represented /w/, as in Greek; and the Etruscans formed the digraph
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
⟨FH⟩ to represent /f/. When the Romans adopted the alphabet, they used ⟨V⟩ (from Greek upsilon) to stand for /w/ as well as /u/, leaving ⟨F⟩ available for /f/. (At that time, the Greek letter phi
Phi
Phi may refer to:In language:*Phi, the Greek letter Φ,φ, the symbol for voiceless bilabial fricativeIn mathematics:*The Golden ratio*Euler's totient function*A statistical measure of association reported with the chi-squared test...
⟨Φ⟩ represented an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive
Voiceless bilabial plosive
The voiceless bilabial plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is p...
/pʰ/, though in Modern Greek it approximates the sound of /f/.)
The lower case ⟨f⟩ is not related to the visually similar long s
Long s
The long, medial or descending s is a form of the minuscule letter s formerly used where s occurred in the middle or at the beginning of a word, for example "ſinfulneſs" . The modern letterform was called the terminal, round, or short s.-History:The long s is derived from the old Roman cursive...
, ⟨ſ⟩. The use of the long s largely died out by the beginning of the 19th century, mostly to prevent confusion with ⟨f⟩.
Related letters and other similar characters
: Latin letter F with hookƒ
The letter ' is a letter of the Latin alphabet, based on the italic form of f; or on its regular form with a descender hook added...
- Ф ф : Cyrillic letter Ef
- Φ φ/ϕ : Greek letter PhiPhi (letter)Phi , pronounced or sometimes in English, and in modern Greek, is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greek, it represents , a voiceless labiodental fricative. In Ancient Greek it represented , an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive...
Computing codes
| character | F | f | ||
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER F | LATIN SMALL LETTER F | ||
| character encoding | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
70 | 0046 | 102 | 0066 |
| UTF-8 UTF-8 UTF-8 is a multibyte character encoding for Unicode. Like UTF-16 and UTF-32, UTF-8 can represent every character in the Unicode character set. Unlike them, it is backward-compatible with ASCII and avoids the complications of endianness and byte order marks... |
70 | 46 | 102 | 66 |
| Numeric character reference Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
F | F | f | f |
| EBCDIC EBCDIC Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code is an 8-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems.... family |
198 | C6 | 134 | 86 |
| ASCII ASCII The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text... 1 |
70 | 46 | 102 | 66 |
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.

