
Timeline of glaciation
Encyclopedia
There have been five known ice age
s in the Earth's history, with the Earth experiencing the Quaternary Ice Age
during the present time. Within ice ages, there exist periods of more severe glacial conditions and more temperate referred to as glacial period
s and interglacial period
s, respectively. The Earth is currently in an interglacial period of the Quaternary Ice Age, with the last glacial period of the Quaternary having ended approximately 10,000 years ago with the start of the Holocene
epoch.

and it has been suggested that it produced a second
name="2nd of two"
>Miracle Planet: Snowball Earth, (2005) documentary, Canadian Film Board, rebroadcast 25 April 2009 on the Science Channel (HD) "Snowball Earth
" in which the earth iced over completely. It has been suggested also that the end of this second cold period
name="2nd of two"
/> was responsible for the subsequent Cambrian Explosion
, a time of rapid diversification of multicelled life during the Cambrian
era. However, this hypothesis is still controversial, though is growing in popularity among researchers as evidence in its favor has mounted.
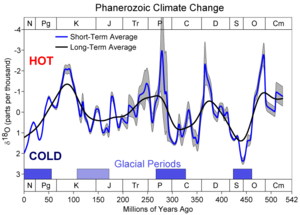
A minor series of glaciations occurred from 460 Ma to 430 Ma. There were extensive glaciations from 350 to 250 Ma. The current ice age
, called the Quaternary glaciation
, has seen more or less extensive glaciation on 40,000 and later, 100,000 year cycles.
number. The marine record preserves all the past glaciations; the land-based evidence is less complete because successive glaciations may wipe out evidence of their predecessors. Ice cores from continental ice accumulations also provide a complete record, but do not go as far back in time as marine data. Pollen
data from lakes and bogs as well as loess
profiles provided important land-based correlation data. The names system has not been completely filled out since the technical discussion moved to using marine isotopic stage numbers. For example, there are five Pleistocene glacial/interglacial cycles recorded in marine sediments during the last half million years, but only three classic interglacials were originally recognized on land during that period (Mindel
, Riss and Würm
).
Land-based evidence works acceptably well back as far as MIS 6, but it has been difficult to coordinate stages using just land-based evidence before that. Hence, the "names" system is incomplete and the land-based identifications of ice ages previous to that are somewhat conjectural. Nonetheless, land based data is essentially useful in discussing landforms, and correlating the known marine isotopic stage with them.
The last glacial
and interglacial
periods of the Quaternary are named, from most recent to most distant, as follows. Dates shown are in thousand years before present.
Older periods of the Quaternary
** Table data is based on Gibbard Figure 22.1.
Antarctic ice core has revealed that between 400,000 and 780,000 years ago, interglacials occupied a considerably larger proportion of each glacial/interglacial cycle, but were not as warm as subsequent interglacials.
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
s in the Earth's history, with the Earth experiencing the Quaternary Ice Age
Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere...
during the present time. Within ice ages, there exist periods of more severe glacial conditions and more temperate referred to as glacial period
Glacial period
A glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
s and interglacial period
Interglacial
An Interglacial period is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age...
s, respectively. The Earth is currently in an interglacial period of the Quaternary Ice Age, with the last glacial period of the Quaternary having ended approximately 10,000 years ago with the start of the Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
epoch.
Known ice ages

| Name | Period (Ma) | Period | Era |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary Quaternary glaciation Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere... |
2.58 - present | Neogene Neogene The Neogene is a geologic period and system in the International Commission on Stratigraphy Geologic Timescale starting 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and ending 2.588 million years ago... |
Cenozoic Cenozoic The Cenozoic era is the current and most recent of the three Phanerozoic geological eras and covers the period from 65.5 mya to the present. The era began in the wake of the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous that saw the demise of the last non-avian dinosaurs and... |
| Karoo Karoo Ice Age The Karoo Ice Age from 360–260 Ma was the second major ice age of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the glacial tills found in the Karoo region of South Africa where evidence for this ice age was first clearly identified.... |
360 - 260 | Carboniferous Carboniferous The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"... and Permian Permian The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian... |
Paleozoic Paleozoic The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly... |
| Andean-Saharan | 450 - 420 | Ordovician Ordovician The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period... and Silurian Silurian The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the... |
Paleozoic Paleozoic The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly... |
| Cryogenian Cryogenian The Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran... (or Sturtian-Varangian) |
800 - 635 | Cryogenian Cryogenian The Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran... |
Neoproterozoic Neoproterozoic The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1,000 to 542.0 ± 1.0 million years ago. The terminal Era of the formal Proterozoic Eon , it is further subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran Periods... |
| Huronian | 2400 - 2100 | Siderian Siderian The Siderian is the first geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from 2500 Mya to 2300 Mya . Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.... and Rhyacian |
Paleoproterozoic Paleoproterozoic The Paleoproterozoic is the first of the three sub-divisions of the Proterozoic occurring between . This is when the continents first stabilized... |

Descriptions
The second ice age, and possibly most severe, is estimated to have occurred from 850 to 635 Ma (million years) ago, in the late Proterozoic AgeNeoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1,000 to 542.0 ± 1.0 million years ago. The terminal Era of the formal Proterozoic Eon , it is further subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran Periods...
and it has been suggested that it produced a second
name="2nd of two"
>Miracle Planet: Snowball Earth, (2005) documentary, Canadian Film Board, rebroadcast 25 April 2009 on the Science Channel (HD) "Snowball Earth
Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis posits that the Earth's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen at least once, some time earlier than 650 Ma . Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposits generally regarded as of glacial origin at tropical...
" in which the earth iced over completely. It has been suggested also that the end of this second cold period
name="2nd of two"
/> was responsible for the subsequent Cambrian Explosion
Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion or Cambrian radiation was the relatively rapid appearance, around , of most major phyla, as demonstrated in the fossil record, accompanied by major diversification of other organisms, including animals, phytoplankton, and calcimicrobes...
, a time of rapid diversification of multicelled life during the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
era. However, this hypothesis is still controversial, though is growing in popularity among researchers as evidence in its favor has mounted.
A minor series of glaciations occurred from 460 Ma to 430 Ma. There were extensive glaciations from 350 to 250 Ma. The current ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, called the Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere...
, has seen more or less extensive glaciation on 40,000 and later, 100,000 year cycles.
Quaternary glacial cycles
Originally, the glacial and interglacial periods of the Quaternary Ice Age were named after characteristic geological features, and these names varied from region to region. It is now more common to refer to the periods by their marine isotopic stageMarine isotopic stage
Marine isotope stages , marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages , are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data reflecting changes in temperature derived from data from deep sea core samples...
number. The marine record preserves all the past glaciations; the land-based evidence is less complete because successive glaciations may wipe out evidence of their predecessors. Ice cores from continental ice accumulations also provide a complete record, but do not go as far back in time as marine data. Pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
data from lakes and bogs as well as loess
Loess
Loess is an aeolian sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown silt, typically in the 20–50 micrometre size range, twenty percent or less clay and the balance equal parts sand and silt that are loosely cemented by calcium carbonate...
profiles provided important land-based correlation data. The names system has not been completely filled out since the technical discussion moved to using marine isotopic stage numbers. For example, there are five Pleistocene glacial/interglacial cycles recorded in marine sediments during the last half million years, but only three classic interglacials were originally recognized on land during that period (Mindel
Kansan glaciation
The Kansan glaciation or Kansan glacial was glacial stage and part of an early conceptual climatic and chronological framework composed of four glacial and interglacial stages.-History:...
, Riss and Würm
Wisconsin glaciation
The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period within the current ice age occurring during the last years of the Pleistocene, from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago....
).
Land-based evidence works acceptably well back as far as MIS 6, but it has been difficult to coordinate stages using just land-based evidence before that. Hence, the "names" system is incomplete and the land-based identifications of ice ages previous to that are somewhat conjectural. Nonetheless, land based data is essentially useful in discussing landforms, and correlating the known marine isotopic stage with them.
The last glacial
Glacial period
A glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
and interglacial
Interglacial
An Interglacial period is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age...
periods of the Quaternary are named, from most recent to most distant, as follows. Dates shown are in thousand years before present.
Land-based chronology of Quaternary glacial cycles
| Backwards Glacial Index |
Names | Inter/Glacial | Period (ka) | MIS Marine isotopic stage Marine isotope stages , marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages , are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data reflecting changes in temperature derived from data from deep sea core samples... |
Epoch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine | N. American | N. European | Great Britain | S. American | |||||
| Flandrian | interglacial | present – 12 | 1 | Holocene Holocene The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"... |
|||||
| 1st | Würm | Wisconsin Wisconsin glaciation The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period within the current ice age occurring during the last years of the Pleistocene, from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago.... |
Weichselian or Vistulian |
Devensian | Llanquihue | glacial period | 12 – 110 | 2-4 & 5a-d |
Pleistocene Pleistocene The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and .... |
| Riss-Würm | Sangamonian Sangamonian Stage The Sangamonian Stage, also known as the Sangamon interglacial, is the name used by Quaternary geologists to designate the last interglacial period in North America from 125,000—75,000 years ago, a period of... |
Eemian | Ipswichian | Valdivia | interglacial | 110 – 130 | 5e (7, 9?) | ||
| 2nd | Riss | Illinoian | Saalian | Wolstonian or Gipping | Santa María | glacial period | 130 – 200 | 6 | |
| Mindel-Riss | Pre-Illinoian | Holstein | Hoxnian | interglacial(s) | 200 – 300/380 | 11 | |||
| 3rd – 5th | Mindel | Pre-Illinoian | Elsterian | Anglian | Río Llico | glacial period(s) | 300/380 – 455 | 12 | |
| Günz-Mindel | Pre-Illinoian | Cromerian* | interglacial(s) | 455 – 620 | 13-15 | ||||
| 7th | Günz | Pre-Illinoian | Menapian | Beestonian Beestonian stage The Beestonian Stage is the name for an early Pleistocene stage used in the British Isles. It precedes the Cromerian Stage and follows the Pastonian Stage. This stage consists of alternating glacial and interglacial phases instead of being a continuous glacial epoch. It is equivalent to the... |
Caracol | glacial period | 620 – 680 | 16 |
Older periods of the Quaternary
| Name | Inter/Glacial | Period (ka) | MIS Marine isotopic stage Marine isotope stages , marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages , are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data reflecting changes in temperature derived from data from deep sea core samples... |
Epoch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pastonian Stage | interglacial | 600 – 800 | |
| Pre-Pastonian Stage | glacial period | 800 – 1300 | |
| Bramertonian Stage | interglacial | 1300 – 1550 |
Ice core evidence of recent glaciation
Ice cores are used to obtain a high resolution record of recent glaciation. It confirms the chronology of the marine isotopic stages. Ice core data shows that the last 400,000 years have consisted of short interglacials (10,000 to 30,000 years) about as warm as the present alternated with much longer (70,000 to 90,000 years) glacials substantially colder than present. The new EPICAEPICA
The European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica is a multinational European project for deep ice core drilling in Antarctica. Its main objective is to obtain full documentation of the climatic and atmospheric record archived in Antarctic ice by drilling and analyzing two ice cores and comparing...
Antarctic ice core has revealed that between 400,000 and 780,000 years ago, interglacials occupied a considerably larger proportion of each glacial/interglacial cycle, but were not as warm as subsequent interglacials.
External links
- Aber, J.S., 2006, Regional Glaciation of Kansas and Nebraska. Emporia State University, Emporia, Kansas.
- anonymous, 2000, Pre-Wisconsin Glaciation of Central North America. Work Group on Geospatial Analysis of Glaciated Environments (GAGE), INQUA Commission on Glaciation, Emporia State University, Emporia, Kansas.
- anonymous, 2007, Global correlation tables for the Quaternary. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England
- Gibbard, P.L., S. Boreham, K.M. Cohen and A. Moscariello, 2007, Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v. 2007b., jpg version 844 KB. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England
- Hambrey, M.J., and W.B. Harland, eds., 1981. Earth's pre-Pleistocene glacial record. Cambridge University Press, 1004 + xv pp. (book downloadable as series of PDF files)
- Silva, P.G. C. Zazo, T. Bardají, J. Baena, J. Lario y A. Rosas, 2007, Tabla Cronoestratigráfica del Cuaternario aequa., PDF version 1.4 MB. asociación española para el estudio del cuaternario (aequa), Departamento de Geología, Universidad de Alcalá Madrid, Spain. (Correlation chart of European Quaternary and cultural stages and fossils)
See also
- Geologic time scaleGeologic time scaleThe geologic time scale provides a system of chronologic measurement relating stratigraphy to time that is used by geologists, paleontologists and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred during the history of the Earth...
- Glacial history of MinnesotaGlacial history of MinnesotaThe glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had...
- Ice ageIce ageAn ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
- Glacial periodGlacial periodA glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
- Last glacial period
- Varanger glaciationCryogenianThe Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran...
- Brunhes–Matuyama reversal occurred about 780,000 years ago

