
Precipitation (meteorology)
Encyclopedia
In meteorology
, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric
water vapor
that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle
, rain
, sleet
, snow
, graupel and hail
. It occurs when a local portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapour and the water condenses. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapour to the air. Generally, precipitation will fall to the surface; an exception is Virga
which evaporates before reaching the surface. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud
. Rain drops range in size from oblate, pancake-like shapes for larger drops, to small spheres for smaller drops. Unlike raindrops, snowflakes grow in a variety of different shapes and patterns, determined by the temperature
and humidity
characteristics of the air the snowflake moves through on its way to the ground. While snow and ice pellets require temperatures close to the ground to be near or below freezing, hail can occur during much warmer temperature regimes due to the process of its formation.
Moisture overriding associated with weather fronts is an overall major method of precipitation production. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds such as cumulonimbus and can organize into narrow rainbands. Where relatively warm water bodies are present, for example due to water evaporation from lakes, lake-effect snowfall becomes a concern downwind of the warm lakes within the cold cyclonic
flow around the backside of extratropical cyclone
s. Lake-effect snowfall can be locally heavy. Thundersnow
is possible within a cyclone's comma head and within lake effect precipitation bands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exist due to the dry air caused by compressional heating. The movement of the monsoon trough
, or intertropical convergence zone
, brings rainy seasons
to savannah
clime
s.
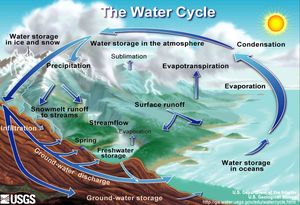
Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle
, and is responsible for depositing the fresh water
on the planet
. Approximately 505000 cubic kilometres (121,155.9 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year; 398000 cubic kilometres (95,485.3 cu mi) of it over the ocean
s. Given the Earth
's surface area, that means the globally averaged annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in). Climate
classification systems such as the Köppen climate classification
system use average annual rainfall to help differentiate between differing climate regimes. The urban heat island
effect may lead to increased rainfall, both in amounts and intensity, downwind of cities. Global warming
is also causing changes in the precipitation pattern globally. Precipitation may occur on other celestial bodies, e.g. when it gets cold, Mars
has precipitation which most likely takes the form of ice needles, rather than rain or snow.
 Any phenomenon which was at some point produced due to condensation or precipitation of moisture within the Earth's atmosphere is known as a hydrometeor. Particles composed of fallen precipitation which fell onto the Earth's surface can become hydrometeors if blown off the landscape by wind. Formations due to condensation such as clouds, haze
Any phenomenon which was at some point produced due to condensation or precipitation of moisture within the Earth's atmosphere is known as a hydrometeor. Particles composed of fallen precipitation which fell onto the Earth's surface can become hydrometeors if blown off the landscape by wind. Formations due to condensation such as clouds, haze
, fog
, and mist
are composed of hydrometeors. All precipitation types are hydrometeors by definition, including virga, which is precipitation which evaporates before reaching the ground. Particles removed from the Earth's surface by wind such as blowing snow and blowing sea spray are also hydrometeors.
Hydrometeors are unrelated to meteors, which are objects from outer space
which have entered the Earth's atmosphere and have produced a light phenomenon.
 Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle
Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle
, and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water
on the planet
. Approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year, 398,000 km3 (95,000 cu mi) of it over the ocean
s. Given the Earth
's surface area, that means the globally averaged annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in).
Mechanisms of producing precipitation include convective, stratiform
, and orographic
rainfall. Convective processes involve strong vertical motions that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation, while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions and less intense precipitation. Precipitation can be divided into three categories, based on whether it falls as liquid water, liquid water that freezes on contact with the surface, or ice. Mixtures of different types of precipitation, including types in different categories, can fall simultaneously. Liquid forms of precipitation include rain and drizzle. Rain or drizzle that freezes on contact within a subfreezing air mass
is called "freezing rain" or "freezing drizzle". Frozen forms of precipitation include snow
, ice needles
, ice pellets, hail
, and graupel.
is the temperature to which a parcel must be cooled in order to become saturated, and (unless super-saturation occurs) condenses to water. Water vapour normally begins to condense on condensation nuclei
such as dust, ice, and salt in order to form clouds. An elevated portion of a frontal zone forces broad areas of lift, which form clouds decks such as altostratus or cirrostratus. Stratus
is a stable cloud deck which tends to form when a cool, stable air mass is trapped underneath a warm air mass. It can also form due to the lifting of advection fog during breezy conditions.
There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to convection
, large-scale atmospheric motions, or a physical barrier such as a mountain (orographic lift
). Conductive cooling occurs when the air comes into contact with a colder surface, usually by being blown from one surface to another, for example from a liquid water surface to colder land. Radiational cooling occurs due to the emission of infrared radiation
, either by the air or by the surface underneath. Evaporative cooling occurs when moisture is added to the air through evaporation, which forces the air temperature to cool to its wet-bulb temperature
, or until it reaches saturation.

occurs when water droplets fuse to create larger water droplets, or when water droplets freeze onto an ice crystal, which is known as the Bergeron process
. The fall rate of very small droplets is negligible, hence clouds do not fall out of the sky; precipitation will only occur when these coalesce into larger drops. When air turbulence occurs, water droplets collide, producing larger droplets. As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from 0.1 millimetre (0.00393700787401575 in) to 9 millimetre (0.354330708661417 in) mean diameter, above which they tend to break up. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Contrary to the cartoon pictures of raindrops, their shape does not resemble a teardrop. Intensity and duration of rainfall are usually inversely related, i.e., high intensity storms are likely to be of short duration and low intensity storms can have a long duration. Rain drops associated with melting hail tend to be larger than other rain drops. The METAR code for rain is RA, while the coding for rain showers is SHRA.
or sleet are a form of precipitation consisting of small, translucent balls of ice. Ice pellets are usually (but not always) smaller than hail
stones. They often bounce when they hit the ground, and generally do not freeze into a solid mass unless mixed with freezing rain
. The METAR
code for ice pellets is PL.
Ice pellets form when a layer of above-freezing air exists with sub-freezing air both above and below it. This causes the partial or complete melting of any snowflakes falling through the warm layer. As they fall back into the sub-freezing layer closer to the surface, they re-freeze into ice pellets. However, if the sub-freezing layer beneath the warm layer is too small, the precipitation will not have time to re-freeze, and freezing rain
will be the result at the surface. A temperature profile showing a warm layer above the ground is most likely to be found in advance of a warm front
during the cold season, but can occasionally be found behind a passing cold front
.
 Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm cloud
Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm cloud
s when supercooled water
droplets freeze on contact with condensation nuclei, such as dust
or dirt
. The storm's updraft blows the hailstones to the upper part of the cloud. The updraft dissipates and the hailstones fall down, back into the updraft, and are lifted up again. Hail has a diameter of 5 millimetre (0.196850393700787 in) or more. Within METAR code, GR is used to indicate larger hail, of a diameter of at least 6.4 millimetre (0.251968503937008 in). GR is derived from the French word grêle. Smaller-sized hail, as well as snow pellets, use the coding of GS, which is short for the French word grésil. Stones just larger than golf ball
-sized are one of the most frequently reported hail sizes. Hailstones can grow to 15 centimetres (6 in) and weigh more than 0.5 kilograms (1.1 lb). In large hailstones, latent heat
released by further freezing may melt the outer shell of the hailstone. The hailstone then may undergo 'wet growth', where the liquid outer shell collects other smaller hailstones. The hailstone gains an ice layer and grows increasingly larger with each ascent. Once a hailstone becomes too heavy to be supported by the storm's updraft, it falls from the cloud.
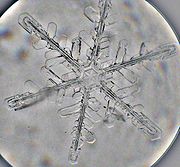 Snow crystals form when tiny supercooled cloud droplets (about 10 μm in diameter) freeze
Snow crystals form when tiny supercooled cloud droplets (about 10 μm in diameter) freeze
. Once a droplet has frozen, it grows in the supersaturated environment. Because water droplets are more numerous than the ice crystals the crystals are able to grow to hundreds of micrometer
s or millimeters in size at the expense of the water droplets. This process is known as the Wegner-Bergeron-Findeison process. The corresponding depletion of water vapor causes the droplets to evaporate, meaning that the ice crystals grow at the droplets' expense. These large crystals are an efficient source of precipitation, since they fall through the atmosphere due to their mass, and may collide and stick together in clusters, or aggregates. These aggregates are snowflakes, and are usually the type of ice particle that falls to the ground. Guinness World Records list the world's largest snowflakes as those of January 1887 at Fort Keogh, Montana; allegedly one measured 38 cm (15 inches) wide. The exact details of the sticking mechanism remain a subject of research.
Although the ice is clear, scattering of light by the crystal facets and hollows/imperfections mean that the crystals often appear white in color due to diffuse reflection
of the whole spectrum
of light
by the small ice particles. The shape of the snowflake is determined broadly by the temperature and humidity at which it is formed. Rarely, at a temperature of around -2 C, snowflakes can form in threefold symmetry—triangular snowflakes. The most common snow particles are visibly irregular, although near-perfect snowflakes may be more common in pictures because they are more visually appealing. No two snowflakes are alike, which grow at different rates and in different patterns depending on the changing temperature and humidity within the atmosphere that the snowflake falls through on its way to the ground. The METAR code for snow is SN, while snow showers are coded SHSN.
(on the order of cm/s), such as over surface cold front
s, and over and ahead of warm front
s. Similar ascent is seen around tropical cyclone
s outside of the eyewall
, and in comma-head precipitation patterns around mid-latitude cyclone
s. A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts usually form around mature low-pressure areas. Precipitation may occur on celestial bodies other than Earth. When it gets cold, Mars
has precipitation that most likely takes the form of ice needles, rather than rain or snow.
 Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds, e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus. It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the tropics
Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds, e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus. It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the tropics
appears to be convective; however, it has been suggested that stratiform precipitation also occurs. Graupel and hail
indicate convection. In mid-latitudes, convective precipitation is intermittent and often associated with baroclinic boundaries such as cold front
s, squall line
s, and warm fronts.
 Orographic precipitation occurs on the windward side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain ridge, resulting in adiabatic cooling and condensation. In mountainous parts of the world subjected to relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade wind
Orographic precipitation occurs on the windward side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain ridge, resulting in adiabatic cooling and condensation. In mountainous parts of the world subjected to relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade wind
s), a more moist climate
usually prevails on the windward side of a mountain than on the leeward or downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air (see katabatic wind
) on the descending and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow
is observed.
In Hawaii
, Mount Waiʻaleʻale, on the island of Kauai, is notable for its extreme rainfall, as it has the second highest average annual rainfall on Earth, with 460 inches (11,684 mm). Storm systems affect the state with heavy rains between October and March. Local climates vary considerably on each island due to their topography, divisible into windward (Koolau) and leeward (Kona) regions based upon location relative to the higher mountains. Windward sides face the east to northeast trade winds and receive much more rainfall; leeward sides are drier and sunnier, with less rain and less cloud cover.
In South America, the Andes
mountain range blocks Pacific moisture that arrives in that continent, resulting in a desertlike climate just downwind across western Argentina. The Sierra Nevada range creates the same effect in North America forming the Great Basin
and Mojave Desert
s.
 Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
s can bring cold and dangerous conditions with heavy rain and snow with winds exceeding 119 km/h (74 mph), (sometimes referred to as windstorms
in Europe). The band of precipitation that is associated with their warm front
is often extensive, forced by weak upward vertical motion of air over the frontal boundary which condenses
as it cools and produces precipitation within an elongated band, which is wide and stratiform, meaning falling out of nimbostratus clouds. When moist air tries to dislodge an arctic air mass, overrunning snow can result within the poleward side of the elongated precipitation band
. In the Northern Hemisphere
, poleward is towards the North Pole
, or north. Within the Southern Hemisphere
, poleward is towards the South Pole
, or south.
Southwest of extratropical cyclones, curved cyclonic flow bringing cold air across the relatively warm water bodies can lead to narrow lake-effect snow bands. Those bands bring strong localized snowfall which can be understood as follows: Large water bodies such as lakes efficiently store heat that results in significant temperature differences (larger than 13 °C or 23 °F) between the water surface and the air above. Because of this temperature difference, warmth and moisture are transported upward, condensing into vertically oriented clouds (see satellite picture) which produce snow showers. The temperature decrease with height and cloud depth are directly affected by both the water temperature and the large-scale environment. The stronger the temperature decrease with height, the deeper the clouds get, and the greater the precipitation rate becomes.
In mountainous areas, heavy snowfall accumulates when air is forced to ascend the mountains and squeeze out precipitation along their windward slopes, which in cold conditions, falls in the form of snow. Because of the ruggedness of terrain, forecasting the location of heavy snowfall remains a significant challenge.
 The wet, or rainy, season is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region falls. The term green season is also sometimes used as a euphemism
The wet, or rainy, season is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region falls. The term green season is also sometimes used as a euphemism
by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the tropics
and subtropics
. Savanna
climates and areas with monsoon
regimes have wet summers and dry winters. Tropical rainforests technically do not have dry or wet seasons, since their rainfall is equally distributed through the year. Some areas with pronounced rainy seasons will see a break in rainfall mid-season when the intertropical convergence zone
or monsoon trough
move poleward of their location during the middle of the warm season. When the wet season occurs during the warm season, or summer
, rain falls mainly during the late afternoon and early evening hours. The wet season is a time when air quality improves, freshwater quality improves, and vegetation grows significantly. Soil
nutrients diminish and erosion increases. Animals have adaptation and survival strategies for the wetter regime. The previous dry season leads to food shortages into the wet season, as the crops have yet to mature. Developing countries have noted that their populations show seasonal weight fluctuations due to food shortages seen before the first harvest, which occurs late in the wet season.
Tropical cyclones, a source of very heavy rainfall, consist of large air masses several hundred miles across with low pressure at the centre and with winds blowing inward towards the centre in either a clockwise direction (southern hemisphere) or counterclockwise (northern hemisphere). Although cyclone
s can take an enormous toll in lives and personal property, they may be important factors in the precipitation regimes of places they impact, as they may bring much-needed precipitation to otherwise dry regions. Areas in their path can receive a year's worth of rainfall from a tropical cyclone passage.
, itself the ascending branch of the Hadley cell
. Mountainous locales near the equator in Colombia are amongst the wettest places on Earth. North and south of this are regions of descending air that form subtropical ridge
s where precipitation is low; the land surface underneath is usually arid, which forms most of the Earth's deserts. An exception to this rule is in Hawaii, where upslope flow due to the trade wind
s lead to one of the wettest locations on Earth. Otherwise, the flow of the Westerlies
into the Rocky Mountains lead to the wettest, and at elevation snowiest, locations within North America
. In Asia
during the wet season, the flow of moist air into the Himalayas
leads to some of the greatest rainfall amounts measured on Earth in northeast India
.

The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100 mm (4 in) plastic and 200 mm (8 in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by 25 mm (1 in) of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to 0.25 mm (0.01 in) resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate 0.25 mm (0.01 in) markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. These gauges are used in the winter by removing the funnel and inner cylinder and allowing snow and freezing rain to collect inside the outer cylinder. Some add anti-freeze to their gauge so they do not have to melt the snow or ice that falls into the gauge. Once the snowfall/ice is finished accumulating, or as 300 mm (12 in) is approached, one can either bring it inside to melt, or use lukewarm water to fill the inner cylinder with in order to melt the frozen precipitation in the outer cylinder, keeping track of the warm fluid added, which is subsequently subtracted from the overall total once all the ice/snow is melted.
Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. The wedge and tipping bucket gauges will have problems with snow. Attempts to compensate for snow/ice by warming the tipping bucket meet with limited success, since snow may sublimate if the gauge is kept much above freezing. Weighing gauges with antifreeze should do fine with snow, but again, the funnel needs to be removed before the event begins. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as CoCoRAHS
or GLOBE. If a network is not available in the area where one lives, the nearest local weather office will likely be interested in the measurement.
or frequency. The intensity of a storm can be predicted for any return period and storm duration, from charts based on historic data for the location. The term 1 in 10 year storm describes a rainfall event which is rare and is only likely to occur once every 10 years, so it has a 10 percent likelihood any given year. The rainfall will be greater and the flooding will be worse than the worst storm expected in any single year. The term 1 in 100 year storm describes a rainfall event which is extremely rare and which will occur with a likelihood of only once in a century, so has a 1 percent likelihood in any given year. The rainfall will be extreme and flooding to be worse than a 1 in 10 year event. As with all probability events, it is possible to have multiple "1 in 100 Year Storms" in a single year.
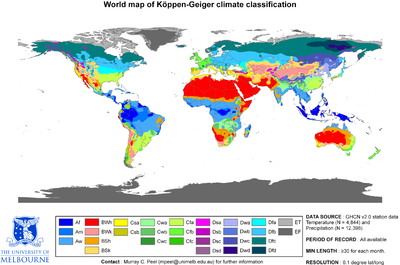
The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used form of the Köppen classification has five primary types labeled A through E. Specifically, the primary types are A, tropical; B, dry; C, mild mid-latitude; D, cold mid-latitude; and E, polar. The five primary classifications can be further divided into secondary classifications such as rain forest, monsoon
, tropical savanna, humid subtropical, humid continental, oceanic climate
, Mediterranean climate
, steppe
, subarctic climate
, tundra
, polar ice cap
, and desert
.
Rain forests are characterized by high rainfall, with definitions setting minimum normal annual rainfall between 1750 millimetres (68.9 in) and 2000 millimetres (78.7 in). A tropical savanna is a grassland
biome
located in semi-arid
to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes, with rainfall between 750 millimetres (29.5 in) and 1270 millimetres (50 in) a year. They are widespread on Africa, and are also found in India, the northern parts of South America, Malaysia, and Australia. The humid subtropical climate zone where winter rainfall (and sometimes snowfall) is associated with large storm
s that the westerlies
steer from west to east. Most summer rainfall occurs during thunderstorm
s and from occasional tropical cyclone
s. Humid subtropical climates lie on the east side continents, roughly between latitude
s 20° and 40° degrees away from the equator.
An oceanic (or maritime) climate is typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of all the world's continents, bordering cool oceans, as well as southeastern Australia, and is accompanied by plentiful precipitation year round. The Mediterranean climate regime resembles the climate of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin
, parts of western North America, parts of Western
and South Australia
, in southwestern South Africa
and in parts of central Chile
. The climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. A steppe is a dry grassland
. Subarctic climates are cold with continuous permafrost
and little precipitation.
 Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture
Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture
. All plant
s need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture
. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plant
s, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops
. Drought
can kill crops and increase erosion, while overly wet weather can cause harmful fungus
growth. Plant
s need varying amounts of rainfall to survive. For example, certain cacti
require small amounts of water, while tropical plants may need up to hundreds of inches of rain per year to survive.
In areas with wet and dry seasons, soil
nutrients diminish and erosion increases during the wet season. Animals have adaptation and survival strategies for the wetter regime. The previous dry season leads to food shortages into the wet season, as the crops have yet to mature. Developing countries have noted that their populations show seasonal weight fluctuations due to food shortages seen before the first harvest, which occurs late in the wet season.
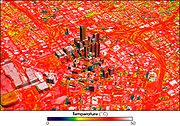
The urban heat island warms cities 0.6 °C (1.1 °F) to 5.6 °C (10.1 °F) above surrounding suburbs and rural areas. This extra heat leads to greater upward motion, which can induce additional shower and thunderstorm activity. Rainfall rates downwind of cities are increased between 48% and 116%. Partly as a result of this warming, monthly rainfall is about 28% greater between 20 miles (32.2 km) to 40 miles (64.4 km) downwind of cities, compared with upwind. Some cities induce a total precipitation increase of 51%.
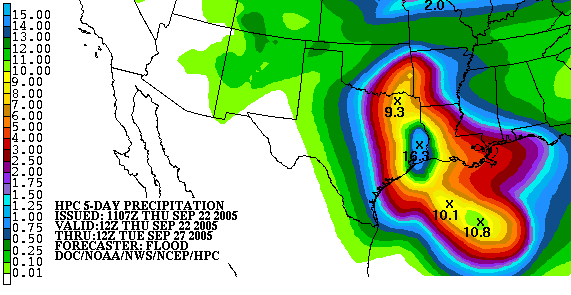 The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States. Forecast models
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States. Forecast models
show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer
, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount
, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill
than model forecasts within six to seven hours of the time of the radar image. The forecasts can be verified through use of rain gauge
measurements, weather radar
estimates, or a combination of both. Various skill scores can be determined to measure the value of the rainfall forecast.
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle
Drizzle
Drizzle is a light rain precipitation consisting of liquid water drops smaller than those of rain, and generally smaller than 0.5 mm in diameter. Drizzle is normally produced by low stratiform clouds and stratocumulus clouds. Precipitation rates due to drizzle are on the order of a millimetre...
, rain
Rain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
, sleet
Sleet
Sleet refers to two distinct forms of precipitation:*Rain and snow mixed, snow that partially melts as it falls. *Ice pellets, one of three forms of precipitation in a US-style "wintry mix", the other two being snow and freezing rain. The latter is referred to as sleet mainly by the United States...
, snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
, graupel and hail
Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is referred to as a hail stone. Hail stones on Earth consist mostly of water ice and measure between and in diameter, with the larger stones coming from severe thunderstorms...
. It occurs when a local portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapour and the water condenses. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapour to the air. Generally, precipitation will fall to the surface; an exception is Virga
Virga
In meteorology, virga is an observable streak or shaft of precipitation that falls from a cloud but evaporates before reaching the ground. At high altitudes the precipitation falls mainly as ice crystals before melting and finally evaporating; this is usually due to compressional heating, because...
which evaporates before reaching the surface. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
. Rain drops range in size from oblate, pancake-like shapes for larger drops, to small spheres for smaller drops. Unlike raindrops, snowflakes grow in a variety of different shapes and patterns, determined by the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
characteristics of the air the snowflake moves through on its way to the ground. While snow and ice pellets require temperatures close to the ground to be near or below freezing, hail can occur during much warmer temperature regimes due to the process of its formation.
Moisture overriding associated with weather fronts is an overall major method of precipitation production. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds such as cumulonimbus and can organize into narrow rainbands. Where relatively warm water bodies are present, for example due to water evaporation from lakes, lake-effect snowfall becomes a concern downwind of the warm lakes within the cold cyclonic
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
flow around the backside of extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
s. Lake-effect snowfall can be locally heavy. Thundersnow
Thundersnow
Thundersnow, also known as a winter thunderstorm or a thunder snowstorm, is a relatively rare kind of thunderstorm with snow falling as the primary precipitation instead of rain. It typically falls in regions of strong upward motion within the cold sector of an extratropical cyclone...
is possible within a cyclone's comma head and within lake effect precipitation bands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exist due to the dry air caused by compressional heating. The movement of the monsoon trough
Monsoon trough
The monsoon trough is that portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone which extends into or through a monsoon circulation, as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and...
, or intertropical convergence zone
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone , known by sailors as The Doldrums, is the area encircling the earth near the equator where winds originating in the northern and southern hemispheres come together....
, brings rainy seasons
Wet season
The the wet season, or rainy season, is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region occurs. The term green season is also sometimes used as a euphemism by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the...
to savannah
Savannah
Savannah or savanna is a type of grassland.It can also mean:-People:* Savannah King, a Canadian freestyle swimmer* Savannah Outen, a singer who gained popularity on You Tube...
clime
Clime
The seven climes was a notion of dividing the Earth into zones in Classical Antiquity....
s.
Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle
Water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and solid at various places in the water cycle...
, and is responsible for depositing the fresh water
Fresh Water
Fresh Water is the debut album by Australian rock and blues singer Alison McCallum, released in 1972. Rare for an Australian artist at the time, it came in a gatefold sleeve...
on the planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
. Approximately 505000 cubic kilometres (121,155.9 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year; 398000 cubic kilometres (95,485.3 cu mi) of it over the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s. Given the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's surface area, that means the globally averaged annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in). Climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
classification systems such as the Köppen climate classification
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
system use average annual rainfall to help differentiate between differing climate regimes. The urban heat island
Urban heat island
An urban heat island is a metropolitan area which is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas. The phenomenon was first investigated and described by Luke Howard in the 1810s, although he was not the one to name the phenomenon. The temperature difference usually is larger at night...
effect may lead to increased rainfall, both in amounts and intensity, downwind of cities. Global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
is also causing changes in the precipitation pattern globally. Precipitation may occur on other celestial bodies, e.g. when it gets cold, Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
has precipitation which most likely takes the form of ice needles, rather than rain or snow.
Hydrometeor

Haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
, fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
, and mist
Mist
Mist is a phenomenon of small droplets suspended in air. It can occur as part of natural weather or volcanic activity, and is common in cold air above warmer water, in exhaled air in the cold, and in a steam room of a sauna. It can also be created artificially with aerosol canisters if the...
are composed of hydrometeors. All precipitation types are hydrometeors by definition, including virga, which is precipitation which evaporates before reaching the ground. Particles removed from the Earth's surface by wind such as blowing snow and blowing sea spray are also hydrometeors.
Hydrometeors are unrelated to meteors, which are objects from outer space
Outer space
Outer space is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, and neutrinos....
which have entered the Earth's atmosphere and have produced a light phenomenon.
Types

Water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and solid at various places in the water cycle...
, and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water
Fresh Water
Fresh Water is the debut album by Australian rock and blues singer Alison McCallum, released in 1972. Rare for an Australian artist at the time, it came in a gatefold sleeve...
on the planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
. Approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year, 398,000 km3 (95,000 cu mi) of it over the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s. Given the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's surface area, that means the globally averaged annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in).
Mechanisms of producing precipitation include convective, stratiform
Stratus cloud
A stratus cloud is a cloud belonging to a class characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective clouds that are as tall or taller than wide . More specifically, the term stratus is used to describe flat, hazy, featureless clouds of low altitude varying in color...
, and orographic
Orographic lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions,...
rainfall. Convective processes involve strong vertical motions that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation, while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions and less intense precipitation. Precipitation can be divided into three categories, based on whether it falls as liquid water, liquid water that freezes on contact with the surface, or ice. Mixtures of different types of precipitation, including types in different categories, can fall simultaneously. Liquid forms of precipitation include rain and drizzle. Rain or drizzle that freezes on contact within a subfreezing air mass
Air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
is called "freezing rain" or "freezing drizzle". Frozen forms of precipitation include snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
, ice needles
Diamond dust
Diamond dust is a ground-level cloud composed of tiny ice crystals. This meteorological phenomenon is also referred to simply as ice crystals and is reported in the METAR code as IC. Diamond dust generally forms under otherwise clear or nearly clear skies, so it is sometimes referred to as...
, ice pellets, hail
Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is referred to as a hail stone. Hail stones on Earth consist mostly of water ice and measure between and in diameter, with the larger stones coming from severe thunderstorms...
, and graupel.
Cooling air to its dew point
The dew pointDew point
The dew point is the temperature to which a given parcel of humid air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to condense into liquid water. The condensed water is called dew when it forms on a solid surface. The dew point is a saturation temperature.The dew point is...
is the temperature to which a parcel must be cooled in order to become saturated, and (unless super-saturation occurs) condenses to water. Water vapour normally begins to condense on condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei or CCNs are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or 1/100 th the size of a cloud droplet ) about which cloud droplets coalesce. Water requires a non-gaseous surface to make the transition from a vapour to a liquid. In the atmosphere, this surface presents itself as tiny...
such as dust, ice, and salt in order to form clouds. An elevated portion of a frontal zone forces broad areas of lift, which form clouds decks such as altostratus or cirrostratus. Stratus
Stratus cloud
A stratus cloud is a cloud belonging to a class characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective clouds that are as tall or taller than wide . More specifically, the term stratus is used to describe flat, hazy, featureless clouds of low altitude varying in color...
is a stable cloud deck which tends to form when a cool, stable air mass is trapped underneath a warm air mass. It can also form due to the lifting of advection fog during breezy conditions.
There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
, large-scale atmospheric motions, or a physical barrier such as a mountain (orographic lift
Orographic lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions,...
). Conductive cooling occurs when the air comes into contact with a colder surface, usually by being blown from one surface to another, for example from a liquid water surface to colder land. Radiational cooling occurs due to the emission of infrared radiation
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation....
, either by the air or by the surface underneath. Evaporative cooling occurs when moisture is added to the air through evaporation, which forces the air temperature to cool to its wet-bulb temperature
Wet-bulb temperature
The wet-bulb temperature is a type of temperature measurement that reflects the physical properties of a system with a mixture of a gas and a vapor, usually air and water vapor. Wet bulb temperature is the lowest temperature that can be reached by the evaporation of water only. It is the...
, or until it reaches saturation.

Adding moisture to the air
The main ways water vapour is added to the air are: wind convergence into areas of upward motion, precipitation or virga falling from above, daytime heating evaporating water from the surface of oceans, water bodies or wet land, transpiration from plants, cool or dry air moving over warmer water, and lifting air over mountains.Formation

Raindrops
CoalescenceCoalescence (meteorology)
Coalescence is the process by which two or more droplets, bubbles or particles merge during contact to form a single daughter droplet, bubble or particle. It can take place in many processes, ranging from meteorology to astrophysics. For example, it is both inve formation of raindrops as well as...
occurs when water droplets fuse to create larger water droplets, or when water droplets freeze onto an ice crystal, which is known as the Bergeron process
Bergeron process
The Bergeron–Findeisen process , also known as the cold rain or ice crystal process, is the formation of precipitation in the cold clouds of the mid and upper latitudes by ice crystal growth. The equilibrium vapor pressure over water is greater than the saturation vapor pressure over ice, at the...
. The fall rate of very small droplets is negligible, hence clouds do not fall out of the sky; precipitation will only occur when these coalesce into larger drops. When air turbulence occurs, water droplets collide, producing larger droplets. As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from 0.1 millimetre (0.00393700787401575 in) to 9 millimetre (0.354330708661417 in) mean diameter, above which they tend to break up. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Contrary to the cartoon pictures of raindrops, their shape does not resemble a teardrop. Intensity and duration of rainfall are usually inversely related, i.e., high intensity storms are likely to be of short duration and low intensity storms can have a long duration. Rain drops associated with melting hail tend to be larger than other rain drops. The METAR code for rain is RA, while the coding for rain showers is SHRA.
Ice pellets
Ice pelletsIce pellets
Ice pellets are a form of precipitation consisting of small, translucent balls of ice. Ice pellets usually are smaller than hailstones. They often bounce when they hit the ground, and generally do not freeze into a solid mass unless mixed with freezing rain...
or sleet are a form of precipitation consisting of small, translucent balls of ice. Ice pellets are usually (but not always) smaller than hail
Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is referred to as a hail stone. Hail stones on Earth consist mostly of water ice and measure between and in diameter, with the larger stones coming from severe thunderstorms...
stones. They often bounce when they hit the ground, and generally do not freeze into a solid mass unless mixed with freezing rain
Freezing rain
Freezing rain is the name given to rain that falls when surface temperatures are below freezing. The raindrops become supercooled while passing through a sub-freezing layer of air, many hundred feet , just above the surface, and then freeze upon impact with any object they encounter. The resulting...
. The METAR
METAR
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by pilots in fulfillment of a part of a pre-flight weather briefing, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting....
code for ice pellets is PL.
Ice pellets form when a layer of above-freezing air exists with sub-freezing air both above and below it. This causes the partial or complete melting of any snowflakes falling through the warm layer. As they fall back into the sub-freezing layer closer to the surface, they re-freeze into ice pellets. However, if the sub-freezing layer beneath the warm layer is too small, the precipitation will not have time to re-freeze, and freezing rain
Freezing rain
Freezing rain is the name given to rain that falls when surface temperatures are below freezing. The raindrops become supercooled while passing through a sub-freezing layer of air, many hundred feet , just above the surface, and then freeze upon impact with any object they encounter. The resulting...
will be the result at the surface. A temperature profile showing a warm layer above the ground is most likely to be found in advance of a warm front
Warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient...
during the cold season, but can occasionally be found behind a passing cold front
Cold front
A cold front is defined as the leading edge of a cooler mass of air, replacing a warmer mass of air.-Development of cold front:The cooler and denser air wedges under the less-dense warmer air, lifting it...
.
Hail

Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
s when supercooled water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
droplets freeze on contact with condensation nuclei, such as dust
Dust
Dust consists of particles in the atmosphere that arise from various sources such as soil dust lifted up by wind , volcanic eruptions, and pollution...
or dirt
Dirt
Dirt is unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin or possessions when they are said to become dirty. Common types of dirt include:* dust — a general powder of organic or mineral matter...
. The storm's updraft blows the hailstones to the upper part of the cloud. The updraft dissipates and the hailstones fall down, back into the updraft, and are lifted up again. Hail has a diameter of 5 millimetre (0.196850393700787 in) or more. Within METAR code, GR is used to indicate larger hail, of a diameter of at least 6.4 millimetre (0.251968503937008 in). GR is derived from the French word grêle. Smaller-sized hail, as well as snow pellets, use the coding of GS, which is short for the French word grésil. Stones just larger than golf ball
Golf ball
A golf ball is a ball designed to be used in the game of golf.Under the Rules of Golf, a golf ball weighs no more than 1.620 oz , has a diameter not less than 1.680 in , and performs within specified velocity, distance, and symmetry limits...
-sized are one of the most frequently reported hail sizes. Hailstones can grow to 15 centimetres (6 in) and weigh more than 0.5 kilograms (1.1 lb). In large hailstones, latent heat
Latent heat
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
released by further freezing may melt the outer shell of the hailstone. The hailstone then may undergo 'wet growth', where the liquid outer shell collects other smaller hailstones. The hailstone gains an ice layer and grows increasingly larger with each ascent. Once a hailstone becomes too heavy to be supported by the storm's updraft, it falls from the cloud.
Snowflakes

Freezing
Freezing or solidification is a phase change in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. The reverse process is melting....
. Once a droplet has frozen, it grows in the supersaturated environment. Because water droplets are more numerous than the ice crystals the crystals are able to grow to hundreds of micrometer
Micrometer
A micrometer , sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw used widely for precise measurement of small distances in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier,...
s or millimeters in size at the expense of the water droplets. This process is known as the Wegner-Bergeron-Findeison process. The corresponding depletion of water vapor causes the droplets to evaporate, meaning that the ice crystals grow at the droplets' expense. These large crystals are an efficient source of precipitation, since they fall through the atmosphere due to their mass, and may collide and stick together in clusters, or aggregates. These aggregates are snowflakes, and are usually the type of ice particle that falls to the ground. Guinness World Records list the world's largest snowflakes as those of January 1887 at Fort Keogh, Montana; allegedly one measured 38 cm (15 inches) wide. The exact details of the sticking mechanism remain a subject of research.
Although the ice is clear, scattering of light by the crystal facets and hollows/imperfections mean that the crystals often appear white in color due to diffuse reflection
Diffuse reflection
Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light from a surface such that an incident ray is reflected at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection...
of the whole spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
by the small ice particles. The shape of the snowflake is determined broadly by the temperature and humidity at which it is formed. Rarely, at a temperature of around -2 C, snowflakes can form in threefold symmetry—triangular snowflakes. The most common snow particles are visibly irregular, although near-perfect snowflakes may be more common in pictures because they are more visually appealing. No two snowflakes are alike, which grow at different rates and in different patterns depending on the changing temperature and humidity within the atmosphere that the snowflake falls through on its way to the ground. The METAR code for snow is SN, while snow showers are coded SHSN.
Diamond dust
Diamond dust, also known as ice needles or ice crystals, forms at temperatures approaching -40 F due to air with slightly higher moisture from aloft mixing with colder, surface based air. They are made of simple ice crystals that are hexagonal in shape. The METAR identifier for diamond dust within international hourly weather reports is IC.Frontal activity
Stratiform or dynamic precipitation occurs as a consequence of slow ascent of air in synoptic systemsSynoptic scale meteorology
The synoptic scale in meteorology is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometres or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions...
(on the order of cm/s), such as over surface cold front
Cold front
A cold front is defined as the leading edge of a cooler mass of air, replacing a warmer mass of air.-Development of cold front:The cooler and denser air wedges under the less-dense warmer air, lifting it...
s, and over and ahead of warm front
Warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient...
s. Similar ascent is seen around tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s outside of the eyewall
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather found at the center of strong tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area and typically 30–65 km in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, a ring of towering thunderstorms where the second most severe weather of a cyclone...
, and in comma-head precipitation patterns around mid-latitude cyclone
Mid-latitude cyclone
Cyclogenesis is the development or strengthening of cyclonic circulation in the atmosphere . Cyclogenesis is an umbrella term for several different processes, all of which result in the development of some sort of cyclone. It can occur at various scales, from the microscale to the synoptic scale...
s. A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts usually form around mature low-pressure areas. Precipitation may occur on celestial bodies other than Earth. When it gets cold, Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
has precipitation that most likely takes the form of ice needles, rather than rain or snow.
Convection

Tropics
The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere at approximately N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth...
appears to be convective; however, it has been suggested that stratiform precipitation also occurs. Graupel and hail
Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is referred to as a hail stone. Hail stones on Earth consist mostly of water ice and measure between and in diameter, with the larger stones coming from severe thunderstorms...
indicate convection. In mid-latitudes, convective precipitation is intermittent and often associated with baroclinic boundaries such as cold front
Cold front
A cold front is defined as the leading edge of a cooler mass of air, replacing a warmer mass of air.-Development of cold front:The cooler and denser air wedges under the less-dense warmer air, lifting it...
s, squall line
Squall line
A squall line is a line of severe thunderstorms that can form along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. It contains heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and possibly tornadoes and waterspouts....
s, and warm fronts.
Orographic effects

Trade wind
The trade winds are the prevailing pattern of easterly surface winds found in the tropics, within the lower portion of the Earth's atmosphere, in the lower section of the troposphere near the Earth's equator...
s), a more moist climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
usually prevails on the windward side of a mountain than on the leeward or downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air (see katabatic wind
Katabatic wind
A katabatic wind, from the Greek word katabatikos meaning "going downhill", is the technical name for a drainage wind, a wind that carries high density air from a higher elevation down a slope under the force of gravity. Such winds are sometimes also called fall winds...
) on the descending and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow
Rain shadow
A rain shadow is a dry area on the lee side of a mountainous area. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems, casting a "shadow" of dryness behind them. As shown by the diagram to the right, the warm moist air is "pulled" by the prevailing winds over a mountain...
is observed.
In Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
, Mount Waiʻaleʻale, on the island of Kauai, is notable for its extreme rainfall, as it has the second highest average annual rainfall on Earth, with 460 inches (11,684 mm). Storm systems affect the state with heavy rains between October and March. Local climates vary considerably on each island due to their topography, divisible into windward (Koolau) and leeward (Kona) regions based upon location relative to the higher mountains. Windward sides face the east to northeast trade winds and receive much more rainfall; leeward sides are drier and sunnier, with less rain and less cloud cover.
In South America, the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
mountain range blocks Pacific moisture that arrives in that continent, resulting in a desertlike climate just downwind across western Argentina. The Sierra Nevada range creates the same effect in North America forming the Great Basin
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds in North America and is noted for its arid conditions and Basin and Range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the...
and Mojave Desert
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert occupies a significant portion of southeastern California and smaller parts of central California, southern Nevada, southwestern Utah and northwestern Arizona, in the United States...
s.
Snow

Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
s can bring cold and dangerous conditions with heavy rain and snow with winds exceeding 119 km/h (74 mph), (sometimes referred to as windstorms
European windstorm
A European windstorm is a severe cyclonic windstorm associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure that track across the North Atlantic towards northwestern Europe. They are most common in the winter months...
in Europe). The band of precipitation that is associated with their warm front
Warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient...
is often extensive, forced by weak upward vertical motion of air over the frontal boundary which condenses
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
as it cools and produces precipitation within an elongated band, which is wide and stratiform, meaning falling out of nimbostratus clouds. When moist air tries to dislodge an arctic air mass, overrunning snow can result within the poleward side of the elongated precipitation band
Rainband
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform or convective, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar imagery, this precipitation elongation is referred to as...
. In the Northern Hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
, poleward is towards the North Pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
, or north. Within the Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
, poleward is towards the South Pole
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
, or south.
Southwest of extratropical cyclones, curved cyclonic flow bringing cold air across the relatively warm water bodies can lead to narrow lake-effect snow bands. Those bands bring strong localized snowfall which can be understood as follows: Large water bodies such as lakes efficiently store heat that results in significant temperature differences (larger than 13 °C or 23 °F) between the water surface and the air above. Because of this temperature difference, warmth and moisture are transported upward, condensing into vertically oriented clouds (see satellite picture) which produce snow showers. The temperature decrease with height and cloud depth are directly affected by both the water temperature and the large-scale environment. The stronger the temperature decrease with height, the deeper the clouds get, and the greater the precipitation rate becomes.
In mountainous areas, heavy snowfall accumulates when air is forced to ascend the mountains and squeeze out precipitation along their windward slopes, which in cold conditions, falls in the form of snow. Because of the ruggedness of terrain, forecasting the location of heavy snowfall remains a significant challenge.
Within the tropics

Euphemism
A euphemism is the substitution of a mild, inoffensive, relatively uncontroversial phrase for another more frank expression that might offend or otherwise suggest something unpleasant to the audience...
by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the tropics
Tropics
The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere at approximately N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth...
and subtropics
Subtropics
The subtropics are the geographical and climatical zone of the Earth immediately north and south of the tropical zone, which is bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, at latitudes 23.5°N and 23.5°S...
. Savanna
Savanna
A savanna, or savannah, is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.Some...
climates and areas with monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
regimes have wet summers and dry winters. Tropical rainforests technically do not have dry or wet seasons, since their rainfall is equally distributed through the year. Some areas with pronounced rainy seasons will see a break in rainfall mid-season when the intertropical convergence zone
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone , known by sailors as The Doldrums, is the area encircling the earth near the equator where winds originating in the northern and southern hemispheres come together....
or monsoon trough
Monsoon trough
The monsoon trough is that portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone which extends into or through a monsoon circulation, as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and...
move poleward of their location during the middle of the warm season. When the wet season occurs during the warm season, or summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
, rain falls mainly during the late afternoon and early evening hours. The wet season is a time when air quality improves, freshwater quality improves, and vegetation grows significantly. Soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
nutrients diminish and erosion increases. Animals have adaptation and survival strategies for the wetter regime. The previous dry season leads to food shortages into the wet season, as the crops have yet to mature. Developing countries have noted that their populations show seasonal weight fluctuations due to food shortages seen before the first harvest, which occurs late in the wet season.
Tropical cyclones, a source of very heavy rainfall, consist of large air masses several hundred miles across with low pressure at the centre and with winds blowing inward towards the centre in either a clockwise direction (southern hemisphere) or counterclockwise (northern hemisphere). Although cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
s can take an enormous toll in lives and personal property, they may be important factors in the precipitation regimes of places they impact, as they may bring much-needed precipitation to otherwise dry regions. Areas in their path can receive a year's worth of rainfall from a tropical cyclone passage.
Large-scale geographical distribution
On the large scale, the highest precipitation amounts outside topography fall in the tropics, closely tied to the Intertropical Convergence ZoneIntertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone , known by sailors as The Doldrums, is the area encircling the earth near the equator where winds originating in the northern and southern hemispheres come together....
, itself the ascending branch of the Hadley cell
Hadley cell
The Hadley cell, named after George Hadley, is a circulation pattern that dominates the tropical atmosphere, with rising motion near the equator, poleward flow 10–15 kilometers above the surface, descending motion in the subtropics, and equatorward flow near the surface...
. Mountainous locales near the equator in Colombia are amongst the wettest places on Earth. North and south of this are regions of descending air that form subtropical ridge
Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge is a significant belt of high pressure situated around the latitudes of 30°N in the Northern Hemisphere and 30°S in the Southern Hemisphere. It is characterized by mostly calm winds, which acts to reduce air quality under its axis by causing fog overnight, and haze during...
s where precipitation is low; the land surface underneath is usually arid, which forms most of the Earth's deserts. An exception to this rule is in Hawaii, where upslope flow due to the trade wind
Trade wind
The trade winds are the prevailing pattern of easterly surface winds found in the tropics, within the lower portion of the Earth's atmosphere, in the lower section of the troposphere near the Earth's equator...
s lead to one of the wettest locations on Earth. Otherwise, the flow of the Westerlies
Westerlies
The Westerlies, anti-trades, or Prevailing Westerlies, are the prevailing winds in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes towards the poles. These prevailing winds blow from the west to the east, and steer extratropical...
into the Rocky Mountains lead to the wettest, and at elevation snowiest, locations within North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. In Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
during the wet season, the flow of moist air into the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
leads to some of the greatest rainfall amounts measured on Earth in northeast India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
.
Measurement

The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100 mm (4 in) plastic and 200 mm (8 in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by 25 mm (1 in) of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to 0.25 mm (0.01 in) resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate 0.25 mm (0.01 in) markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. These gauges are used in the winter by removing the funnel and inner cylinder and allowing snow and freezing rain to collect inside the outer cylinder. Some add anti-freeze to their gauge so they do not have to melt the snow or ice that falls into the gauge. Once the snowfall/ice is finished accumulating, or as 300 mm (12 in) is approached, one can either bring it inside to melt, or use lukewarm water to fill the inner cylinder with in order to melt the frozen precipitation in the outer cylinder, keeping track of the warm fluid added, which is subsequently subtracted from the overall total once all the ice/snow is melted.
Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. The wedge and tipping bucket gauges will have problems with snow. Attempts to compensate for snow/ice by warming the tipping bucket meet with limited success, since snow may sublimate if the gauge is kept much above freezing. Weighing gauges with antifreeze should do fine with snow, but again, the funnel needs to be removed before the event begins. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as CoCoRAHS
Community Collaborative Rain, Hail and Snow network
The Community Collaborative Rain, Hail and Snow Network, or CoCoRaHS, is a network of volunteer weather watchers who take daily readings of precipitation, and report them online or by phone.-History:...
or GLOBE. If a network is not available in the area where one lives, the nearest local weather office will likely be interested in the measurement.
Return period
The likelihood or probability of an event with a specified intensity and duration, is called the return periodReturn period
A return period also known as a recurrence interval is an estimate of the interval of time between events like an earthquake, flood or river discharge flow of a certain intensity or size. It is a statistical measurement denoting the average recurrence interval over an extended period of time, and...
or frequency. The intensity of a storm can be predicted for any return period and storm duration, from charts based on historic data for the location. The term 1 in 10 year storm describes a rainfall event which is rare and is only likely to occur once every 10 years, so it has a 10 percent likelihood any given year. The rainfall will be greater and the flooding will be worse than the worst storm expected in any single year. The term 1 in 100 year storm describes a rainfall event which is extremely rare and which will occur with a likelihood of only once in a century, so has a 1 percent likelihood in any given year. The rainfall will be extreme and flooding to be worse than a 1 in 10 year event. As with all probability events, it is possible to have multiple "1 in 100 Year Storms" in a single year.
Role in Köppen climate classification

The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used form of the Köppen classification has five primary types labeled A through E. Specifically, the primary types are A, tropical; B, dry; C, mild mid-latitude; D, cold mid-latitude; and E, polar. The five primary classifications can be further divided into secondary classifications such as rain forest, monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
, tropical savanna, humid subtropical, humid continental, oceanic climate
Oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also called marine west coast climate, maritime climate, Cascadian climate and British climate for Köppen climate classification Cfb and subtropical highland for Köppen Cfb or Cwb, is a type of climate typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of some of the...
, Mediterranean climate
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
, steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
, subarctic climate
Subarctic climate
The subarctic climate is a climate characterized by long, usually very cold winters, and short, cool to mild summers. It is found on large landmasses, away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N poleward of the humid continental climates...
, tundra
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
, polar ice cap
Polar ice cap
A polar ice cap is a high latitude region of a planet or natural satellite that is covered in ice. There are no requirements with respect to size or composition for a body of ice to be termed a polar ice cap, nor any geological requirement for it to be over land; only that it must be a body of...
, and desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
.
Rain forests are characterized by high rainfall, with definitions setting minimum normal annual rainfall between 1750 millimetres (68.9 in) and 2000 millimetres (78.7 in). A tropical savanna is a grassland
Grassland
Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants . However, sedge and rush families can also be found. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica...
biome
Biome
Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a...
located in semi-arid
Semi-arid
A semi-arid climate or steppe climate describes climatic regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not extremely...
to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes, with rainfall between 750 millimetres (29.5 in) and 1270 millimetres (50 in) a year. They are widespread on Africa, and are also found in India, the northern parts of South America, Malaysia, and Australia. The humid subtropical climate zone where winter rainfall (and sometimes snowfall) is associated with large storm
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of an astronomical body's atmosphere, especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather...
s that the westerlies
Westerlies
The Westerlies, anti-trades, or Prevailing Westerlies, are the prevailing winds in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes towards the poles. These prevailing winds blow from the west to the east, and steer extratropical...
steer from west to east. Most summer rainfall occurs during thunderstorm
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm, a lightning storm, thundershower or simply a storm is a form of weather characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere known as thunder. The meteorologically assigned cloud type associated with the...
s and from occasional tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s. Humid subtropical climates lie on the east side continents, roughly between latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
s 20° and 40° degrees away from the equator.
An oceanic (or maritime) climate is typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of all the world's continents, bordering cool oceans, as well as southeastern Australia, and is accompanied by plentiful precipitation year round. The Mediterranean climate regime resembles the climate of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin refers to the lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation...
, parts of western North America, parts of Western
Western Australia
Western Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east...
and South Australia
South Australia
South Australia is a state of Australia in the southern central part of the country. It covers some of the most arid parts of the continent; with a total land area of , it is the fourth largest of Australia's six states and two territories.South Australia shares borders with all of the mainland...
, in southwestern South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
and in parts of central Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
. The climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. A steppe is a dry grassland
Grassland
Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants . However, sedge and rush families can also be found. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica...
. Subarctic climates are cold with continuous permafrost
Permafrost
In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of...
and little precipitation.
Effect on agriculture

Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. All plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops
Crop (agriculture)
A crop is a non-animal species or variety that is grown to be harvested as food, livestock fodder, fuel or for any other economic purpose. Major world crops include maize , wheat, rice, soybeans, hay, potatoes and cotton. While the term "crop" most commonly refers to plants, it can also include...
. Drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
can kill crops and increase erosion, while overly wet weather can cause harmful fungus
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
growth. Plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s need varying amounts of rainfall to survive. For example, certain cacti
Cactus
A cactus is a member of the plant family Cactaceae. Their distinctive appearance is a result of adaptations to conserve water in dry and/or hot environments. In most species, the stem has evolved to become photosynthetic and succulent, while the leaves have evolved into spines...
require small amounts of water, while tropical plants may need up to hundreds of inches of rain per year to survive.
In areas with wet and dry seasons, soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
nutrients diminish and erosion increases during the wet season. Animals have adaptation and survival strategies for the wetter regime. The previous dry season leads to food shortages into the wet season, as the crops have yet to mature. Developing countries have noted that their populations show seasonal weight fluctuations due to food shortages seen before the first harvest, which occurs late in the wet season.
Changes due to global warming
Increasing temperatures tend to increase evaporation which leads to more precipitation. Precipitation has generally increased over land north of 30°N from 1900 through 2005 but has declined over the tropics since the 1970s. Globally there has been no statistically significant overall trend in precipitation over the past century, although trends have varied widely by region and over time. Eastern portions of North and South America, northern Europe, and northern and central Asia have become wetter. The Sahel, the Mediterranean, southern Africa and parts of southern Asia have become drier. There has been an increase in the number of heavy precipitation events over many areas during the past century, as well as an increase since the 1970s in the prevalence of droughts—especially in the tropics and subtropics. Changes in precipitation and evaporation over the oceans are suggested by the decreased salinity of mid- and high-latitude waters (implying more precipitation), along with increased salinity in lower latitudes (implying less precipitation, more evaporation, or both). Over the contiguous United States, total annual precipitation increased at an average rate of 6.1 percent per century since 1900, with the greatest increases within the East North Central climate region (11.6 percent per century) and the South (11.1 percent). Hawaii was the only region to show a decrease (-9.25 percent).Changes due to urban heat island

The urban heat island warms cities 0.6 °C (1.1 °F) to 5.6 °C (10.1 °F) above surrounding suburbs and rural areas. This extra heat leads to greater upward motion, which can induce additional shower and thunderstorm activity. Rainfall rates downwind of cities are increased between 48% and 116%. Partly as a result of this warming, monthly rainfall is about 28% greater between 20 miles (32.2 km) to 40 miles (64.4 km) downwind of cities, compared with upwind. Some cities induce a total precipitation increase of 51%.
Forecasting

Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer
Planetary boundary layer
The planetary boundary layer , also known as the atmospheric boundary layer , is the lowest part of the atmosphere and its behavior is directly influenced by its contact with a planetary surface. On Earth it usually responds to changes in surface forcing in an hour or less...
, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount
Probability of Precipitation
A probability of precipitation is a formal measure of the likelihood of precipitation that is often published from weather forecasting models. Its definition varies.-U.S. usage:...
, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill
Forecast skill
Skill in forecasting is a scaled representation of forecast error that relates the forecast accuracy of a particular forecast model to some reference model....
than model forecasts within six to seven hours of the time of the radar image. The forecasts can be verified through use of rain gauge
Rain gauge
A rain gauge is a type of instrument used by meteorologists and hydrologists to gather and measure the amount of liquid precipitation over a set period of time....
measurements, weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
estimates, or a combination of both. Various skill scores can be determined to measure the value of the rainfall forecast.
See also
- List of meteorology topics
- Mango showersMango showersMango showers are the pre-monsoon showers in the Indian states of Karnataka and Kerala that help in the ripening of mangoes. Also known as April rains or Summer showers, they are a result of thunderstorms over the Bay of Bengal...
, pre-monsoonMonsoonMonsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
showers in the IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n states of KarnatakaKarnatakaKarnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
and KeralaKeralaor Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
that help in the ripening of mangoes. - SunshowerSunshowerA sunshower or sun shower is a meteorological phenomenon in which rain falls while the sun is shining. These conditions often lead to the appearance of a rainbow, if the sun is at a low enough angle. Although used in the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, and parts of Britain,...
, an unusual meteorological phenomenonMeteorological phenomenonA meteorological phenomenon is a weather event that can be explained by the principles of meteorology. Such events include:* Air mass* Anticyclone* Arctic cyclone* Clouds* Crow Instability* Derecho* Diamond dust* Drought* Dust devil* Dust storm...
in which rainRainRain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
falls while the sun is shining. - Wintry showers, an informal meteorologicalMeteorologyMeteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
term for various mixtures of rainRainRain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
, freezing rainFreezing rainFreezing rain is the name given to rain that falls when surface temperatures are below freezing. The raindrops become supercooled while passing through a sub-freezing layer of air, many hundred feet , just above the surface, and then freeze upon impact with any object they encounter. The resulting...
, sleetRain and snow mixedRain and snow mixed is precipitation composed of rain and partially melted snow. This precipitation can occur where the temperature in the lower part of the atmosphere is slightly above the freezing point...
and snowSnowSnow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
.

