
Last Glacial Maximum
Encyclopedia
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's climate history when ice sheet
Ice sheet
An ice sheet is a mass of glacier ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than 50,000 km² , thus also known as continental glacier...
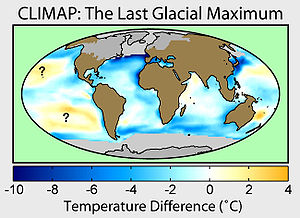
s were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and Asia. These ice sheets profoundly impacted Earth's climate, causing drought, desertification, and a dramatic drop in sea levels. It was followed by the Late Glacial Maximum.
Glacial climate

Ice cap
An ice cap is an ice mass that covers less than 50 000 km² of land area . Masses of ice covering more than 50 000 km² are termed an ice sheet....
requires both prolonged cold and precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
(snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
). Hence, despite having temperatures similar to those of glaciated areas in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
and parts of Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
remained unglaciated except at higher elevations. This difference was caused by the fact that the ice sheets in Europe produced extensive anticyclone
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined by the United States' National Weather Service's glossary as "[a] large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere"...
s above them. These anticyclones generated air mass
Air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
es that were so dry on reaching Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
and Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
that precipitation sufficient for the formation of glaciers could never occur (except in Kamchatka
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west...
where these westerly winds lifted moisture from the Sea of Japan
Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific...
). The relative warmth of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
due to the shutting down of the Oyashio Current
Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. It collides with the Kuroshio Current off the eastern shore of Japan to form the North Pacific Current...
and the presence of large east-west mountain ranges were secondary factors preventing continental glaciation in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
.
In warmer regions of the world, climates at the Last Glacial Maximum were cooler and almost everywhere drier. In extreme cases, such as South Australia
South Australia
South Australia is a state of Australia in the southern central part of the country. It covers some of the most arid parts of the continent; with a total land area of , it is the fourth largest of Australia's six states and two territories.South Australia shares borders with all of the mainland...
and the Sahel
Sahel
The Sahel is the ecoclimatic and biogeographic zone of transition between the Sahara desert in the North and the Sudanian Savannas in the south.It stretches across the North African continent between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea....
, rainfall could be diminished by up to ninety percent from present, with floras diminished to almost the same degree as in glaciated areas of Europe and North America. Even in less affected regions, rainforest
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall, with definitions based on a minimum normal annual rainfall of 1750-2000 mm...
cover was greatly diminished, especially in West Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of the African continent. Geopolitically, the UN definition of Western Africa includes the following 16 countries and an area of approximately 5 million square km:-Flags of West Africa:...
where a few refugia were surrounded by tropical grassland
Grassland
Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants . However, sedge and rush families can also be found. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica...
. The Amazon rainforest
Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest , also known in English as Amazonia or the Amazon Jungle, is a moist broadleaf forest that covers most of the Amazon Basin of South America...
was split into two large blocks by extensive savanna
Savanna
A savanna, or savannah, is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.Some...
, and it is probable that the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
were similarly affected, with deciduous forests expanding in their place except on the east and west extremities of the Sundaland shelf. Only in Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
and the Chocó region of Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
did tropical rainforests remain substantially intact – probably due to the extraordinarily heavy rainfall of these regions.
Most of the world's deserts expanded. Exceptions were in what is now the western United States
Western United States
.The Western United States, commonly referred to as the American West or simply "the West," traditionally refers to the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. Because the U.S. expanded westward after its founding, the meaning of the West has evolved over time...
, where changes in the jet stream
Jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow air currents found in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. The main jet streams are located near the tropopause, the transition between the troposphere and the stratosphere . The major jet streams on Earth are westerly winds...
brought heavy rain to areas that are now desert and large pluvial lake
Pluvial lake
A pluvial lake is a landlocked basin which fills with rainwater during times of glaciation, when precipitation is higher. Pluvial lakes that have since evaporated and dried out may also be referred to as paleolakes.-Geology:...
s formed, the best known being Lake Bonneville
Lake Bonneville
Lake Bonneville was a prehistoric pluvial lake that covered much of North America's Great Basin region. Most of the territory it covered was in present-day Utah, though parts of the lake extended into present-day Idaho and Nevada. Formed about 32,000 years ago, it existed until about 14,500 years...
in Utah
Utah
Utah is a state in the Western United States. It was the 45th state to join the Union, on January 4, 1896. Approximately 80% of Utah's 2,763,885 people live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City. This leaves vast expanses of the state nearly uninhabited, making the population the...
. This also occurred in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
and Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
where a major lake formed in the Dasht-e Kavir
Dasht-e Kavir
Dasht-e Kavir , also known as Kavir-e Namak or Great Salt Desert is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian plateau. It is about 800 kilometers long and 320 kilometers wide with a total surface area of about 77,600 square kilometers , making it the Earth's 23rd largest desert...
. In Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, shifting sand dunes covered half the continent, whilst the Chaco
Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semi-arid lowland region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, northern Argentina and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region...
and Pampas in South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
became similarly dry. Present-day subtropical regions also lost most of their forest cover, notably in eastern Australia, the Atlantic Forest of Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, and southern China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, where open woodland
Woodland
Ecologically, a woodland is a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of...
became dominant due to drier conditions. In northern China – unglaciated despite its cold climate – a mixture of grassland and tundra
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
prevailed, and even here, the northern limit of tree growth was at least twenty degrees further south than today.
In the period immediately before the Last Glacial Maximum, many areas that became completely barren desert were wetter than they are today, notably in southern Australia where Aboriginal
Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are the original inhabitants of the Australian continent and nearby islands. The Aboriginal Indigenous Australians migrated from the Indian continent around 75,000 to 100,000 years ago....
occupation is believed to coincide with a wet period between 40,000 and 60,000 years BP
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
(Before Present, a formal measurement of uncalibrated radiocarbon years
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon-14 to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58,000 to 62,000 years. Raw, i.e. uncalibrated, radiocarbon ages are usually reported in radiocarbon years "Before Present" ,...
, counted from 1950 CE).
World Impact
During the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) much of the world was cold, dry, and inhospitable, with frequent storms and a dust laden atmosphere. The massive sheets of ice locked away water, lowering the sea level, exposing continental shelves, joining land masses together, and creating extensive coastal plains.Europe
Northern Europe was largely covered by ice, the southern boundary of the ice sheets passing through Germany and Poland. This ice extended northward to cover SvalbardSvalbard
Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the...
and Franz Josef Land
Franz Josef Land
Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a...
and eastward to occupy the northern half of the West Siberian Plain
West Siberian Plain
The West Siberian Plain is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei River in the east, and by the Altay Mountains on the South-East. Much of the plain is poorly drained and consists of some of the world's largest swamps and...
, ending at the Taymyr Peninsula
Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia...
. It dammed the Ob
Ob River
The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the...
and Yenisei
Yenisei River
Yenisei , also written as Yenisey, is the largest river system flowing to the Arctic Ocean. It is the central of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean...
rivers, forming a West Siberian Glacial Lake
West Siberian Glacial Lake
The West Siberian Glacial Lake, also known as West Siberian Lake, or Mansiyskoe Lake , was a periglacial lake formed when the Arctic Ocean outlets for each of the Ob and Yenisei rivers were blocked by the Barents-Kara Ice Sheet during the Weichselian Glaciation, approximately 80,000 years ago...
. Permafrost
Permafrost
In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of...
covered Europe south of the ice sheet down to present-day Szeged
Szeged
' is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county town of Csongrád county. The University of Szeged is one of the most distinguished universities in Hungary....
. Ice covered the whole of Iceland and almost all of the British Isles but southern England. Britain was no more than a peninsula of Europe, its north capped in ice, and its south a polar desert.
Asia
There were ice sheets in modern Tibet (although scientists continue to debate the extent to which the Tibetan Plateau was covered with ice) as well as in BaltistanBaltistan
Baltistan , also known as بلتیول བལིུལ་ in the Balti language, is a region in northern Pakistan which forms Gilgit-Baltistan, bordering the Xinjiang Autonomous Region of China. In addition, a part of Baltistan also falls into Jammu and Kashmir of India. It is situated in the Karakoram mountains...
and Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
. In Southeast Asia, many smaller mountain glaciers formed, and permafrost covered Asia down to Beijing. Because of lowered sea levels, many of today's islands were joined to the continents: The Indonesian islands as far east as Borneo and Bali were connected to the Asian continent in a landmass called Sundaland
Sundaland
Sundaland is a biogeographical region of Southeastern Asia which encompasses the areas of the Asian continental shelf that was exposed during the last ice age. It included the Malay Peninsula on the Asian mainland, as well as the large islands of Borneo, Java, and Sumatra and their surrounding...
. Palawan
Palawan
Palawan is an island province of the Philippines located in the MIMAROPA region or Region 4. Its capital is Puerto Princesa City, and it is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of jurisdiction. The islands of Palawan stretch from Mindoro in the northeast to Borneo in the...
was also part of Sundaland, while the rest of the Philippine Islands formed one large island separated from the continent only by the Sibutu Passage
Sibutu Passage
Sibutu Passage is a safe and deep channel some 18 miles wide that separates Borneo from the Sulu Archipelago. It has a deep sill allowing entry of deep water into the Sulu basin while connecting the Sulu Sea with the Sulawesi Sea that feeds from the Pacific Ocean by the Mindanao Current.At the...
and the Mindoro Strait
Mindoro Strait
Mindoro Strait is a strait in the Philippines, separating Mindoro Island from Busuanga Island of Palawan. Located within its waters is the Apo Reef, the largest coral reef system in the Philippines....
.
Africa and the Middle East
In Africa and the Middle East, many smaller mountain glaciers formed, and the Sahara, Gobi, and other sandy deserts were greatly expanded in extent.Australasia
Australia, New Guinea, and Tasmania were one land mass called Sahulland. Between the East Asian mass of SundalandSundaland
Sundaland is a biogeographical region of Southeastern Asia which encompasses the areas of the Asian continental shelf that was exposed during the last ice age. It included the Malay Peninsula on the Asian mainland, as well as the large islands of Borneo, Java, and Sumatra and their surrounding...
and Sahulland, Wallacea
Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of Indonesian islands separated by deep water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and...
remained islands, though the number and width of water gaps between the two continents were considerably smaller.
North America
In North America, the ice covered essentially all of Canada and extended roughly to the Missouri River and Ohio Rivers, and eastward to New York City. In addition to the large Cordilleran Ice Sheet in Canada and MontanaMontana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
, Alpine glaciers advanced and (in some locations) ice caps covered much of the Rocky Mountains in the United States. In North America, latitudinal gradients were so sharp that permafrost did not reach far south of the ice sheets except at high elevations. LGM glaciers forced early human populations who had originally migrated from northeast Siberia into refugia, reshaping their genetic variation
Genetic variation
Genetic variation, variation in alleles of genes, occurs both within and among populations. Genetic variation is important because it provides the “raw material” for natural selection. Genetic variation is brought about by mutation, a change in a chemical structure of a gene. Polyploidy is an...
through mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
and drift
Genetic drift
Genetic drift or allelic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant in a population due to random sampling.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces...
. This phenomenon established the older haplogroups
Haplogroup
In the study of molecular evolution, a haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor having the same single nucleotide polymorphism mutation in both haplotypes. Because a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, this is what makes it possible to predict a haplogroup...
found among Native Americans
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
, whereas post LGM migrations are responsible for northern North American haplogroups.
South America
In the Southern Hemisphere, the Patagonian Ice SheetPatagonian Ice Sheet
350px|thumb|right|Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the [[Strait of Magellan]] area during the [[last glacial period]]. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots...
covered the whole southern third of Chile and adjacent areas of Argentina. On the western side of the Andes the ice sheet reached sea level as far north as in the 41 degrees south
41st parallel south
The 41st parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 41 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, Australasia, the Pacific Ocean and South America....
at Chacao Channel
Chacao Channel
The Chacao Channel is located in Los Lagos Region, Chile and separates Chiloé Island from mainland Chile. The channel was created during the Quaternary glaciations by successive glaciers that flowed down fron the Andes to the coast...
. The western coast of Patagonia
Patagonia
Patagonia is a region located in Argentina and Chile, integrating the southernmost section of the Andes mountains to the southwest towards the Pacific ocean and from the east of the cordillera to the valleys it follows south through Colorado River towards Carmen de Patagones in the Atlantic Ocean...
was largely glaciated but some authors have pointed out the possible existence of ice-free refugia for some plant species. On the eastern side of the Andes glacier lobes occupied the depressions of Seno Skyring
Seno Skyring
Seno Skyring is a large inland sound lying north of Riesco Island and south of mainland South America in southern Chile. Alternatively called Skyring Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the retreat of a glacier during the last glacial period...
, Seno Otway
Seno Otway
Seno Otway is a large inland sound lying between Brunswick Peninsula and Riesco Island in southern Chile. Alternatively called Otway Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the retreat of a glacier during the last glacial period.USGS, 2008 In spite...
, Inútil Bay
Inútil Bay
thumb|right|300px|Satellite image of Inútil Bay and the Strai of Magellan. Selected settlements are marked with yellow dots.Inútil Bay is bay in the western and Chilean part of Tierra del Fuego Island. Located as a body of water in the Strait of Magellan Inútil Bay provides access to Camerón and...
and Beagle Channel
Beagle Channel
thumb|right|300px|Aereal view of Beagle Channel. The Chilean [[Navarino Island]] is seen in the top-right while the Argentine part of [[Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego]] is seen at the bottom-left....
. On the Straits of Magellan, ice reached as far as Segunda Angostura
Segunda Angostura
Segunda Angostura is a sound of the Strait of Magellan between the Patagonian mainland and Tierra del Fuego. It is located southwest of Primera Angostura, the narrowest part of the Strait between the island and the continent...
.
See also
- Glacial periodGlacial periodA glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
- Last glacial period
- Ice ageIce ageAn ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
- Climate: Long range Investigation, Mapping, and PredictionClimate: Long range Investigation, Mapping, and PredictionClimate: Long range Investigation, Mapping, and Prediction, known as CLIMAP, was a major research project of the 1970s and 80s to produce a map of climate conditions during the last glacial maximum...
- Sea level rise
- Timeline of glaciationTimeline of glaciationThere have been five known ice ages in the Earth's history, with the Earth experiencing the Quaternary Ice Age during the present time. Within ice ages, there exist periods of more severe glacial conditions and more temperate referred to as glacial periods and interglacial periods, respectively...
Further reading
- Ehlers, J., and P.L. Gibbard, 2004a, Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 2: Part II North America. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0-444-51462-7
- Ehlers, J., and P L. Gibbard, 2004b, Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 3: Part III: South America, Asia, Africa, Australia, Antarctica. ISBN 0-444-51593-3
- Gillespie, A.R., S.C. Porter, and B.F. Atwater, 2004, The Quaternary Period in the United States. Developments in Quaternary Science no. 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 978-0-444-51471-4
- Mangerud, J., J. Ehlers, and P. Gibbard, 2004, Quaternary Glaciations : Extent and Chronology 1: Part I Europe. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0-444-51462-7
- Sibrava, V., Bowen, D.Q, and Richmond, G.M., 1986, Quaternary Glaciations in the Northern Hemisphere, Quaternary Science Reviews. vol. 5, pp. 1-514.
External links
- Adams, J.M., 1997, Global land environments since the last interglacial. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, TN. (Atlas of Palaeovegetation: Preliminary land ecosystem maps of the world since the Last Glacial Maximum.)
- BRITICE, 2004, Map and GIS database of glacial landforms and features related to the last British Ice Sheet. Department of Geology, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom.
- Dyke, A.S., A. Moore, and L. Robertson, 2003, Deglaciation of North America. Geological Survey of Canada Open File, 1574. (Thirty-two digital maps at 1:7 000 000 scale with accompanying digital chronological database and one poster (two sheets) with full map series.)
- Manley, W., and D. Kuaffman. nd, Alaska PaleoGlacier Atlas: A Geospatial Compilation of Pleistocene Glacier Extents. INSTAAR, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado.
- Paleoclimate Modelling Intercomparison Project (PMIP) PMIP Web Site and 'Publications : Last Glacial Maximum.
- Paleoclimate Modelling Intercomparison Project Phase II (PMIP2) PMIP2 Home page and PMIP 2 Publications.
- Eduard Y. Osipov ., Oleg M. Khlystov. Glaciers and meltwater flux to Lake Baikal during the Last Glacial Maximum.

