FTTX
Encyclopedia
Fiber to the x is a generic term for any broadband
network architecture using optical fiber
to replace all or part of the usual metal local loop
used for last mile
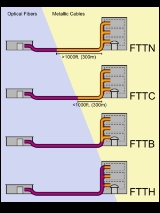
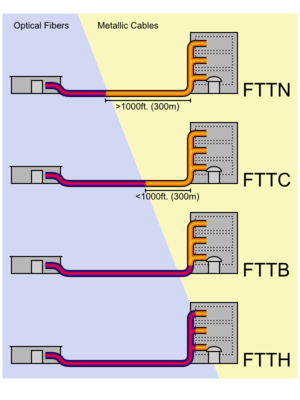
telecommunications. The generic term was initially a generalization for several configurations of fiber deployment (FTTN, FTTC, FTTB, FTTH...), all starting by FTT but differentiated by the last letter, which is substituted by an x in the generalization.
To promote consistency, especially when comparing FTTH penetration rates between countries, the three FTTH Councils of Europe, North America and Asia-Pacific agreed upon definitions for FTTH and FTTB in 2006, with an update in 2009. The FTTH Councils do not have formal definitions for FTTC and FTTN.
To some, fiber to the telecom enclosure
(FTTE) is not considered to be part of the FTTx group of technologies, despite the similarity in name. FTTE is a form of structured cabling
typically used in the enterprise local area network
, where fiber is used to link the main computer equipment room to an enclosure close to the desk or workstation. Passive optical network
s and Point-to-Point Ethernet
are architectures that deliver triple-play services over FTTH networks directly from an operator‘s central office.
runs over relatively economical category 5e, category 6
, or augmented category 6 unshielded twisted pair copper cabling but only to 100 meters. However, over the right kind of fiber, Gigabit Ethernet can easily reach tens of kilometers.
Even in the commercial world, most computers have copper communication cables. But these cables are short, typically tens of meters. Most metropolitan network links (e.g., those based on telephone or cable television services) are several kilometers long, in the range where fiber significantly outperforms copper. Replacing at least part of these links with fiber shortens the remaining copper segments and allows them to run much faster.
Fiber configurations that bring fiber right into the building can offer the highest speeds since the remaining segments can use standard Ethernet or coaxial cable. Fiber configurations that transition to copper in a street cabinet are generally too far from the users for standard Ethernet configurations over existing copper cabling. They generally use very high bitrate digital subscriber line (VDSL) at downstream rates of several tens of megabits per second.
Fiber is often said to be 'future proof' because the data rate of the connection is usually limited by the terminal equipment rather than the fiber , permitting at least some speed improvements by equipment upgrades before the fiber itself must be upgraded. Still, the type and length of employed fibers chosen, e.g. multimode vs single mode, are critical for applicability for future high gigabit connections.
is a common way of delivering triple (and quad) play (voice, video, data and mobile) services over both fiber
and hybrid fiber coax [HFC] networks. Active Ethernet Point-to-Point uses dedicated fiber from an operator’s central office all the way to the subscribers’ home, while hybrid networks (often FTTN) use it to transport data via fiber to a node, and then to ensure the highest possible throughput speeds over last mile
copper connections.
This approach has become increasingly popular in recent years with telecoms service providers in both North America AT&T
, Telus
, for example] and Europe's Fastweb, Telecom Italia
, Telekom Austria
and Deutsche Telecom, for example]. Search specialist Google
has also looked into this approach, amongst others, as a way to deliver multiple services over open-access networks in the United States.
is a telecommunication architecture based on fiber-optic
cables run to a cabinet serving a neighborhood. Customers typically connect to this cabinet using traditional coaxial cable
or twisted pair
wiring. The area served by the cabinet is usually less than 1,500 m in radius and can contain several hundred customers. (If the cabinet serves an area of less than 300 m in radius then the architecture is typically called fiber to the curb.)
Fiber to the node allows delivery of broadband services such as high speed Internet. High speed communications protocol
s such as broadband cable access (typically DOCSIS
) or some form of digital subscriber line
(DSL) are used between the cabinet and the customers. The data rates vary according to the exact protocol used and according to how close the customer is to the cabinet.
Unlike the competing fiber to the premises technology, fiber to the node often uses the existing coaxial or twisted pair infrastructure to provide last mile
service. For this reason, fiber to the node is less costly to deploy. In the long-term, however, its bandwidth potential is limited relative to implementations which bring the fiber still closer to the subscriber.
A variant of this technique for cable television
providers is used in a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) system. It is sometimes given the acronym FTTN for Fiber To The Last Amplifier when it replaces analog amplifiers up to the last one before the customer (or neighborhood of customers).
cables run to a platform that serves several customers. Each of these customers has a connection to this platform via coaxial cable
or twisted pair
.
Fiber to the curb allows delivery of broadband services such as high speed internet. High speed communications protocol
s such as broadband cable access (typically DOCSIS
) or some form of DSL
are used between the cabinet and the customers. The data rates vary according to the exact protocol used and according to how close the customer is to the cabinet.
FTTC is subtly distinct from FTTN or FTTP (all are versions of Fiber in the Loop). The main difference is the placement of the cabinet. FTTC will be placed near the "curb" which differs from FTTN which is placed far from the customer and FTTP which is placed right at the serving location.
Unlike the competing fiber to the premises (FTTP) technology, fiber to the curb can use the existing coaxial or twisted pair infrastructure to provide last mile service. For this reason, fiber to the curb costs less to deploy. However, it also has lower bandwidth potential than fiber to the premises.
In the United States of America and Canada, the largest deployment of FTTC was carried out by BellSouth Telecommunications
. With the acquisition of BellSouth by AT&T
, deployment of FTTC will end. Future deployments will be based on either FTTN or FTTP. Existing FTTC plant may be removed and replaced with FTTP.
delivery in which an optical fiber
is run in a distribution network from the central office all the way to the premises
occupied by the subscriber. Fiber to the premises is often abbreviated with the acronym FTTP. However, this acronym has become ambiguous and may instead refer to a form of fiber to the curb where the fiber terminates at a utility pole
without reaching the premises.
An apartment
building may provide an example of the distinction between FTTH and FTTB. If a fiber is run to a panel at each subscriber's apartment, this is FTTH. If instead the fiber goes only as far as the apartment building's shared electrical room
, then this is FTTB.
The deployment of an FTTH network meant Fastweb was the first telecom operator to deliver true triple-play services to its subscribers. This contributed to its ARPU [Average Revenue Per User] being amongst the highest in the industry for a number of years during the early 2000s. Its FTTH network also puts it at the forefront of advanced connected home services.
Both Fiber for Italy participants and Telecom Italia are working with Advanced Digital Broadcast
to provide residential gateway
technology with embedded fiber termination.
Since 2006, Television Sierre SA deploys a FTTH network in most municipalities in the district of Sierre in Switzerland. Triple Play services are offered to the public under the brand Vario.
In October 2011, British operator Hyperoptic launched a 1Gbit/sec FTTH service in London.
in the United States for its U-Verse
service, Deutsche Telekom
in Germany, Swisscom
and Canadian operator Telus
. It is seen as an interim step towards full FTTH and in many cases services triple play services delivered using this approach has been proven to grow subscriber numbers and ARPU considerably.
, Active Optical Network, etc. From a regulatory point of view it leads to least implications as any form of regulatory remedy is still possible using this topology.
s (PONs).
 Active optical networks rely on some sort of electrically powered equipment in Optical Distribution Network(ODN) to distribute the signal, such as a switch
Active optical networks rely on some sort of electrically powered equipment in Optical Distribution Network(ODN) to distribute the signal, such as a switch
or router. Normally, optical signals need O-E-O transformation in ODN. Each signal leaving the central office is directed only to the customer for which it is intended. Incoming signals from the customers avoid colliding at the intersection because the powered equipment there provides buffering.
As of 2007, the most common type of active optical networks are called active Ethernet, a type of Ethernet in the first mile
(EFM). Active Ethernet uses optical Ethernet switches to distribute the signal, thus incorporating the customers' premises and the central office into one giant switched Ethernet
network. Such networks are identical to the Ethernet computer networks used in businesses and academic institutions, except that their purpose is to connect homes and buildings to a central office rather than to connect computers and printers within a campus. Each switching cabinet can handle up to 1,000 customers, although 400-500 is more typical. This neighborhood equipment performs layer 2/layer 3 switching and routing, offloading full layer 3 routing
to the carrier's central office. The IEEE 802.3ah
standard enables service providers to deliver up to 100 Mbit/s full-duplex
over one single-mode optical fiber
to the premises depending on the provider. Speeds of 1Gbit/s are becoming commercially available.
Downstream signal coming from the central office is broadcast to each customer premises sharing a fiber. Encryption
is used to prevent eavesdropping.
Upstream signals are combined using a multiple access protocol, usually time division multiple access
(TDMA). The OLTs
"range" the ONUs
in order to provide time slot assignments for upstream communication.
A device called an Optical Network Terminal (ONT), also called an Optical Network Unit (ONU), converts the optical signal into an electrical signal. (ONT is an ITU-T
term, whereas ONU is an IEEE
term, but the two terms mean exactly the same thing.) Optical network terminals require electrical power for their operation, so some providers connect them to back-up batteries in case of power outages. Optical network units use thin film
filter technology to convert between optical and electrical signals.
For fiber to the home and for some forms of fiber to the building, it is common for the building's existing phone systems, local area network
s, and cable TV systems to connect directly to the ONT.
If all three systems cannot directly reach the ONT, it is possible to combine signals and transport them over a common medium. Once closer to the end-user, equipment such as a router, modem
, and/or network interface
module can separate the signals and convert them into the appropriate protocol. For example, one solution for apartment buildings uses VDSL to combine data (and / or video) with voice. With this approach, the combined signal travels through the building over the existing telephone wiring until it reaches the end-user's living space. Once there, a VDSL modem copies the data and video signals and converts them into Ethernet protocol. These are then sent over the end user's category 5 cable
. A network interface module can then separate out the video signal and convert it into an RF signal that is sent over the end-user's coaxial cable
. The voice signal continues to travel over the phone wiring and is sent through DSL filter
s to remove the video and data signals. An alternative strategy allows data and / or voice to be transmitted over coaxial cable. In yet another strategy, some office buildings dispense with the telephone wiring altogether, instead using voice over Internet Protocol phones that can plug directly into the local area network.
Broadband
The term broadband refers to a telecommunications signal or device of greater bandwidth, in some sense, than another standard or usual signal or device . Different criteria for "broad" have been applied in different contexts and at different times...
network architecture using optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
to replace all or part of the usual metal local loop
Local loop
In telephony, the local loop is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider's network...
used for last mile
Last mile
The "last mile" or "last kilometer" is the final leg of delivering connectivity from a communications provider to a customer. The phrase is therefore often used by the telecommunications and cable television industries. The actual distance of this leg may be considerably more than a mile,...
telecommunications. The generic term was initially a generalization for several configurations of fiber deployment (FTTN, FTTC, FTTB, FTTH...), all starting by FTT but differentiated by the last letter, which is substituted by an x in the generalization.

Definition of terms
The telecommunications industry differentiates between several distinct configurations. The terms in most widespread use today are:- FTTN - Fiber-to-the-node - fiber is terminated in a street cabinet up to several kilometers away from the customer premises, with the final connection being copper. Fiber-to-the-node is often seen as an interim step towards full FTTH and is currently used by telecoms service providers like AT&TAT&TAT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications corporation headquartered in Whitacre Tower, Dallas, Texas, United States. It is the largest provider of mobile telephony and fixed telephony in the United States, and is also a provider of broadband and subscription television services...
, Deutsche TelekomDeutsche TelekomDeutsche Telekom AG is a telecommunications company headquartered in Bonn, Germany. It is the largest telecommunications company in Europe....
, Telekom AustriaTelekom AustriaTelekom Austria is a provider of a range of fixed line, mobile, data, and Internet communications services. The company has a 100 per cent share in telecommunications provider A1 Telekom Austria....
and SwisscomSwisscomSwisscom AG is a major telecommunications provider in Switzerland. Along with Swiss Post, it is a successor company to the former state-owned PTT. Its headquarters are located at Worblaufen near Bern...
to deliver advanced triple-playTriple play (telecommunications)In telecommunications, triple play service is a marketing term for the provisioning of two bandwidth-intensive services, high-speed Internet access and television, and a less bandwidth-demanding service, telephone, over a single broadband connection. Triple play focuses on a combined business...
services. - FTTC - Fiber-to-the-curb - this is very similar to FTTN, but the street cabinet is closer to the user's premises; typically within 300m.
- FTTB - Fiber-to-the-building or Fiber-to-the-basement - fiber reaches the boundary of the building, such as the basement in a multi-dwelling unit, with the final connection to the individual living space being made via alternative means.
- FTTH - Fiber-to-the-home - fiber reaches the boundary of the living space, such as a box on the outside wall of a home.
- FTTP - Fiber-to-the premises - this term is used in several contexts: as a blanket term for both FTTH and FTTB, or where the fiber network includes both homes and small businesses.
- FTTD - Fiber-to-the-desk - fiber connection is installed from the main computer room to a terminal or fiber media converterFiber media converterFiber media converters are simple networking devices that make it possible to connect two dissimilar media types such as twisted pair with fiber optic cabling. They were introduced to the industry nearly two decades ago, and are important in interconnecting fiber optic cabling-based systems with...
near the users desk.
To promote consistency, especially when comparing FTTH penetration rates between countries, the three FTTH Councils of Europe, North America and Asia-Pacific agreed upon definitions for FTTH and FTTB in 2006, with an update in 2009. The FTTH Councils do not have formal definitions for FTTC and FTTN.
To some, fiber to the telecom enclosure
Fiber to the Telecom Enclosure
Fiber to the telecom enclosure , also sometimes called fiber to the zone , is a standards-compliant structured cabling system architecture that extends the optical fiber backbone network from the equipment room, through the telecom room, and directly to a telecommunications enclosure installed in...
(FTTE) is not considered to be part of the FTTx group of technologies, despite the similarity in name. FTTE is a form of structured cabling
Structured cabling
Structured cabling is building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements called subsystems.Structured cabling falls into six subsystems:...
typically used in the enterprise local area network
Local area network
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
, where fiber is used to link the main computer equipment room to an enclosure close to the desk or workstation. Passive optical network
Passive optical network
A passive optical network is a point-to-multipoint, fiber to the premises network architecture in which unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple premises, typically 16-128. A PON consists of an optical line terminal at the service provider's central...
s and Point-to-Point Ethernet
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
The Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol frames inside Ethernet frames. It is used mainly with DSL services where individual users connect to the DSL modem over Ethernet and in plain Metro Ethernet networks...
are architectures that deliver triple-play services over FTTH networks directly from an operator‘s central office.
Benefits
The speeds of fiber optic and copper cables are both limited by length, but copper is much more sharply limited in this respect. For example, the common form of Gigabit EthernetGigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
runs over relatively economical category 5e, category 6
Category 6
Category 6 may refer to:* Category 6: Day of Destruction, a 2004 made-for-TV movie.* Category 6 cable, a type of cable used for computer networking.* A proposed hurricane level above Category 5, on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale....
, or augmented category 6 unshielded twisted pair copper cabling but only to 100 meters. However, over the right kind of fiber, Gigabit Ethernet can easily reach tens of kilometers.
Even in the commercial world, most computers have copper communication cables. But these cables are short, typically tens of meters. Most metropolitan network links (e.g., those based on telephone or cable television services) are several kilometers long, in the range where fiber significantly outperforms copper. Replacing at least part of these links with fiber shortens the remaining copper segments and allows them to run much faster.
Fiber configurations that bring fiber right into the building can offer the highest speeds since the remaining segments can use standard Ethernet or coaxial cable. Fiber configurations that transition to copper in a street cabinet are generally too far from the users for standard Ethernet configurations over existing copper cabling. They generally use very high bitrate digital subscriber line (VDSL) at downstream rates of several tens of megabits per second.
Fiber is often said to be 'future proof' because the data rate of the connection is usually limited by the terminal equipment rather than the fiber , permitting at least some speed improvements by equipment upgrades before the fiber itself must be upgraded. Still, the type and length of employed fibers chosen, e.g. multimode vs single mode, are critical for applicability for future high gigabit connections.
Ethernet Point-to-Point
Point-to-Point Protocol over EthernetPoint-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
The Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol frames inside Ethernet frames. It is used mainly with DSL services where individual users connect to the DSL modem over Ethernet and in plain Metro Ethernet networks...
is a common way of delivering triple (and quad) play (voice, video, data and mobile) services over both fiber
Fiber
Fiber is a class of materials that are continuous filaments or are in discrete elongated pieces, similar to lengths of thread.They are very important in the biology of both plants and animals, for holding tissues together....
and hybrid fiber coax [HFC] networks. Active Ethernet Point-to-Point uses dedicated fiber from an operator’s central office all the way to the subscribers’ home, while hybrid networks (often FTTN) use it to transport data via fiber to a node, and then to ensure the highest possible throughput speeds over last mile
Last mile
The "last mile" or "last kilometer" is the final leg of delivering connectivity from a communications provider to a customer. The phrase is therefore often used by the telecommunications and cable television industries. The actual distance of this leg may be considerably more than a mile,...
copper connections.
This approach has become increasingly popular in recent years with telecoms service providers in both North America AT&T
AT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications corporation headquartered in Whitacre Tower, Dallas, Texas, United States. It is the largest provider of mobile telephony and fixed telephony in the United States, and is also a provider of broadband and subscription television services...
, Telus
TELUS
Telus is a national telecommunications company in Canada that provides a wide range of telecommunications products and services including internet access, voice, entertainment, video, and satellite television. The company is based in Burnaby, British Columbia, part of Greater Vancouver...
, for example] and Europe's Fastweb, Telecom Italia
Telecom Italia
Telecom Italia is the largest Italian telecommunications company, also active in the media and manufacturing industries. Now a private concern listed on the Borsa Italiana, it was founded in 1994 by the merger of several state-owned telecommunications companies, the most important of which was...
, Telekom Austria
Telekom Austria
Telekom Austria is a provider of a range of fixed line, mobile, data, and Internet communications services. The company has a 100 per cent share in telecommunications provider A1 Telekom Austria....
and Deutsche Telecom, for example]. Search specialist Google
Google
Google Inc. is an American multinational public corporation invested in Internet search, cloud computing, and advertising technologies. Google hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products, and generates profit primarily from advertising through its AdWords program...
has also looked into this approach, amongst others, as a way to deliver multiple services over open-access networks in the United States.
Fiber to the node
Fiber to the node (FTTN), also called fiber to the neighborhood or fiber to the cabinet (FTTCab),is a telecommunication architecture based on fiber-optic
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
cables run to a cabinet serving a neighborhood. Customers typically connect to this cabinet using traditional coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
or twisted pair
Twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
wiring. The area served by the cabinet is usually less than 1,500 m in radius and can contain several hundred customers. (If the cabinet serves an area of less than 300 m in radius then the architecture is typically called fiber to the curb.)
Fiber to the node allows delivery of broadband services such as high speed Internet. High speed communications protocol
Communications protocol
A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications...
s such as broadband cable access (typically DOCSIS
DOCSIS
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification is an international telecommunications standard that permits the addition of high-speed data transfer to an existing cable TV system...
) or some form of digital subscriber line
Digital Subscriber Line
Digital subscriber line is a family of technologies that provides digital data transmission over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL originally stood for digital subscriber loop. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line ,...
(DSL) are used between the cabinet and the customers. The data rates vary according to the exact protocol used and according to how close the customer is to the cabinet.
Unlike the competing fiber to the premises technology, fiber to the node often uses the existing coaxial or twisted pair infrastructure to provide last mile
Last mile
The "last mile" or "last kilometer" is the final leg of delivering connectivity from a communications provider to a customer. The phrase is therefore often used by the telecommunications and cable television industries. The actual distance of this leg may be considerably more than a mile,...
service. For this reason, fiber to the node is less costly to deploy. In the long-term, however, its bandwidth potential is limited relative to implementations which bring the fiber still closer to the subscriber.
A variant of this technique for cable television
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
providers is used in a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) system. It is sometimes given the acronym FTTN for Fiber To The Last Amplifier when it replaces analog amplifiers up to the last one before the customer (or neighborhood of customers).
Fiber to the curb
Fiber to the curb (FTTC) is a telecommunications system based on fiber-opticOptical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
cables run to a platform that serves several customers. Each of these customers has a connection to this platform via coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
or twisted pair
Twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
.
Fiber to the curb allows delivery of broadband services such as high speed internet. High speed communications protocol
Communications protocol
A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications...
s such as broadband cable access (typically DOCSIS
DOCSIS
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification is an international telecommunications standard that permits the addition of high-speed data transfer to an existing cable TV system...
) or some form of DSL
Digital Subscriber Line
Digital subscriber line is a family of technologies that provides digital data transmission over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL originally stood for digital subscriber loop. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line ,...
are used between the cabinet and the customers. The data rates vary according to the exact protocol used and according to how close the customer is to the cabinet.
FTTC is subtly distinct from FTTN or FTTP (all are versions of Fiber in the Loop). The main difference is the placement of the cabinet. FTTC will be placed near the "curb" which differs from FTTN which is placed far from the customer and FTTP which is placed right at the serving location.
Unlike the competing fiber to the premises (FTTP) technology, fiber to the curb can use the existing coaxial or twisted pair infrastructure to provide last mile service. For this reason, fiber to the curb costs less to deploy. However, it also has lower bandwidth potential than fiber to the premises.
In the United States of America and Canada, the largest deployment of FTTC was carried out by BellSouth Telecommunications
BellSouth Telecommunications
BellSouth Telecommunications, LLC is the Bell Operating Company of AT&T that serves the southeastern United States. It absorbed the operations of South Central Bell in 1992....
. With the acquisition of BellSouth by AT&T
AT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications corporation headquartered in Whitacre Tower, Dallas, Texas, United States. It is the largest provider of mobile telephony and fixed telephony in the United States, and is also a provider of broadband and subscription television services...
, deployment of FTTC will end. Future deployments will be based on either FTTN or FTTP. Existing FTTC plant may be removed and replaced with FTTP.
Fiber to the premises
Fiber to the premises is a form of fiber-optic communicationFiber-optic communication
Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information...
delivery in which an optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
is run in a distribution network from the central office all the way to the premises
Premises
Premises are land and buildings together considered as a property. This usage arose from property owners finding the word in their title deeds, where it originally correctly meant "the aforementioned; what this document is about", from Latin prae-missus = "placed before".In this sense, the word is...
occupied by the subscriber. Fiber to the premises is often abbreviated with the acronym FTTP. However, this acronym has become ambiguous and may instead refer to a form of fiber to the curb where the fiber terminates at a utility pole
Utility pole
A utility pole is a pole used to support overhead power lines and various other public utilities, such as cable, fibre optic cable, and related equipment such as transformers and street lights. It can be referred to as a telephone pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post,...
without reaching the premises.
FTTH vs. FTTB
Fiber to the premises can be categorized according to where the optical fiber ends:- FTTH (fiber to the home) is a form of fiber optic communication delivery that reaches one living or working space. The fiber extends from the central office to the subscriber's living or working space. Once at the subscriber's living or working space, the signal may be conveyed throughout the space using any means, including twisted pairTwisted pairTwisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
, coaxial cableCoaxial cableCoaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
, wirelessWirelessWireless telecommunications is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not physically connected. Distances can be short, such as a few meters for television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications...
, power line communicationPower line communicationPower line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
, or optical fiber.
- FTTB (fiber to the building, also called fiber to the basement) is a form of fiber optic communication delivery that necessarily applies only to those properties which contain multiple living or working spaces. The optical fiber terminates before actually reaching the subscribers living or working space itself, but does extend to the property containing that living or working space. The signal is conveyed the final distance using any non-optical means, including twisted pairTwisted pairTwisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
, coaxial cableCoaxial cableCoaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
, wirelessWirelessWireless telecommunications is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not physically connected. Distances can be short, such as a few meters for television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications...
, or power line communicationPower line communicationPower line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
.
An apartment
Apartment
An apartment or flat is a self-contained housing unit that occupies only part of a building...
building may provide an example of the distinction between FTTH and FTTB. If a fiber is run to a panel at each subscriber's apartment, this is FTTH. If instead the fiber goes only as far as the apartment building's shared electrical room
Electrical room
An electrical room is a room or space in a building dedicated to electrical equipment. The size of the electrical room is usually proportional to the size of the building. In large buildings there may be a main and subsidiary electrical rooms...
, then this is FTTB.
FTTH
- Fastweb - Italian operator FastwebFastwebFASTWEB S.p.A. is an Italian broadband telecommunications company. It provides voice, Internet, cable television, IPTV and FTTH connection. The cable television and IPTV services were developed by Fastweb themselves as the technology market in 2000 was not mature enough to offer the level of...
launched the first commercial fiber-to-the-home service in 2001. Using an Active Ethernet Point-to-PointPoint-to-Point Protocol over EthernetThe Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol frames inside Ethernet frames. It is used mainly with DSL services where individual users connect to the DSL modem over Ethernet and in plain Metro Ethernet networks...
architecture, the service delivered voice, video and data services to thousands of subscribers’ homes in Italy over a 10MB symmetrical dedicated fiber connection. Fastweb used one of the first residential gatewayResidential gatewayA residential gateway is a home networking device, used as a gateway to connect devices in the home to the Internet or other WAN.It is an umbrella term, used to cover multi-function networking computer appliances used in homes, which may combine a DSL or cable modem, a firewall, a consumer-grade...
s for both multiple dwelling units [MDUs] as well as residential homes that provided embedded fiber-termination, designed and built by Advanced Digital BroadcastAdvanced Digital BroadcastAdvanced Digital Broadcast designs, manufactures and deploys solutions to distribute pay-TV and multimedia services to the connected home, for all types of networks. The company has its global headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland and regional headquarters in Denver, USA and Taipei, Taiwan...
, to enable consumers to share services with a range of CECECE, Ce or ce may refer to:* Common Era , secular alternative to Anno Domini * Cerium, chemical element with symbol Ce- Titles :* Chief Executive, administrative head of some regions...
devices around the home.
The deployment of an FTTH network meant Fastweb was the first telecom operator to deliver true triple-play services to its subscribers. This contributed to its ARPU [Average Revenue Per User] being amongst the highest in the industry for a number of years during the early 2000s. Its FTTH network also puts it at the forefront of advanced connected home services.
- Fiber for Italy - The Fiber For Italy Initiative has the stated goal of offering 100MBps symmetrical connections to 10 million Italian subscribers across 15 cities by [2018] and up to 1GBps for business customers. It involves operators WindWindWind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
, Tele2Tele2Tele2 AB is a major European telecommunications operator, with about 34 million customers in 11 countries. It serves as a fixed-line telephone operator, cable television provider, mobile phone operator and Internet service provider.- Overview :...
, VodafoneVodafoneVodafone Group Plc is a global telecommunications company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is the world's largest mobile telecommunications company measured by revenues and the world's second-largest measured by subscribers , with around 341 million proportionate subscribers as of...
and FastwebFastwebFASTWEB S.p.A. is an Italian broadband telecommunications company. It provides voice, Internet, cable television, IPTV and FTTH connection. The cable television and IPTV services were developed by Fastweb themselves as the technology market in 2000 was not mature enough to offer the level of...
. An ongoing pilot project in the Italian capital Rome delivers symmetrical speeds of up to 100MBps to small businesses. Italian state operator Telecom ItaliaTelecom ItaliaTelecom Italia is the largest Italian telecommunications company, also active in the media and manufacturing industries. Now a private concern listed on the Borsa Italiana, it was founded in 1994 by the merger of several state-owned telecommunications companies, the most important of which was...
is not a participant in the Fiber For Italy programme, but has independently committed to provide ultra-high speed broadband up to 100MBps symmetrical connections to 50 percent of the country’s population (138 cities) by 2018.
Both Fiber for Italy participants and Telecom Italia are working with Advanced Digital Broadcast
Advanced Digital Broadcast
Advanced Digital Broadcast designs, manufactures and deploys solutions to distribute pay-TV and multimedia services to the connected home, for all types of networks. The company has its global headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland and regional headquarters in Denver, USA and Taipei, Taiwan...
to provide residential gateway
Residential gateway
A residential gateway is a home networking device, used as a gateway to connect devices in the home to the Internet or other WAN.It is an umbrella term, used to cover multi-function networking computer appliances used in homes, which may combine a DSL or cable modem, a firewall, a consumer-grade...
technology with embedded fiber termination.
Since 2006, Television Sierre SA deploys a FTTH network in most municipalities in the district of Sierre in Switzerland. Triple Play services are offered to the public under the brand Vario.
In October 2011, British operator Hyperoptic launched a 1Gbit/sec FTTH service in London.
FTTN
FTTN, or Fiber-to-the-node, is currently used by a number of multiple-service operators to deliver advanced triple play services to consumers, including AT&TAT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications corporation headquartered in Whitacre Tower, Dallas, Texas, United States. It is the largest provider of mobile telephony and fixed telephony in the United States, and is also a provider of broadband and subscription television services...
in the United States for its U-Verse
U-Verse
AT&T U-verse is a registered service mark under which AT&T offers Internet access, television, and telephone services in various parts of the United States. It began in 2008 to serve mostly residences and small businesses in urban and suburban areas.-Services:...
service, Deutsche Telekom
Deutsche Telekom
Deutsche Telekom AG is a telecommunications company headquartered in Bonn, Germany. It is the largest telecommunications company in Europe....
in Germany, Swisscom
Swisscom
Swisscom AG is a major telecommunications provider in Switzerland. Along with Swiss Post, it is a successor company to the former state-owned PTT. Its headquarters are located at Worblaufen near Bern...
and Canadian operator Telus
TELUS
Telus is a national telecommunications company in Canada that provides a wide range of telecommunications products and services including internet access, voice, entertainment, video, and satellite television. The company is based in Burnaby, British Columbia, part of Greater Vancouver...
. It is seen as an interim step towards full FTTH and in many cases services triple play services delivered using this approach has been proven to grow subscriber numbers and ARPU considerably.
Direct fiber
The simplest optical distribution network can be called direct fiber. In this architecture, each fiber leaving the central office goes to exactly one customer. Such networks can provide excellent bandwidth since each customer gets their own dedicated fiber extending all the way to the central office. However, this approach is about 10% more costly due to the amount of fiber and central office machinery required. The approach is generally favored by new entrants and competitive operators. A benefit of this approach is that it doesn't exclude any layer 2 networking technologies, be they Passive optical networkPassive optical network
A passive optical network is a point-to-multipoint, fiber to the premises network architecture in which unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple premises, typically 16-128. A PON consists of an optical line terminal at the service provider's central...
, Active Optical Network, etc. From a regulatory point of view it leads to least implications as any form of regulatory remedy is still possible using this topology.
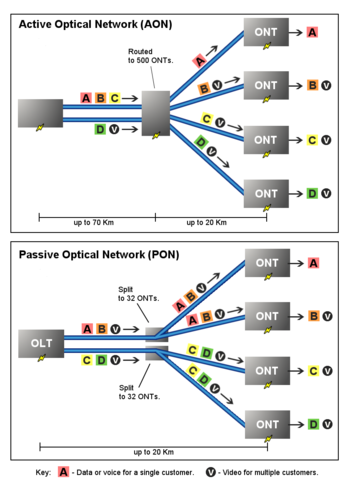
Shared fiber
More commonly each fiber leaving the central office is actually shared by many customers. It is not until such a fiber gets relatively close to the customers that it is split into individual customer-specific fibers. There are two competing optical distribution network architectures which achieve this split: active optical networks (AONs) and passive optical networkPassive optical network
A passive optical network is a point-to-multipoint, fiber to the premises network architecture in which unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple premises, typically 16-128. A PON consists of an optical line terminal at the service provider's central...
s (PONs).
Active optical network

Network switch
A network switch or switching hub is a computer networking device that connects network segments.The term commonly refers to a multi-port network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer of the OSI model...
or router. Normally, optical signals need O-E-O transformation in ODN. Each signal leaving the central office is directed only to the customer for which it is intended. Incoming signals from the customers avoid colliding at the intersection because the powered equipment there provides buffering.
As of 2007, the most common type of active optical networks are called active Ethernet, a type of Ethernet in the first mile
Ethernet in the First Mile
Ethernet in the first mile refers to using one of the Ethernet family of computer network protocols between a telecommunications company and a customer's premise. From the customer's point of view it is their "first" mile, although from the access networks' point of view it is known as the "last...
(EFM). Active Ethernet uses optical Ethernet switches to distribute the signal, thus incorporating the customers' premises and the central office into one giant switched Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
network. Such networks are identical to the Ethernet computer networks used in businesses and academic institutions, except that their purpose is to connect homes and buildings to a central office rather than to connect computers and printers within a campus. Each switching cabinet can handle up to 1,000 customers, although 400-500 is more typical. This neighborhood equipment performs layer 2/layer 3 switching and routing, offloading full layer 3 routing
Routing
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network , electronic data networks , and transportation networks...
to the carrier's central office. The IEEE 802.3ah
Ethernet in the First Mile
Ethernet in the first mile refers to using one of the Ethernet family of computer network protocols between a telecommunications company and a customer's premise. From the customer's point of view it is their "first" mile, although from the access networks' point of view it is known as the "last...
standard enables service providers to deliver up to 100 Mbit/s full-duplex
Duplex (telecommunications)
A duplex communication system is a system composed of two connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. The term multiplexing is used when describing communication between more than two parties or devices....
over one single-mode optical fiber
Single-mode optical fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single ray of light . Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions...
to the premises depending on the provider. Speeds of 1Gbit/s are becoming commercially available.
Passive optical network
A passive optical network (PON) is a point-to-multipoint, fiber to the premises network architecture in which unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple premises, typically 32-128. A PON configuration reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point to point architectures.Downstream signal coming from the central office is broadcast to each customer premises sharing a fiber. Encryption
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge, usually referred to as a key. The result of the process is encrypted information...
is used to prevent eavesdropping.
Upstream signals are combined using a multiple access protocol, usually time division multiple access
Time division multiple access
Time division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This...
(TDMA). The OLTs
Optical line termination
An optical line termination , also called an optical line terminal, is a device which serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network...
"range" the ONUs
Optical Network Unit
An optical network unit is a device that transforms incoming optical signals into electronics at a customer's premises in order to provide telecommunications services over an optical fiber network.-Definition:...
in order to provide time slot assignments for upstream communication.
Electrical portion
Once on private property, the signal typically travels the final distance to the end user's equipment using an electrical format.A device called an Optical Network Terminal (ONT), also called an Optical Network Unit (ONU), converts the optical signal into an electrical signal. (ONT is an ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
term, whereas ONU is an IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers is a non-profit professional association headquartered in New York City that is dedicated to advancing technological innovation and excellence...
term, but the two terms mean exactly the same thing.) Optical network terminals require electrical power for their operation, so some providers connect them to back-up batteries in case of power outages. Optical network units use thin film
Thin film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer to several micrometers in thickness. Electronic semiconductor devices and optical coatings are the main applications benefiting from thin film construction....
filter technology to convert between optical and electrical signals.
For fiber to the home and for some forms of fiber to the building, it is common for the building's existing phone systems, local area network
Local area network
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
s, and cable TV systems to connect directly to the ONT.
If all three systems cannot directly reach the ONT, it is possible to combine signals and transport them over a common medium. Once closer to the end-user, equipment such as a router, modem
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
, and/or network interface
Network interface
Network interface may refer to:* Network interface controller, the device a computer uses to connect to a computer network* Network interface device, a demarcation point for a telephone network...
module can separate the signals and convert them into the appropriate protocol. For example, one solution for apartment buildings uses VDSL to combine data (and / or video) with voice. With this approach, the combined signal travels through the building over the existing telephone wiring until it reaches the end-user's living space. Once there, a VDSL modem copies the data and video signals and converts them into Ethernet protocol. These are then sent over the end user's category 5 cable
Category 5 cable
Category 5 cable is a twisted pair cable for carrying signals. This type of cable is used in structured cabling for computer networks such as Ethernet. It is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video. The cable is commonly connected using punch down blocks and modular connectors...
. A network interface module can then separate out the video signal and convert it into an RF signal that is sent over the end-user's coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
. The voice signal continues to travel over the phone wiring and is sent through DSL filter
DSL filter
A DSL filter is an analog low-pass filter installed between analog devices and a plain old telephone service telephone line, in order to prevent interference between such devices and a digital subscriber line service operating on the same line...
s to remove the video and data signals. An alternative strategy allows data and / or voice to be transmitted over coaxial cable. In yet another strategy, some office buildings dispense with the telephone wiring altogether, instead using voice over Internet Protocol phones that can plug directly into the local area network.
See also
- Broadband Internet accessBroadband Internet accessBroadband Internet access, often shortened to just "broadband", is a high data rate, low-latency connection to the Internet— typically contrasted with dial-up access using a 56 kbit/s modem or satellite Internet with inherently high latency....
- Fiber-optic communicationFiber-optic communicationFiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information...
- Fiber to the premises by countryFiber to the premises by countryThis article lists the deployment of fiber to the premises by country.-Kenya: broadband residential and SOHO packages 1Mbps, 4Mbit/s and 8Mbit/s currently available in Nairobi’s Kileleshwa, Kilimani and Lavington suburbs...
- Next generation accessNext generation accessNext-generation access is term used by British Telecommunications describing a significant upgrade to the telecommunication access network replacing some or all of the copper cable with optical fibre...
- Hybrid fiber-coaxial
- Fiber in the loopFiber in the loopFiber In The Loop is a system implementing or upgrading portions of the POTS local loop with fiber optic technology from the central office of a telephone carrier to a remote Serving area interface located in a neighborhood or to an Optical Network Unit located at the customer premises...
External links
- Fiber to the Home Council: Asia & The Pacific
- Fiber to the Home Council: Europe
- Fiber to the Home Council: Northern America
- Fiber to the Home Conference: Europe
- Fiber Optics LAN Section of the Telecommunications Industry Association
- Telephony Magazine — FTTH One-Stop news, metrics, technology, regulatory information and industry commentary
- Kingfisher International Application Notes Fiber Optic Testing information about FTTH backbone Terminology.
- Can You Say FTTN? Annie Lindstrom, Telephony Online, January 22, 2001
- SBC clarifies FTTN, FTTP plans Ed Gubbins, Telephony Online, November 12, 2004
- Network intelligence — optical networks of new generation August 2008
- FTTx Primer, July 2008
- Developments in Fibre Technologies and Investment, [OECD], 2008
- San Francisco Draft Fiber Study
- UOC University article

