
Franco-Cantabric Region
Encyclopedia

Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
and History
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
to refer to an area that stretches from Asturias
Asturias
The Principality of Asturias is an autonomous community of the Kingdom of Spain, coextensive with the former Kingdom of Asturias in the Middle Ages...
, in northern Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, to Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
in SE France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. It includes the southern half of France and the northern strip of Spain looking at the Bay of Biscay
Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Brest south to the Spanish border, and the northern coast of Spain west to Cape Ortegal, and is named in English after the province of Biscay, in the Spanish...
(known as Cantabrian Sea in Spanish, hence the name). Northern Catalonia
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
is sometimes included as well.
This region shows intense homogeneity in the prehistorical
Prehistory
Prehistory is the span of time before recorded history. Prehistory can refer to the period of human existence before the availability of those written records with which recorded history begins. More broadly, it refers to all the time preceding human existence and the invention of writing...
record and was possibly the most densely populated region of Europe in the Late Paleolithic
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic Age, Era or Period, is a prehistoric period of human history distinguished by the development of the most primitive stone tools discovered , and covers roughly 99% of human technological prehistory...
.
Archaeology
It experienced successively the ChatelperronianChâtelperronian
Châtelperronian was the earliest industry of the Upper Palaeolithic in central and south western France, extending also into Northern Spain. It derives its name from the site of la Grotte des Fées, in Châtelperron, Allier, France....
, Aurignacian
Aurignacian
The Aurignacian culture is an archaeological culture of the Upper Palaeolithic, located in Europe and southwest Asia. It lasted broadly within the period from ca. 45,000 to 35,000 years ago in terms of conventional radiocarbon dating, or between ca. 47,000 and 41,000 years ago in terms of the most...
, Gravettian
Gravettian
thumb|right|Burins to the Gravettian culture.The Gravettian toolmaking culture was a specific archaeological industry of the European Upper Palaeolithic era prevalent before the last glacial epoch. It is named after the type site of La Gravette in the Dordogne region of France where its...
, Solutrean
Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Palaeolithic, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP.-Details:...
, Magdalenian
Magdalenian
The Magdalenian , refers to one of the later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic in western Europe, dating from around 17,000 BP to 9,000 BP...
, Azilian
Azilian
The Azilian is a name given by archaeologists to an industry of the Epipaleolithic in northern Spain and southern France.It probably dates to the period of the Allerød Oscillation around 10,000 years ago and followed the Magdalenian culture...
and post Azilian geometric
Tardenoisian
The Tardenoisian is an archaeological culture of the Epipaleolithic period from north-western France and Belgium. Similar cultures are known further east in central Europe and west across Spain....
cultures, with their respective cultural expressions, noticeably the most famous mural art
Cave painting
Cave paintings are paintings on cave walls and ceilings, and the term is used especially for those dating to prehistoric times. The earliest European cave paintings date to the Aurignacian, some 32,000 years ago. The purpose of the paleolithic cave paintings is not known...
. Solutrean, Magdalenian and Azilian cultures evolved locally in this area.
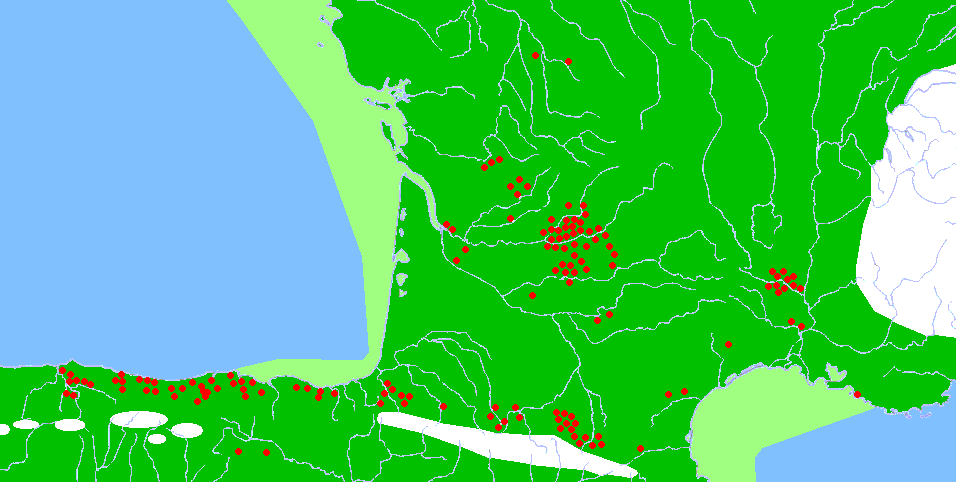
Glacial refugium and Late Glacial population expansion
The region may have been a major refugium for Paleolithic peoples during the Last Glacial MaximumLast Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
, apparently playing a major role as source for the repopulation of Europe after this extremely cold period ended.
From an archaeological viewpoint, Jean-Pierre Bocquet-Appel has argued that there are grounds for considering that the Aquitaine and French-Cantabrian refuge zone, may have been the principal source of Late Glacial re-colonisation. His demographic simulations, based in archaeological data, suggest that it was by large the most densely populated region of Europe through all the Upper Paleolithic
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. Very broadly it dates to between 40,000 and 10,000 years ago, roughly coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity and before the advent of...
.
Dissolution of the regional homogeneity in the Neolithic
The area became culturally divided between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic subareas in the NeolithicNeolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
period losing its homogeneity as the Eastern part incorporated strongly the Cardium Pottery
Cardium Pottery
Cardium Pottery or Cardial Ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the shell of the Cardium edulis, a marine mollusk...
culture, while the West remained less developed (subneolithic
Subneolithic
The term subneolithic is used in archaeological contexts to refer to peoples that, while being in contact with neolithic groups, remain attached to their traditional hunter-gatherer practices, incorporating only some secondary neolithic elements ....
). Basques
Basque people
The Basques as an ethnic group, primarily inhabit an area traditionally known as the Basque Country , a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France.The Basques are known in the...
and Gascons
Gascony
Gascony is an area of southwest France that was part of the "Province of Guyenne and Gascony" prior to the French Revolution. The region is vaguely defined and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; sometimes they are considered to overlap, and sometimes Gascony is considered a...
are arguably the direct descendants of the peoples of the Atlantic area, who remained more closed (relatively) to the new tendencies from the Mediterranean and Central Europe.
Main sites
- Altamira, CantabriaCantabriaCantabria is a Spanish historical region and autonomous community with Santander as its capital city. It is bordered on the east by the Basque Autonomous Community , on the south by Castile and León , on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.Cantabria...
, Spain. Important cave paintings - AurignacAurignacAurignac is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France on the edge of the Pyrénées. It is the seat of the canton of Aurignac , which is composed of 19 communes. It is part of the ancient region known as the Comminges....
, France - LascauxLascauxLascaux is the setting of a complex of caves in southwestern France famous for its Paleolithic cave paintings. The original caves are located near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne. They contain some of the best-known Upper Paleolithic art. These paintings are estimated to be...
, France - La MadeleineAbri de la MadeleineThe Abri de la Madeleine is a prehistoric shelter under an overhanging cliff situated near Tursac, in the Dordogne département and the Aquitaine Région of South-Western France. The Magdalenian culture of the Upper Paleolithic is named after it, as the type site. Prehistoric finds from the site...
, France - SantimamiñeSantimamiñeSantimamiñe cave, Kortezubi, Biscay, Basque Country, Spain, is one of the most important archaeological sites of the Basque Country, including a nearly complete sequence from the Middle Paleolithic to the Iron Age....
, Basque CountryBasque Country (autonomous community)The Basque Country is an autonomous community of northern Spain. It includes the Basque provinces of Álava, Biscay and Gipuzkoa, also called Historical Territories....
, Spain - Grotte Chauvet, France
See also
- Prehistoric artPrehistoric artIn the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of record-keeping, or it makes significant contact with another...
- Upper PaleolithicUpper PaleolithicThe Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. Very broadly it dates to between 40,000 and 10,000 years ago, roughly coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity and before the advent of...
- Cro-MagnonCro-MagnonThe Cro-Magnon were the first early modern humans of the European Upper Paleolithic. The earliest known remains of Cro-Magnon-like humans are radiometrically dated to 35,000 years before present....
- Basque Country (greater region)

