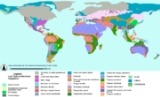
Wisconsin glaciation
Encyclopedia
The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period
within the current ice age
occurring during the last years of the Pleistocene
, from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago.
During this period there were several changes between glacier advance and retreat. The maximum extent
of glaciation was approximately 18,000 years ago. While the general pattern of global cooling and glacier advance was similar, local differences in the development of glacier advance and retreat make it difficult to compare the details from continent to continent (see picture of ice core data below for differences).
From the point of view of human archaeology
, it falls in the Paleolithic
and Mesolithic
periods.
is a longer period of cold temperature in which ice sheet
s cover large parts of the Earth, such as Antarctica. Glacials, on the other hand, refer to colder phases within an ice age that separate interglacial
s. Thus, the end of the last glacial period is not the end of the last ice age. The end of the last glacial period was about 12,500 years ago, while the end of the last ice age may not yet have come: little evidence points to a stop of the glacial-interglacial cycle of the last million years.
The last glacial period is the best-known part of the current ice age, and has been intensively studied in North America, northern Eurasia, the Himalaya and other formerly glaciated regions around the world. The glaciations that occurred during this glacial period covered many areas, mainly on the Northern Hemisphere
and to a lesser extent on the Southern Hemisphere
. They have different names, historically developed and depending on their geographic distributions: Fraser (in the Pacific Cordillera
of North America
), Pinedale, Wisconsinan or Wisconsin (in central North America
), Devensian (in the British Isles
), Midlandian (in Ireland
), Würm (in the Alps
), Mérida (in Venezuela
), Weichselian (in Scandinavia
and Northern Europe
), Vistulian (in northern Central Europe
), Valdai in Eastern Europe
and Zyryanka in Siberia
, Llanquihue in Chile
, and Otira in New Zealand
.
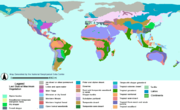
 The last glaciation centered on the huge ice sheets of North America and Eurasia. Considerable areas in the Alps, the Himalaya and the Andes were ice-covered, and Antarctica remained glaciated.
The last glaciation centered on the huge ice sheets of North America and Eurasia. Considerable areas in the Alps, the Himalaya and the Andes were ice-covered, and Antarctica remained glaciated.
Canada was nearly completely covered by ice, as well as the northern part of the USA, both blanketed by the huge Laurentide ice sheet
. Alaska remained mostly ice free due to arid
climate conditions. Local glaciations existed in the Rocky Mountains
and the Cordilleran ice sheet
and as ice field
s and ice cap
s in the Sierra Nevada in northern California. In Britain
, mainland Europe
, and northwestern Asia
, the Scandinavian ice sheet once again reached the northern parts of the British Isles, Germany
, Poland
, and Russia
, extending as far east as the Taimyr Peninsula in western Siberia. The maximum extent of western Siberian glaciation was reached approximately 18,000 to 17,000 BP and thus later than in Europe (22,000–18,000 BP). Northeastern Siberia was not covered by a continental-scale ice sheet. Instead, large, but restricted, icefield complexes covered mountain ranges within northeast Siberia, including the Kamchatka-Koryak Mountains.
The Arctic Ocean
between the huge ice sheets of America and Eurasia was not frozen throughout, but like today probably was only covered by relatively shallow ice, subject to seasonal changes and riddled with iceberg
s calving
from the surrounding ice sheets. According to the sediment composition retrieved from deep-sea core
s there must even have been times of seasonally open waters.
Outside the main ice sheets, widespread glaciation occurred on the Alps
-Himalaya mountain chain. In contrast to the earlier glacial stages, the Würm glaciation was composed of smaller ice caps and mostly confined to valley glaciers, sending glacial lobes into the Alpine foreland
. To the east the Caucasus
and the mountains of Turkey
and Iran
were capped by local ice fields or small ice sheets.,
In the Himalaya and the Tibetan Plateau
, glaciers advanced considerably, particularly between 47,000–27,000 BP and in contrast to the widespread contemporaneous warming elsewhere. The formation of a contiguous ice sheet on the Tibetan Plateau is controversial.
Other areas of the Northern Hemisphere did not bear extensive ice sheets but local glaciers in high areas. Parts of Taiwan
for example were repeatedly glaciated between 44,250 and 10,680 BP as well as the Japanese Alps
. In both areas maximum glacier advance occurred between 60,000 and 30,000 BP (starting roughly during the Toba catastrophe
). To a still lesser extent glaciers existed in Africa, for example in the High Atlas
, the mountains of Morocco
, the Mount Atakor massif in southern Algeria
, and several mountains in Ethiopia
. In the Southern Hemisphere, an ice cap of several hundred square kilometers was present on the east African mountains in the Kilimanjaro
Massif, Mount Kenya
and the Ruwenzori Mountains, still bearing remnants of glaciers today.
Glaciation of the Southern Hemisphere was less extensive because of current configuration of continents. Ice sheet
s existed in the Andes (Patagonian Ice Sheet
), where six glacier advances between 33,500 and 13,900 BP in the Chilean Andes have been reported. Antarctica was entirely glaciated, much like today, but the ice sheet left no uncovered area. In mainland Australia only a very small area in the vicinity of Mount Kosciuszko
was glaciated, whereas in Tasmania
glaciation was more widespread. An ice sheet formed in New Zealand
, covering all of the Southern Alps, where at least three glacial advances can be distinguished. Local ice caps existed in Irian Jaya, Indonesia
, where in three ice areas remnants of the Pleistocene glaciers are still preserved today.
in the United States. The Pinedale lasted from approximately 30,000 to 10,000 years ago and was at its greatest extent between 23,500 and 21,000 years ago. This glaciation was somewhat distinct from the main Wisconsin glaciation as it was only loosely related to the giant ice sheets and was instead composed of mountain glaciers, merging into the Cordilleran Ice Sheet
. The Cordilleran ice sheet produced features such as glacial Lake Missoula
, which would break free from its ice dam causing the massive Missoula floods
. Geologists estimate that the cycle of flooding and reformation of the lake lasted on average of 55 years and that the floods occurred approximately 40 times over the 2,000 year period between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. Glacial lake outburst floods
such as these are not uncommon today in Iceland
and other places.
was the last major advance of continental glacier
s in the North American Laurentide ice sheet
. At the height of glaciation the Bering land bridge
potentially permitted migration of mammals, including people
, to North America from Siberia
.
It radically altered the geography of North America north of the Ohio River
. At the height of the Wisconsin Episode glaciation, ice covered most of Canada
, the Upper Midwest
, and New England
, as well as parts of Montana
and Washington. On Kelleys Island in Lake Erie
or in New York's Central Park
, the grooves
left by these glaciers can be easily observed. In southwestern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta a suture zone between the Laurentide
and Cordilleran
ice sheet
s formed the Cypress Hills, which is the northernmost point in North America that remained south of the continental ice sheets.
The Great Lakes are the result of glacial scour and pooling of meltwater at the rim of the receding ice. When the enormous mass of the continental ice sheet retreated, the Great Lakes began gradually moving south due to isostatic rebound of the north shore. Niagara Falls
is also a product of the glaciation, as is the course of the Ohio River, which largely supplanted the prior Teays River
.
With the assistance of several very broad glacial lakes, it carved the gorge now known as the Upper Mississippi River
, filling into the Driftless Area and probably releasing an annual ice-dam-burst.
In its retreat, the Wisconsin Episode glaciation left terminal moraine
s that form Long Island
, Block Island
, Cape Cod
, Nomans Land, Marthas Vineyard, Nantucket, Sable Island
and the Oak Ridges Moraine
in south central Ontario, Canada. In Wisconsin itself, it left the Kettle Moraine
. The drumlin
s and esker
s formed at its melting edge are landmarks of the Lower Connecticut River Valley.
s and archaeologists and refers to what is often popularly meant by the latest Ice Age
. Irish geologist
s, geographer
s, and archaeologists refer to the Midlandian glaciation as its effects in Ireland
are largely visible in the Irish Midlands. The name Devensian is derived from the Latin
Dēvenses, people living by the Dee (Dēva in Latin), a river on the Welsh border near which deposits from the period are particularly well represented.
The effects of this glaciation can be seen in many geological features of England
, Wales
, Scotland
, and Northern Ireland
. Its deposits have been found overlying material from the preceding Ipswichian Stage and lying beneath those from the following Flandrian stage of the Holocene
.
The latter part of the Devensian includes Pollen zone
s I-IV, the Allerød
and Bølling Oscillation
s, and the Older
and Younger Dryas
climatic stages.
or its German name Weichsel). During the glacial maximum
in Scandinavia, only the western parts of Jutland
were ice-free, and a large part of what is today the North Sea
was dry land connecting Jutland with Britain. It is also in Denmark that the only Scandinavian ice-age animals older than 13,000 BC are found. In the period following the last interglacial
before the current one (Eemian Stage), the coast of Norway
was also ice-free.
The Baltic Sea
, with its unique brackish water
, is a result of meltwater from the Weichsel glaciation combining with saltwater from the North Sea when the straits between Sweden and Denmark opened. Initially, when the ice began melting about 10,300 ybp
, seawater filled the isostatically depressed
area, a temporary marine incursion
that geologists dub the Yoldia Sea
. Then, as post-glacial isostatic rebound
lifted the region about 9500 ybp, the deepest basin of the Baltic became a freshwater lake, in palaeological contexts referred to as Ancylus Lake
, which is identifiable in the freshwater fauna found in sediment cores. The lake was filled by glacial runoff, but as worldwide sea level continued rising, saltwater again breached the sill about 8000 ybp, forming a marine Littorina Sea
which was followed by another freshwater phase before the present brackish marine system was established. "At its present state of development, the marine life of the Baltic Sea is less than about 4000 years old," Drs. Thulin and Andrushaitis remarked when reviewing these sequences in 2003.
Overlying ice had exerted pressure on the Earth's surface. As a result of melting ice, the land has continued to rise yearly in Scandinavia, mostly in northern Sweden
and Finland
where the land is rising at a rate of as much as 8–9 mm per year, or 1 meter in 100 years. This is important for archaeologists since a site that was coastal in the Nordic Stone Age
now is inland and can be dated by its relative distance from the present shore.
is derived from a river in the Alpine foreland, approximately marking the maximum glacier advance of this particular glacial period. The Alps have been the area where first systematic scientific research on ice ages has been conducted by Louis Agassiz
in the beginning of the 19th century. Here the Würm glaciation of the last glacial period was intensively studied. Pollen analysis
, the statistical analyses of microfossilized plant pollens found in geological deposits, has chronicled the dramatic changes in the European environment during the Würm glaciation. During the height of Würm glaciation, ca 24,000–10,000 ybp, most of western and central Europe and Eurasia was open steppe-tundra, while the Alps presented solid ice field
s and montane glaciers. Scandinavia and much of Britain were under ice.
During the Würm, the Rhône Glacier
covered the whole western Swiss plateau, reaching today's regions of Solothurn and Aarau. In the region of Bern it merged with the Aar glacier. The Rhine Glacier
is currently the subject of the most detailed studies. Glaciers of the Reuss and the Limmat advanced sometimes as far as the Jura. Montane and piedmont glaciers formed the land by grinding away virtually all traces of the older Günz and Mindel glaciation, by depositing base moraines and terminal moraines of different retraction phases and loess
deposits, and by the pro-glacial rivers' shifting and redepositing gravels. Beneath the surface, they had profound and lasting influence on geothermal heat and the patterns of deep groundwater flow.
; during the Late Pleistocene. Two main moraine levels have been recognized: one between 2600 and 2700 m, and another between 3000 and 3500 m elevation. The snow line during the last glacial advance was lowered approximately 1200 m below the present snow line (3700 m). The glaciated area in the Cordillera de Mérida
was approximately 600 km2; this included the following high areas from southwest to northeast: Páramo de Tamá, Páramo Batallón, Páramo Los Conejos, Páramo Piedras Blancas, and Teta de Niquitao. Approximately 200 km2 of the total glaciated area was in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida
, and of that amount, the largest concentration, 50 km2, was in the areas of Pico Bolívar
, Pico Humboldt
(4,942 m), and Pico Bonpland
(4,893 m). Radiocarbon dating indicates that the moraines are older than 10,000 years B.P., and probably older than 13,000 years B.P. The lower moraine level probably corresponds to the main Wisconsin glacial advance. The upper level probably represents the last glacial advance (Late Wisconsin).
which is a fan-shaped piedmont
glacial lake
. On the lake's western shores there are large moraine systems of which the innermost belong to the last glacial period. Llanquihue Lake's varve
s are a node point in southern Chile's varve geochronology
. During the last glacial maximum the Patagonian Ice Sheet
extended over the Andes from about 35°S to Tierra del Fuego
at 55°S. The western part appears to have been very active, with wet basal conditions, while the eastern part was cold based. Palsa
s seems to have developed at least in the unglaciated parts of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
. The area west of Llanquihue Lake was ice-free during the LGM
, and had sparsely distributed vegetation dominated by Nothofagus
. Valdivian temperate rainforest was reduced to scattered remnants in the western side of the Andes.
Glacial period
A glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
within the current ice age
Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere...
occurring during the last years of the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
, from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago.
During this period there were several changes between glacier advance and retreat. The maximum extent
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
of glaciation was approximately 18,000 years ago. While the general pattern of global cooling and glacier advance was similar, local differences in the development of glacier advance and retreat make it difficult to compare the details from continent to continent (see picture of ice core data below for differences).
From the point of view of human archaeology
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
, it falls in the Paleolithic
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic Age, Era or Period, is a prehistoric period of human history distinguished by the development of the most primitive stone tools discovered , and covers roughly 99% of human technological prehistory...
and Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
periods.
Origin and definition
The last glacial period is sometimes colloquially referred to as the "last ice age", though this use is incorrect because an ice ageIce age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
is a longer period of cold temperature in which ice sheet
Ice sheet
An ice sheet is a mass of glacier ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than 50,000 km² , thus also known as continental glacier...
s cover large parts of the Earth, such as Antarctica. Glacials, on the other hand, refer to colder phases within an ice age that separate interglacial
Interglacial
An Interglacial period is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age...
s. Thus, the end of the last glacial period is not the end of the last ice age. The end of the last glacial period was about 12,500 years ago, while the end of the last ice age may not yet have come: little evidence points to a stop of the glacial-interglacial cycle of the last million years.
The last glacial period is the best-known part of the current ice age, and has been intensively studied in North America, northern Eurasia, the Himalaya and other formerly glaciated regions around the world. The glaciations that occurred during this glacial period covered many areas, mainly on the Northern Hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and to a lesser extent on the Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
. They have different names, historically developed and depending on their geographic distributions: Fraser (in the Pacific Cordillera
Pacific Cordillera
The Pacific Cordillera is a top-level physiographic region of Canada. This cordillera is part of the Western Cordillera of North America. The mountain ranges in this region were covered during the Pleistocene by the Cordilleran Ice Sheet...
of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
), Pinedale, Wisconsinan or Wisconsin (in central North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
), Devensian (in the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
), Midlandian (in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
), Würm (in the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
), Mérida (in Venezuela
Venezuela
Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
), Weichselian (in Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
and Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
), Vistulian (in northern Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
), Valdai in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
and Zyryanka in Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
, Llanquihue in Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, and Otira in New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
.
Overview


Canada was nearly completely covered by ice, as well as the northern part of the USA, both blanketed by the huge Laurentide ice sheet
Laurentide ice sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered hundreds of thousands of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the northern United States, multiple times during Quaternary glacial epochs. It last covered most of northern North America between c. 95,000 and...
. Alaska remained mostly ice free due to arid
Arid
A region is said to be arid when it is characterized by a severe lack of available water, to the extent of hindering or even preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life...
climate conditions. Local glaciations existed in the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
and the Cordilleran ice sheet
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
and as ice field
Ice field
An ice field is an area less than 50,000 km² of ice often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation. It is an extensive area of interconnected valley glaciers from which the higher peaks rise as nunataks...
s and ice cap
Ice cap
An ice cap is an ice mass that covers less than 50 000 km² of land area . Masses of ice covering more than 50 000 km² are termed an ice sheet....
s in the Sierra Nevada in northern California. In Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, mainland Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, and northwestern Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, the Scandinavian ice sheet once again reached the northern parts of the British Isles, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, extending as far east as the Taimyr Peninsula in western Siberia. The maximum extent of western Siberian glaciation was reached approximately 18,000 to 17,000 BP and thus later than in Europe (22,000–18,000 BP). Northeastern Siberia was not covered by a continental-scale ice sheet. Instead, large, but restricted, icefield complexes covered mountain ranges within northeast Siberia, including the Kamchatka-Koryak Mountains.
The Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
between the huge ice sheets of America and Eurasia was not frozen throughout, but like today probably was only covered by relatively shallow ice, subject to seasonal changes and riddled with iceberg
Iceberg
An iceberg is a large piece of ice from freshwater that has broken off from a snow-formed glacier or ice shelf and is floating in open water. It may subsequently become frozen into pack ice...
s calving
Ice calving
Ice calving, also known as glacier calving or iceberg calving, is a form of ice ablation or ice disruption. It is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse...
from the surrounding ice sheets. According to the sediment composition retrieved from deep-sea core
Core
- Science and Academics :* Core , in mathematics, an object in group theory* Core , in mathematics, a subset of the domain of a closable operator* Core , in mathematics, the homomorphically minimal subgraph of a graph...
s there must even have been times of seasonally open waters.
Outside the main ice sheets, widespread glaciation occurred on the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
-Himalaya mountain chain. In contrast to the earlier glacial stages, the Würm glaciation was composed of smaller ice caps and mostly confined to valley glaciers, sending glacial lobes into the Alpine foreland
Foreland
Foreland is the easternmost point of the Isle of Wight. It is located three miles east of the town of Brading, and due south of the city of Portsmouth on the British mainland. It is characterised by a pub called the Crab and Lobster and various beach huts plus a beach cafe and a coast guard...
. To the east the Caucasus
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
and the mountains of Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
were capped by local ice fields or small ice sheets.,
In the Himalaya and the Tibetan Plateau
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau , also known as the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau is a vast, elevated plateau in Central Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai, in addition to smaller portions of western Sichuan, southwestern Gansu, and northern Yunnan in Western China and Ladakh in...
, glaciers advanced considerably, particularly between 47,000–27,000 BP and in contrast to the widespread contemporaneous warming elsewhere. The formation of a contiguous ice sheet on the Tibetan Plateau is controversial.
Other areas of the Northern Hemisphere did not bear extensive ice sheets but local glaciers in high areas. Parts of Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
for example were repeatedly glaciated between 44,250 and 10,680 BP as well as the Japanese Alps
Japanese Alps
The is a series of mountain ranges in Japan that bisect the main island of Honshū. The name was coined by William Gowland, the "Father of Japanese Archaeology," and later popularized by Reverend Walter Weston , an English missionary for whom a memorial plaque is located at Kamikochi, a tourist...
. In both areas maximum glacier advance occurred between 60,000 and 30,000 BP (starting roughly during the Toba catastrophe
Toba catastrophe theory
The Toba supereruption was a supervolcanic eruption that occurred some time between 69,000 and 77,000 years ago at Lake Toba . It is recognized as one of the Earth's largest known eruptions...
). To a still lesser extent glaciers existed in Africa, for example in the High Atlas
High Atlas
High Atlas, also called the Grand Atlas Mountains is a mountain range in central Morocco in Northern Africa.The High Atlas rises in the west at the Atlantic Ocean and stretches in an eastern direction to the Moroccan-Algerian border. At the Atlantic and to the southwest the range drops abruptly...
, the mountains of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, the Mount Atakor massif in southern Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, and several mountains in Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
. In the Southern Hemisphere, an ice cap of several hundred square kilometers was present on the east African mountains in the Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro
Kilimanjaro, with its three volcanic cones, Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira, is a dormant volcano in Kilimanjaro National Park, Tanzania and the highest mountain in Africa at above sea level .-Geology:...
Massif, Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya is the highest mountain in Kenya and the second-highest in Africa, after Kilimanjaro. The highest peaks of the mountain are Batian , Nelion and Point Lenana . Mount Kenya is located in central Kenya, just south of the equator, around north-northeast of the capital Nairobi...
and the Ruwenzori Mountains, still bearing remnants of glaciers today.
Glaciation of the Southern Hemisphere was less extensive because of current configuration of continents. Ice sheet
Ice sheet
An ice sheet is a mass of glacier ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than 50,000 km² , thus also known as continental glacier...
s existed in the Andes (Patagonian Ice Sheet
Patagonian Ice Sheet
350px|thumb|right|Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the [[Strait of Magellan]] area during the [[last glacial period]]. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots...
), where six glacier advances between 33,500 and 13,900 BP in the Chilean Andes have been reported. Antarctica was entirely glaciated, much like today, but the ice sheet left no uncovered area. In mainland Australia only a very small area in the vicinity of Mount Kosciuszko
Mount Kosciuszko
Mount Kosciuszko is a mountain located in the Snowy Mountains in Kosciuszko National Park. With a height of 2,228 metres above sea level, it is the highest mountain in Australia...
was glaciated, whereas in Tasmania
Tasmania
Tasmania is an Australian island and state. It is south of the continent, separated by Bass Strait. The state includes the island of Tasmania—the 26th largest island in the world—and the surrounding islands. The state has a population of 507,626 , of whom almost half reside in the greater Hobart...
glaciation was more widespread. An ice sheet formed in New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, covering all of the Southern Alps, where at least three glacial advances can be distinguished. Local ice caps existed in Irian Jaya, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, where in three ice areas remnants of the Pleistocene glaciers are still preserved today.
Pinedale or Fraser glaciation, Rocky Mountains, USA
The Pinedale (central Rocky Mountains) or Fraser (Cordilleran ice sheet) glaciation was the last of the major glaciations to appear in the Rocky MountainsRocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
in the United States. The Pinedale lasted from approximately 30,000 to 10,000 years ago and was at its greatest extent between 23,500 and 21,000 years ago. This glaciation was somewhat distinct from the main Wisconsin glaciation as it was only loosely related to the giant ice sheets and was instead composed of mountain glaciers, merging into the Cordilleran Ice Sheet
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
. The Cordilleran ice sheet produced features such as glacial Lake Missoula
Glacial Lake Missoula
Glacial Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago...
, which would break free from its ice dam causing the massive Missoula floods
Missoula Floods
The Missoula Floods refer to the cataclysmic floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Gorge at the end of the last ice age. The glacial flood events have been researched since the 1920s...
. Geologists estimate that the cycle of flooding and reformation of the lake lasted on average of 55 years and that the floods occurred approximately 40 times over the 2,000 year period between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. Glacial lake outburst floods
Glacial lake outburst flood
A glacial lake outburst flood is a type of outburst flood that occurs when the dam containing a glacial lake fails. The dam can consist of glacier ice or a terminal moraine...
such as these are not uncommon today in Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
and other places.
Wisconsin glaciation, North America
The Wisconsin Glacial EpisodeWisconsinan glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode was the most recent major advance of the North American Laurentide ice sheet. Globally, this advance is known as the last glacial period. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 110,000 to 10,000 years ago, between the Eemian interglacial and the current...
was the last major advance of continental glacier
Continental Glacier
Continental Glacier is located in Bridger-Teton and Shoshone National Forests, in the U.S. state of Wyoming and straddles the Continental Divide in the northern Wind River Range. Continental Glacier is in both the Bridger and Fitzpatrick Wildernesses, and is part of the largest grouping of glaciers...
s in the North American Laurentide ice sheet
Laurentide ice sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered hundreds of thousands of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the northern United States, multiple times during Quaternary glacial epochs. It last covered most of northern North America between c. 95,000 and...
. At the height of glaciation the Bering land bridge
Bering land bridge
The Bering land bridge was a land bridge roughly 1,000 miles wide at its greatest extent, which joined present-day Alaska and eastern Siberia at various times during the Pleistocene ice ages. Like most of Siberia and all of Manchuria, Beringia was not glaciated because snowfall was extremely light...
potentially permitted migration of mammals, including people
People
People is a plurality of human beings or other beings possessing enough qualities constituting personhood. It has two usages:* as the plural of person or a group of people People is a plurality of human beings or other beings possessing enough qualities constituting personhood. It has two usages:*...
, to North America from Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
.
It radically altered the geography of North America north of the Ohio River
Ohio River
The Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River. At the confluence, the Ohio is even bigger than the Mississippi and, thus, is hydrologically the main stream of the whole river system, including the Allegheny River further upstream...
. At the height of the Wisconsin Episode glaciation, ice covered most of Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, the Upper Midwest
Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a region in the northern portion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. It is largely a sub-region of the midwest. Although there are no uniformly agreed-upon boundaries, the region is most commonly used to refer to the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, and...
, and New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
, as well as parts of Montana
Montana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
and Washington. On Kelleys Island in Lake Erie
Lake Erie
Lake Erie is the fourth largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America, and the tenth largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. It is bounded on the north by the...
or in New York's Central Park
Central Park
Central Park is a public park in the center of Manhattan in New York City, United States. The park initially opened in 1857, on of city-owned land. In 1858, Frederick Law Olmsted and Calvert Vaux won a design competition to improve and expand the park with a plan they entitled the Greensward Plan...
, the grooves
Glacial striations
Glacial striations or glacial grooves are scratches or gouges cut into bedrock by process of glacial abrasion. Glacial striations usually occur as multiple straight, parallel grooves representing the movement of the sediment-loaded base of the glacier...
left by these glaciers can be easily observed. In southwestern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta a suture zone between the Laurentide
Laurentide ice sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered hundreds of thousands of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the northern United States, multiple times during Quaternary glacial epochs. It last covered most of northern North America between c. 95,000 and...
and Cordilleran
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
ice sheet
Ice sheet
An ice sheet is a mass of glacier ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than 50,000 km² , thus also known as continental glacier...
s formed the Cypress Hills, which is the northernmost point in North America that remained south of the continental ice sheets.
The Great Lakes are the result of glacial scour and pooling of meltwater at the rim of the receding ice. When the enormous mass of the continental ice sheet retreated, the Great Lakes began gradually moving south due to isostatic rebound of the north shore. Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls
The Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River draining Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, is the collective name for the Horseshoe Falls and the adjacent American Falls along with the comparatively small Bridal Veil Falls, which combined form the highest flow rate of any waterfalls in the world and has...
is also a product of the glaciation, as is the course of the Ohio River, which largely supplanted the prior Teays River
Teays River
The Teays River was an important preglacial river that drained much of the area now drained by the Ohio River, and more. Traces of the Teays across northern Ohio and Indiana are represented by a network of river valleys. These valleys were carved in the late Cenozoic and eventually led to the...
.
With the assistance of several very broad glacial lakes, it carved the gorge now known as the Upper Mississippi River
Upper Mississippi River
The Upper Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River upstream of Cairo, Illinois, United States. From the headwaters at Lake Itasca, Minnesota, the river flows approximately 2000 kilometers to Cairo, where it is joined by the Ohio River to form the Lower Mississippi...
, filling into the Driftless Area and probably releasing an annual ice-dam-burst.
In its retreat, the Wisconsin Episode glaciation left terminal moraine
Terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a moraine that forms at the end of the glacier called the snout.Terminal moraines mark the maximum advance of the glacier. An end moraine is at the present boundary of the glacier....
s that form Long Island
Long Island
Long Island is an island located in the southeast part of the U.S. state of New York, just east of Manhattan. Stretching northeast into the Atlantic Ocean, Long Island contains four counties, two of which are boroughs of New York City , and two of which are mainly suburban...
, Block Island
Block Island
Block Island is part of the U.S. state of Rhode Island and is located in the Atlantic Ocean approximately south of the coast of Rhode Island, east of Montauk Point on Long Island, and is separated from the Rhode Island mainland by Block Island Sound. The United States Census Bureau defines Block...
, Cape Cod
Cape Cod
Cape Cod, often referred to locally as simply the Cape, is a cape in the easternmost portion of the state of Massachusetts, in the Northeastern United States...
, Nomans Land, Marthas Vineyard, Nantucket, Sable Island
Sable Island
Sable Island is a small Canadian island situated 300 km southeast of mainland Nova Scotia in the Atlantic Ocean. The island is a year-round home to approximately five people...
and the Oak Ridges Moraine
Oak Ridges Moraine
The Oak Ridges Moraine is an ecologically important geological landform in the Mixedwood Plains of south-central Ontario, Canada. The moraine covers a geographic area of between Caledon and Rice Lake, near Peterborough...
in south central Ontario, Canada. In Wisconsin itself, it left the Kettle Moraine
Kettle Moraine
Kettle Moraine is a large moraine in the state of Wisconsin stretching from Walworth County in the south to Kewaunee County in the north. It has also been referred to as the Kettle Range and, in geological texts, as the Kettle Interlobate Moraine....
. The drumlin
Drumlin
A drumlin, from the Irish word droimnín , first recorded in 1833, is an elongated whale-shaped hill formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated till or ground moraine.-Drumlin formation:...
s and esker
Esker
An esker is a long winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North America...
s formed at its melting edge are landmarks of the Lower Connecticut River Valley.
Tahoe, Tenaya, and Tioga, Sierra Nevada, USA
In the Sierra Nevada, there are three named stages of glacial maxima (sometimes incorrectly called ice ages) separated by warmer periods. These glacial maxima are called, from oldest to youngest, Tahoe, Tenaya, and Tioga. The Tahoe reached its maximum extent perhaps about 70,000 years ago. Little is known about the Tenaya. The Tioga was the least severe and last of the Wisconsin Episode. It began about 30,000 years ago, reached its greatest advance 21,000 years ago, and ended about 10,000 years ago.Greenland glaciation
In Northwest Greenland, ice coverage attained a very early maximum in the last glacial period around 114,000. After this early maximum, the ice coverage was similar to today until the end of the last glacial period. Towards the end glaciers readvanced once more before retreating to their present extent. According to ice core data, the Greenland climate was dry during the last glacial period, precipitation reaching perhaps only 20% of today's value.Devensian & Midlandian glaciation, in Britain and Ireland
The name Devensian glaciation is used by British geologistGeologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using...
s and archaeologists and refers to what is often popularly meant by the latest Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Irish geologist
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using...
s, geographer
Geographer
A geographer is a scholar whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society.Although geographers are historically known as people who make maps, map making is actually the field of study of cartography, a subset of geography...
s, and archaeologists refer to the Midlandian glaciation as its effects in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
are largely visible in the Irish Midlands. The name Devensian is derived from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
Dēvenses, people living by the Dee (Dēva in Latin), a river on the Welsh border near which deposits from the period are particularly well represented.
The effects of this glaciation can be seen in many geological features of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
. Its deposits have been found overlying material from the preceding Ipswichian Stage and lying beneath those from the following Flandrian stage of the Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
.
The latter part of the Devensian includes Pollen zone
Pollen zone
Pollen zones are a system of subdividing the last glacial period and Holocene paleoclimate using the data from pollen cores. The sequence provides a global chronological structure to a wide variety of scientists, such as geologists, climatologisists, geographists and archaeologists, who study the...
s I-IV, the Allerød
Allerød Oscillation
The Allerød period was a warm and moist global interstadial that occurred at the end of the last glacial period. The Allerød oscillation raised temperatures , before they declined again in the succeeding Younger Dryas period, which was followed by the present interglacial period.In some regions,...
and Bølling Oscillation
Bølling Oscillation
The Bølling oscillation was a warm interstadial period between the Oldest Dryas and Older Dryas stadials, at the end of the last glacial period. It is named after a peat sequence discovered at Bølling lake, central Jutland...
s, and the Older
Older Dryas
The Older Dryas was a stadial period between the Bølling and Allerød oscillations during the Pleistocene glacial period of ~11,700—12,000 uncalibrated years ago...
and Younger Dryas
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas stadial, also referred to as the Big Freeze, was a geologically brief period of cold climatic conditions and drought between approximately 12.8 and 11.5 ka BP, or 12,800 and 11,500 years before present...
climatic stages.
Weichselian glaciation, Scandinavia and northern Europe
Alternative names include: Weichsel glaciation or Vistulian glaciation (referring to the Polish river VistulaVistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
or its German name Weichsel). During the glacial maximum
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
in Scandinavia, only the western parts of Jutland
Jutland
Jutland , historically also called Cimbria, is the name of the peninsula that juts out in Northern Europe toward the rest of Scandinavia, forming the mainland part of Denmark. It has the North Sea to its west, Kattegat and Skagerrak to its north, the Baltic Sea to its east, and the Danish–German...
were ice-free, and a large part of what is today the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
was dry land connecting Jutland with Britain. It is also in Denmark that the only Scandinavian ice-age animals older than 13,000 BC are found. In the period following the last interglacial
Interglacial
An Interglacial period is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age...
before the current one (Eemian Stage), the coast of Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
was also ice-free.
The Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, with its unique brackish water
Brackish water
Brackish water is water that has more salinity than fresh water, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing of seawater with fresh water, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root "brak," meaning "salty"...
, is a result of meltwater from the Weichsel glaciation combining with saltwater from the North Sea when the straits between Sweden and Denmark opened. Initially, when the ice began melting about 10,300 ybp
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
, seawater filled the isostatically depressed
Isostasy
Isostasy is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. This concept is invoked to explain how different topographic...
area, a temporary marine incursion
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
that geologists dub the Yoldia Sea
Yoldia Sea
Yoldia Sea is a name given by geologists to a variable brackish-water stage in the Baltic Sea basin that prevailed after the Baltic ice lake was drained to sea level during the Weichsel glaciation...
. Then, as post-glacial isostatic rebound
Post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostasy...
lifted the region about 9500 ybp, the deepest basin of the Baltic became a freshwater lake, in palaeological contexts referred to as Ancylus Lake
Ancylus Lake
Ancylus lake is a name given by geologists to the body of fresh water that replaced the Yoldia Sea after the latter had been severed from its saline intake across central Sweden by the isostatic rise of south Scandinavian landforms. The dates are approximately 9500-8000 BP calibrated, during the...
, which is identifiable in the freshwater fauna found in sediment cores. The lake was filled by glacial runoff, but as worldwide sea level continued rising, saltwater again breached the sill about 8000 ybp, forming a marine Littorina Sea
Littorina Sea
Littorina Sea is a geological brackish-water stage of the Baltic Sea, which existed around 7500–4000 BP and followed the Mastogloia Sea, transitional stage of the Ancylus Lake...
which was followed by another freshwater phase before the present brackish marine system was established. "At its present state of development, the marine life of the Baltic Sea is less than about 4000 years old," Drs. Thulin and Andrushaitis remarked when reviewing these sequences in 2003.
Overlying ice had exerted pressure on the Earth's surface. As a result of melting ice, the land has continued to rise yearly in Scandinavia, mostly in northern Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
and Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
where the land is rising at a rate of as much as 8–9 mm per year, or 1 meter in 100 years. This is important for archaeologists since a site that was coastal in the Nordic Stone Age
Nordic Stone Age
The Nordic Stone Age refers to the Stone Age of Scandinavia.-Late Upper Paleolithic:As the ice receded, reindeer grazed on the plains of Denmark and southernmost Sweden, while along the coast of western Sweden, marine resources were exploited...
now is inland and can be dated by its relative distance from the present shore.
Würm glaciation, the Alps
The term WürmWürm
The Würm is a river in Bavaria, Germany, right tributary of the Amper. It drains the overflow from Lake Starnberg and flows swiftly through the villages of Gauting, Krailling, Planegg, Gräfelfing and Lochham as well as part of Munich before joining, near Dachau, the Amper, which soon afterwards...
is derived from a river in the Alpine foreland, approximately marking the maximum glacier advance of this particular glacial period. The Alps have been the area where first systematic scientific research on ice ages has been conducted by Louis Agassiz
Louis Agassiz
Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz was a Swiss paleontologist, glaciologist, geologist and a prominent innovator in the study of the Earth's natural history. He grew up in Switzerland and became a professor of natural history at University of Neuchâtel...
in the beginning of the 19th century. Here the Würm glaciation of the last glacial period was intensively studied. Pollen analysis
Palynology
Palynology is the science that studies contemporary and fossil palynomorphs, including pollen, spores, orbicules, dinoflagellate cysts, acritarchs, chitinozoans and scolecodonts, together with particulate organic matter and kerogen found in sedimentary rocks and sediments...
, the statistical analyses of microfossilized plant pollens found in geological deposits, has chronicled the dramatic changes in the European environment during the Würm glaciation. During the height of Würm glaciation, ca 24,000–10,000 ybp, most of western and central Europe and Eurasia was open steppe-tundra, while the Alps presented solid ice field
Ice field
An ice field is an area less than 50,000 km² of ice often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation. It is an extensive area of interconnected valley glaciers from which the higher peaks rise as nunataks...
s and montane glaciers. Scandinavia and much of Britain were under ice.
During the Würm, the Rhône Glacier
Rhône Glacier
The Rhone Glacier, or sometimes Rhône Glacier is a glacier in the Swiss Alps and the source of the Rhone River and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva in the far eastern end of the Swiss canton of Valais...
covered the whole western Swiss plateau, reaching today's regions of Solothurn and Aarau. In the region of Bern it merged with the Aar glacier. The Rhine Glacier
Rhine Glacier
The Rhine Glacier was a glacier during the Last glacial period which is responsible for the formation of the Lake Constance....
is currently the subject of the most detailed studies. Glaciers of the Reuss and the Limmat advanced sometimes as far as the Jura. Montane and piedmont glaciers formed the land by grinding away virtually all traces of the older Günz and Mindel glaciation, by depositing base moraines and terminal moraines of different retraction phases and loess
Loess
Loess is an aeolian sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown silt, typically in the 20–50 micrometre size range, twenty percent or less clay and the balance equal parts sand and silt that are loosely cemented by calcium carbonate...
deposits, and by the pro-glacial rivers' shifting and redepositing gravels. Beneath the surface, they had profound and lasting influence on geothermal heat and the patterns of deep groundwater flow.
Merida glaciation, Venezuelan Andes
The name Mérida Glaciation is proposed to designate the alpine glaciation which affected the central Venezuelan AndesCordillera de Mérida
The Cordillera de Mérida is a series of mountain ranges, or massif, in northwestern Venezuela. The Cordillera de Mérida is a northeastern extension of the Andes Mountains. The ranges run southwest–northeast between the Venezuelan–Colombian border and the Venezuelan coastal range...
; during the Late Pleistocene. Two main moraine levels have been recognized: one between 2600 and 2700 m, and another between 3000 and 3500 m elevation. The snow line during the last glacial advance was lowered approximately 1200 m below the present snow line (3700 m). The glaciated area in the Cordillera de Mérida
Cordillera de Mérida
The Cordillera de Mérida is a series of mountain ranges, or massif, in northwestern Venezuela. The Cordillera de Mérida is a northeastern extension of the Andes Mountains. The ranges run southwest–northeast between the Venezuelan–Colombian border and the Venezuelan coastal range...
was approximately 600 km2; this included the following high areas from southwest to northeast: Páramo de Tamá, Páramo Batallón, Páramo Los Conejos, Páramo Piedras Blancas, and Teta de Niquitao. Approximately 200 km2 of the total glaciated area was in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida
Sierra Nevada de Mérida
The Sierra Nevada de Mérida is the highest mountain range in the largest massif in Venezuela, the Cordillera de Mérida, which in turn is part of the northern extent of the Cordillera de los Andes...
, and of that amount, the largest concentration, 50 km2, was in the areas of Pico Bolívar
Pico Bolívar
Pico Bolívar is the highest mountain in Venezuela, at 4,981 metres. Located in Mérida State, its top is permanently covered with névé snow and three small glaciers. It can be reached only by walking; the Mérida cable car, the highest cable car in the world, only reaches Pico Espejo. From there it...
, Pico Humboldt
Pico Humboldt
Pico Humboldt is Venezuela's second highest peak, at 4,940 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of...
(4,942 m), and Pico Bonpland
Pico Bonpland
Pico Bonpland is Venezuela's third highest peak, at 4,883 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of . The peak with its sister peak Pico Humboldt, and the surrounding páramos are protected by the Sierra Nevada National Park. It shares with the...
(4,893 m). Radiocarbon dating indicates that the moraines are older than 10,000 years B.P., and probably older than 13,000 years B.P. The lower moraine level probably corresponds to the main Wisconsin glacial advance. The upper level probably represents the last glacial advance (Late Wisconsin).
Llanquihue glaciation, southern Andes
The Llanquihue glaciation takes its name from Llanquihue Lake in southern ChileZona Sur
The Zona Sur is one of the five natural regions on which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. Its northern border is formed by the Bío-Bío River, the limit with the Central Chile Zone. By west with the Pacific Ocean, by the east with the Andean mountains and Argentina. Its southern border is...
which is a fan-shaped piedmont
Foothills
Foothills are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills to the adjacent topographically high mountains.-Examples:...
glacial lake
Glacial lake
A glacial lake is a lake with origins in a melted glacier. Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,000 years ago, glaciers began to retreat. A retreating glacier often left behind large deposits of ice in hollows between drumlins or hills. As the ice age ended, these melted to create...
. On the lake's western shores there are large moraine systems of which the innermost belong to the last glacial period. Llanquihue Lake's varve
Varve
A varve is an annual layer of sediment or sedimentary rock.The word 'varve' is derived from the Swedish word varv whose meanings and connotations include 'revolution', 'in layers', and 'circle'. The term first appeared as Hvarfig lera on the first map produced by the Geological Survey of Sweden in...
s are a node point in southern Chile's varve geochronology
Geochronology
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments, within a certain degree of uncertainty inherent to the method used. A variety of dating methods are used by geologists to achieve this, and schemes of classification and terminology have been proposed...
. During the last glacial maximum the Patagonian Ice Sheet
Patagonian Ice Sheet
350px|thumb|right|Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the [[Strait of Magellan]] area during the [[last glacial period]]. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots...
extended over the Andes from about 35°S to Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of a main island Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego divided between Chile and Argentina with an area of , and a group of smaller islands including Cape...
at 55°S. The western part appears to have been very active, with wet basal conditions, while the eastern part was cold based. Palsa
Palsa
thumb|right|300px|A group of well developed palsas as seen from abovePalsas are low, often oval, frost heaves occurring in polar and subpolar climates, which contain permanently frozen ice lenses...
s seems to have developed at least in the unglaciated parts of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan...
. The area west of Llanquihue Lake was ice-free during the LGM
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
, and had sparsely distributed vegetation dominated by Nothofagus
Nothofagus
Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 35 species of trees and shrubs native to the temperate oceanic to tropical Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and Australasia...
. Valdivian temperate rainforest was reduced to scattered remnants in the western side of the Andes.

Antarctica glaciation
During the last glacial period Antarctica was blanketed by a massive ice sheet, much like it is today. The ice covered all land areas and extended into the ocean onto the middle and outer continental shelf. According to ice modelling, ice over central East Antarctica was generally thinner than today.See also
- Glacial history of MinnesotaGlacial history of MinnesotaThe glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had...
- Glacial lake outburst floodGlacial lake outburst floodA glacial lake outburst flood is a type of outburst flood that occurs when the dam containing a glacial lake fails. The dam can consist of glacier ice or a terminal moraine...
- Glacial periodGlacial periodA glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate within an ice age...
- Ice ageIce ageAn ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
- Last Glacial MaximumLast Glacial MaximumThe Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
- Late Glacial Maximum
- Sea level rise
- Timeline of glaciationTimeline of glaciationThere have been five known ice ages in the Earth's history, with the Earth experiencing the Quaternary Ice Age during the present time. Within ice ages, there exist periods of more severe glacial conditions and more temperate referred to as glacial periods and interglacial periods, respectively...
- Valparaiso MoraineValparaiso MoraineThe Valparaiso Moraine is a terminal moraine around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It is a band of high, hilly terrain made up of glacial till and sand that reaches an elevation of near 300 feet above the level of Lake Michigan at its maximum height in Indiana and 17 miles wide at its...
Further reading
- Bowen, D.Q., 1978, Quaternary geology: a stratigraphic framework for multidisciplinary work. Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom. 221 pp. ISBN 978-0-08-020409-3
- Ehlers, J., and P.L. Gibbard, 2004a, Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 2: Part II North America. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0-444-51462-7
- Ehlers, J., and P L. Gibbard, 2004b, Quaternary Glaciations: Extent and Chronology 3: Part III: South America, Asia, Africa, Australia, Antarctica. ISBN 0-444-51593-3
- Gillespie, A.R., S.C. Porter, and B.F. Atwater, 2004, The Quaternary Period in the United States [of America]. Developments in Quaternary Science no. 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 978-0-444-51471-4
- Harris, A.G., E. Tuttle, S.D. Tuttle, 1997, Geology of National Parks: Fifth Edition. Kendall/Hunt Publishing, Iowa. ISBN 0-7872-5353-7
- Matthias KuhleMatthias KuhleMatthias Kuhle is a German geographer and professor at the University of Göttingen. He edits the book series Geography International published by Shaker Verlag.-Education and career:...
, 1988: The Pleistocene Glaciation of Tibet and the Onset of Ice Ages- An Autocycle Hypothesis. In: GeoJournal 17 (4), Tibet and High-Asia I. 581–596. - Mangerud, J., J. Ehlers, and P. Gibbard, 2004, Quaternary Glaciations : Extent and Chronology 1: Part I Europe. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0-444-51462-7
- Sibrava, V., Bowen, D.Q, and Richmond, G.M., 1986, Quaternary Glaciations in the Northern Hemisphere, Quaternary Science Reviews. vol. 5, pp. 1–514.
- Pielou, E.C., 1991. After the Ice Age : The Return of Life to Glaciated North America. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois. ISBN 0-226-66812-6 (paperback 1992)
External links
- National Atlas of the USA: Wisconsin Glaciation in North America: Present state of knowledge
- ncdc.noaa.gov

