
Palatal consonant
Encyclopedia
Palatal consonants are consonant
s articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate
(the middle part of the roof of the mouth). Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex
.
[ɲ] is also common, occurring in around 35 percent of the world's languages, in most of which its equivalent obstruent
is not the plosive [c], but the affricate
t͡ʃ. Only a few languages in northern Eurasia, the Americas and central Africa contrast palatal plosives with postalveolar affricates - as in Hungarian
, Czech
, Latvian
, Slovak
, Turkish
and Albanian
.
Consonants with other primary articulations may be palatalized
, that is, accompanied by the raising of the tongue surface towards the hard palate. For example, English [ʃ] (spelled sh) has such a palatal component, although its primary articulation involves the tip of the tongue and the upper gum (this type of articulation is called palatoalveolar).
In phonology
, alveolo-palatal
, palatoalveolar and palatovelar consonants are commonly grouped as palatals, since these categories rarely contrast with true palatals. Sometimes palatalized alveolars
or dentals can be analyzed in this manner as well.
, whereas palatalized consonants have a primary articulation in some other area and a secondary articulation
involving movement towards the hard palate. Palatal and palatalized consonants are both single phonemes, whereas a sequence of a consonant and /j/ is logically two phonemes.
Some languages have more than one of the above types of consonants, for example:
Note that sometimes the term "palatal" is used imprecisely to mean "palatalized". Also, languages that have sequences of consonants and /j/, but no separate palatal or palatalized consonants (e.g. English
), will often pronounce the sequence with /j/ as a single palatal or palatalized consonant. This is due to the principle of least effort
and is an example of the general phenomenon of coarticulation
. (On the other hand, Spanish speakers are very often careful to pronounce /nj/ as two separate sounds to avoid possible confusion with /ɲ/.)
are:
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate
Hard palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate of the skull, located in the roof of the mouth. It spans the arch formed by the upper teeth.It is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone....
(the middle part of the roof of the mouth). Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex
Retroflex consonant
A retroflex consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants, especially in Indology...
.
Characteristics
The most common type of palatal consonant is the extremely common approximant [j], which ranks as overall, among the ten most common sounds in the world's languages. The nasalNasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
[ɲ] is also common, occurring in around 35 percent of the world's languages, in most of which its equivalent obstruent
Obstruent
An obstruent is a consonant sound formed by obstructing airflow, causing increased air pressure in the vocal tract, such as [k], [d͡ʒ] and [f]. In phonetics, articulation may be divided into two large classes: obstruents and sonorants....
is not the plosive [c], but the affricate
Affricate consonant
Affricates are consonants that begin as stops but release as a fricative rather than directly into the following vowel.- Samples :...
t͡ʃ. Only a few languages in northern Eurasia, the Americas and central Africa contrast palatal plosives with postalveolar affricates - as in Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, Czech
Czech language
Czech is a West Slavic language with about 12 million native speakers; it is the majority language in the Czech Republic and spoken by Czechs worldwide. The language was known as Bohemian in English until the late 19th century...
, Latvian
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
, Slovak
Slovak language
Slovak , is an Indo-European language that belongs to the West Slavic languages .Slovak is the official language of Slovakia, where it is spoken by 5 million people...
, Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
and Albanian
Albanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
.
Consonants with other primary articulations may be palatalized
Palatalization
In linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate....
, that is, accompanied by the raising of the tongue surface towards the hard palate. For example, English [ʃ] (spelled sh) has such a palatal component, although its primary articulation involves the tip of the tongue and the upper gum (this type of articulation is called palatoalveolar).
In phonology
Phonology
Phonology is, broadly speaking, the subdiscipline of linguistics concerned with the sounds of language. That is, it is the systematic use of sound to encode meaning in any spoken human language, or the field of linguistics studying this use...
, alveolo-palatal
Alveolo-palatal consonant
In phonetics, alveolo-palatal consonants are palatalized postalveolar sounds, usually fricatives and affricates, articulated with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge, and the body of the tongue raised toward the palate...
, palatoalveolar and palatovelar consonants are commonly grouped as palatals, since these categories rarely contrast with true palatals. Sometimes palatalized alveolars
Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
or dentals can be analyzed in this manner as well.
Palatal vs. palatalized vs. sequences with /j/
It is important to distinguish between true palatal consonants, palatalized consonants, and sequences of a consonant and a /j/. Palatal consonants have their primary articulation toward or in contact with the hard palateHard palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate of the skull, located in the roof of the mouth. It spans the arch formed by the upper teeth.It is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone....
, whereas palatalized consonants have a primary articulation in some other area and a secondary articulation
Secondary articulation
Secondary articulation refers to co-articulated consonants where the two articulations are not of the same manner. The approximant-like secondary articulation is weaker than the primary, and colors it rather than obscuring it...
involving movement towards the hard palate. Palatal and palatalized consonants are both single phonemes, whereas a sequence of a consonant and /j/ is logically two phonemes.
Some languages have more than one of the above types of consonants, for example:
- IrishIrish phonologyThe phonology of the Irish language varies from dialect to dialect; there is no standard pronunciation of the language. Therefore, this article focuses on phenomena that pertain generally to most or all dialects, and on the major differences among the dialects...
has both a palatal nasalPalatal nasalThe palatal nasal is a type of consonant, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a lowercase letter n with a leftward-pointing tail protruding from the bottom of the left stem of the letter. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J...
/ɲ/ and a palatalized alveolar nasalAlveolar nasalThe alveolar nasal is a type of consonantal sound used in numerous spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar nasals is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n....
/nʲ/. In fact, some conservative Irish dialects have two palatalized alveolar nasal consonants, distinguished as "fortisFortis and lenisIn linguistics, fortis and lenis are terms generally used to refer to groups of consonants that are produced with greater and lesser energy, respectively, such as in energy applied, articulation, etc....
" (apicalApicalApical, from the Latin apex meaning to be at the apex or tip, may refer to:*Apical , an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure...
and somewhat lengthened) vs. "lenis" (laminal). - SpanishSpanish phonologyThis article is about the phonology and phonetics of the Spanish language. Unless otherwise noted, statements refer to Castilian Spanish, the standard dialect used in Spain on radio and television. For historical development of the sound system see History of Spanish...
has both a palatal nasalPalatal nasalThe palatal nasal is a type of consonant, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a lowercase letter n with a leftward-pointing tail protruding from the bottom of the left stem of the letter. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J...
/ɲ/ and a sequence /nj/, distinguished e.g. in uñón /uɲon/ "large nail" (of the finger or toe) vs. unión /unjon/ "union". - RussianRussian phonologyThis article discusses the phonological system of standard Russian based on the Moscow dialect . For discussion of other dialects, see Russian dialects...
has a three-way distinction between palatalized consonants, palatalized consonants followed by /j/, and non-palatalized consonants followed by /j/.
Note that sometimes the term "palatal" is used imprecisely to mean "palatalized". Also, languages that have sequences of consonants and /j/, but no separate palatal or palatalized consonants (e.g. English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
), will often pronounce the sequence with /j/ as a single palatal or palatalized consonant. This is due to the principle of least effort
Principle of least effort
The principle of least effort is a broad theory that covers diverse fields from evolutionary biology to webpage design. It postulates that animals, people, even well designed machines will naturally choose the path of least resistance or "effort". It is closely related to many other similar...
and is an example of the general phenomenon of coarticulation
Coarticulation
Coarticulation in its general sense refers to a situation in which a conceptually isolated speech sound is influenced by, and becomes more like, a preceding or following speech sound...
. (On the other hand, Spanish speakers are very often careful to pronounce /nj/ as two separate sounds to avoid possible confusion with /ɲ/.)
Palatal consonant in IPA
The palatal consonants identified by the International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
are:
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
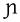 |
palatal nasal Palatal nasal The palatal nasal is a type of consonant, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a lowercase letter n with a leftward-pointing tail protruding from the bottom of the left stem of the letter. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J... |
French French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... |
agneau | [aɲo] | lamb |
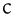 |
voiceless palatal plosive Voiceless palatal plosive The voiceless palatal plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is c.... |
Hungarian Hungarian language Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe.... |
hattyú | [hɒcːuː] | swan |
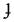 |
voiced palatal plosive Voiced palatal plosive The voiced palatal plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨⟩, a barred dotless ⟨j⟩ , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J\.The sound does not exist as a phoneme in English, but is... |
Latvian Latvian language Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language... |
ģimene | [ɟimene] | family |
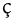 |
voiceless palatal fricative Voiceless palatal fricative The voiceless palatal fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . The symbol ç is the letter c with a cedilla, as used to spell French words such as façade... |
German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... |
nicht | [nɪçt] | not |
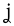 |
voiced palatal fricative | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
yema | [ʝema] | egg yolk |
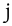 |
palatal approximant Palatal approximant The palatal approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is '... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
yes | [jɛs] | yes |
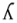 |
palatal lateral approximant Palatal lateral approximant The palatal lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a rotated lowercase letter ⟨y⟩ , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L.-Features:Features of the palatal lateral... |
Italian Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... |
gli | [ʎi] | the (masculine plural) |
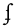 |
voiced palatal implosive Voiced palatal implosive The voiced palatal implosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J\_<... |
Swahili Swahili language Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia... |
hujambo | [huʄambo] | hello |
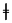 |
palatal click Palatal click The palato-alveolar clicks are a family of click consonants found only in Africa. They are commonly called palatal clicks.The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the place of articulation of these sounds is , a pipe... |
Nǁng | ǂoo | [ǂoo] | man Man The term man is used for an adult human male . However, man is sometimes used to refer to humanity as a whole... , male Male Male refers to the biological sex of an organism, or part of an organism, which produces small mobile gametes, called spermatozoa. Each spermatozoon can fuse with a larger female gamete or ovum, in the process of fertilization... |

