
Y
Encyclopedia
Y is the twenty-fifth letter
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
and represents either a vowel
or a consonant
in English.
Old English borrowed Latin Y to write the native Old English sound /y/ (previously written with the rune yr ). When the letter came to be analyzed as a V atop an I (First Grammatical Treatise
), it was renamed VI (/uː iː/), which was simplified to one syllable
(/wiː/), and by the Great Vowel Shift
became the Modern English
wy (/waɪ/).
Y is the only letter (other than US/Irish "zee" for Z) whose name in English is wholly unrelated to its name in French (and other Romance languages).

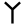 The furthest back direct ancestor of English letter Y was the Semitic
The furthest back direct ancestor of English letter Y was the Semitic
letter waw
, from which also come F
, U
, V
, and W
. See F
for details. The Greek and Latin alphabets developed from the Phoenician
form of this early alphabet. In Modern English, there is also some historical influence from the old English letter yogh
(Ȝȝ), which develop from Semitic gimel, as shown below.
, /j/ (year, German Jahr). This is possibly influenced by the Middle English letter yogh
(Ȝȝ), which represented /j/. Yogh's other sound, /ɣ/, came to be written "gh
" in Modern English.
. The Romans
borrowed a small form of upsilon as the single letter V, representing both /u/ and its consonantal variant /w/. In later ways of writing Latin, V is typically written as U, for a vowel, or V for the consonant. However, this first loaning of upsilon into Latin is not the source of Modern English Y.
The usage of the capital form of upsilon, Y as opposed to U, V, or W, dates back to the Latin of the first century BC, when upsilon was introduced a second time, this time with its "foot" to distinguish it. It was used to transcribe loanwords from the prestigious Attic
dialect of Greek, which had the non-Latin sound /y/. Because it was not a native sound of Latin it was usually pronounced /u/ or /i/. The latter pronunciation was the most common in the Classical period and was used by most people except the educated ones.
The letter was also used for other languages with a /y/ sound. Some words of Italic
origin were re-spelled with a y: Latin silva 'forest' was commonly spelled sylva, in analogy with the Greek cognate and synonym ὕλη.
The Roman Emperor Claudius proposed introducing a new letter into the Latin alphabet to transcribe the so-called sonus medius (a short vowel before labial consonants), which in inscriptions was sometimes used for Greek upsilon instead.
In Old English there was a native /y/ sound, and so both Latin U and Y were adapted for use. By the time of Middle English
, /y/ had lost its roundedness
and became identical to I (/iː/ and /ɪ/). Therefore, many words that originally had I were spelled with Y, and vice-versa. (Some dialects, however, retained the sound /y/ and spelled it U, following French usage.)
Likewise, Modern English vocalic Y is pronounced identically to the letter I. But Modern English uses it in only certain places, unlike Middle and early Modern English. It has three uses: for upsilon in Greek loan-words (system: Greek σύστημα), at the end of a word (rye, city; compare cities, where S is final), and before vowel endings (dy-ing, justify-ing).
and other English printers used Y in place of Þ (thorn
: Modern English th), which did not exist in continental typeface
s. From this convention comes the spelling of the as ye in the mock archaism "Ye Olde Shoppe". But in spite of the spelling, pronunciation was the same as for modern the (stressed /ðiː/, unstressed /ðə/). Ye (/jiː/) is purely a modern spelling pronunciation
.
.
After fronting from /u/, Greek
/y/ de-rounded to /i/.
In English
morphology
, -y is an adjectival
suffix.
. It can never be a consonant (except for loanword
s), but can appear in diphthongs, as in the name Meyer, where it serves as a variant of ⟨i⟩.
In Dutch
, Y appears only in loanword
s and names and usually represents /i/. It is often left out of the Dutch alphabet
and replaced with the "ligature IJ". In the Afrikaans language, a descendant of Dutch, Y denotes the diphthong [ɛi], which may derive from the IJ ligature.
In Faroese
and Icelandic
, Y is always pronounced /i/. In both languages, it can also form part of diphthongs such as ⟨ey⟩ (both language) and ⟨oy⟩ (Faroese only).
, Y was used as a word-initial form of I that was more visible. (German has used J
in a similar way.) Hence "el yugo y las flechas" was a symbol sharing the initials of Isabella I of Castille (Ysabel) and Ferdinand II of Aragon
. This spelling was reformed by the Royal Spanish Academy and currently is only found in proper names spelled archaically, such as Ybarra
or CYII, the symbol of the Canal de Isabel II
. X
is also still used in Spanish with a different sound in some archaisms.
Appearing alone as a word, the letter Y is a grammatical conjunction
with the meaning "and" in Spanish
and is pronounced /i/.
In Spanish family names, y can separate the father's surname from the mother's surname as in "Santiago Ramón y Cajal
"; another example is "Maturin y Domanova", from the Jack Aubrey
novel
sequence. Catalan names use i for this. Otherwise, Y represents ʝ in Spanish. When coming before the sound /i/, Y is replaced with E: "español e inglés". This is to avoid pronouncing /i/ twice.
The letter Y is called "i/y griega", literally meaning "Greek I", after the Greek letter ypsilon, or ye.
, too, has Y (i greca or ipsilon) in a small number of loanwords.
In Polish
and Guaraní
, it represents the vowel ɨ.
In Welsh
it is pronounced ə in monosyllabic words or non-final syllables, and /ɨ/ or i (depending on the accent) in final syllables.
In Finnish
and Albanian
, Y is always pronounced y.
In Lithuanian
Y is the 15th letter and is a vowel. It is called the long i and is pronounced /iː/ like in English see.
When used as a vowel in Vietnamese
, the letter y represents the close front unrounded vowel
. When used as a monophthong, it is functionally equivalent to the Vietnamese letter i. Thus, Mỹ Lai does not rhyme but mỳ Lee does. There have been efforts to replace all such uses with i altogether, but they have been largely unsuccessful. As a consonant, it represents the palatal approximant
.
In Aymara
, Turkish
, Quechua
as in Romaji in Japanese
, all Y is a palatal consonant
, always denoting j, as in English.
In Malagasy
, the letter y represents the final variation of /ɨ/.
In Turkmen
, Y represents ɯ.
In Japan, Ⓨ is a symbol used for resale price maintenance
.
, and the slightly different character [ʏ] corresponds to the near-close near-front rounded vowel.
It is indicative of the rarity of front rounded vowels that [y] is the rarest sound represented in the IPA by a letter of the Latin alphabet, being cross-linguistically less than half as frequent as q or c and only about a quarter as frequent as x.
The IPA symbol [j] ("jod") represents the sound of the English letter ⟨y⟩ in the word "yes".
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
Basic modern Latin alphabet
The International Organization for Standardization basic Latin alphabet consists of the following 26 letters:By the 1960s it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed...
and represents either a vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
or a consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
in English.
Name
In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing /y/, which was not a native sound. In Romance languages, the pronunciation became the regular name: Spanish i griega, French i grec, etc.Old English borrowed Latin Y to write the native Old English sound /y/ (previously written with the rune yr ). When the letter came to be analyzed as a V atop an I (First Grammatical Treatise
First Grammatical Treatise
The First Grammatical Treatise is a 12th-century work on the phonology of the Old Norse or Old Icelandic language. It was given this name because it is the first of four grammatical works bound in the Icelandic manuscript Codex Wormianus...
), it was renamed VI (/uː iː/), which was simplified to one syllable
Synizesis
Synizesis is a sound change in which two originally syllabic vowels are pronounced as a single syllable without change in writing. In Latin and Greek, this was often to preserve meter, but similar changes occur naturally in languages....
(/wiː/), and by the Great Vowel Shift
Great Vowel Shift
The Great Vowel Shift was a major change in the pronunciation of the English language that took place in England between 1350 and 1500.The Great Vowel Shift was first studied by Otto Jespersen , a Danish linguist and Anglicist, who coined the term....
became the Modern English
Modern English
Modern English is the form of the English language spoken since the Great Vowel Shift in England, completed in roughly 1550.Despite some differences in vocabulary, texts from the early 17th century, such as the works of William Shakespeare and the King James Bible, are considered to be in Modern...
wy (/waɪ/).
Y is the only letter (other than US/Irish "zee" for Z) whose name in English is wholly unrelated to its name in French (and other Romance languages).
Semitic, Phoenician, Greek and Latin

Semitic
In linguistics and ethnology, Semitic was first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin, now called the Semitic languages...
letter waw
Waw (letter)
Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic ....
, from which also come F
F
F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club...
, U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
, V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
, and W
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
. See F
F
F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club...
for details. The Greek and Latin alphabets developed from the Phoenician
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
form of this early alphabet. In Modern English, there is also some historical influence from the old English letter yogh
Yogh
The letter yogh , was used in Middle English and Older Scots, representing y and various velar phonemes. It was derived from the Old English form of the letter g.In Middle English writing, tailed z came to be indistinguishable from yogh....
(Ȝȝ), which develop from Semitic gimel, as shown below.
| Phoenician | | Greek | | Latin | | English (approximate times of changes) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | Middle | Modern | |||
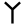 |
V → | U → | V/U/UU → | V/U/W | |
| Y → | Y (vowel /y/) → | Y (vowel /i/) → | Y (vowels) | ||
 |
 |
C → | |||
| G → | Ȝ → | G → | |||
| consonantal Y /j/ → | Y (consonant) | ||||
| Þ → | Y /th/ | - | |||
Consonant
As a consonant in English, Y is normally a palatal approximantPalatal approximant
The palatal approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is '...
, /j/ (year, German Jahr). This is possibly influenced by the Middle English letter yogh
Yogh
The letter yogh , was used in Middle English and Older Scots, representing y and various velar phonemes. It was derived from the Old English form of the letter g.In Middle English writing, tailed z came to be indistinguishable from yogh....
(Ȝȝ), which represented /j/. Yogh's other sound, /ɣ/, came to be written "gh
Gh (digraph)
Gh is a digraph found in many languages.-English:In English, ⟨gh⟩ historically represented . In modern English, ⟨gh⟩ is almost always either silent or pronounced...
" in Modern English.
Vowel
Y first appeared as the Greek letter upsilonUpsilon
Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or...
. The Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
borrowed a small form of upsilon as the single letter V, representing both /u/ and its consonantal variant /w/. In later ways of writing Latin, V is typically written as U, for a vowel, or V for the consonant. However, this first loaning of upsilon into Latin is not the source of Modern English Y.
The usage of the capital form of upsilon, Y as opposed to U, V, or W, dates back to the Latin of the first century BC, when upsilon was introduced a second time, this time with its "foot" to distinguish it. It was used to transcribe loanwords from the prestigious Attic
Attic Greek
Attic Greek is the prestige dialect of Ancient Greek that was spoken in Attica, which includes Athens. Of the ancient dialects, it is the most similar to later Greek, and is the standard form of the language studied in courses of "Ancient Greek". It is sometimes included in Ionic.- Origin and range...
dialect of Greek, which had the non-Latin sound /y/. Because it was not a native sound of Latin it was usually pronounced /u/ or /i/. The latter pronunciation was the most common in the Classical period and was used by most people except the educated ones.
The letter was also used for other languages with a /y/ sound. Some words of Italic
Italic languages
The Italic subfamily is a member of the Indo-European language family. It includes the Romance languages derived from Latin , and a number of extinct languages of the Italian Peninsula, including Umbrian, Oscan, Faliscan, and Latin.In the past various definitions of "Italic" have prevailed...
origin were re-spelled with a y: Latin silva 'forest' was commonly spelled sylva, in analogy with the Greek cognate and synonym ὕλη.
The Roman Emperor Claudius proposed introducing a new letter into the Latin alphabet to transcribe the so-called sonus medius (a short vowel before labial consonants), which in inscriptions was sometimes used for Greek upsilon instead.
In Old English there was a native /y/ sound, and so both Latin U and Y were adapted for use. By the time of Middle English
Middle English
Middle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
, /y/ had lost its roundedness
Roundedness
In phonetics, vowel roundedness refers to the amount of rounding in the lips during the articulation of a vowel. That is, it is vocalic labialization. When pronouncing a rounded vowel, the lips form a circular opening, while unrounded vowels are pronounced with the lips relaxed...
and became identical to I (/iː/ and /ɪ/). Therefore, many words that originally had I were spelled with Y, and vice-versa. (Some dialects, however, retained the sound /y/ and spelled it U, following French usage.)
Likewise, Modern English vocalic Y is pronounced identically to the letter I. But Modern English uses it in only certain places, unlike Middle and early Modern English. It has three uses: for upsilon in Greek loan-words (system: Greek σύστημα), at the end of a word (rye, city; compare cities, where S is final), and before vowel endings (dy-ing, justify-ing).
Orthographic confusion with the letter thorn
When printing was introduced from the continent, CaxtonWilliam Caxton
William Caxton was an English merchant, diplomat, writer and printer. As far as is known, he was the first English person to work as a printer and the first to introduce a printing press into England...
and other English printers used Y in place of Þ (thorn
Thorn (letter)
Thorn or þorn , is a letter in the Old English, Old Norse, and Icelandic alphabets, as well as some dialects of Middle English. It was also used in medieval Scandinavia, but was later replaced with the digraph th. The letter originated from the rune in the Elder Fuþark, called thorn in the...
: Modern English th), which did not exist in continental typeface
Typeface
In typography, a typeface is the artistic representation or interpretation of characters; it is the way the type looks. Each type is designed and there are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly....
s. From this convention comes the spelling of the as ye in the mock archaism "Ye Olde Shoppe". But in spite of the spelling, pronunciation was the same as for modern the (stressed /ðiː/, unstressed /ðə/). Ye (/jiː/) is purely a modern spelling pronunciation
Spelling pronunciation
A spelling pronunciation is a pronunciation that, instead of reflecting the way the word was pronounced by previous generations of speakers, is a rendering in sound of the word's spelling.-Examples of English words with common spelling pronunciations:...
.
Usage
In Spanish, Y is called i/y griega, in Catalan i grega, in French and Romanian i grec, in Polish igrek - all meaning "Greek i" (except for Polish, where it is simply a phonetic transcription of the French name); in most other European languages the Greek name is still used; in German, for example, it is called Ypsilon and in Portuguese and Italian it's called ípsilon or ípsilo (although in Portuguese there is also the name "Greek i"). http://www.omniglot.com/writing/portuguese.htm The letter Y was originally established as a vowel. In the standard English language, the letter Y is traditionally regarded as a consonant, but a survey of almost any English text will show that Y more commonly functions as a vowel. In many cases, it is known as a semivowelSemivowel
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:...
.
After fronting from /u/, Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
/y/ de-rounded to /i/.
In English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
morphology
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the identification, analysis and description, in a language, of the structure of morphemes and other linguistic units, such as words, affixes, parts of speech, intonation/stress, or implied context...
, -y is an adjectival
Adjective
In grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
suffix.
Other Germanic languages
Y has the sound values /y/ or /ʏ/ in the Scandinavian languages and in GermanGerman language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
. It can never be a consonant (except for loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s), but can appear in diphthongs, as in the name Meyer, where it serves as a variant of ⟨i⟩.
In Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, Y appears only in loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s and names and usually represents /i/. It is often left out of the Dutch alphabet
Dutch alphabet
The modern Dutch alphabet consists of the 26 letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet and is used for the Dutch language. Five letters are vowels and 21 letters are consonants.- History :...
and replaced with the "ligature IJ". In the Afrikaans language, a descendant of Dutch, Y denotes the diphthong [ɛi], which may derive from the IJ ligature.
In Faroese
Faroese language
Faroese , is an Insular Nordic language spoken by 48,000 people in the Faroe Islands and about 25,000 Faroese people in Denmark and elsewhere...
and Icelandic
Icelandic language
Icelandic is a North Germanic language, the main language of Iceland. Its closest relative is Faroese.Icelandic is an Indo-European language belonging to the North Germanic or Nordic branch of the Germanic languages. Historically, it was the westernmost of the Indo-European languages prior to the...
, Y is always pronounced /i/. In both languages, it can also form part of diphthongs such as ⟨ey⟩ (both language) and ⟨oy⟩ (Faroese only).
Spanish
In the Spanish languageSpanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, Y was used as a word-initial form of I that was more visible. (German has used J
J
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic...
in a similar way.) Hence "el yugo y las flechas" was a symbol sharing the initials of Isabella I of Castille (Ysabel) and Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand the Catholic was King of Aragon , Sicily , Naples , Valencia, Sardinia, and Navarre, Count of Barcelona, jure uxoris King of Castile and then regent of that country also from 1508 to his death, in the name of...
. This spelling was reformed by the Royal Spanish Academy and currently is only found in proper names spelled archaically, such as Ybarra
Ybarra
Ybarra is a surname of Basque origin, and may refer to:* Jason Ybarra, American actor, stuntman and wrestler* Joe Ybarra, American video game producer* Rocío Ybarra, Spanish hockey player* Rosario Ybarra, Mexican politician* Sam Ybarra, American soldier...
or CYII, the symbol of the Canal de Isabel II
Canal de Isabel II
Canal de Isabel II is the public company that manages the water supplies for Madrid, Spain. It is owned by the Autonomous Community of Madrid.The Y in the abbreviation is from the old spelling Ysabel.- External links :*...
. X
X
X is the twenty-fourth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Uses:In mathematics, x is commonly used as the name for an independent variable or unknown value. The usage of x to represent an independent or unknown variable can be traced back to the Arabic word šay شيء = “thing,” used in Arabic...
is also still used in Spanish with a different sound in some archaisms.
Appearing alone as a word, the letter Y is a grammatical conjunction
Grammatical conjunction
In grammar, a conjunction is a part of speech that connects two words, sentences, phrases or clauses together. A discourse connective is a conjunction joining sentences. This definition may overlap with that of other parts of speech, so what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each...
with the meaning "and" in Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
and is pronounced /i/.
In Spanish family names, y can separate the father's surname from the mother's surname as in "Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Santiago Ramón y Cajal ForMemRS was a Spanish pathologist, histologist, neuroscientist, and Nobel laureate. His pioneering investigations of the microscopic structure of the brain were original: he is considered by many to be the father of modern neuroscience...
"; another example is "Maturin y Domanova", from the Jack Aubrey
Jack Aubrey
John "Jack" Aubrey, KB , is a fictional character in the Aubrey–Maturin series of novels by Patrick O'Brian. The series portrays his rise from Lieutenant to Rear-Admiral in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars. The twenty -book series encompasses Aubrey's adventures and various commands along...
novel
Novel
A novel is a book of long narrative in literary prose. The genre has historical roots both in the fields of the medieval and early modern romance and in the tradition of the novella. The latter supplied the present generic term in the late 18th century....
sequence. Catalan names use i for this. Otherwise, Y represents ʝ in Spanish. When coming before the sound /i/, Y is replaced with E: "español e inglés". This is to avoid pronouncing /i/ twice.
The letter Y is called "i/y griega", literally meaning "Greek I", after the Greek letter ypsilon, or ye.
Other languages
ItalianItalian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, too, has Y (i greca or ipsilon) in a small number of loanwords.
In Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
and Guaraní
Guaraní language
Guaraní, specifically the primary variety known as Paraguayan Guaraní , is an indigenous language of South America that belongs to the Tupí–Guaraní subfamily of the Tupian languages. It is one of the official languages of Paraguay , where it is spoken by the majority of the population, and half of...
, it represents the vowel ɨ.
In Welsh
Welsh language
Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
it is pronounced ə in monosyllabic words or non-final syllables, and /ɨ/ or i (depending on the accent) in final syllables.
In Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
and Albanian
Albanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
, Y is always pronounced y.
In Lithuanian
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
Y is the 15th letter and is a vowel. It is called the long i and is pronounced /iː/ like in English see.
When used as a vowel in Vietnamese
Vietnamese language
Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam...
, the letter y represents the close front unrounded vowel
Close front unrounded vowel
The close front unrounded vowel, or high front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ....
. When used as a monophthong, it is functionally equivalent to the Vietnamese letter i. Thus, Mỹ Lai does not rhyme but mỳ Lee does. There have been efforts to replace all such uses with i altogether, but they have been largely unsuccessful. As a consonant, it represents the palatal approximant
Palatal approximant
The palatal approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is '...
.
In Aymara
Aymara language
Aymara is an Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Andes. It is one of only a handful of Native American languages with over three million speakers. Aymara, along with Quechua and Spanish, is an official language of Peru and Bolivia...
, Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, Quechua
Quechua languages
Quechua is a Native South American language family and dialect cluster spoken primarily in the Andes of South America, derived from an original common ancestor language, Proto-Quechua. It is the most widely spoken language family of the indigenous peoples of the Americas, with a total of probably...
as in Romaji in Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
, all Y is a palatal consonant
Palatal consonant
Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate...
, always denoting j, as in English.
In Malagasy
Malagasy language
Malagasy is the national language of Madagascar, a member of the Austronesian family of languages. Most people in Madagascar speak it as a first language as do some people of Malagasy descent elsewhere.-History:...
, the letter y represents the final variation of /ɨ/.
In Turkmen
Turkmen language
Turkmen is the national language of Turkmenistan...
, Y represents ɯ.
In Japan, Ⓨ is a symbol used for resale price maintenance
Resale price maintenance
Resale price maintenance is the practice whereby a manufacturer and its distributors agree that the latter will sell the former's product at certain prices , at or above a price floor or at or below a price ceiling...
.
International Phonetic Alphabet
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, [y] corresponds to the close front rounded vowelClose front rounded vowel
The close front rounded vowel, or high front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is y...
, and the slightly different character [ʏ] corresponds to the near-close near-front rounded vowel.
It is indicative of the rarity of front rounded vowels that [y] is the rarest sound represented in the IPA by a letter of the Latin alphabet, being cross-linguistically less than half as frequent as q or c and only about a quarter as frequent as x.
The IPA symbol [j] ("jod") represents the sound of the English letter ⟨y⟩ in the word "yes".
Related letters and other similar characters
- Υ υ : Greek letter UpsilonUpsilonUpsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or...
- У у : Cyrillic letter UU (Cyrillic)U is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the close back rounded vowel , somewhat like the pronunciation of ⟨oo⟩ in "boot"...
: Cyrillic letter UeUe (Cyrillic)Ue or Straight U is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It is a form of the Cyrillic letter U with a vertical, rather than diagonal, center line...
(Straight U) - Ы ы : Cyrillic letter YeryYeryYery or Yeru is a letter in the Cyrillic alphabet. It represents the phoneme after non-palatalised consonants in the Belarusian and Russian alphabets...
, commonly romanized as ⟨y⟩ : a currency symbol
Computing codes
| character | Y | y | ||
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER Y | LATIN SMALL LETTER Y | ||
| character encoding | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
89 | 0059 | 121 | 0079 |
| UTF-8 UTF-8 UTF-8 is a multibyte character encoding for Unicode. Like UTF-16 and UTF-32, UTF-8 can represent every character in the Unicode character set. Unlike them, it is backward-compatible with ASCII and avoids the complications of endianness and byte order marks... |
89 | 59 | 121 | 79 |
| Numeric character reference Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
Y | Y | y | y |
| EBCDIC EBCDIC Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code is an 8-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems.... family |
232 | E8 | 168 | A8 |
| ASCII ASCII The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text... 1 |
89 | 59 | 121 | 79 |
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.

