
Flowering plant
Encyclopedia
The flowering plants also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants
like the gymnosperm
s and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies
(derived characteristics). These characteristics include flower
s, endosperm
within the seeds, and the production of fruit
s that contain the seeds.
The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 140 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 100 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.
The flowers, which are the reproductive organs of flowering plants, are the most remarkable feature distinguishing them from other seed plants. Flowers aid angiosperms by enabling a wider range of adaptability and broadening the ecological niche
s open to them. This has allowed flowering plants to largely dominate terrestrial ecosystems.
Stamens are much lighter than the corresponding organs of gymnosperms and have contributed to the diversification of angiosperms through time with adaptation
s to specialized pollination
syndromes, such as particular pollinators. Stamens have also become modified through time to prevent self-fertilization, which has permitted further diversification, allowing angiosperms eventually to fill more niches.
The male gametophyte
in angiosperms is significantly reduced in size compared to those of gymnosperm seed plants. The smaller pollen decreases the time from pollination — the pollen grain reaching the female plant — to fertilization of the ovary; in gymnosperms, fertilization can occur up to a year after pollination, whereas, in angiosperms, the fertilization begins very soon after pollination. The shorter time leads to angiosperm plants' setting seeds sooner and faster than gymnosperms, which is a distinct evolutionary advantage.
The closed carpel of angiosperms also allows adaptations to specialized pollination syndromes and controls. This helps to prevent self-fertilization, thereby maintaining increased diversity. Once the ovary is fertilized, the carpel and some surrounding tissues develop into a fruit. This fruit often serves as an attractant to seed-dispersing animals. The resulting cooperative relationship presents another advantage to angiosperms in the process of dispersal
.
The reduced female gametophyte, like the reduced male gametophyte, may be an adaptation allowing for more rapid seed set, eventually leading to such flowering plant adaptations as annual herbaceous life-cycles, allowing the flowering plants to fill even more niches.
In general, endosperm formation begins after fertilization and before the first division of the zygote
. Endosperm is a highly nutritive tissue that can provide food for the developing embryo
, the cotyledons, and sometimes the seedling
when it first appears.
These distinguishing characteristics taken together have made the angiosperms the most diverse and numerous land plants and the most commercially important group to humans. The major exception to the dominance of terrestrial ecosystems by flowering plants is the coniferous forest.
s suggest that higher plants (embryophyte
s) have lived on the land for at least 475 million years. Early land plants reproduced
sexually with flagellated, swimming sperm, like the green algae from which they evolved. An adaptation to terrestrialization was the development of upright meiosporangia for dispersal by spore
s to new habitats. This feature is lacking in the descendants of their nearest algal relatives, the Charophycean
green algae. A later terrestrial adaptation took place with retention of the delicate, avascular sexual stage, the gametophyte, within the tissues of the vascular sporophyte. This occurred by spore germination within sporangia rather than spore release, as in non-seed plants. A current example of how this might have happened can be seen in the precocious spore germination in Sellaginella, the spike-moss. The result for the ancestors of angiosperms was enclosing them in a case, the seed
. The first seed bearing plants, like the ginkgo
, and conifers (such as pine
s and fir
s), did not produce flowers. The pollen grains (males) of Ginkgo and cycads produce a pair of flagellated, mobile sperm cells that "swim" down the developing pollen tube to the female and her eggs.
The apparently sudden appearance of relatively modern flowers in the fossil record initially posed such a problem for the theory of evolution
that it was called an "abominable mystery" by Charles Darwin
. However, the fossil record has considerably grown since the time of Darwin, and recently discovered angiosperm fossils such as Archaefructus
, along with further discoveries of fossil gymnosperms, suggest how angiosperm characteristics may have been acquired in a series of steps. Several groups of extinct gymnosperms, in particular seed ferns, have been proposed as the ancestors
of flowering plants, but there is no continuous fossil evidence showing exactly how flowers evolved. Some older fossils, such as the upper Triassic
Sanmiguelia, have been suggested. Based on current evidence, some propose that the ancestors of the angiosperms diverged from an unknown group of gymnosperms during the late Triassic
(245–202 million years ago). A close relationship between angiosperms and gnetophytes, proposed on the basis of morphological
evidence, has more recently been disputed on the basis of molecular evidence
that suggest gnetophytes are instead more closely related to other gymnosperm
s.
The evolution of seed plants and later angiosperms appears to be the result of two distinct rounds of whole genome duplication events. These occurred in and respectively.
The earliest known macrofossil
confidently identified as an angiosperm, Archaefructus liaoningensis, is dated to about 125 million years BP (the Cretaceous
period), while pollen considered to be of angiosperm origin takes the fossil
record back to about 130 million years BP. However, one study has suggested that the early-middle Jurassic
plant Schmeissneria
, traditionally considered a type of ginkgo
, may be the earliest known angiosperm, or at least a close relative. In addition, circumstantial chemical evidence has been found for the existence of angiosperms as early as 250 million years ago. Oleanane
, a secondary metabolite
produced by many flowering plants, has been found in Permian
deposits of that age together with fossils of gigantopterid
s. Gigantopterids are a group of extinct seed plants that share many morphological traits with flowering plants, although they are not known to have been flowering plants themselves.
Recent DNA
analysis based on molecular systematics showed that Amborella trichopoda
, found on the Pacific island of New Caledonia
, belongs to a sister group of the other flowering plants, and morphological studies suggest that it has features that may have been characteristic of the earliest flowering plants.
The orders Amborellales, Nymphaeales
, and Austrobaileyales
diverged as separate lineages from the remaining angiosperm clade at a very early stage in flowering plant evolution.
The great angiosperm radiation
, when a great diversity of angiosperms appears in the fossil record, occurred in the mid-Cretaceous
(approximately 100 million years ago). However, a study in 2007 estimated that the division of the five most recent (the genus Ceratophyllum
, the family Chloranthaceae
, the eudicots, the magnoliids, and the monocots) of the eight main groups occurred around 140 million years ago.
By the late Cretaceous, angiosperms appear to have dominated environments formerly occupied by fern
s and cycadophytes, but large canopy-forming trees replaced conifers as the dominant trees only close to the end of the Cretaceous
65 millions years ago or even later, at the beginning of the Tertiary
. The radiation of herbaceous angiosperm occurred much later. Yet, many fossil plants recognizable as belonging to modern families (including beech
, oak
, maple
, and magnolia
) appeared already at late Cretaceous
.
 It is generally assumed that the function
It is generally assumed that the function
of flowers, from the start, was to involve mobile animal
s in their reproduction processes. That is, pollen can be scattered even if the flower is not brightly color
ed or oddly shaped in a way that attracts animals; however, by expending the energy required to create such traits, angiosperms can enlist the aid of animals and, thus, reproduce more efficiently.
Island genetics provides one proposed explanation for the sudden, fully developed appearance of flowering plants. Island genetics is believed to be a common source of speciation
in general, especially when it comes to radical adaptations that seem to have required inferior transitional forms. Flowering plants may have evolved in an isolated setting like an island
or island chain, where the plants bearing them were able to develop a highly specialized relationship with some specific animal (a wasp
, for example). Such a relationship, with a hypothetical wasp carrying pollen from one plant to another much the way fig wasp
s do today, could result in the development of a high degree of specialization in both the plant(s) and their partners. Note that the wasp example is not incidental; bees, which, it is postulated, evolved specifically due to mutualistic plant relationships, are descended from wasps.
Animals are also involved in the distribution of seeds. Fruit
, which is formed by the enlargement of flower parts, is frequently a seed-dispersal tool that attracts animals to eat or otherwise disturb it, incidentally scattering the seeds it contains (see frugivory). While many such mutualistic relationships remain too fragile to survive competition
and to spread widely, flowering proved to be an unusually effective means of reproduction, spreading (whatever its origin) to become the dominant form of land plant life.
Flower ontogeny
uses a combination of gene
s normally responsible for forming new shoots. The most primitive flowers are thought to have had a variable number of flower parts, often separate from (but in contact with) each other. The flowers would have tended to grow in a spiral pattern, to be bisexual (in plants, this means both male and female parts on the same flower), and to be dominated by the ovary
(female part). As flowers grew more advanced, some variations developed parts fused together, with a much more specific number and design, and with either specific sexes per flower or plant, or at least "ovary-inferior".
Flower evolution continues to the present day; modern flowers have been so profoundly influenced by humans that some of them cannot be pollinated in nature. Many modern, domesticated flowers used to be simple weeds, which sprouted only when the ground was disturbed. Some of them tended to grow with human crops, perhaps already having symbiotic companion plant relationships with them, and the prettiest did not get plucked because of their beauty, developing a dependence upon and special adaptation to human affection.
A few palaeontologists have also come up with a theory that flowering plants, or angiosperms, might have evolved because of dinosaurs; in other words, they believe that dinosaurs "created" flowers. One of the theory's biggest proponents is Robert T. Bakker
. He theorizes that herbivorous dinosaurs, with their eating habits, forced plants to find new ways to develop new adaptations, in order to avoid predation by herbivores.
There are eight groups of living angiosperms:
The exact relationship between these eight groups is not yet clear, although there is agreement that the first three groups to diverge from the ancestral angiosperm were Amborellales, Nymphaeales
, and Austrobaileyales
. The term basal angiosperms refers to these three groups. The five other groups form the clade Mesangiospermae. The relationship between the three largest of these groups (magnoliids, monocots and eudicots) remains unclear. Some analyses make the magnoliids the first to diverge, others the monocots. Ceratophyllum
seems to group with the eudicots
rather than with the monocots.
αγγείον, angeíon (receptacle, vessel) and σπέρμα, (seed), was coined in the form Angiospermae by Paul Hermann
in 1690, as the name of that one of his primary divisions of the plant kingdom
. This included flowering plants possessing seeds enclosed in capsules, distinguished from his Gymnospermae, or flowering plants with achenial
or schizo-carpic fruits, the whole fruit or each of its pieces being here regarded as a seed and naked. The term and its antonym were maintained by Carolus Linnaeus
with the same sense, but with restricted application, in the names of the orders of his class Didynamia. Its use with any approach to its modern scope became possible only after 1827, when Robert Brown
established the existence of truly naked ovules in the Cycadeae and Coniferae
, and applied to them the name Gymnosperms. From that time onward, as long as these Gymnosperms were, as was usual, reckoned as dicotyledonous flowering plants, the term Angiosperm was used antithetically by botanical writers, with varying scope, as a group-name for other dicotyledonous plants.
 In 1851, Hofmeister discovered the changes occurring in the embryo-sac of flowering plants, and determined the correct relationships of these to the Cryptogamia
In 1851, Hofmeister discovered the changes occurring in the embryo-sac of flowering plants, and determined the correct relationships of these to the Cryptogamia
. This fixed the position of Gymnosperms as a class distinct from Dicotyledons, and the term Angiosperm then gradually came to be accepted as the suitable designation for the whole of the flowering plants other than Gymnosperms, including the classes of Dicotyledons and Monocotyledons. This is the sense in which the term is used today.
In most taxonomies, the flowering plants are treated as a coherent group. The most popular descriptive name has been Angiospermae (Angiosperms), with Anthophyta ("flowering plants") a second choice. These names are not linked to any rank. The Wettstein system
and the Engler system
use the name Angiospermae, at the assigned rank of subdivision. The Reveal system
treated flowering plants as subdivision Magnoliophytina (Frohne & U. Jensen ex Reveal, Phytologia 79: 70 1996), but later split it to Magnoliopsida, Liliopsida, and Rosopsida. The Takhtajan system
and Cronquist system
treat this group at the rank of division, leading to the name Magnoliophyta (from the family name Magnoliaceae). The Dahlgren system
and Thorne system (1992)
treat this group at the rank of class, leading to the name Magnoliopsida. The APG system
of 1998, and the later 2003 and 2009 revisions, treat the flowering plants as a clade called angiosperms without a formal botanical name
. However, a formal classification was published alongside the 2009 revision in which the flowering plants form the Subclass Magnoliidae.
The internal classification of this group has undergone considerable revision. The Cronquist system
, proposed by Arthur Cronquist
in 1968 and published in its full form in 1981, is still widely used but is no longer believed to accurately reflect phylogeny. A consensus about how the flowering plants should be arranged has recently begun to emerge through the work of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
(APG), which published an influential reclassification of the angiosperms in 1998. Updates incorporating more recent research were published as APG II in 2003 and as APG III in 2009.
 Traditionally, the flowering plants are divided into two groups, which in the Cronquist system are called Magnoliopsida (at the rank of class, formed from the family name Magnoliacae) and Liliopsida (at the rank of class, formed from the family name Liliaceae
Traditionally, the flowering plants are divided into two groups, which in the Cronquist system are called Magnoliopsida (at the rank of class, formed from the family name Magnoliacae) and Liliopsida (at the rank of class, formed from the family name Liliaceae
). Other descriptive names allowed by Article 16 of the ICBN include Dicotyledones or Dicotyledoneae, and Monocotyledones or Monocotyledoneae, which have a long history of use. In English a member of either group may be called a dicotyledon
(plural dicotyledons) and monocotyledon
(plural monocotyledons), or abbreviated, as dicot (plural dicots) and monocot (plural monocots). These names derive from the observation that the dicots most often have two cotyledon
s, or embryonic leaves, within each seed. The monocots usually have only one, but the rule is not absolute either way. From a diagnostic point of view, the number of cotyledons is neither a particularly handy nor a reliable character.
Recent studies, as by the APG, show that the monocots form a monophyletic group (clade
) but that the dicots do not (they are paraphyletic). Nevertheless, the majority of dicot species do form a monophyletic group, called the eudicots
or tricolpates. Of the remaining dicot species, most belong to a third major clade known as the Magnoliidae
, containing about 9,000 species. The rest include a paraphyletic grouping of primitive species known collectively as the basal angiosperms
, plus the families Ceratophyllaceae and Chloranthaceae
.
of flowering plants is estimated to be in the range of 250,000 to 400,000.
The number of families
in APG
(1998) was 462. In APG II (2003) it is not settled; at maximum it is 457, but within this number there are 55 optional segregates, so that the minimum number of families in this system is 402. In APG III (2009) there are 415 families.
The diversity of flowering plants is not evenly distributed. Nearly all species belong to the eudicot (75%), monocot (23%) and magnoliid (2%) clades. The remaining 5 clades contain a little over 250 species in total, i.e., less than 0.1% of flowering plant diversity, divided among 9 families.
The most diverse families of flowering plants, in their APG circumscriptions, in order of number of species, are:
In the list above (showing only the 10 largest families), the Orchidaceae and Poaceae are monocot families; the others are eudicot families.
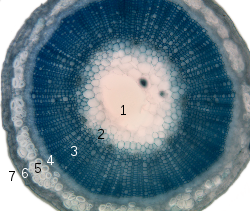 The amount and complexity
The amount and complexity
of tissue-formation in flowering plants exceeds that of gymnosperms. The vascular bundle
s of the stem are arranged such that the xylem
and phloem
form concentric rings.
In the dicotyledons, the bundles in the very young stem are arranged in an open ring, separating a central pith from an outer cortex. In each bundle, separating the xylem and phloem, is a layer of meristem
or active formative tissue known as cambium
. By the formation of a layer of cambium between the bundles (interfascicular cambium), a complete ring is formed, and a regular periodical increase in thickness results from the development of xylem on the inside and phloem on the outside. The soft phloem becomes crushed, but the hard wood persists and forms the bulk of the stem and branches of the woody perennial. Owing to differences in the character of the elements produced at the beginning and end of the season, the wood is marked out in transverse section into concentric rings, one for each season
of growth, called annual rings.
Among the monocotyledons, the bundles are more numerous in the young stem and are scattered through the ground tissue. They contain no cambium and once formed the stem increases in diameter only in exceptional cases.
containing seed
s. The floral apparatus may arise terminally on a shoot or from the axil of a leaf (where the petiole
attaches to the stem). Occasionally, as in violets
, a flower arises singly in the axil of an ordinary foliage-leaf. More typically, the flower-bearing portion of the plant is sharply distinguished from the foliage-bearing or vegetative portion, and forms a more or less elaborate branch-system called an inflorescence
.
There are two kinds of reproductive cells produced by flowers. Microspores, which will divide to become pollen grains
, are the "male" cells and are borne in the stamen
s (or microsporophylls). The "female" cells called megaspores, which will divide to become the egg-cell (megagametogenesis
), are contained in the ovule
and enclosed in the carpel (or megasporophyll).
The flower may consist only of these parts, as in willow
, where each flower comprises only a few stamens or two carpels. Usually, other structures are present and serve to protect the sporophylls and to form an envelope attractive to pollinators. The individual members of these surrounding structures are known as sepal
s and petal
s (or tepal
s in flowers such as Magnolia
where sepals and petals are not distinguishable from each other). The outer series (calyx of sepals) is usually green and leaf-like, and functions to protect the rest of the flower, especially the bud. The inner series (corolla of petals) is, in general, white or brightly colored, and is more delicate in structure. It functions to attract insect
or bird
pollinators. Attraction is effected by color, scent, and nectar, which may be secreted in some part of the flower. The characteristics that attract pollinators account for the popularity of flowers and flowering plants among humans.
While the majority of flowers are perfect or hermaphrodite
(having both male and female parts in the same flower structure), flowering plants have developed numerous morphological and physiological mechanisms to reduce or prevent self-fertilization. Heteromorphic flowers have short carpels and long stamens, or vice versa, so animal pollinator
s cannot easily transfer pollen to the pistil (receptive part of the carpel). Homomorphic flowers may employ a biochemical (physiological) mechanism called self-incompatibility
to discriminate between self- and non-self pollen grains. In other species, the male and female parts are morphologically separated, developing on different flowers.
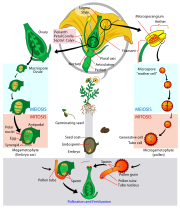 Double fertilization
Double fertilization
refers to a process in which two sperm
cells fertilize cells
in the ovary. This process begins when a pollen
grain adheres to the stigma of the pistil (female reproductive structure), germinates, and grows a long pollen tube
. While this pollen tube is growing, a haploid generative cell travels down the tube behind the tube nucleus. The generative cell divides by mitosis to produce two haploid (n) sperm cells. As the pollen tube grows, it makes its way from the stigma, down the style and into the ovary. Here the pollen tube reaches the micropyle of the ovule and digests its way into one of the synergids, releasing its contents (which include the sperm cells). The synergid that the cells were released into degenerates and one sperm makes its way to fertilize the egg cell, producing a diploid (2n) zygote. The second sperm cell fuses with both central cell nuclei, producing a triploid (3n) cell. As the zygote develops into an embryo, the triploid cell develops into the endosperm, which serves as the embryo's food supply. The ovary now will develop into fruit and the ovule will develop into seed.
 As the development of embryo and endosperm proceeds within the embryo-sac, the sac wall enlarges and combines with the nucellus (which is likewise enlarging) and the integument to form the seed-coat. The ovary wall develops to form the fruit
As the development of embryo and endosperm proceeds within the embryo-sac, the sac wall enlarges and combines with the nucellus (which is likewise enlarging) and the integument to form the seed-coat. The ovary wall develops to form the fruit
or pericarp, whose form is closely associated with the manner of distribution of the seed.
Frequently, the influence of fertilization is felt beyond the ovary
, and other parts of the flower take part in the formation of the fruit, e.g., the floral receptacle in the apple
, strawberry, and others.
The character of the seed-coat bears a definite relation to that of the fruit. They protect the embryo and aid in dissemination; they may also directly promote germination. Among plants with indehiscent fruits, in general, the fruit provides protection for the embryo and secures dissemination. In this case, the seed-coat is only slightly developed. If the fruit is dehiscent
and the seed is exposed, in general, the seed-coat is well developed, and must discharge the functions otherwise executed by the fruit.
is almost entirely dependent on angiosperms, either directly or indirectly through livestock
feed. Of all the families plants, the Poaceae
, or grass family, is by far the most important, providing the bulk of all feedstocks (rice
, corn — maize
, wheat
, barley
, rye
, oat
s, pearl millet
, sugar cane, sorghum
). The Fabaceae
, or legume family, comes in second place. Also of high importance are the Solanaceae
, or nightshade family (potato
es, tomato
es, and pepper
s, among others), the Cucurbitaceae
, or gourd
family (also including pumpkin
s and melon
s), the Brassicaceae
, or mustard plant
family (including rapeseed
and the innumerable varieties of the cabbage
species Brassica oleracea
), and the Apiaceae
, or parsley
family. Many of our fruits come from the Rutaceae
, or rue family (including orange
s, lemon
s, grapefruits, etc.), and the Rosaceae
, or rose family (including apple
s, pear
s, cherries
, apricots, plums, etc.).
In some parts of the world, certain single species assume paramount importance because of their variety of uses, for example the coconut (Cocos nucifera
) on Pacific atoll
s, and the olive (Olea europaea
) in the Mediterranean region.
Flowering plants also provide economic resources in the form of wood
, paper
, fiber (cotton
, flax
, and hemp
, among others), medicines (digitalis
, camphor
), decorative and landscaping plants, and many other uses. The main area in which they are surpassed by other plants is timber
production.
Spermatophyte
The spermatophytes comprise those plants that produce seeds. They are a subset of the embryophytes or land plants...
like the gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies
Synapomorphy
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character is a trait that is shared by two or more taxa and their most recent common ancestor, whose ancestor in turn does not possess the trait. A synapomorphy is thus an apomorphy visible in multiple taxa, where the trait in question originates in...
(derived characteristics). These characteristics include flower
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
s, endosperm
Endosperm
Endosperm is the tissue produced inside the seeds of most flowering plants around the time of fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein. This makes endosperm an important source of nutrition in human diet...
within the seeds, and the production of fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
s that contain the seeds.
The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 140 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 100 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.
Angiosperm derived characteristics
- FlowerFlowerA flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
s
The flowers, which are the reproductive organs of flowering plants, are the most remarkable feature distinguishing them from other seed plants. Flowers aid angiosperms by enabling a wider range of adaptability and broadening the ecological niche
Ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other; e.g. a dolphin could potentially be in another ecological niche from one that travels in a different pod if the members of these pods utilize significantly different food...
s open to them. This has allowed flowering plants to largely dominate terrestrial ecosystems.
- StamenStamenThe stamen is the pollen producing reproductive organ of a flower...
s with two pairs of pollen sacs
Stamens are much lighter than the corresponding organs of gymnosperms and have contributed to the diversification of angiosperms through time with adaptation
Adaptation
An adaptation in biology is a trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection. An adaptation refers to both the current state of being adapted and to the dynamic evolutionary process that leads to the adaptation....
s to specialized pollination
Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred in plants, thereby enabling fertilisation and sexual reproduction. Pollen grains transport the male gametes to where the female gamete are contained within the carpel; in gymnosperms the pollen is directly applied to the ovule itself...
syndromes, such as particular pollinators. Stamens have also become modified through time to prevent self-fertilization, which has permitted further diversification, allowing angiosperms eventually to fill more niches.
- Reduced male parts, three cells
The male gametophyte
Gametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
in angiosperms is significantly reduced in size compared to those of gymnosperm seed plants. The smaller pollen decreases the time from pollination — the pollen grain reaching the female plant — to fertilization of the ovary; in gymnosperms, fertilization can occur up to a year after pollination, whereas, in angiosperms, the fertilization begins very soon after pollination. The shorter time leads to angiosperm plants' setting seeds sooner and faster than gymnosperms, which is a distinct evolutionary advantage.
- Closed carpel enclosing the ovules (carpel or carpels and accessory parts may become the fruitFruitIn broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
)
The closed carpel of angiosperms also allows adaptations to specialized pollination syndromes and controls. This helps to prevent self-fertilization, thereby maintaining increased diversity. Once the ovary is fertilized, the carpel and some surrounding tissues develop into a fruit. This fruit often serves as an attractant to seed-dispersing animals. The resulting cooperative relationship presents another advantage to angiosperms in the process of dispersal
Biological dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to species movement away from an existing population or away from the parent organism. Through simply moving from one habitat patch to another, the dispersal of an individual has consequences not only for individual fitness, but also for population dynamics, population...
.
- Reduced female gametophyte, seven cells with eight nuclei
The reduced female gametophyte, like the reduced male gametophyte, may be an adaptation allowing for more rapid seed set, eventually leading to such flowering plant adaptations as annual herbaceous life-cycles, allowing the flowering plants to fill even more niches.
- EndospermEndospermEndosperm is the tissue produced inside the seeds of most flowering plants around the time of fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein. This makes endosperm an important source of nutrition in human diet...
In general, endosperm formation begins after fertilization and before the first division of the zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
. Endosperm is a highly nutritive tissue that can provide food for the developing embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
, the cotyledons, and sometimes the seedling
Seedling
thumb|Monocot and dicot seedlingsA seedling is a young plant sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle , the hypocotyl , and the cotyledons...
when it first appears.
These distinguishing characteristics taken together have made the angiosperms the most diverse and numerous land plants and the most commercially important group to humans. The major exception to the dominance of terrestrial ecosystems by flowering plants is the coniferous forest.
Evolution
Fossilized sporeSpore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s suggest that higher plants (embryophyte
Embryophyte
The land plants or embryophytes, more formally Embryophyta or Metaphyta, are the most familiar group of plants. They are called 'land plants' because they live primarily in terrestrial habitats, in contrast with the related green algae that are primarily aquatic. The embryophytes include trees,...
s) have lived on the land for at least 475 million years. Early land plants reproduced
Plant sexuality
Plant sexuality covers the wide variety of sexual reproduction systems found across the plant kingdom. This article describes morphological aspects of sexual reproduction of plants....
sexually with flagellated, swimming sperm, like the green algae from which they evolved. An adaptation to terrestrialization was the development of upright meiosporangia for dispersal by spore
Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s to new habitats. This feature is lacking in the descendants of their nearest algal relatives, the Charophycean
Charophyceae
Charophyceae is a taxon of green algae whose exact rank is the matter of some current debate. Some botanists recommend expanding the existing plant kingdom to include charophyceans and chlorophytes while others consider Charophyceae to be a class within either the divisions Chlorophyta,...
green algae. A later terrestrial adaptation took place with retention of the delicate, avascular sexual stage, the gametophyte, within the tissues of the vascular sporophyte. This occurred by spore germination within sporangia rather than spore release, as in non-seed plants. A current example of how this might have happened can be seen in the precocious spore germination in Sellaginella, the spike-moss. The result for the ancestors of angiosperms was enclosing them in a case, the seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
. The first seed bearing plants, like the ginkgo
Ginkgo
Ginkgo , also spelled gingko and known as the Maidenhair Tree, is a unique species of tree with no close living relatives...
, and conifers (such as pine
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
s and fir
Fir
Firs are a genus of 48–55 species of evergreen conifers in the family Pinaceae. They are found through much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa, occurring in mountains over most of the range...
s), did not produce flowers. The pollen grains (males) of Ginkgo and cycads produce a pair of flagellated, mobile sperm cells that "swim" down the developing pollen tube to the female and her eggs.
The apparently sudden appearance of relatively modern flowers in the fossil record initially posed such a problem for the theory of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
that it was called an "abominable mystery" by Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
. However, the fossil record has considerably grown since the time of Darwin, and recently discovered angiosperm fossils such as Archaefructus
Archaefructus
Archaefructus is an extinct genus of herbaceous aquatic seed plants with 3 known species. Fossil material assigned to this genus originates from the Yixian Formation in northeastern China, originally dated as late Jurassic but now thought to be approximately 125 million years old, or early...
, along with further discoveries of fossil gymnosperms, suggest how angiosperm characteristics may have been acquired in a series of steps. Several groups of extinct gymnosperms, in particular seed ferns, have been proposed as the ancestors
Most recent common ancestor
In genetics, the most recent common ancestor of any set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all organisms in the group are directly descended...
of flowering plants, but there is no continuous fossil evidence showing exactly how flowers evolved. Some older fossils, such as the upper Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
Sanmiguelia, have been suggested. Based on current evidence, some propose that the ancestors of the angiosperms diverged from an unknown group of gymnosperms during the late Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
(245–202 million years ago). A close relationship between angiosperms and gnetophytes, proposed on the basis of morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
evidence, has more recently been disputed on the basis of molecular evidence
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
that suggest gnetophytes are instead more closely related to other gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s.
The evolution of seed plants and later angiosperms appears to be the result of two distinct rounds of whole genome duplication events. These occurred in and respectively.
The earliest known macrofossil
Macrofossil
Macrofossils are preserved organic remains large enough to be visible without a microscope. Most fossils discussed in the article Fossil are macrofossils.-Macrofossil contrasted with Microfossil:...
confidently identified as an angiosperm, Archaefructus liaoningensis, is dated to about 125 million years BP (the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
period), while pollen considered to be of angiosperm origin takes the fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
record back to about 130 million years BP. However, one study has suggested that the early-middle Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
plant Schmeissneria
Schmeissneria
Schmeissneria is a possible early angiosperm recorded from the Lower Jurassic of Europe and the Middle Jurassic of China , traditionally included in the Ginkgophyta....
, traditionally considered a type of ginkgo
Ginkgo
Ginkgo , also spelled gingko and known as the Maidenhair Tree, is a unique species of tree with no close living relatives...
, may be the earliest known angiosperm, or at least a close relative. In addition, circumstantial chemical evidence has been found for the existence of angiosperms as early as 250 million years ago. Oleanane
Oleanane
Oleanane is a natural triterpene. It forms the central core for a wide variety of chemical compounds found in flowering plants which are referred to collectively as oleanane triterpenes.Some oleanane triterpenes have a suppressing effect on insect pests...
, a secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds that are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of an organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolities does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's...
produced by many flowering plants, has been found in Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
deposits of that age together with fossils of gigantopterid
Gigantopterid
Gigantopterids is the name given to fossils of a group of plants existing in the Late Permian, some . Gigantopterids were among the most advanced land plants of the Paleozoic and disappeared soon after the massive Permian–Triassic extinction event...
s. Gigantopterids are a group of extinct seed plants that share many morphological traits with flowering plants, although they are not known to have been flowering plants themselves.
Recent DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
analysis based on molecular systematics showed that Amborella trichopoda
Amborella
Amborella is a genus of rare understory shrubs or small trees endemic to the island of New Caledonia. The genus consists of only a single species, Amborella trichopoda, and is the only member of the family Amborellaceae. Wood of Amborella lacks the vessels characteristic of most flowering plants...
, found on the Pacific island of New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, belongs to a sister group of the other flowering plants, and morphological studies suggest that it has features that may have been characteristic of the earliest flowering plants.
The orders Amborellales, Nymphaeales
Nymphaeales
Nymphaeales is an order of plants, which consists of water lilies and other aquatic plants.This order is considered to be a basal, or early diverging, group of angiosperms...
, and Austrobaileyales
Austrobaileyales
Austrobaileyales is the botanical name for an order of flowering plants, consisting of about 100 species of woody plants, perhaps the most famous of which is the spice star anise.- In different classifications :...
diverged as separate lineages from the remaining angiosperm clade at a very early stage in flowering plant evolution.
The great angiosperm radiation
Adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is the evolution of ecological and phenotypic diversity within a rapidly multiplying lineage. Starting with a recent single ancestor, this process results in the speciation and phenotypic adaptation of an array of species exhibiting different...
, when a great diversity of angiosperms appears in the fossil record, occurred in the mid-Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
(approximately 100 million years ago). However, a study in 2007 estimated that the division of the five most recent (the genus Ceratophyllum
Ceratophyllum
Ceratophyllum is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plants, commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions...
, the family Chloranthaceae
Chloranthaceae
Chloranthaceae is the botanical name of a family of flowering plants. The family consists of four genera, totalling several dozen species, of herbaceous or woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central & South America, and the West Indies...
, the eudicots, the magnoliids, and the monocots) of the eight main groups occurred around 140 million years ago.
By the late Cretaceous, angiosperms appear to have dominated environments formerly occupied by fern
Fern
A fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s and cycadophytes, but large canopy-forming trees replaced conifers as the dominant trees only close to the end of the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
65 millions years ago or even later, at the beginning of the Tertiary
Tertiary
The Tertiary is a deprecated term for a geologic period 65 million to 2.6 million years ago. The Tertiary covered the time span between the superseded Secondary period and the Quaternary...
. The radiation of herbaceous angiosperm occurred much later. Yet, many fossil plants recognizable as belonging to modern families (including beech
Beech
Beech is a genus of ten species of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia and North America.-Habit:...
, oak
Oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
, maple
Maple
Acer is a genus of trees or shrubs commonly known as maple.Maples are variously classified in a family of their own, the Aceraceae, or together with the Hippocastanaceae included in the family Sapindaceae. Modern classifications, including the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group system, favour inclusion in...
, and magnolia
Magnolia
Magnolia is a large genus of about 210 flowering plant species in the subfamily Magnolioideae of the family Magnoliaceae. It is named after French botanist Pierre Magnol....
) appeared already at late Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
.

Function (biology)
A function is part of an answer to a question about why some object or process occurred in a system that evolved through a process of selection. Thus, function refers forward from the object or process, along some chain of causation, to the goal or success...
of flowers, from the start, was to involve mobile animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s in their reproduction processes. That is, pollen can be scattered even if the flower is not brightly color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
ed or oddly shaped in a way that attracts animals; however, by expending the energy required to create such traits, angiosperms can enlist the aid of animals and, thus, reproduce more efficiently.
Island genetics provides one proposed explanation for the sudden, fully developed appearance of flowering plants. Island genetics is believed to be a common source of speciation
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. The biologist Orator F. Cook seems to have been the first to coin the term 'speciation' for the splitting of lineages or 'cladogenesis,' as opposed to 'anagenesis' or 'phyletic evolution' occurring within lineages...
in general, especially when it comes to radical adaptations that seem to have required inferior transitional forms. Flowering plants may have evolved in an isolated setting like an island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
or island chain, where the plants bearing them were able to develop a highly specialized relationship with some specific animal (a wasp
Wasp
The term wasp is typically defined as any insect of the order Hymenoptera and suborder Apocrita that is neither a bee nor an ant. Almost every pest insect species has at least one wasp species that preys upon it or parasitizes it, making wasps critically important in natural control of their...
, for example). Such a relationship, with a hypothetical wasp carrying pollen from one plant to another much the way fig wasp
Fig wasp
Fig wasps are wasps of the family Agaonidae which pollinate figs or are otherwise associated with figs, a coevolutional relationship that has been developing for at least 80 million years...
s do today, could result in the development of a high degree of specialization in both the plant(s) and their partners. Note that the wasp example is not incidental; bees, which, it is postulated, evolved specifically due to mutualistic plant relationships, are descended from wasps.
Animals are also involved in the distribution of seeds. Fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
, which is formed by the enlargement of flower parts, is frequently a seed-dispersal tool that attracts animals to eat or otherwise disturb it, incidentally scattering the seeds it contains (see frugivory). While many such mutualistic relationships remain too fragile to survive competition
Competition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
and to spread widely, flowering proved to be an unusually effective means of reproduction, spreading (whatever its origin) to become the dominant form of land plant life.
Flower ontogeny
Ontogeny
Ontogeny is the origin and the development of an organism – for example: from the fertilized egg to mature form. It covers in essence, the study of an organism's lifespan...
uses a combination of gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s normally responsible for forming new shoots. The most primitive flowers are thought to have had a variable number of flower parts, often separate from (but in contact with) each other. The flowers would have tended to grow in a spiral pattern, to be bisexual (in plants, this means both male and female parts on the same flower), and to be dominated by the ovary
Ovary (plants)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals...
(female part). As flowers grew more advanced, some variations developed parts fused together, with a much more specific number and design, and with either specific sexes per flower or plant, or at least "ovary-inferior".
Flower evolution continues to the present day; modern flowers have been so profoundly influenced by humans that some of them cannot be pollinated in nature. Many modern, domesticated flowers used to be simple weeds, which sprouted only when the ground was disturbed. Some of them tended to grow with human crops, perhaps already having symbiotic companion plant relationships with them, and the prettiest did not get plucked because of their beauty, developing a dependence upon and special adaptation to human affection.
A few palaeontologists have also come up with a theory that flowering plants, or angiosperms, might have evolved because of dinosaurs; in other words, they believe that dinosaurs "created" flowers. One of the theory's biggest proponents is Robert T. Bakker
Robert T. Bakker
Robert T. Bakker is an American paleontologist who helped reshape modern theories about dinosaurs, particularly by adding support to the theory that some dinosaurs were endothermic...
. He theorizes that herbivorous dinosaurs, with their eating habits, forced plants to find new ways to develop new adaptations, in order to avoid predation by herbivores.
Classification
| {clade| style=font-size:75%;line-height:75% | label1=Angiospermae | 1= }} |
| The phylogeny Phylogenetics In biology, phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relatedness among groups of organisms , which is discovered through molecular sequencing data and morphological data matrices... of the flowering plants, as of APG III (2009). |
||
| {clade| style=font-size:75%;line-height:75% | label1=Angiospermae | 1= }} |
| Alternative phylogeny (2010) |
There are eight groups of living angiosperms:
- AmborellaAmborellaAmborella is a genus of rare understory shrubs or small trees endemic to the island of New Caledonia. The genus consists of only a single species, Amborella trichopoda, and is the only member of the family Amborellaceae. Wood of Amborella lacks the vessels characteristic of most flowering plants...
— a single species of shrub from New CaledoniaNew CaledoniaNew Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of... - NymphaealesNymphaealesNymphaeales is an order of plants, which consists of water lilies and other aquatic plants.This order is considered to be a basal, or early diverging, group of angiosperms...
— about 80 species — water liliesNymphaeaceaeNymphaeaceae is a family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called water lilies and live in freshwater areas in temperate and tropical climates around the world. The family contains eight genera. There are about 70 species of water lilies around the world. The genus...
and HydatellaceaeHydatellaceaeHydatellaceae are small, aquatic flowering plants. The family includes the genus Trithuria, which has been recently re-defined to include the genus Hydatella. The family consists of about a dozen species. These tiny , relatively simple, aquatic plants occur in Australasia and India. The simple... - AustrobaileyalesAustrobaileyalesAustrobaileyales is the botanical name for an order of flowering plants, consisting of about 100 species of woody plants, perhaps the most famous of which is the spice star anise.- In different classifications :...
— about 100 species of woody plantWoody plantA woody plant is a plant that uses wood as its structural tissue. These are typically perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced adjacent to the vascular tissues. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of...
s from various parts of the world - Chloranthales — several dozen species of aromatic plants with toothed leaves
- MagnoliidaeMagnoliidaeMagnoliids are a group of about 9,000 species of flowering plants, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, and many others. They are characterized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves.-Classification:Traditionally,...
— about 9,000 species, characterized by trimerousMerosityMerosity is the number of component parts in each whorl of a plant structure. It is most commonly used in the context of flowers, in which case it refers to the number of sepals in the calyx, the number of petals in the corolla, and the number of stamens in each whorl of the androecium...
flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves — for example magnoliaMagnoliaMagnolia is a large genus of about 210 flowering plant species in the subfamily Magnolioideae of the family Magnoliaceae. It is named after French botanist Pierre Magnol....
s, bay laurelBay LaurelThe bay laurel , also known as sweet bay, bay tree, true laurel, Grecian laurel, laurel tree, or simply laurel, is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glossy leaves, native to the Mediterranean region. It is the source of the bay leaf used in cooking...
, and black pepperBlack pepperBlack pepper is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit, known as a peppercorn when dried, is approximately in diameter, dark red when fully mature, and, like all drupes, contains a single seed... - MonocotyledonMonocotyledonMonocotyledons, also known as monocots, are one of two major groups of flowering plants that are traditionally recognized, the other being dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocot seedlings typically have one cotyledon , in contrast to the two cotyledons typical of dicots...
ae — about 70,000 species, characterized by trimerous flowers, a single cotyledonCotyledonA cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
, pollen with one pore, and usually parallel-veined leaves — for example grassPoaceaeThe Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
es, orchids, and palmArecaceaeArecaceae or Palmae , are a family of flowering plants, the only family in the monocot order Arecales. There are roughly 202 currently known genera with around 2600 species, most of which are restricted to tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate climates...
s - CeratophyllumCeratophyllumCeratophyllum is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plants, commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions...
— about 6 species of aquatic plantAquatic plantAquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments. They are also referred to as hydrophytes or aquatic macrophytes. These plants require special adaptations for living submerged in water, or at the water's surface. Aquatic plants can only grow in water or in soil that is...
s, perhaps most familiar as aquariumAquariumAn aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
plants - EudicotyledonaeEudicotsEudicots and Eudicotyledons are botanical terms introduced by Doyle & Hotton to refer to a monophyletic group of flowering plants that had been called tricolpates or non-Magnoliid dicots by previous authors...
— about 175,000 species, characterized by 4- or 5- merousMerosityMerosity is the number of component parts in each whorl of a plant structure. It is most commonly used in the context of flowers, in which case it refers to the number of sepals in the calyx, the number of petals in the corolla, and the number of stamens in each whorl of the androecium...
flowers, pollen with three pores, and usually branching-veined leaves — for example sunflowerSunflowerSunflower is an annual plant native to the Americas. It possesses a large inflorescence . The sunflower got its name from its huge, fiery blooms, whose shape and image is often used to depict the sun. The sunflower has a rough, hairy stem, broad, coarsely toothed, rough leaves and circular heads...
s, petuniaPetuniaPetunia is a widely cultivated genus of flowering plants of South American origin, closely related with tobacco, cape gooseberries, tomatoes, deadly nightshades, potatoes and chili peppers; in the family Solanaceae. The popular flower derived its name from French, which took the word petun, meaning...
, buttercup, appleAppleThe apple is the pomaceous fruit of the apple tree, species Malus domestica in the rose family . It is one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits, and the most widely known of the many members of genus Malus that are used by humans. Apple grow on small, deciduous trees that blossom in the spring...
s and oakOakAn oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
s
The exact relationship between these eight groups is not yet clear, although there is agreement that the first three groups to diverge from the ancestral angiosperm were Amborellales, Nymphaeales
Nymphaeales
Nymphaeales is an order of plants, which consists of water lilies and other aquatic plants.This order is considered to be a basal, or early diverging, group of angiosperms...
, and Austrobaileyales
Austrobaileyales
Austrobaileyales is the botanical name for an order of flowering plants, consisting of about 100 species of woody plants, perhaps the most famous of which is the spice star anise.- In different classifications :...
. The term basal angiosperms refers to these three groups. The five other groups form the clade Mesangiospermae. The relationship between the three largest of these groups (magnoliids, monocots and eudicots) remains unclear. Some analyses make the magnoliids the first to diverge, others the monocots. Ceratophyllum
Ceratophyllum
Ceratophyllum is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plants, commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions...
seems to group with the eudicots
Eudicots
Eudicots and Eudicotyledons are botanical terms introduced by Doyle & Hotton to refer to a monophyletic group of flowering plants that had been called tricolpates or non-Magnoliid dicots by previous authors...
rather than with the monocots.
History of classification
The botanical term "Angiosperm", from the Ancient GreekAncient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
αγγείον, angeíon (receptacle, vessel) and σπέρμα, (seed), was coined in the form Angiospermae by Paul Hermann
Paul Hermann
Paul Hermann was a German born physician and botanist who for 15 years was director of the Hortus Botanicus Leiden....
in 1690, as the name of that one of his primary divisions of the plant kingdom
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, kingdom is a taxonomic rank, which is either the highest rank or in the more recent three-domain system, the rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla or divisions in botany...
. This included flowering plants possessing seeds enclosed in capsules, distinguished from his Gymnospermae, or flowering plants with achenial
Achene
An achene is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate and indehiscent...
or schizo-carpic fruits, the whole fruit or each of its pieces being here regarded as a seed and naked. The term and its antonym were maintained by Carolus Linnaeus
Carolus Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus , also known after his ennoblement as , was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern scheme of binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology...
with the same sense, but with restricted application, in the names of the orders of his class Didynamia. Its use with any approach to its modern scope became possible only after 1827, when Robert Brown
Robert Brown (botanist)
Robert Brown was a Scottish botanist and palaeobotanist who made important contributions to botany largely through his pioneering use of the microscope...
established the existence of truly naked ovules in the Cycadeae and Coniferae
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 13 or 14 division level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae. Pinophytes are gymnosperms. They are cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue; all extant conifers are woody plants, the great majority being...
, and applied to them the name Gymnosperms. From that time onward, as long as these Gymnosperms were, as was usual, reckoned as dicotyledonous flowering plants, the term Angiosperm was used antithetically by botanical writers, with varying scope, as a group-name for other dicotyledonous plants.

Vascular plant
Vascular plants are those plants that have lignified tissues for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, Equisetum, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms...
. This fixed the position of Gymnosperms as a class distinct from Dicotyledons, and the term Angiosperm then gradually came to be accepted as the suitable designation for the whole of the flowering plants other than Gymnosperms, including the classes of Dicotyledons and Monocotyledons. This is the sense in which the term is used today.
In most taxonomies, the flowering plants are treated as a coherent group. The most popular descriptive name has been Angiospermae (Angiosperms), with Anthophyta ("flowering plants") a second choice. These names are not linked to any rank. The Wettstein system
Wettstein system
A system of plant taxonomy, the Wettstein system recognised the following main groups, according to* I. phylum Schizophyta*::: 1. classis Schizophyceae*::: 2. classis Schizomycetes* II. phylum Monadophyta* III. phylum Myxophyta...
and the Engler system
Engler system
One of the prime systems of plant taxonomy, the Engler system was devised by Adolf Engler.According to Engler, Syllabus der Pflanzenfamilien the main groups of plants are:* I. divisio Schizophyta* II. divisio Phytosarcodina...
use the name Angiospermae, at the assigned rank of subdivision. The Reveal system
Reveal system
A modern system of plant taxonomy, the Reveal system of plant classification was drawn up by the botanist J.L. Reveal , professor emeritus at the Norton Brown Herbarium, Maryland .The last update of the system was made in 1999...
treated flowering plants as subdivision Magnoliophytina (Frohne & U. Jensen ex Reveal, Phytologia 79: 70 1996), but later split it to Magnoliopsida, Liliopsida, and Rosopsida. The Takhtajan system
Takhtajan system
A system of plant taxonomy, the Takhtajan system of plant classification was published by Armen Takhtajan, in several versions from the 1950s onwards. It is usually compared to the Cronquist system. Key publications:-External links:* Takhtajan system at...
and Cronquist system
Cronquist system
The Cronquist system is a taxonomic classification system of flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in his texts An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants and The Evolution and Classification of Flowering Plants .Cronquist's system places flowering plants into two...
treat this group at the rank of division, leading to the name Magnoliophyta (from the family name Magnoliaceae). The Dahlgren system
Dahlgren system
One of the modern systems of plant taxonomy, the Dahlgren system was published by monocot specialist Rolf Dahlgren. His wife Gertrud Dahlgren carried on after his death.According to the extensive listing by Professor Reveal One of the modern systems of plant taxonomy, the Dahlgren system was...
and Thorne system (1992)
Thorne system (1992)
A modern system of plant taxonomy, the Thorne system of plant classification was drawn up by the botanist Robert F. Thorne . He replaced it in 2000 with a new system. These two systems were published in:...
treat this group at the rank of class, leading to the name Magnoliopsida. The APG system
APG system
The APG system of plant classification is the first, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy that was published in 1998 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. It was superseded in 2003 by a revision, the APG II system, and then in 2009 by a further...
of 1998, and the later 2003 and 2009 revisions, treat the flowering plants as a clade called angiosperms without a formal botanical name
Botanical name
A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar and/or Group epithets must conform to the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants...
. However, a formal classification was published alongside the 2009 revision in which the flowering plants form the Subclass Magnoliidae.
The internal classification of this group has undergone considerable revision. The Cronquist system
Cronquist system
The Cronquist system is a taxonomic classification system of flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in his texts An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants and The Evolution and Classification of Flowering Plants .Cronquist's system places flowering plants into two...
, proposed by Arthur Cronquist
Arthur Cronquist
Arthur John Cronquist was a North American botanist and a specialist on Compositae. He is considered one of the most influential botanists of the 20th century, largely due to his formulation of the Cronquist system. Two plant genera in the aster family have been named in his honor...
in 1968 and published in its full form in 1981, is still widely used but is no longer believed to accurately reflect phylogeny. A consensus about how the flowering plants should be arranged has recently begun to emerge through the work of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, or APG, refers to an informal international group of systematic botanists who came together to try to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants that would reflect new knowledge about plant relationships discovered through phylogenetic studies., three...
(APG), which published an influential reclassification of the angiosperms in 1998. Updates incorporating more recent research were published as APG II in 2003 and as APG III in 2009.

Liliaceae
The Liliaceae, or the lily family, is a family of monocotyledons in the order Liliales. Plants in this family have linear leaves, mostly with parallel veins but with several having net venation , and flower arranged in threes. Several have bulbs, while others have rhizomes...
). Other descriptive names allowed by Article 16 of the ICBN include Dicotyledones or Dicotyledoneae, and Monocotyledones or Monocotyledoneae, which have a long history of use. In English a member of either group may be called a dicotyledon
Dicotyledon
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots, are a group of flowering plants whose seed typically has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. There are around 199,350 species within this group...
(plural dicotyledons) and monocotyledon
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons, also known as monocots, are one of two major groups of flowering plants that are traditionally recognized, the other being dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocot seedlings typically have one cotyledon , in contrast to the two cotyledons typical of dicots...
(plural monocotyledons), or abbreviated, as dicot (plural dicots) and monocot (plural monocots). These names derive from the observation that the dicots most often have two cotyledon
Cotyledon
A cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
s, or embryonic leaves, within each seed. The monocots usually have only one, but the rule is not absolute either way. From a diagnostic point of view, the number of cotyledons is neither a particularly handy nor a reliable character.
Recent studies, as by the APG, show that the monocots form a monophyletic group (clade
Clade
A clade is a group consisting of a species and all its descendants. In the terms of biological systematics, a clade is a single "branch" on the "tree of life". The idea that such a "natural group" of organisms should be grouped together and given a taxonomic name is central to biological...
) but that the dicots do not (they are paraphyletic). Nevertheless, the majority of dicot species do form a monophyletic group, called the eudicots
Eudicots
Eudicots and Eudicotyledons are botanical terms introduced by Doyle & Hotton to refer to a monophyletic group of flowering plants that had been called tricolpates or non-Magnoliid dicots by previous authors...
or tricolpates. Of the remaining dicot species, most belong to a third major clade known as the Magnoliidae
Magnoliidae
Magnoliids are a group of about 9,000 species of flowering plants, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, and many others. They are characterized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves.-Classification:Traditionally,...
, containing about 9,000 species. The rest include a paraphyletic grouping of primitive species known collectively as the basal angiosperms
Basal angiosperms
The basal angiosperms are the first flowering plants to diverge from the ancestral angiosperm. In particular, the most basal angiosperms are the so-called ANITA grade which is made up of Amborella , Nymphaeales and Austrobaileyales...
, plus the families Ceratophyllaceae and Chloranthaceae
Chloranthaceae
Chloranthaceae is the botanical name of a family of flowering plants. The family consists of four genera, totalling several dozen species, of herbaceous or woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central & South America, and the West Indies...
.
Flowering plant diversity
The number of speciesSpecies
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
of flowering plants is estimated to be in the range of 250,000 to 400,000.
The number of families
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
in APG
APG system
The APG system of plant classification is the first, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy that was published in 1998 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. It was superseded in 2003 by a revision, the APG II system, and then in 2009 by a further...
(1998) was 462. In APG II (2003) it is not settled; at maximum it is 457, but within this number there are 55 optional segregates, so that the minimum number of families in this system is 402. In APG III (2009) there are 415 families.
The diversity of flowering plants is not evenly distributed. Nearly all species belong to the eudicot (75%), monocot (23%) and magnoliid (2%) clades. The remaining 5 clades contain a little over 250 species in total, i.e., less than 0.1% of flowering plant diversity, divided among 9 families.
The most diverse families of flowering plants, in their APG circumscriptions, in order of number of species, are:
In the list above (showing only the 10 largest families), the Orchidaceae and Poaceae are monocot families; the others are eudicot families.
Vascular anatomy

Complexity
In general usage, complexity tends to be used to characterize something with many parts in intricate arrangement. The study of these complex linkages is the main goal of complex systems theory. In science there are at this time a number of approaches to characterizing complexity, many of which are...
of tissue-formation in flowering plants exceeds that of gymnosperms. The vascular bundle
Vascular bundle
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in vascular tissue, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues...
s of the stem are arranged such that the xylem
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
and phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
form concentric rings.
In the dicotyledons, the bundles in the very young stem are arranged in an open ring, separating a central pith from an outer cortex. In each bundle, separating the xylem and phloem, is a layer of meristem
Meristem
A meristem is the tissue in most plants consisting of undifferentiated cells , found in zones of the plant where growth can take place....
or active formative tissue known as cambium
Cambium (botany)
A cambium , in botany, is a tissue layer that provide undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues....
. By the formation of a layer of cambium between the bundles (interfascicular cambium), a complete ring is formed, and a regular periodical increase in thickness results from the development of xylem on the inside and phloem on the outside. The soft phloem becomes crushed, but the hard wood persists and forms the bulk of the stem and branches of the woody perennial. Owing to differences in the character of the elements produced at the beginning and end of the season, the wood is marked out in transverse section into concentric rings, one for each season
Season
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology, and hours of daylight.Seasons result from the yearly revolution of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's axis relative to the plane of revolution...
of growth, called annual rings.
Among the monocotyledons, the bundles are more numerous in the young stem and are scattered through the ground tissue. They contain no cambium and once formed the stem increases in diameter only in exceptional cases.
Flowers
The characteristic feature of angiosperms is the flower. Flowers show remarkable variation in form and elaboration, and provide the most trustworthy external characteristics for establishing relationships among angiosperm species. The function of the flower is to ensure fertilization of the ovule and development of fruitFruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
containing seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
s. The floral apparatus may arise terminally on a shoot or from the axil of a leaf (where the petiole
Petiole (botany)
In botany, the petiole is the stalk attaching the leaf blade to the stem. The petiole usually has the same internal structure as the stem. Outgrowths appearing on each side of the petiole are called stipules. Leaves lacking a petiole are called sessile, or clasping when they partly surround the...
attaches to the stem). Occasionally, as in violets
Violet (plant)
Viola is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with around 400–500 species distributed around the world. Most species are found in the temperate Northern Hemisphere; however, viola species are also found in widely divergent areas such as Hawaii, Australasia, and the Andes in...
, a flower arises singly in the axil of an ordinary foliage-leaf. More typically, the flower-bearing portion of the plant is sharply distinguished from the foliage-bearing or vegetative portion, and forms a more or less elaborate branch-system called an inflorescence
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Strictly, it is the part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed and which is accordingly modified...
.
There are two kinds of reproductive cells produced by flowers. Microspores, which will divide to become pollen grains
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
, are the "male" cells and are borne in the stamen
Stamen
The stamen is the pollen producing reproductive organ of a flower...
s (or microsporophylls). The "female" cells called megaspores, which will divide to become the egg-cell (megagametogenesis
Megagametogenesis
Megagametogenesis is the development of a megaspore into an embryo sac, which is the gametophyte - though a highly reduced one - stage in the life cycle of vascular plants.-Eudicots:...
), are contained in the ovule
Ovule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
and enclosed in the carpel (or megasporophyll).
The flower may consist only of these parts, as in willow
Willow
Willows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
, where each flower comprises only a few stamens or two carpels. Usually, other structures are present and serve to protect the sporophylls and to form an envelope attractive to pollinators. The individual members of these surrounding structures are known as sepal
Sepal
A sepal is a part of the flower of angiosperms . Collectively the sepals form the calyx, which is the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. Usually green, sepals have the typical function of protecting the petals when the flower is in bud...
s and petal
Petal
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They often are brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. Together, all of the petals of a flower are called a corolla. Petals are usually accompanied by another set of special leaves called sepals lying...
s (or tepal
Tepal
Tepals are elements of the perianth, or outer part of a flower, which include the petals or sepals. The term tepal is more often applied specifically when all segments of the perianth are of similar shape and color, or undifferentiated, which is called perigone...
s in flowers such as Magnolia
Magnolia
Magnolia is a large genus of about 210 flowering plant species in the subfamily Magnolioideae of the family Magnoliaceae. It is named after French botanist Pierre Magnol....
where sepals and petals are not distinguishable from each other). The outer series (calyx of sepals) is usually green and leaf-like, and functions to protect the rest of the flower, especially the bud. The inner series (corolla of petals) is, in general, white or brightly colored, and is more delicate in structure. It functions to attract insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
or bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
pollinators. Attraction is effected by color, scent, and nectar, which may be secreted in some part of the flower. The characteristics that attract pollinators account for the popularity of flowers and flowering plants among humans.
While the majority of flowers are perfect or hermaphrodite
Hermaphrodite
In biology, a hermaphrodite is an organism that has reproductive organs normally associated with both male and female sexes.Many taxonomic groups of animals do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which both...
(having both male and female parts in the same flower structure), flowering plants have developed numerous morphological and physiological mechanisms to reduce or prevent self-fertilization. Heteromorphic flowers have short carpels and long stamens, or vice versa, so animal pollinator
Pollinator
A pollinator is the biotic agent that moves pollen from the male anthers of a flower to the female stigma of a flower to accomplish fertilization or syngamy of the female gamete in the ovule of the flower by the male gamete from the pollen grain...
s cannot easily transfer pollen to the pistil (receptive part of the carpel). Homomorphic flowers may employ a biochemical (physiological) mechanism called self-incompatibility
Self-incompatibility in plants
Self-incompatibility is a general name for several genetic mechanisms in angiosperms, which prevent self-fertilization and thus encourage outcrossing...
to discriminate between self- and non-self pollen grains. In other species, the male and female parts are morphologically separated, developing on different flowers.
Fertilization and embryogenesis

Double fertilization
Double fertilization is a complex fertilization mechanism that has evolved in flowering plants . This process involves the joining of a female gametophyte with two male gametes . It begins when a pollen grain adheres to the stigma of the carpel, the female reproductive structure of a flower...
refers to a process in which two sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
cells fertilize cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
in the ovary. This process begins when a pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
grain adheres to the stigma of the pistil (female reproductive structure), germinates, and grows a long pollen tube
Pollen tube
The pollen tubes is the male gametophyte of seed plants that acts as a conduit to transport the male sperm cells from the pollen grain, either from the stigma to the ovules at the base of the pistil, or directly through ovule tissue in some gymnosperms .After pollination, the pollen tube...
. While this pollen tube is growing, a haploid generative cell travels down the tube behind the tube nucleus. The generative cell divides by mitosis to produce two haploid (n) sperm cells. As the pollen tube grows, it makes its way from the stigma, down the style and into the ovary. Here the pollen tube reaches the micropyle of the ovule and digests its way into one of the synergids, releasing its contents (which include the sperm cells). The synergid that the cells were released into degenerates and one sperm makes its way to fertilize the egg cell, producing a diploid (2n) zygote. The second sperm cell fuses with both central cell nuclei, producing a triploid (3n) cell. As the zygote develops into an embryo, the triploid cell develops into the endosperm, which serves as the embryo's food supply. The ovary now will develop into fruit and the ovule will develop into seed.
Fruit and seed

Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
or pericarp, whose form is closely associated with the manner of distribution of the seed.
Frequently, the influence of fertilization is felt beyond the ovary
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
, and other parts of the flower take part in the formation of the fruit, e.g., the floral receptacle in the apple
Apple
The apple is the pomaceous fruit of the apple tree, species Malus domestica in the rose family . It is one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits, and the most widely known of the many members of genus Malus that are used by humans. Apple grow on small, deciduous trees that blossom in the spring...
, strawberry, and others.
The character of the seed-coat bears a definite relation to that of the fruit. They protect the embryo and aid in dissemination; they may also directly promote germination. Among plants with indehiscent fruits, in general, the fruit provides protection for the embryo and secures dissemination. In this case, the seed-coat is only slightly developed. If the fruit is dehiscent
Dehiscence (botany)
Dehiscence is the opening, at maturity, in a pre-defined way, of a plant structure, such as a fruit, anther, or sporangium, to release its contents. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that open in this way are said to be dehiscent...
and the seed is exposed, in general, the seed-coat is well developed, and must discharge the functions otherwise executed by the fruit.
Economic importance
AgricultureAgriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
is almost entirely dependent on angiosperms, either directly or indirectly through livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
feed. Of all the families plants, the Poaceae
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
, or grass family, is by far the most important, providing the bulk of all feedstocks (rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
, corn — maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
, rye
Rye
Rye is a grass grown extensively as a grain and as a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe and is closely related to barley and wheat. Rye grain is used for flour, rye bread, rye beer, some whiskeys, some vodkas, and animal fodder...
, oat
Oat
The common oat is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name . While oats are suitable for human consumption as oatmeal and rolled oats, one of the most common uses is as livestock feed...
s, pearl millet
Pearl millet
Pearl millet is the most widely grown type of millet. Grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times, it is generally accepted that pearl millet originated in Africa and was subsequently introduced into India. The center of diversity, and suggested area of domestication, for...
, sugar cane, sorghum
Sorghum
Sorghum is a genus of numerous species of grasses, one of which is raised for grain and many of which are used as fodder plants either cultivated or as part of pasture. The plants are cultivated in warmer climates worldwide. Species are native to tropical and subtropical regions of all continents...
). The Fabaceae
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and economically important family of flowering plants. The group is the third largest land plant family, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species...
, or legume family, comes in second place. Also of high importance are the Solanaceae
Solanaceae
Solanaceae are a family of flowering plants that include a number of important agricultural crops as well as many toxic plants. The name of the family comes from the Latin Solanum "the nightshade plant", but the further etymology of that word is unclear...
, or nightshade family (potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
es, tomato
Tomato
The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
es, and pepper
Capsicum
Capsicum is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. Its species are native to the Americas where they have been cultivated for thousands of years, but they are now also cultivated worldwide, used as spices, vegetables, and medicines - and have become are a key element in...
s, among others), the Cucurbitaceae
Cucurbitaceae
The plant family Cucurbitaceae consists of various squashes, melons, and gourds, including crops such as cucumber, pumpkins, luffas, and watermelons...
, or gourd
Gourd
A gourd is a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae. Gourd is occasionally used to describe crops like cucumbers, squash, luffas, and melons. The term 'gourd' however, can more specifically, refer to the plants of the two Cucurbitaceae genera Lagenaria and Cucurbita or also to their hollow dried out shell...
family (also including pumpkin
Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a gourd-like squash of the genus Cucurbita and the family Cucurbitaceae . It commonly refers to cultivars of any one of the species Cucurbita pepo, Cucurbita mixta, Cucurbita maxima, and Cucurbita moschata, and is native to North America...
s and melon
Melon
thumb|200px|Various types of melonsThis list of melons includes members of the plant family Cucurbitaceae with edible, fleshy fruit e.g. gourds or cucurbits. The word "melon" can refer to either the plant or specifically to the fruit...
s), the Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae, a medium sized and economically important family of flowering plants , are informally known as the mustards, mustard flowers, the crucifers or the cabbage family....
, or mustard plant
Mustard plant
Mustards are several plant species in the genera Brassica and Sinapis whose small mustard seeds are used as a spice and, by grinding and mixing them with water, vinegar or other liquids, are turned into the condiment known as mustard or prepared mustard...
family (including rapeseed
Rapeseed
Rapeseed , also known as rape, oilseed rape, rapa, rappi, rapaseed is a bright yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae...
and the innumerable varieties of the cabbage
Cabbage
Cabbage is a popular cultivar of the species Brassica oleracea Linne of the Family Brassicaceae and is a leafy green vegetable...
species Brassica oleracea
Brassica oleracea
Brassica oleracea, or wild cabbage, is a species of Brassica native to coastal southern and western Europe, where its tolerance of salt and lime and its intolerance of competition from other plants typically restrict its natural occurrence to limestone sea cliffs, like the chalk cliffs on both...
), and the Apiaceae
Apiaceae
The Apiaceae , commonly known as carrot or parsley family, is a group of mostly aromatic plants with hollow stems. The family is large, with more than 3,700 species spread across 434 genera, it is the sixteenth largest family of flowering plants...
, or parsley
Parsley
Parsley is a species of Petroselinum in the family Apiaceae, native to the central Mediterranean region , naturalized elsewhere in Europe, and widely cultivated as an herb, a spice and a vegetable.- Description :Garden parsley is a bright green hairless biennial herbaceous plant in temperate...
family. Many of our fruits come from the Rutaceae
Rutaceae
Rutaceae, commonly known as the rue or citrus family, is a family of flowering plants, usually placed in the order Sapindales.Species of the family generally have flowers that divide into four or five parts, usually with strong scents...
, or rue family (including orange
Orange (fruit)
An orange—specifically, the sweet orange—is the citrus Citrus × sinensis and its fruit. It is the most commonly grown tree fruit in the world....
s, lemon
Lemon
The lemon is both a small evergreen tree native to Asia, and the tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit. The fruit is used for culinary and non-culinary purposes throughout the world – primarily for its juice, though the pulp and rind are also used, mainly in cooking and baking...
s, grapefruits, etc.), and the Rosaceae
Rosaceae
Rosaceae are a medium-sized family of flowering plants, including about 2830 species in 95 genera. The name is derived from the type genus Rosa. Among the largest genera are Alchemilla , Sorbus , Crataegus , Cotoneaster , and Rubus...
, or rose family (including apple
Apple
The apple is the pomaceous fruit of the apple tree, species Malus domestica in the rose family . It is one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits, and the most widely known of the many members of genus Malus that are used by humans. Apple grow on small, deciduous trees that blossom in the spring...
s, pear
Pear
The pear is any of several tree species of genus Pyrus and also the name of the pomaceous fruit of these trees. Several species of pear are valued by humans for their edible fruit, but the fruit of other species is small, hard, and astringent....
s, cherries
Cherry
The cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy stone fruit. The cherry fruits of commerce are usually obtained from a limited number of species, including especially cultivars of the wild cherry, Prunus avium....
, apricots, plums, etc.).
In some parts of the world, certain single species assume paramount importance because of their variety of uses, for example the coconut (Cocos nucifera
Coconut
The coconut palm, Cocos nucifera, is a member of the family Arecaceae . It is the only accepted species in the genus Cocos. The term coconut can refer to the entire coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which is not a botanical nut. The spelling cocoanut is an old-fashioned form of the word...
) on Pacific atoll
Atoll
An atoll is a coral island that encircles a lagoon partially or completely.- Usage :The word atoll comes from the Dhivehi word atholhu OED...
s, and the olive (Olea europaea
Olive
The olive , Olea europaea), is a species of a small tree in the family Oleaceae, native to the coastal areas of the eastern Mediterranean Basin as well as northern Iran at the south end of the Caspian Sea.Its fruit, also called the olive, is of major agricultural importance in the...
) in the Mediterranean region.
Flowering plants also provide economic resources in the form of wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
, paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
, fiber (cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, flax
Flax
Flax is a member of the genus Linum in the family Linaceae. It is native to the region extending from the eastern Mediterranean to India and was probably first domesticated in the Fertile Crescent...
, and hemp
Hemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
, among others), medicines (digitalis
Digitalis
Digitalis is a genus of about 20 species of herbaceous perennials, shrubs, and biennials that are commonly called foxgloves. This genus was traditionally placed in the figwort family Scrophulariaceae, but recent reviews of phylogenetic research have placed it in the much enlarged family...
, camphor
Camphor
Camphor is a waxy, white or transparent solid with a strong, aromatic odor. It is a terpenoid with the chemical formula C10H16O. It is found in wood of the camphor laurel , a large evergreen tree found in Asia and also of Dryobalanops aromatica, a giant of the Bornean forests...
), decorative and landscaping plants, and many other uses. The main area in which they are surpassed by other plants is timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
production.
External links
- Angiosperm Phylogeny Poster - Flowering Plant Systamatics Cole, T.C.H. & Hilger, H.H.
- Anatomy of a Flowering Land Plant
- Cronquist, Arthur. (1981) An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants. Columbia Univ. Press, New York.
- Dilcher, D. 2000. Toward a new synthesis: Major evolutionary trends in the angiosperm fossil record. PNAS [Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America] 97: 7030-7036 (available online here http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/abstract/97/13/7030?ck=nck)
- Oldest Known Flowering Plants Identified By Genes, William J. Cromie, Harvard Gazette, December 16, 1999.
- L. Watson and M.J. Dallwitz (1992 onwards). The families of flowering plants: descriptions, illustrations, identification, information retrieval.
- Simpson, M.G. Plant Systematics, 2nd Edition. Elsevier/Academic Press. 2010.
- Raven, P.H., R.F. Evert, S.E. Eichhorn. Biology of Plants, 7th Edition. W.H. Freeman. 2004.

