
Fragment antigen binding
Encyclopedia
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain
Immunoglobulin light chain
]The immunoglobulin light chain is the small polypeptide subunit of an antibody .A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin heavy chains and two Ig light chains.-In humans:...
. These domains shape the paratope — the antigen-binding site — at the amino terminal end
N-terminal end
The N-terminus refers to the start of a protein or polypeptide terminated by an amino acid with a free amine group . The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the N-terminus on the left and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus...
of the monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
. The two variable domains bind the epitope
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that recognizes the epitope is called a paratope...
on their specific antigens.
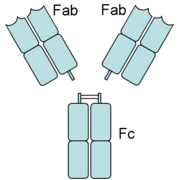
In an experimental setting, Fc and Fab fragments can be generated in the laboratory. The enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
papain
Papain
Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya .-Papain family:...
can be used to cleave an immunoglobulin monomer into two Fab fragments and an Fc fragment. The enzyme pepsin
Pepsin
Pepsin is an enzyme whose precursor form is released by the chief cells in the stomach and that degrades food proteins into peptides. It was discovered in 1836 by Theodor Schwann who also coined its name from the Greek word pepsis, meaning digestion...
cleaves below hinge region, so a F(ab')2 fragment and a pFc' fragment is formed. Recently another enzyme for generation of F(ab')2 has been commercially available. The enzyme IdeS (Immunoglobulin degrading enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes is a spherical, Gram-positive bacterium that is the cause of group A streptococcal infections. S. pyogenes displays streptococcal group A antigen on its cell wall. S...
, trade name FabRICATOR) cleaves IgG in a sequence specific manner at neutral pH. The F(ab')2 fragment can be split into two Fab' fragments by mild reduction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
.
The variable regions of the heavy and light chains can be fused together to form a single-chain variable fragment (scFv), which is only half the size of the Fab fragment, yet retains the original specificity of the parent immunoglobulin.

