
Kamchatka Peninsula
Encyclopedia
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1250 kilometres (776.7 mi) peninsula
in the Russian Far East
, with an area of 472300 km² (182,356 sq mi). It lies between the Pacific Ocean
to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk
to the west. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10500 metres (34,448.8 ft) deep Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
.
The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and Karaginsky Island
constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 402,500 inhabitants are Russians
, but there are also about 8,743 Koryaks
. More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
(198,028 people) and nearby Yelizovo
(41,533).
The Kamchatka peninsula contains the Volcanoes of Kamchatka
, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Kamchatka receives up to 2700 mm (106.3 in) of precipitation per year. The summers are moderately cool, and the winters tend to be rather stormy with rare amounts of lightning.
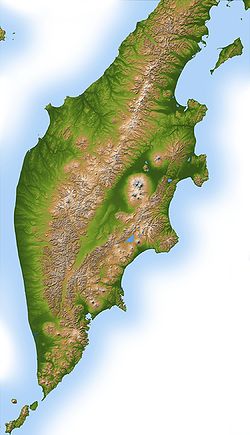 Politically, the peninsula is part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka
Politically, the peninsula is part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka
. The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Avacha Bay
with the capital, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
. North up the Pacific side, the four peninsulas are called Shipunsky Point, Kronotsky Point, Kamchatsky Point and Ozernoy Point. North of Ozernoy is the large Karaginsky Bay and island. Northeast of this off the map is Korfa Bay
with the town of Tilichiki
. On the opposite side is the Shelikhov Gulf.
The spine of the peninsula is the Kamchatka or Central (Sredinny
) Range. Along the southeast coast is the Vostochny or Eastern Range. Between these is the central valley. The Kamchatka River
starts northwest of Avacha
and flows north down the central valley, turning east near Klyuchi to enter the Pacific south of Kamchatsky Point at Ust-Kamchatsk
. In the nineteenth century a trail led west from near Klychi over the mountains to Tegil river and town which was the main trading post on the west coast. North of Tegil is Koryak okrug. South of the Tegil is the Icha River. Just south of the headwaters of the Kamchatka, the Bistraya River curves southwest to enter the Sea of Okhotsk at Bolsheretsk, which was once a port connecting the peninsula to Okhotsk
. South of the Bistraya is the Golygina River
.
There is a road from Bolsheretsk to Petropavlovsk and another from this road up the central valley (with a bus service) to Ust-Kamchatsk
. The northern end of the road is of poorer quality. Apart from the two roads, transport is by small plane, helicopter, four-wheel drive truck and army truck.
The obvious circular area in the central valley is the Klyuchevskaya Sopka
, an isolated volcanic group southeast of the curve of the Kamchatka River. West of Kronotsky Point is the Kronotsky
Biosphere Reserve with the Valley of Geysers
. At the southern tip is the Southern Kamchatka Wildlife Refuge with Kurile Lake
. There are several other protected areas: Palana
is located in the Koryak area on the northwest coast.
, cold arctic winds from Siberia
combined with the cold Oyashio sea current result in the peninsula being covered in snow from October to late May. Under the Köppen climate classification
Kamchatka generally has a subarctic climate
(Dfc) but higher and more northerly areas have a polar climate (ET). Kamchatka is much wetter and milder than eastern Siberia, and is essentially transitional from the hypercontinental climate of Siberia and Manchuria
to the rain-drenched subpolar oceanic climate of the Aleutian Islands.
There is considerable variation, however, between the rain-drenched and heavily glaciated east coast and the drier and more continental interior valley. In the heavily glaciated Kronotsky Peninsula where maritime influences are most pronounced annual precipitation can reach as high as 2500 millimetres (98.4 in), whilst the southeast coast south of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky generally receives around 1350 millimetres (53.1 in) of rainfall equivalent per year. Considerable local variations exist: southern parts of the Patropavlovsk-Kamchatsky metropolitan area can receive as much as 430 millimetres (17 in) more than the northern part of the city. Temperatures here are very mild, with summer maxima no higher than 15 °C (59 °F) and winter lows around −8 C, whilst diurnal temperature ranges are seldom more than 5˚C (9˚F) due to persistent fog
on exposed parts of the coast. South of 57˚N there is no permafrost
due to the relatively mild winters and heavy snow cover, whilst northward discontinuous permafrost prevails. The west coastal plain has a similar climate, though rather drier with precipitation ranging from 880 millimetres (34.6 in) in the south to as little as 430 millimetres (16.9 in) in the north, where winter temperatures become considerably colder at around -20 C.
In the interior valley of the Kamchatka River
, represented by Klyuchi, precipitation is much lower at around 450 to 650 mm (17.7 to 25.6 in) and temperatures are significantly more continental, reaching 19 °C (66.2 °F) on a typical summer day and during extreme cold winter spells falling as low as -41 C. Sporadic permafrost prevails over the lower part of this valley, but it becomes more widespread at higher altitudes and glaciers or continuous permafrost prevail north of 55˚N.
The summer months are popular with tourists when maximum temperatures range from 15 to 20 °C (59 to 68 F), but a growing trend in winter sports keeps tourism pulsing year-round. The volcanoes and glaciers play a role in forming of Kamchatka's climate, and hot springs have kept alive dozens of species decimated during the last ice age.
.jpg)
 When Russian explorer Ivan Moskvitin
When Russian explorer Ivan Moskvitin
reached the Sea of Okhotsk
in 1639, further exploration was impeded by the lack of skills and equipment to build sea-going ships and by the harsh land to the northeast inhabited by the warlike Koryak
people. Kamchatka was, consequently, entered from the north. In 1651, after having assisted in the foundation of the Anadyrsk
ostrog
, explorer Mikhail Stadukhin
went south and followed the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk from Penzhina Bay to Okhotsk
. From about 1667 there were reports of a Kamchatka River to the south. Some time before 1700 a group of Russians
were stranded and died on Kamchatka.
In 1695 explorer Vladimir Atlasov
was made commander of Anadyrsk. In 1696 he sent the Cossack Luka Morozko south. Morozko got as far as the Tigil River
and returned with reports and some mysterious writings, probably Japanese. In 1697-1699 Atlasov explored nearly the whole of the peninsula. He built an ostrog at Verkhny-Kamchatsk and rescued or captured a Japanese castaway
and went to Moscow to report. In 1699 the Russians at Verkhny-Kamchatsk were killed by the Koryaks on their way back to Anadyrsk. The 1700 punitive expedition destroyed a Koryak village and founded Nizhne-Kamchatsk on the lower river. Bolskeretsk was founded in 1703. From about 1705 there was a breakdown of order. There were numerous mutinies and native wars all over the peninsula and north to the Koryak country of the Penzhina River and Olyutorsky Gulf
. Several people were sent out to restore order, including Atlasov who was murdered in 1711. Some degree of order was restored by Vasily Merlin in 1733-39. There was no significant resistance after 1756. A major smallpox epidemic that hit in 1768-69 quickly decimated the native population; the roughly 2,500 Itelmens
present in 1773 were reduced to 1,900 in 1820, from an original population of 12–25,000. Those who survived adopted Russian customs and there was a great deal of intermarriage so that "Kamchadal", the original Russian name for the Itelmens, came to mean any Russian or part-Russian born on the peninsula.
In 1713 Peter the Great sent shipbuilders to Okhotsk. A fifty-four-foot boat was built and sailed to the Tegil River in June 1716. This one week journey, later shifted to Okhotsk-Bolseretsk, became the standard route to Kamchatka. In 1720 Kamchatka and the Kurils were mapped by Ivan Yevreinov
. Danish explorer Vitus Bering
left Nezhe-Kamchatsk for his first voyage in 1728 and, as part of his second voyage, he founded Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
in 1740.
Vitus Bering's Second Kamchatka Expedition, in the service of the Russian Navy, began the final "opening" of Kamchatka, helped by the fact that the government began to use the area to exile people. In 1755, Stepan Krasheninnikov
published the first detailed description of the peninsula, An Account of the Land of Kamchatka. The Russian government encouraged the commercial activities of the Russian-American Company
by granting land to newcomers on the peninsula. By 1812, the indigenous
population had fallen to less than 3,200, while the Russian population had risen to 2,500.
In 1854, the French
and British
, who were battling Russian forces on the Crimean Peninsula
, attacked Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
. During the Siege of Petropavlovsk
, 988 men with a mere 68 guns managed to defend the outpost against 6 ships with 206 guns and 2,540 French and British soldiers. Despite the heroic defense, Petropavlovsk was abandoned as a strategic liability after the Anglo-French forces withdrew. The next year when a second enemy force came to attack the port, they found it deserted. Frustrated, the ships bombarded the city and withdrew.
The next fifty years were lean ones for Kamchatka. The naval port was moved to Ust-Amur and in 1867 Alaska
was sold to the United States
, making Petropavlovsk obsolete as a transit point for traders and explorers on their way to the American territories. In 1860, a Primorsky (Maritime) Region was established and Kamchatka was placed under its jurisdiction. In 1875, the Kuril Islands
were ceded to Japan
in return for Russian sovereignty over Sakhalin
island. The Russian population of Kamchatka stayed around 2,500 until the turn of the century, while the native population increased to 5,000.
World War II
hardly affected Kamchatka except for its service as a launch site for the invasion of the Kurils in late 1945. After the war, Kamchatka was declared a military zone. Kamchatka remained closed
to Russians until 1989 and to foreigners until 1990.
The Kamchatka River
and the surrounding central side valley are flanked by large volcanic belt
s containing around 160 volcano
es, 29 of them still active. The peninsula has a high density of volcanoes and associated volcanic phenomena, with 19 active volcanoes being included in the six UNESCO
World Heritage List sites in the Volcanoes of Kamchatka group, most of them on the Kamchatka Peninsula.
The highest volcano is Klyuchevskaya Sopka
(4,750 m or 15,584 ft), the largest active volcano in the Northern Hemisphere, while the most striking is Kronotsky
, whose perfect cone was said by celebrated volcanologists Robert and Barbara Decker to be a prime candidate for the world's most beautiful volcano. Somewhat more accessible are the three volcanoes visible from Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
: Koryaksky
, Avachinsky, and Kozelsky. In the center of Kamchatka is Eurasia's world famous Geyser Valley which was partly destroyed by a massive mudslide in June 2007.
Owing to the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
, deep-focus seismic events and tsunamis are fairly common. A pair of megathrust earthquake
s occurred off the coast
on October 16, 1737, and on November 4, 1952, in the magnitude of ~9.3 and 8.2 respectively. A chain of more shallow earthquakes
were recorded as recently as April 2006.
These volcanic features are the site of occurrence of certain extremophile
micro-organisms, that are capable of surviving in extremely hot environments.
 Kamchatka boasts diverse and abundant wildlife. This is due to climates ranging from temperate to subarctic, diverse topography and geography, many free-flowing rivers, proximity to highly productive waters from the northwestern Pacific Ocean
Kamchatka boasts diverse and abundant wildlife. This is due to climates ranging from temperate to subarctic, diverse topography and geography, many free-flowing rivers, proximity to highly productive waters from the northwestern Pacific Ocean
and the Bering
and Okhotsk Seas, and to the low human density and minimal development. It also boasts the southernmost expanse of Arctic tundra
in the world. Commercial exploitation of marine resources and a history of fur trapping has taken its toll on several species.
Among terrestrial mammals, Kamchatka is best known for the abundance and size of its brown bear
s. In the Kronotsky Nature Preserve there are estimated to be three to four bears per 100 square kilometres. Other fauna of note include carnivores such as wolf, arctic
and other fox, lynx
, wolverine
, sable
, several species of weasel
, ermine
and river otter
; several large ungulates, such as bighorn sheep
, reindeer
, and moose
; and rodents/leporids, including hares, marmot
, lemming
and several species of squirrel
.
The peninsula is the breeding ground for Steller's sea eagle
, one of the largest eagle species, along with the golden eagle
and gyr falcon.
Kamchatka contains probably the world's greatest diversity of salmon
id fish, including all six species of anadromous Pacific salmon (chinook
, chum
, coho
, seema
, pink
, and sockeye
). Biologists estimate that a sixth to a quarter of all Pacific salmon originates in Kamchatka. Kuril Lake is recognized as the biggest spawning-ground for sockeye in Eurasia. In response to pressure from poaching and to worldwide decreases in salmon stocks, some 24000 square kilometres (9,266.5 sq mi) along nine of the more productive salmon rivers are in the process of being set aside as a nature preserve. Stickleback species, particularly Gasterosteus aculeatus and Pungitius pungitius, also occur in many coastal drainages, and are likely present in freshwater as well.
Cetaceans that frequent the highly productive waters of the northwestern Pacific and the Okhotsk Sea include: orca
s, Dall
's and harbor porpoises, humpback whales, sperm whale
s and fin whale
s. Less frequently, gray whale
s (from the Eastern population), the critically endangered North Pacific Right Whale
and Bowhead Whale
, beaked whale
s and minke whale
s are encountered. Blue whale are known to feed off of the southeastern shelf in summer. Among pinniped
s, Steller's sea lion
s, northern fur seals
, spotted seals
and harbor seal
s are abundant along much of the peninsula. Further north, walrus
es and bearded seal
s can be encountered on the Pacific side, and ribbon seal
s reproduce on the ice of Karaginsky Bay. Sea otters are concentrated primarily on the southern end of the peninsula.
Seabirds include northern fulmar
s, thick and thin-billed murres, kittiwakes, tufted and horned puffins, red-faced, pelagic and other cormorants, and many other species. Typical of the northern seas, the marine fauna is likewise rich. Of commercial importance are Kamchatka crab (king crab), scallop
, squid
, pollock
, cod
, herring
, halibut
and several species of flatfish
.
Peninsula
A peninsula is a piece of land that is bordered by water on three sides but connected to mainland. In many Germanic and Celtic languages and also in Baltic, Slavic and Hungarian, peninsulas are called "half-islands"....
in the Russian Far East
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
, with an area of 472300 km² (182,356 sq mi). It lies between the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and...
to the west. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10500 metres (34,448.8 ft) deep Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench or Kuril Trench is an oceanic trench in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido...
.
The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and Karaginsky Island
Karaginsky Island
Karaginsky Island or Karaginskiy Island is an island in the Karaginsky Gulf of the Bering Sea. The 40 km wide strait between the Kamchatka Peninsula and this island is called Litke Strait....
constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 402,500 inhabitants are Russians
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
, but there are also about 8,743 Koryaks
Koryaks
Koryaks are an indigenous people of Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East, who inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea to the south of the Anadyr basin and the country to the immediate north of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the southernmost limit of their range being Tigilsk. They are akin to the...
. More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy...
(198,028 people) and nearby Yelizovo
Yelizovo
Yelizovo is a town in Kamchatka Krai, Russia, located on the Avacha River northwest of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Population: Founded in 1848 as the village of Stary Ostrog , it was renamed Zavoyko in 1897, after the Russian admiral Vasily Zavoyko who led the defense of Petropavlovsk in 1854....
(41,533).
The Kamchatka peninsula contains the Volcanoes of Kamchatka
Volcanoes of Kamchatka
The Volcanoes of Kamchatka are a large group of volcanoes situated on the Kamchatka peninsula. The Kamchatka River and the surrounding central side valley are flanked by large volcanic belts containing around 160 volcanoes, 29 of them still active...
, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Kamchatka receives up to 2700 mm (106.3 in) of precipitation per year. The summers are moderately cool, and the winters tend to be rather stormy with rare amounts of lightning.
Geography

Cape Lopatka
Cape Lopatka is the southernmost point of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia, with the rural locality of Semenovka at its southernmost point. Cape Lopatka lies about north of Shumshu, the northernmost island of the Kuril Islands...
. The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Avacha Bay
Avacha Bay
Avacha Bay is a Pacific Ocean bay on the southeastern coast of Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It is long and wide , with a maximum depth of 26 m....
with the capital, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy...
. North up the Pacific side, the four peninsulas are called Shipunsky Point, Kronotsky Point, Kamchatsky Point and Ozernoy Point. North of Ozernoy is the large Karaginsky Bay and island. Northeast of this off the map is Korfa Bay
Korfa Bay
The Korfa Bay is a bay on the Kamchatka coast of the Bering Sea in Russia. It is approximately triangular being about 70 km wide at the mouth and extending inland about 75 km. On the west side, the Il'pinsky Peninsula separates it from Anapka Bay which forms the north end of Karaginsky...
with the town of Tilichiki
Tilichiki
Tilichiki is a rural locality and the administrative center of Olyutorsky District of Koryak Okrug of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It is located on the Korfa Bay of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Tilichiki Airport is located to the south of it, and it is also connected by ferry service to the port village...
. On the opposite side is the Shelikhov Gulf.
The spine of the peninsula is the Kamchatka or Central (Sredinny
Sredinny Range
Sredinny Range is a mountain range in Kamchatka, Russia, at . It stretches from northeast to southwest along the center of the peninsula and is made up of volcanoes, mostly shield volcanoes and stratovolcanoes. The highest peak of the range is Ichinsky, a stratovolcano some ) high...
) Range. Along the southeast coast is the Vostochny or Eastern Range. Between these is the central valley. The Kamchatka River
Kamchatka River
The Kamchatka River runs eastward for through Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East towards the Pacific Ocean. The river is rich with salmon, millions of which spawn yearly and which once supported the settlements of the native Itelmen....
starts northwest of Avacha
Avacha
Avacha may refer to:*Avacha Bay, Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia*Avacha River, Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia*Avacha Volcano, Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia, also called Avachinsky...
and flows north down the central valley, turning east near Klyuchi to enter the Pacific south of Kamchatsky Point at Ust-Kamchatsk
Ust-Kamchatsk
Ust-Kamchatsk is a settlement in Kamchatka Krai, Russia, located on the eastern shore of the Kamchatka Peninsula at the mouth of the Kamchatka River some away from the Klyuchevskaya Sopka volcano and from Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Population: 4,400 ; Ust-Kamchatsk was founded in 1731 as a...
. In the nineteenth century a trail led west from near Klychi over the mountains to Tegil river and town which was the main trading post on the west coast. North of Tegil is Koryak okrug. South of the Tegil is the Icha River. Just south of the headwaters of the Kamchatka, the Bistraya River curves southwest to enter the Sea of Okhotsk at Bolsheretsk, which was once a port connecting the peninsula to Okhotsk
Okhotsk
Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;...
. South of the Bistraya is the Golygina River
Golygina River
The Golygina River is a river on the southwest coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. A Russian expedition under Vladimir Atlasov first reached it in the last decade of the seventeenth century....
.
There is a road from Bolsheretsk to Petropavlovsk and another from this road up the central valley (with a bus service) to Ust-Kamchatsk
Ust-Kamchatsk
Ust-Kamchatsk is a settlement in Kamchatka Krai, Russia, located on the eastern shore of the Kamchatka Peninsula at the mouth of the Kamchatka River some away from the Klyuchevskaya Sopka volcano and from Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Population: 4,400 ; Ust-Kamchatsk was founded in 1731 as a...
. The northern end of the road is of poorer quality. Apart from the two roads, transport is by small plane, helicopter, four-wheel drive truck and army truck.
The obvious circular area in the central valley is the Klyuchevskaya Sopka
Klyuchevskaya Sopka
Klyuchevskaya Sopka is a stratovolcano which is the highest mountain on the Kamchatka Peninsula of Russia and the highest active volcano of Eurasia. Its steep, symmetrical cone towers about from the Bering Sea...
, an isolated volcanic group southeast of the curve of the Kamchatka River. West of Kronotsky Point is the Kronotsky
Kronotsky
Kronotsky is a major stratovolcano of the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It has a particularly symmetrical conical shape, comparable to Mount Fuji in Japan and to Mayon Volcano in the Philippines. The summit crater is plugged by a volcanic neck, and the summit itself is ice capped. It exhibits the...
Biosphere Reserve with the Valley of Geysers
Valley of Geysers
The Valley of Geysers is a geyser field in Russia, and has the second largest concentration of geysers in the world. This 6 km long basin with approximately ninety geysers and many hot springs is situated on the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East, predominantly on the left bank of...
. At the southern tip is the Southern Kamchatka Wildlife Refuge with Kurile Lake
Kurile Lake
Kurile Lake is a large caldera containing a crater lake located at the southern tip of Kamchatka Peninsula, within the Southern Kamchatka Wildlife Refuge in Russia....
. There are several other protected areas: Palana
Palana
Palana is an urban locality and the administrative center of Koryak Okrug of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It is located on the west coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula on the right bank of the Palana River, within from the Sea of Okhotsk. Population: Administratively, Palana is subordinated to Tigilsky...
is located in the Koryak area on the northwest coast.
Climate
Although Kamchatka lies at similar latitudes to Great BritainGreat Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, cold arctic winds from Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
combined with the cold Oyashio sea current result in the peninsula being covered in snow from October to late May. Under the Köppen climate classification
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
Kamchatka generally has a subarctic climate
Subarctic climate
The subarctic climate is a climate characterized by long, usually very cold winters, and short, cool to mild summers. It is found on large landmasses, away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N poleward of the humid continental climates...
(Dfc) but higher and more northerly areas have a polar climate (ET). Kamchatka is much wetter and milder than eastern Siberia, and is essentially transitional from the hypercontinental climate of Siberia and Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
to the rain-drenched subpolar oceanic climate of the Aleutian Islands.
There is considerable variation, however, between the rain-drenched and heavily glaciated east coast and the drier and more continental interior valley. In the heavily glaciated Kronotsky Peninsula where maritime influences are most pronounced annual precipitation can reach as high as 2500 millimetres (98.4 in), whilst the southeast coast south of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky generally receives around 1350 millimetres (53.1 in) of rainfall equivalent per year. Considerable local variations exist: southern parts of the Patropavlovsk-Kamchatsky metropolitan area can receive as much as 430 millimetres (17 in) more than the northern part of the city. Temperatures here are very mild, with summer maxima no higher than 15 °C (59 °F) and winter lows around −8 C, whilst diurnal temperature ranges are seldom more than 5˚C (9˚F) due to persistent fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
on exposed parts of the coast. South of 57˚N there is no permafrost
Permafrost
In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of...
due to the relatively mild winters and heavy snow cover, whilst northward discontinuous permafrost prevails. The west coastal plain has a similar climate, though rather drier with precipitation ranging from 880 millimetres (34.6 in) in the south to as little as 430 millimetres (16.9 in) in the north, where winter temperatures become considerably colder at around -20 C.
In the interior valley of the Kamchatka River
Kamchatka River
The Kamchatka River runs eastward for through Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East towards the Pacific Ocean. The river is rich with salmon, millions of which spawn yearly and which once supported the settlements of the native Itelmen....
, represented by Klyuchi, precipitation is much lower at around 450 to 650 mm (17.7 to 25.6 in) and temperatures are significantly more continental, reaching 19 °C (66.2 °F) on a typical summer day and during extreme cold winter spells falling as low as -41 C. Sporadic permafrost prevails over the lower part of this valley, but it becomes more widespread at higher altitudes and glaciers or continuous permafrost prevail north of 55˚N.
The summer months are popular with tourists when maximum temperatures range from 15 to 20 °C (59 to 68 F), but a growing trend in winter sports keeps tourism pulsing year-round. The volcanoes and glaciers play a role in forming of Kamchatka's climate, and hot springs have kept alive dozens of species decimated during the last ice age.
History and exploration
.jpg)

Ivan Moskvitin
Ivan Yuryevich Moskvitin was a Russian explorer, presumably a native of Moscow, who led a Russian reconnaissance party to the Pacific Ocean, becoming the first Russian to reach the Sea of Okhotsk....
reached the Sea of Okhotsk
Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and...
in 1639, further exploration was impeded by the lack of skills and equipment to build sea-going ships and by the harsh land to the northeast inhabited by the warlike Koryak
Koryak
Koryak may refer to:*Koryak Autonomous Okrug, a federal subject of Russia*Koryaks, a people of northeastern Siberia*Koryak language, language of the Koryaks*Koryak, the illegitimate son of Aquaman, a fictional character in DC Comics...
people. Kamchatka was, consequently, entered from the north. In 1651, after having assisted in the foundation of the Anadyrsk
Anadyrsk
thumb|Anadyrsk was on the east-west part of the Anadyr River at the point where it swings northAnadyrsk was an important Russian ostrog in far northeastern Siberia from 1649 to 1764...
ostrog
Ostrog (fortress)
Ostrog was a Russian term for a small fort, typically wooden and often non-permanently manned. Ostrogs were encircled by 4-6 metres high palisade walls made from sharpened trunks. The name derives from the Russian word строгать , "to shave the wood". Ostrogs were smaller and exclusively military...
, explorer Mikhail Stadukhin
Mikhail Stadukhin
Mikhail Vasilyevich Stadukhin was a Russian explorer of far northeast Siberia, one of the first to reach the Kolyma, Anadyr, Penzhina and Gizhiga Rivers and the northern Sea of Okhotsk. He was a Pomor, probably born in the village of Pinega, and the nephew of a Moscow merchant...
went south and followed the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk from Penzhina Bay to Okhotsk
Okhotsk
Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;...
. From about 1667 there were reports of a Kamchatka River to the south. Some time before 1700 a group of Russians
Fedot Alekseyev Popov
Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov...
were stranded and died on Kamchatka.
In 1695 explorer Vladimir Atlasov
Vladimir Atlasov
Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov or Otlasov was a Siberian Cossack who was the first Russian to explore the Kamchatka Peninsula. Atlasov Island, an uninhabited volcanic island off the southern tip of Kamchatka, is named after him....
was made commander of Anadyrsk. In 1696 he sent the Cossack Luka Morozko south. Morozko got as far as the Tigil River
Tigil River
The Tigil River is a river on the western side of the Kamchatka Peninsula. The Cossack Luka Morozko was the first European to reach it in 1696....
and returned with reports and some mysterious writings, probably Japanese. In 1697-1699 Atlasov explored nearly the whole of the peninsula. He built an ostrog at Verkhny-Kamchatsk and rescued or captured a Japanese castaway
Dembei
Dembei was a Japanese castaway who, through Vladimir Atlasov, provided Russia with some of its first knowledge of Japan. He was a fisherman who, along with a number of others, had been caught in a storm; they found their way to Kamchatka, where Dembei was found by Atlasov in 1701 or 1702. Despite...
and went to Moscow to report. In 1699 the Russians at Verkhny-Kamchatsk were killed by the Koryaks on their way back to Anadyrsk. The 1700 punitive expedition destroyed a Koryak village and founded Nizhne-Kamchatsk on the lower river. Bolskeretsk was founded in 1703. From about 1705 there was a breakdown of order. There were numerous mutinies and native wars all over the peninsula and north to the Koryak country of the Penzhina River and Olyutorsky Gulf
Olyutorsky Gulf
The Olyutorsky Bay is a gulf or bay of the Bering Sea in the northern part of Kamchatka Krai, Russia.It is bounded on the west by the Govena Peninsula which separates it from Korfa Bay and on the east by the Olyutorsky Peninsula. It extends roughly 83 km inland and is 228 km at its...
. Several people were sent out to restore order, including Atlasov who was murdered in 1711. Some degree of order was restored by Vasily Merlin in 1733-39. There was no significant resistance after 1756. A major smallpox epidemic that hit in 1768-69 quickly decimated the native population; the roughly 2,500 Itelmens
Itelmens
The Itelmen, sometimes known as Kamchadal, are an ethnic group who are the original inhabitants living on the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The Itelmen language is distantly related to Chukchi and Koryak, forming the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family, but it is now virtually extinct, the vast...
present in 1773 were reduced to 1,900 in 1820, from an original population of 12–25,000. Those who survived adopted Russian customs and there was a great deal of intermarriage so that "Kamchadal", the original Russian name for the Itelmens, came to mean any Russian or part-Russian born on the peninsula.
In 1713 Peter the Great sent shipbuilders to Okhotsk. A fifty-four-foot boat was built and sailed to the Tegil River in June 1716. This one week journey, later shifted to Okhotsk-Bolseretsk, became the standard route to Kamchatka. In 1720 Kamchatka and the Kurils were mapped by Ivan Yevreinov
Ivan Yevreinov
Ivan Mikhaylovich Yevreinov was a Russian geodesist and explorer.Ivan Yevreinov was born in Poland, then brought to Russia and baptized into Orthodox Christianity....
. Danish explorer Vitus Bering
Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands...
left Nezhe-Kamchatsk for his first voyage in 1728 and, as part of his second voyage, he founded Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy...
in 1740.
Vitus Bering's Second Kamchatka Expedition, in the service of the Russian Navy, began the final "opening" of Kamchatka, helped by the fact that the government began to use the area to exile people. In 1755, Stepan Krasheninnikov
Stepan Krasheninnikov
Stepan Petrovich Krasheninnikov was a Russian explorer of Siberia, naturalist and geographer who gave the first full description of Kamchatka in the early 18th century. He was elected to the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1745...
published the first detailed description of the peninsula, An Account of the Land of Kamchatka. The Russian government encouraged the commercial activities of the Russian-American Company
Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)...
by granting land to newcomers on the peninsula. By 1812, the indigenous
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
population had fallen to less than 3,200, while the Russian population had risen to 2,500.
In 1854, the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, who were battling Russian forces on the Crimean Peninsula
Crimean War
The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining...
, attacked Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy...
. During the Siege of Petropavlovsk
Siege of Petropavlovsk
The Siege of Petropavlovsk was the main operation on the Pacific Theatre of the Crimean War. The Russian casualties are estimated at 100 soldiers; the Allies lost five times as many....
, 988 men with a mere 68 guns managed to defend the outpost against 6 ships with 206 guns and 2,540 French and British soldiers. Despite the heroic defense, Petropavlovsk was abandoned as a strategic liability after the Anglo-French forces withdrew. The next year when a second enemy force came to attack the port, they found it deserted. Frustrated, the ships bombarded the city and withdrew.
The next fifty years were lean ones for Kamchatka. The naval port was moved to Ust-Amur and in 1867 Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
was sold to the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, making Petropavlovsk obsolete as a transit point for traders and explorers on their way to the American territories. In 1860, a Primorsky (Maritime) Region was established and Kamchatka was placed under its jurisdiction. In 1875, the Kuril Islands
Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater...
were ceded to Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
in return for Russian sovereignty over Sakhalin
Sakhalin
Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast...
island. The Russian population of Kamchatka stayed around 2,500 until the turn of the century, while the native population increased to 5,000.
World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
hardly affected Kamchatka except for its service as a launch site for the invasion of the Kurils in late 1945. After the war, Kamchatka was declared a military zone. Kamchatka remained closed
Closed city
A closed city or closed town is a settlement with travel and residency restrictions in the Soviet Union and some of its successor countries. In modern Russia, such places are officially known as "closed administrative-territorial formations" ....
to Russians until 1989 and to foreigners until 1990.
Volcanoes
List of volcanoes in Russia has a list of most Kamchatka volcanoes with links.The Kamchatka River
Kamchatka River
The Kamchatka River runs eastward for through Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East towards the Pacific Ocean. The river is rich with salmon, millions of which spawn yearly and which once supported the settlements of the native Itelmen....
and the surrounding central side valley are flanked by large volcanic belt
Volcanic belt
A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature where magma is created by partial melting of solid material in the Earth's crust and upper mantle....
s containing around 160 volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es, 29 of them still active. The peninsula has a high density of volcanoes and associated volcanic phenomena, with 19 active volcanoes being included in the six UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
World Heritage List sites in the Volcanoes of Kamchatka group, most of them on the Kamchatka Peninsula.
The highest volcano is Klyuchevskaya Sopka
Klyuchevskaya Sopka
Klyuchevskaya Sopka is a stratovolcano which is the highest mountain on the Kamchatka Peninsula of Russia and the highest active volcano of Eurasia. Its steep, symmetrical cone towers about from the Bering Sea...
(4,750 m or 15,584 ft), the largest active volcano in the Northern Hemisphere, while the most striking is Kronotsky
Kronotsky
Kronotsky is a major stratovolcano of the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It has a particularly symmetrical conical shape, comparable to Mount Fuji in Japan and to Mayon Volcano in the Philippines. The summit crater is plugged by a volcanic neck, and the summit itself is ice capped. It exhibits the...
, whose perfect cone was said by celebrated volcanologists Robert and Barbara Decker to be a prime candidate for the world's most beautiful volcano. Somewhat more accessible are the three volcanoes visible from Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy...
: Koryaksky
Koryaksky
Koryaksky or Koryakskaya Sopka is a volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula in the far east of Russia. It lies within sight of Kamchatka Krai's administrative center, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky...
, Avachinsky, and Kozelsky. In the center of Kamchatka is Eurasia's world famous Geyser Valley which was partly destroyed by a massive mudslide in June 2007.
Owing to the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
Kuril-Kamchatka Trench
The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench or Kuril Trench is an oceanic trench in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido...
, deep-focus seismic events and tsunamis are fairly common. A pair of megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at subduction zones at destructive plate boundaries , where one tectonic plate is forced under another. Due to the shallow dip of the plate boundary, which causes large sections to get stuck, these earthquakes are among the world's largest, with moment magnitudes ...
s occurred off the coast
Kamchatka earthquakes
3 earthquakes, which occurred off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula in far eastern Russia in 1737, 1923 and 1952, were megathrust earthquakes and caused tsunamis. They occurred where the Pacific Plate subducts under the Okhotsk Plate at the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench. The depth of the trench at the...
on October 16, 1737, and on November 4, 1952, in the magnitude of ~9.3 and 8.2 respectively. A chain of more shallow earthquakes
2006 Kamchatka earthquakes
The 2006 Kamchatka earthquakes were a series of powerful earthquakes that started on April 20, 2006 at 23:25 UTC as a major quake with the magnitude of 7.6 on the Richter scale. The epicenter was located near coast of Koryak Autonomous Okrug at 61.075°N, 167.085°E at an estimated depth of...
were recorded as recently as April 2006.
These volcanic features are the site of occurrence of certain extremophile
Extremophile
An extremophile is an organism that thrives in physically or geochemically extreme conditions that are detrimental to most life on Earth. In contrast, organisms that live in more moderate environments may be termed mesophiles or neutrophiles...
micro-organisms, that are capable of surviving in extremely hot environments.
Terrestrial flora
Kamchatka boasts abundant flora. The variable climate promotes different flora zones where tundra and muskeg are dominant succeeded by grasses, flowering shrubs and forests of pine, birch, alder and willow. The wide variety of plant forms spread throughout the Peninsula promotes just as wide a variation in animal species that feed off them. Although Kamchatka is mostly tundra, deciduous and coniferous trees are abundant and forests can be found throughout the peninsula.Terrestrial and aquatic fauna

Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
and the Bering
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves....
and Okhotsk Seas, and to the low human density and minimal development. It also boasts the southernmost expanse of Arctic tundra
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
in the world. Commercial exploitation of marine resources and a history of fur trapping has taken its toll on several species.
Among terrestrial mammals, Kamchatka is best known for the abundance and size of its brown bear
Brown Bear
The brown bear is a large bear distributed across much of northern Eurasia and North America. It can weigh from and its largest subspecies, the Kodiak Bear, rivals the polar bear as the largest member of the bear family and as the largest land-based predator.There are several recognized...
s. In the Kronotsky Nature Preserve there are estimated to be three to four bears per 100 square kilometres. Other fauna of note include carnivores such as wolf, arctic
Arctic fox
The arctic fox , also known as the white fox, polar fox or snow fox, is a small fox native to Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and is common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. The Greek word alopex, means a fox and Vulpes is the Latin version...
and other fox, lynx
Lynx
A lynx is any of the four Lynx genus species of medium-sized wildcats. The name "lynx" originated in Middle English via Latin from Greek word "λύγξ", derived from the Indo-European root "*leuk-", meaning "light, brightness", in reference to the luminescence of its reflective eyes...
, wolverine
Wolverine
The wolverine, pronounced , Gulo gulo , also referred to as glutton, carcajou, skunk bear, or quickhatch, is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae . It is a stocky and muscular carnivore, more closely resembling a small bear than other mustelids...
, sable
Sable
The sable is a species of marten which inhabits forest environments, primarily in Russia from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, in northern Mongolia and China and on Hokkaidō in Japan. Its range in the wild originally extended through European Russia to Poland and Scandinavia...
, several species of weasel
Weasel
Weasels are mammals forming the genus Mustela of the Mustelidae family. They are small, active predators, long and slender with short legs....
, ermine
Ermine
Ermine has several uses:* A common name for the stoat * The white fur and black tail end of this animal, which is historically worn by and associated with royalty and high officials...
and river otter
European Otter
The European Otter , also known as the Eurasian otter, Eurasian river otter, common otter and Old World otter, is a European and Asian member of the Lutrinae or otter subfamily, and is typical of freshwater otters....
; several large ungulates, such as bighorn sheep
Snow sheep
The snow sheep , or Siberian bighorn sheep, is a species of sheep, which comes from the mountainous areas in the northeast of Siberia. One subspecies, the Putorana Snow Sheep lives isolated from the other forms in the Putoran mountains...
, reindeer
Reindeer
The reindeer , also known as the caribou in North America, is a deer from the Arctic and Subarctic, including both resident and migratory populations. While overall widespread and numerous, some of its subspecies are rare and one has already gone extinct.Reindeer vary considerably in color and size...
, and moose
Moose
The moose or Eurasian elk is the largest extant species in the deer family. Moose are distinguished by the palmate antlers of the males; other members of the family have antlers with a dendritic configuration...
; and rodents/leporids, including hares, marmot
Marmot
The marmots are a genus, Marmota, of squirrels. There are 14 species in this genus.Marmots are generally large ground squirrels. Those most often referred to as marmots tend to live in mountainous areas such as the Alps, northern Apennines, Eurasian steppes, Carpathians, Tatras, and Pyrenees in...
, lemming
Lemming
Lemmings are small rodents, usually found in or near the Arctic, in tundra biomes. They are subniveal animals, and together with voles and muskrats, they make up the subfamily Arvicolinae , which forms part of the largest mammal radiation by far, the superfamily Muroidea, which also includes rats,...
and several species of squirrel
Squirrel
Squirrels belong to a large family of small or medium-sized rodents called the Sciuridae. The family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels, chipmunks, marmots , flying squirrels, and prairie dogs. Squirrels are indigenous to the Americas, Eurasia, and Africa and have been introduced to Australia...
.
The peninsula is the breeding ground for Steller's sea eagle
Steller's Sea Eagle
The Steller's Sea Eagle, Haliaeetus pelagicus, is a large bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It lives in coastal northeastern Asia and mainly preys on fish. It is, on average, the heaviest eagle in the world, at about , but often lags behind the Harpy Eagle and Philippine Eagle in other...
, one of the largest eagle species, along with the golden eagle
Golden Eagle
The Golden Eagle is one of the best known birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. Once widespread across the Holarctic, it has disappeared from many of the more heavily populated areas...
and gyr falcon.
Kamchatka contains probably the world's greatest diversity of salmon
Salmon
Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true...
id fish, including all six species of anadromous Pacific salmon (chinook
Chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, is the largest species in the pacific salmon family. Other commonly used names for the species include King salmon, Quinnat salmon, Spring salmon and Tyee salmon...
, chum
Chum salmon
The chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta, is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It is a Pacific salmon, and may also be known as dog salmon or Keta salmon, and is often marketed under the name Silverbrite salmon...
, coho
Coho salmon
The Coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". It is the state animal of Chiba, Japan.-Description:...
, seema
Seema
Oncorhynchus masou, has three different subspecies. 'Song-eo; 송어' or 'Sancheoneo; 산천어' Oncorhynchus masou masou in Korea, and 'Formosan salmon; Oncorhynchus masou formosanum as in Tiwan, and as Masu salmon Oncorhynchus masou macrostomus in Japan. Pacific Ocean:...
, pink
Pink salmon
Pink salmon or humpback salmon, Oncorhynchus gorbuscha, is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It is the smallest and most abundant of the Pacific salmon.- Appearance :...
, and sockeye
Sockeye salmon
Sockeye salmon , also called red salmon or blueback salmon in the USA, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it...
). Biologists estimate that a sixth to a quarter of all Pacific salmon originates in Kamchatka. Kuril Lake is recognized as the biggest spawning-ground for sockeye in Eurasia. In response to pressure from poaching and to worldwide decreases in salmon stocks, some 24000 square kilometres (9,266.5 sq mi) along nine of the more productive salmon rivers are in the process of being set aside as a nature preserve. Stickleback species, particularly Gasterosteus aculeatus and Pungitius pungitius, also occur in many coastal drainages, and are likely present in freshwater as well.
Cetaceans that frequent the highly productive waters of the northwestern Pacific and the Okhotsk Sea include: orca
Orca
The killer whale , commonly referred to as the orca, and less commonly as the blackfish, is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family. Killer whales are found in all oceans, from the frigid Arctic and Antarctic regions to tropical seas...
s, Dall
Dall's Porpoise
Dall's porpoise is a species of porpoise found on the North Pacific. It came to worldwide attention in the 1970s when it was disclosed for the first time to the public that salmon fishing trawls were killing a lot, thousands of Dall's porpoises and other cetaceans each year by accidentally...
's and harbor porpoises, humpback whales, sperm whale
Sperm Whale
The sperm whale, Physeter macrocephalus, is a marine mammal species, order Cetacea, a toothed whale having the largest brain of any animal. The name comes from the milky-white waxy substance, spermaceti, found in the animal's head. The sperm whale is the only living member of genus Physeter...
s and fin whale
Fin Whale
The fin whale , also called the finback whale, razorback, or common rorqual, is a marine mammal belonging to the suborder of baleen whales. It is the second longest whale and the sixth largest living animal after the blue whale, bowhead whale, and right whales, growing to nearly 27 metres long...
s. Less frequently, gray whale
Gray Whale
The gray whale, Eschrichtius robustus, is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and breeding grounds yearly. It reaches a length of about , a weight of , and lives 50–70 years. The common name of the whale comes from the gray patches and white mottling on its dark skin. Gray whales were...
s (from the Eastern population), the critically endangered North Pacific Right Whale
North Pacific Right Whale
The North Pacific right whale is a very large, robust baleen whale species that is now extremely rare and endangered. The Northeast Pacific subpopulation, that summers in the southeastern Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska, may have no more than 50 animals...
and Bowhead Whale
Bowhead Whale
The bowhead whale is a baleen whale of the right whale family Balaenidae in suborder Mysticeti. A stocky dark-colored whale without a dorsal fin, it can grow to in length. This thick-bodied species can weigh to , second only to the blue whale, although the bowhead's maximum length is less than...
, beaked whale
Beaked whale
Beaked whales are 21 species of toothed whales, members of the family Ziphiidae, are notable for their elongated beaks. Beaked whales are one of the world's most extreme divers. They can dive for long periods—20 to 30 minutes is common, and 85 minute dives have been recorded—and to...
s and minke whale
Minke Whale
Minke whale , or lesser rorqual, is a name given to two species of marine mammal belonging to a clade within the suborder of baleen whales. The minke whale was given its official designation by Lacepède in 1804, who described a dwarf form of Balænoptera acuto-rostrata...
s are encountered. Blue whale are known to feed off of the southeastern shelf in summer. Among pinniped
Pinniped
Pinnipeds or fin-footed mammals are a widely distributed and diverse group of semiaquatic marine mammals comprising the families Odobenidae , Otariidae , and Phocidae .-Overview: Pinnipeds are typically sleek-bodied and barrel-shaped...
s, Steller's sea lion
Steller's Sea Lion
The Steller sea lion also known as the northern sea lion, is a threatened species of sea lion in the northern Pacific. It is the sole member of the genus Eumetopias and the largest of the eared seals . Among pinnipeds, it is inferior in size only to the walrus and the two elephant seals...
s, northern fur seals
Northern Fur Seal
The Northern fur seal is an eared seal found along the north Pacific Ocean, the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk. It is the largest member of the fur seal subfamily and the only species in the genus Callorhinus.-Physical description:Northern fur seals have extreme sexual dimorphism, with males...
, spotted seals
Spotted Seal
The spotted seal , also known as the larga or largha seal, is a member of the family Phocidae, and is considered a "true seal". It inhabits ice floes and waters of the north Pacific Ocean and adjacent seas...
and harbor seal
Harbor Seal
The harbor seal , also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere...
s are abundant along much of the peninsula. Further north, walrus
Walrus
The walrus is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous circumpolar distribution in the Arctic Ocean and sub-Arctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the Odobenidae family and Odobenus genus. It is subdivided into three subspecies: the Atlantic...
es and bearded seal
Bearded Seal
The bearded seal , also called the square flipper seal, is a medium-sized pinniped that is found in and near to the Arctic Ocean. It gets its generic name from two Greek words that refer to its heavy jaw...
s can be encountered on the Pacific side, and ribbon seal
Ribbon Seal
The ribbon seal is a medium-sized pinniped from the true seal family . A seasonally ice-bound species, it is found in the Arctic and Subarctic regions of the North Pacific Ocean, notably in the Bering Sea and Sea of Okhotsk. It is distinguished by its striking coloration, with two wide white...
s reproduce on the ice of Karaginsky Bay. Sea otters are concentrated primarily on the southern end of the peninsula.
Seabirds include northern fulmar
Northern Fulmar
The Northern Fulmar, Fulmarus glacialis, Fulmar, or Arctic Fulmar is a highly abundant sea bird found primarily in subarctic regions of the north Atlantic and north Pacific oceans. Fulmars come in one of two color morphs: a light one which is almost entirely white, and a dark one which is...
s, thick and thin-billed murres, kittiwakes, tufted and horned puffins, red-faced, pelagic and other cormorants, and many other species. Typical of the northern seas, the marine fauna is likewise rich. Of commercial importance are Kamchatka crab (king crab), scallop
Scallop
A scallop is a marine bivalve mollusk of the family Pectinidae. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family, found in all of the world's oceans. Many scallops are highly prized as a food source...
, squid
Squid
Squid are cephalopods of the order Teuthida, which comprises around 300 species. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, a mantle, and arms. Squid, like cuttlefish, have eight arms arranged in pairs and two, usually longer, tentacles...
, pollock
Pollock
Pollock is the common name used for either of the two species of marine fish in the Pollachius genus. Both P. pollachius and P. virens are commonly referred to as pollock. Other names for P...
, cod
Cod
Cod is the common name for genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae, and is also used in the common name for various other fishes. Cod is a popular food with a mild flavor, low fat content and a dense, flaky white flesh. Cod livers are processed to make cod liver oil, an important source of...
, herring
Herring
Herring is an oily fish of the genus Clupea, found in the shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and the North Atlantic oceans, including the Baltic Sea. Three species of Clupea are recognized. The main taxa, the Atlantic herring and the Pacific herring may each be divided into subspecies...
, halibut
Halibut
Halibut is a flatfish, genus Hippoglossus, from the family of the right-eye flounders . Other flatfish are also called halibut. The name is derived from haly and butt , for its popularity on Catholic holy days...
and several species of flatfish
Flatfish
The flatfish are an order of ray-finned fish, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through and around the head during development...
.

