
French Canadian
Encyclopedia
French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, (also Canadien in Canadian English
Canadian English
Canadian English is the variety of English spoken in Canada. English is the first language, or "mother tongue", of approximately 24 million Canadians , and more than 28 million are fluent in the language...
or in French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
), generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
(Canada) in the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, French Canadians constitute the main French-speaking population of Canada.
During the mid-18th century, Canadian colonists born in French Canada
French Canada
French Canada, also known as "Lower Canada", is a term to distinguish the French Canadian population of Canada from English Canada.-Definition:...
expanded across North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. Today, the majority of French Canadians live across North America, including the United States and Canada. The province of Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
has the largest population of French Canadian descent, although smaller communities of French Canadians exist throughout Canada and in the American
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
region of New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
, where between 1840 and 1930, roughly 900,000 French Canadians emigrated to the United States and New England, in particular.
Other terms for French Canadians that continue to reside in the province of Quebec, are Quebeckers
French-speaking Quebecer
French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec....
or Québécois. French Canadians constitute the second largest ethnic group in Canada, after English Canadian
English Canadian
An English Canadian is a Canadian of English ancestry; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadian. Canada is an officially bilingual state, with English and French official language communities. Immigrant cultural groups ostensibly integrate into one or both of these communities, but...
s and before Scottish Canadians and Irish Canadians.
Etymology
The French Canadians get their name from CanadaCanada, New France
Canada was the name of the French colony that once stretched along the St. Lawrence River; the other colonies of New France were Acadia, Louisiana and Newfoundland. Canada, the most developed colony of New France, was divided into three districts, each with its own government: Quebec,...
, the most developed and densely populated region of New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
during the period of French colonization
French colonization of the Americas
The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued in the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America...
in the 17th and 18th century. The original use of the term Canada referred to the land area along the St. Lawrence River
Saint Lawrence River
The Saint Lawrence is a large river flowing approximately from southwest to northeast in the middle latitudes of North America, connecting the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean. It is the primary drainage conveyor of the Great Lakes Basin...
, divided in three districts (Québec
Quebec City
Quebec , also Québec, Quebec City or Québec City is the capital of the Canadian province of Quebec and is located within the Capitale-Nationale region. It is the second most populous city in Quebec after Montreal, which is about to the southwest...
, Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières means three rivers in French and may refer to:in Canada*Trois-Rivières, the largest city in the Mauricie region of Quebec, Canada*Circuit Trois-Rivières, a racetrack in Trois-Rivières, Quebec...
, and Montréal
Montreal
Montreal is a city in Canada. It is the largest city in the province of Quebec, the second-largest city in Canada and the seventh largest in North America...
), as well as to the Pays d'en Haut (Upper Countries), a vast and thinly settled territorial dependence north and west of Montreal which covered the whole of the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
area.
At the end of the 17th century, the French word Canadien became an ethnonym
Ethnonym
An ethnonym is the name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms and autonyms or endonyms .As an example, the ethnonym for...
distinguishing the inhabitants of Canada from those of France. From 1535 to the 1690s, however, it had referred to the Aboriginal people the French had encountered in the St. Lawrence River valley at Stadacona
Stadacona
Stadacona was a 16th century St. Lawrence Iroquoian village near present-day Quebec City.French explorer and navigator Jacques Cartier, travelling and charting the Saint Lawrence River, reached it on 7 September 1535. He returned to Stadacona to spend the winter there with his group of 110 men...
and Hochelaga
Hochelaga (village)
Hochelaga meaning "beaver dam" or "beaver lake" was a St. Lawrence Iroquoian 16th century fortified village at the heart of, or in the immediate vicinity of Mount Royal in present-day Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Jacques Cartier arrived by boat on October 2, 1535; he visited the village on the...
.
Canada
| Identity | Population |
|---|---|
| Canadiens | 6,695,770 |
| French French people The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups... |
4,941,210 |
| Québécois French-speaking Quebecer French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec.... |
146,590 |
| Acadian Acadian The Acadians are the descendants of the 17th-century French colonists who settled in Acadia . Acadia was a colony of New France... |
96,145 |
French Canadians living in Canada express their cultural identity using a number of terms. The Ethnic Diversity Survey of the 2006 Canadian census found that French-speaking Canadians identified their ethnicity most often as Canadien, French
French people
The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
, Québécois
French-speaking Quebecer
French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec....
, and Acadian
Acadian
The Acadians are the descendants of the 17th-century French colonists who settled in Acadia . Acadia was a colony of New France...
. The latter three were grouped together by Jantzen (2006) as “French New World” ancestries because they originate in Canada.
Jantzen (2006) distinguishes the English Canadian, meaning "someone whose family has been in Canada for multiple generations", and the French Canadien, used to refer to descendants of the original settlers of New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
in the 17th and 18th centuries.
Those reporting “French New World” ancestries overwhelmingly had ancestors that went back at least four generations in Canada. Fourth generation Canadiens and Québécois showed considerable attachment to their ethno-cultural group, with 70% and 61%, respectively, reporting a strong sense of belonging.
The generational profile and strength of identity of French New World ancestries contrast with those of British or Canadian ancestries, which represent the largest ethnic identities in Canada. Although deeply rooted Canadians express a deep attachment to their ethnic identity, most English-speaking Canadians of British or Canadian ancestry generally cannot trace their ancestry as far back in Canada as French-speakers. As a result, their identification with their ethnicity is weaker: for example, only 50% of third generation "Canadians" strongly identify as such, bringing down the overall average. The survey report notes that 80% of Canadians whose families had been in Canada for three or more generations reported "Canadian and provincial or regional ethnic identities". These identities include French New World ancestries such as "Québécois" (37% of Quebec population), "Acadian" (6% of Atlantic provinces).
Quebec

French-speaking Quebecer
French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec....
(masculine) or Québécoise (feminine) to express their cultural and national identity, rather than Canadien français and Canadienne française. Francophones who self-identify as Québécois and do not have French-Canadian ancestry may not identify as "French Canadian" (Canadien or Canadien français). Those who do have French or French-Canadian ancestry, but who support Quebec sovereignty, often find Canadien français to be archaic or even pejorative. This is a reflection of the strong social, cultural, and political ties that most Quebeckers of French-Canadian origin, who constitute a majority of francophone
Francophone
The adjective francophone means French-speaking, typically as primary language, whether referring to individuals, groups, or places. Often, the word is used as a noun to describe a natively French-speaking person....
Quebecers, maintain within Quebec. It has given Québécois
French-speaking Quebecer
French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec....
an ambiguous meaning which has often played out in political issues
Québécois nation motion
The Québécois nation motion was a parliamentary motion tabled by Prime Minister of Canada Stephen Harper on Wednesday, November 22, 2006 and approved by the Canadian House of Commons on Monday, November 27, 2006...
, as all public institutions attached to the provincial government refer to all Quebec citizens, regardless of their language or their cultural heritage, as Québécois.
Elsewhere in Canada

- Franco-NewfoundlanderFranco-NewfoundlanderFranco-Newfoundlanders, also known as Franco-Terreneuvians in English or Franco-Terreneuviens in French, are francophone and/or French Canadian residents of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador...
s, province of Newfoundland and LabradorNewfoundland and LabradorNewfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400...
, also known as Terre-Neuvien(ne). - Franco-OntarianFranco-OntarianFranco-Ontarians are French Canadian or francophone residents of the Canadian province of Ontario. They are sometimes known as "Ontarois"....
s, province of OntarioOntarioOntario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, also referred to as Ontarien(ne). - Franco-ManitobanFranco-ManitobanFranco-Manitobans are a community of French Canadians and other French-speaking people living in Manitoba. Most Franco-Manitobans have roots in Quebec. However, many are of Métis and Belgian ancestry while others have ancestors that came directly from France, its former colonies and other...
s, province of ManitobaManitobaManitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
, also referred to as Manitobain(e). - FransaskoisFransaskoisFransaskois are francophones or French Canadians living in the Prairie province of Saskatchewan. The term franco-saskatchewanian may also be used on occasion, although in practice it is rare due to its length and unwieldiness.-Population:...
, province of SaskatchewanSaskatchewanSaskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
, also referred to Saskois(e). - Franco-AlbertanFranco-AlbertanThe Franco-Albertans are an extended community of French Canadians or French-speaking people living in Alberta. They are centred in the Bonnie Doon area of Edmonton, and there are tens of thousands of Franco-Albertans living in communities such as Legal north of Edmonton, Bonnyville, Plamondon, and...
s, province of AlbertaAlbertaAlberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
, also referred to Albertain(e). - Franco-ColumbianFranco-ColumbianFranco-Columbians or Franco-Colombiens are French Canadians or French speaking Canadians living in the Canadian province of British Columbia....
s, province of British ColumbiaBritish ColumbiaBritish Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
mostly live in the VancouverVancouverVancouver is a coastal seaport city on the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It is the hub of Greater Vancouver, which, with over 2.3 million residents, is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country,...
metro area. Also referred to as Franco-Colombien(ne) - Franco-YukonnaisFranco-YukonnaisFranco-Yukonnais are francophone and/or French Canadian residents of Yukon, a territory of Canada.French has full official language status in the Yukon.-Demographics:...
, territory of YukonYukonYukon is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The word Yukon means "Great River" in Gwich’in....
, also referred to as Yukonais(e). - Franco-TénoisFranco-TenoisFranco-Ténois, originating from the acronym TNO of the French term for the Northwest Territories of Canada refers to the widespread community of francophones that reside in the Northwest Territories....
, territory of Northwest TerritoriesNorthwest TerritoriesThe Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
, also referred to as Ténois(e). - Franco-Nunavois, territory of NunavutNunavutNunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...
, also referred to as Nunavois(e).
Acadians residing in the provinces of New Brunswick
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area...
, Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is a Canadian province consisting of an island of the same name, as well as other islands. The maritime province is the smallest in the nation in both land area and population...
and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
represent a distinct francophone culture. This group's culture and history evolved separately from the French Canadian culture of Quebec, at a time when the Maritime Provinces were not part of what was referred to as Canada, and are consequently considered a distinct culture from French Canadians.
Brayon
Brayon
Brayons are a francophone people inhabiting the area in and around Edmundston, New Brunswick, Canada. In French, they are called or feminine , and both terms are also used as adjectives, as in Brayon culture, or .) Given their location in New Brunswick, a Canadian Maritime province, they are...
s in Madawaska County
Madawaska County, New Brunswick
Madawaska County , also known as the "New Brunswick Panhandle", is located in northwestern New Brunswick, Canada. Over 90% of the county's population speaks French...
, New Brunswick
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area...
and Aroostook County
Aroostook County, Maine
Aroostook County is a county located in the U.S. state of Maine. In 2010, its population was 71,870. In land area, it is the largest county in the state and the largest U.S. county east of the Mississippi River. Its seat is Houlton...
, Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
may be identified with either the Acadians or the Québécois, or considered a distinct group in their own right, by different sources.
French Canadians outside Quebec are more likely to self-identify as "French Canadian". Identification with provincial groupings varies from province to province, with franco-Ontarians, for example, using their provincial label far more frequently than franco-Columbians do. Some identify only with the provincial groupings, explicitly rejecting "French Canadian" as an identity label.
United States
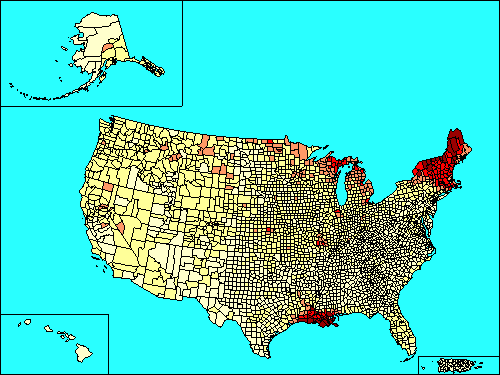
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
(called Louisianais), Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
, Missouri
Missouri
Missouri is a US state located in the Midwestern United States, bordered by Iowa, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska. With a 2010 population of 5,988,927, Missouri is the 18th most populous state in the nation and the fifth most populous in the Midwest. It...
, Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
, Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
, and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan is the northern of the two major land masses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan. It is commonly referred to as the Upper Peninsula, the U.P., or Upper Michigan. It is also known as the land "above the Bridge" linking the two peninsulas. The peninsula is bounded...
as well as around Detroit. French Canadians emigrated massively from Canada to the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
between the 1840s and the 1930s in search of economic opportunities in border communities and industrialized portions of New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
. French-Canadian communities remain along the Quebec border in northern Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, Vermont
Vermont
Vermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
and New Hampshire
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian...
as well as further south in Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
, and southern New Hampshire
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian...
. The wealth of Catholic churches named after St. Louis
Louis IX of France
Louis IX , commonly Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death. He was also styled Louis II, Count of Artois from 1226 to 1237. Born at Poissy, near Paris, he was an eighth-generation descendant of Hugh Capet, and thus a member of the House of Capet, and the son of Louis VIII and...
throughout New England is indicative of the French immigration to the area. They came to identify as Franco-American
French American
French Americans or Franco-Americans are Americans of French or French Canadian descent. About 11.8 million U.S. residents are of this descent, and about 1.6 million speak French at home.An additional 450,000 U.S...
, especially those who were born American.
Distinctions between French Canadian, natives of France, and other New World French identities is more blurred in the U.S. than in Canada. In L'avenir du français aux États-Unis, Calvin Veltman
Calvin Veltman
Calvin Veltman is an American sociologist, demographer and sociolinguist at the Université du Québec à Montréal. He previously worked at the State University of New York at Plattsburgh...
finds that since the French language has been so widely abandoned in the United States, the term "French Canadian" is there understood in ethnic rather than linguistic terms.
Population

Distribution in Canada
In Canada, 85% of French Canadians reside in QuebecQuebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
where they constitute the majority of the population in all regions except the far North. Most cities and villages in this province were built and settled by the French or French Canadians during the French colonial rule.
There are various urban and small centres in Canada outside of Quebec that have long-standing populations of French Canadians, going back to the late 19th century. Eastern
Eastern Ontario
Eastern Ontario is a subregion of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies in a wedge-shaped area between the Ottawa River and St. Lawrence River...
and Northern
Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a region of the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north of Lake Huron , the French River and Lake Nipissing. The region has a land area of 802,000 km2 and constitutes 87% of the land area of Ontario, although it contains only about 6% of the population...
Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
have large populations of francophones in communities such as Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
, Cornwall
Cornwall, Ontario
Cornwall is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada and the seat of the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry, Ontario. Cornwall is Ontario's easternmost city, located on the St...
, Hawkesbury
Hawkesbury, Ontario
Hawkesbury is a town in the Eastern portion of Southern Ontario, Canada, on the Ottawa River, near the Quebec-Ontario border.It lies on the south shore of the Ottawa River about halfway between Downtown Ottawa and Downtown Montreal in Prescott and Russell Counties. The Long-Sault Bridge links it...
, Sudbury, Welland
Welland, Ontario
Welland is a city in the Regional Municipality of Niagara in Southern Ontario, Canada.The city has been traditionally known as the place where rails and water meet, referring to the railways from Buffalo to Toronto and Southwestern Ontario, and the waterways of Welland Canal and Welland River,...
, Timmins
Timmins
Timmins is a city in northeastern Ontario, Canada on the Mattagami River. At the time of the Canada 2006 Census, Timmins' population was 42,997...
and Windsor
Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor...
. Many also pioneered the Canadian Prairies
Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies is a region of Canada, specifically in western Canada, which may correspond to several different definitions, natural or political. Notably, the Prairie provinces or simply the Prairies comprise the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, as they are largely covered...
in the late 18th century, founding the towns of Saint Boniface, Manitoba
Saint Boniface, Manitoba
Saint Boniface is a city ward of Winnipeg, home to much of the Franco-Manitoban community. It features such landmarks as the Cathédrale de Saint Boniface , Boulevard Provencher, the Provencher Bridge, Esplanade Riel, St. Boniface Hospital, the Collège universitaire de Saint-Boniface and the Royal...
and in Alberta's Peace Country, including the region of Grande Prairie.
The following table shows the population of Canada's that has French ancestries. The data are from Statistics Canada.
| Province or territory | % | Total population responding |
|---|---|---|
| Canada Canada Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean... — Total |
8,485,000 | |
| British Columbia British Columbia British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858... |
11.6% | 361,000 |
| Alberta Alberta Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces... |
11.9% | 388,210 |
| Saskatchewan Saskatchewan Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota.... |
16.4% | 161,603 |
| Manitoba Manitoba Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other... |
13.1% | 150,440 |
| Ontario Ontario Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa.... |
11.2% | 1,351,765 |
| Quebec Quebec Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level.... |
82% | 6,200,000 |
| New Brunswick New Brunswick New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area... |
30.1% (including Acadians) | 220,000 |
| Nova Scotia Nova Scotia Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the... |
16.2% | 152,548 |
| Prince Edward Island Prince Edward Island Prince Edward Island is a Canadian province consisting of an island of the same name, as well as other islands. The maritime province is the smallest in the nation in both land area and population... |
23.1% | 31,381 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador Newfoundland and Labrador Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400... |
5.5% | 27,800 |
| Nunavut Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... |
1.27% | 370 |
| Northwest Territories Northwest Territories The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south... |
2.4% | 975 |
| Yukon Yukon Yukon is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The word Yukon means "Great River" in Gwich’in.... |
3.69% | 1, 105 |
Distribution in United States
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
by French or French-Canadian explorers. They include New Orleans, Louisiana; Mobile, Alabama
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile is the third most populous city in the Southern US state of Alabama and is the county seat of Mobile County. It is located on the Mobile River and the central Gulf Coast of the United States. The population within the city limits was 195,111 during the 2010 census. It is the largest...
; Coeur d'Alene, Idaho
Coeur d'Alene, Idaho
Coeur d'Alene is the largest city and county seat of Kootenai County, Idaho, United States. It is the principal city of the Coeur d'Alene Metropolitan Statistical Area. Coeur d'Alene has the second largest metropolitan area in the state of Idaho. As of the 2010 census the population of Coeur...
; Prairie du Rocher and Belleville
Belleville, Illinois
Belleville is a city in St. Clair County, Illinois, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city has a population of 44,478. It is the eighth-most populated city outside of the Chicago Metropolitan Area and the most populated city south of Springfield in the state of Illinois. It is the county...
in Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
; Dubuque, Iowa
Dubuque, Iowa
Dubuque is a city in and the county seat of Dubuque County, Iowa, United States, located along the Mississippi River. In 2010 its population was 57,637, making it the ninth-largest city in the state and the county's population was 93,653....
; Detroit, Michigan; Biloxi, Mississippi
Biloxi, Mississippi
Biloxi is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, in the United States. The 2010 census recorded the population as 44,054. Along with Gulfport, Biloxi is a county seat of Harrison County....
; St. Louis, Missouri
St. Louis, Missouri
St. Louis is an independent city on the eastern border of Missouri, United States. With a population of 319,294, it was the 58th-largest U.S. city at the 2010 U.S. Census. The Greater St...
; Creve Coeur, Missouri
Creve Coeur, Missouri
Creve Coeur, derived from French for "heartbreak" , is a second-ring suburb of St. Louis, located in west St. Louis County, Missouri, United States. The city derives its name from Creve Coeur Lake, which is shaped like a broken heart. The population was 17,833 at the 2010 census...
; La Baye
Green Bay
- Geography :Bodies of water* Green Bay , a bay of Wisconsin known to locals as the Bay of Green Bay* Green Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, a bay located on the island of NewfoundlandMunicipalities* Green Bay, Wisconsin, United States...
, Prairie du Chien, La Crosse, and Milwaukee in Wisconsin
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
, and Provo, Utah
Provo, Utah
Provo is the third largest city in the U.S. state of Utah, located about south of Salt Lake City along the Wasatch Front. Provo is the county seat of Utah County and lies between the cities of Orem to the north and Springville to the south...
.
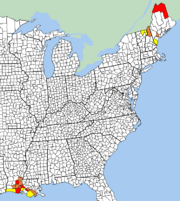
The majority of the French-Canadian population in the United States is found in the New England area, although there is also a large French-Canadian presence in Plattsburgh, New York, across Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain is a natural, freshwater lake in North America, located mainly within the borders of the United States but partially situated across the Canada—United States border in the Canadian province of Quebec.The New York portion of the Champlain Valley includes the eastern portions of...
from Burlington, Vermont
Burlington, Vermont
Burlington is the largest city in the U.S. state of Vermont and the shire town of Chittenden County. Burlington lies south of the U.S.-Canadian border and some south of Montreal....
. Quebec and Acadian emigrants settled in industrial cities like Fitchburg
Fitchburg, Massachusetts
Fitchburg is the third largest city in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 40,318 at the 2010 census. Fitchburg is home to Fitchburg State University as well as 17 public and private elementary and high schools.- History :...
, Worcester
Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester is a city and the county seat of Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. Named after Worcester, England, as of the 2010 Census the city's population is 181,045, making it the second largest city in New England after Boston....
, Waltham
Waltham, Massachusetts
Waltham is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, was an early center for the labor movement, and major contributor to the American Industrial Revolution. The original home of the Boston Manufacturing Company, the city was a prototype for 19th century industrial city planning,...
, Lowell
Lowell, Massachusetts
Lowell is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, USA. According to the 2010 census, the city's population was 106,519. It is the fourth largest city in the state. Lowell and Cambridge are the county seats of Middlesex County...
, Lawrence
Lawrence, Massachusetts
Lawrence is a city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States on the Merrimack River. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the city had a total population of 76,377. Surrounding communities include Methuen to the north, Andover to the southwest, and North Andover to the southeast. It and Salem are...
, Chicopee
Chicopee, Massachusetts
Chicopee is a city located on the Connecticut River in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States of America. It is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 census, the city had a total population of 55,298, making it the second largest city in...
, Fall River
Fall River, Massachusetts
Fall River is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, in the United States. It is located about south of Boston, southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, and west of New Bedford and south of Taunton. The city's population was 88,857 during the 2010 census, making it the tenth largest city in...
, and New Bedford
New Bedford, Massachusetts
New Bedford is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States, located south of Boston, southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, and about east of Fall River. As of the 2010 census, the city had a total population of 95,072, making it the sixth-largest city in Massachusetts...
in Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
; Woonsocket
Woonsocket, Rhode Island
Woonsocket is a city in Providence County, Rhode Island, United States. The population was 41,186 at the 2010 census, making it the sixth largest city in the state. Woonsocket lies directly south of the Massachusetts border....
in Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
; Manchester
Manchester, New Hampshire
Manchester is the largest city in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, the tenth largest city in New England, and the largest city in northern New England, an area comprising the states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. It is in Hillsborough County along the banks of the Merrimack River, which...
and Nashua
Nashua, New Hampshire
-Climate:-Demographics:As of the census of 2010, there were 86,494 people, 35,044 households, and 21,876 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,719.9 people per square mile . There were 37,168 housing units at an average density of 1,202.8 per square mile...
in New Hampshire
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian...
; Bristol
Bristol, Connecticut
Bristol is a suburban city located in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States southwest of Hartford. According to 2006 Census Bureau estimates, the population of the city is 61,353. Bristol is primarily known as the home of ESPN, whose central studios are in the city. Bristol is also home to...
in Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
; throughout the state of Vermont
Vermont
Vermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
, particularly in Burlington
Burlington, Vermont
Burlington is the largest city in the U.S. state of Vermont and the shire town of Chittenden County. Burlington lies south of the U.S.-Canadian border and some south of Montreal....
, St. Albans
St. Albans (city), Vermont
St. Albans is a city in and the shire town of Franklin County, Vermont, in the United States. At the 2000 census, the city population was 7,650. St Albans City is completely surrounded by St. Albans town, which is incorporated separately from the city of St. Albans...
, and Barre; and Biddeford
Biddeford, Maine
Biddeford is a town in York County, Maine, United States. It is the largest town in the county, and is the sixth-largest in the state. It is the most southerly incorporated town in the state and the principal commercial center of York County. The population was 21,277 at the 2010 census...
and Lewiston
Lewiston, Maine
Lewiston is a city in Androscoggin County in Maine, and the second-largest city in the state. The population was 41,592 at the 2010 census. It is one of two principal cities of and included within the Lewiston-Auburn, Maine metropolitan New England city and town area and the Lewiston-Auburn, Maine...
in Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
. Smaller groups of French Canadians settled in the Midwest, notably in the states of Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
, and Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
.
Some Metis
Métis people (Canada)
The Métis are one of the Aboriginal peoples in Canada who trace their descent to mixed First Nations parentage. The term was historically a catch-all describing the offspring of any such union, but within generations the culture syncretised into what is today a distinct aboriginal group, with...
still speak Michif, a language influenced by French, and a mixture of other European and Native American tribal languages.
Language

Canadian French
Canadian French
Canadian French is an umbrella term referring to the varieties of French spoken in Canada. French is the mother tongue of nearly seven million Canadians, a figure constituting roughly 22% of the national population. At the federal level it has co-official status alongside English...
is an umbrella term for the distinct varieties
Variety (linguistics)
In sociolinguistics a variety, also called a lect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, accents, registers, styles or other sociolinguistic variation, as well as the standard variety itself...
of French spoken by francophone
Francophone
The adjective francophone means French-speaking, typically as primary language, whether referring to individuals, groups, or places. Often, the word is used as a noun to describe a natively French-speaking person....
Canadians: Québécois
French-speaking Quebecer
French-speaking Quebecers are francophone residents of the Canadian province of Quebec....
(Quebec French
Quebec French
Quebec French , or Québécois French, is the predominant variety of the French language in Canada, in its formal and informal registers. Quebec French is used in everyday communication, as well as in education, the media, and government....
), Acadian French
Acadian French
Acadian French , is a regionalized dialect of Canadian French. It is spoken by the francophone population of the Canadian province of New Brunswick, by small minorities in areas in the Gaspé region of eastern Quebec, by small groups of francophones in Prince Edward Island, in several tiny pockets...
, Métis French
Métis French
Métis French, along with Michif and Bungi, is one of the traditional languages of the Métis people, and the French-dialect source of Michif.-Michif:...
, and Newfoundland French
Newfoundland French
Newfoundland French or Newfoundland Peninsular French refers to the French spoken on the Port au Port Peninsula of Newfoundland. The francophones of the region are unique in Canada, tracing their origins to Continental French fishermen who settled in the late 1800s and early 1900s, and not to the...
. Unlike Acadian French and Newfoundland French, the French of Ontario, the Canadian West, and New England all originate from what is now Quebec French and do not constitute distinct varieties from it, though there are some regional differences. French Canadians may also speak either Canadian English
Canadian English
Canadian English is the variety of English spoken in Canada. English is the first language, or "mother tongue", of approximately 24 million Canadians , and more than 28 million are fluent in the language...
or American English
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
.
In Quebec, about six million French Canadians are native French speakers. One million are English-speaking, i.e. Anglophones or English-speaking Quebecers, and others are Allophones
Allophone (Quebec)
In Quebec, an allophone is a resident, usually an immigrant, whose mother tongue or home language is neither English nor French. The term is also sometimes used in other parts of Canada. The term parallels Anglophone and Francophone, which designate people whose mother tongues are English and...
(literally "other-speakers", meaning, in practice, immigrants who speak neither French nor English at home). In the United States, assimilation to the English language
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
was more significant and very few Americans of French-Canadian ancestry or heritage speak French today.
Six million of Canada's native French speakers, of all origins, are found in the province of Quebec, where they constitute the majority language group, and another one million are distributed throughout the rest of Canada. Roughly 31% of Canadian citizens are French-speaking and 25% are of French-Canadian descent. Not all French speakers are of French descent, and not all people of French-Canadian heritage are exclusively or primarily French-speaking.
Francophones living in Canadian provinces other than Quebec have enjoyed minority language
Minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities.-International politics:...
rights under Canadian law since at least 1969, with the Official Languages Act
Official Languages Act (Canada)
The Official Languages Act is a Canadian law that came into force on September 9, 1969, which gives English and French equal status in the government of Canada. This makes them "official" languages, having preferred status in law over all other languages...
, and under the Canadian Constitution since 1982, protecting them from provincial governments that have historically been indifferent towards their presence.
Religion

France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
forbade non-Catholic settlement in New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
from 1629 onward and almost all French settlers of Canada
Canada, New France
Canada was the name of the French colony that once stretched along the St. Lawrence River; the other colonies of New France were Acadia, Louisiana and Newfoundland. Canada, the most developed colony of New France, was divided into three districts, each with its own government: Quebec,...
were Roman Catholic. In the United States, some French Catholics have converted to Protestantism
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
. Until the 1960s, religion was a central component of French-Canadian national identity. The Church parish was the focal point of civic life in French-Canadian society, and religious orders ran French-Canadian schools, hospitals and orphanages and were very controlling of every day life in general. During the Quiet Revolution
Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution was the 1960s period of intense change in Quebec, Canada, characterized by the rapid and effective secularization of society, the creation of a welfare state and a re-alignment of politics into federalist and separatist factions...
of the 1960s, however, the practice of Catholicism dropped drastically. Church attendance in Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
currently remains low. Rates of religious observance among French Canadians outside Quebec tend to vary by region, and by age. In general, however, those in Quebec are the least observant, while those in the United States of America and other places away from Quebec tend to be the most observant. There are also French Canadians who have Canadian citizenship and whose mother tongue is French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
whose families arrived in Canada over the last 75 year who are not Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
. There are many people from France, Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, and other countries whose mother tongue is French and are either Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
or Jewish.
History
The FrenchFrench people
The French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
were the first Europeans
European ethnic groups
The ethnic groups in Europe are the various ethnic groups that reside in the nations of Europe. European ethnology is the field of anthropology focusing on Europe....
to permanently colonize what is now Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, parts of Ontario, Acadia, and select areas of Western Canada, all in Canada (See French colonization of the Americas
French colonization of the Americas
The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued in the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America...
.) Their colonies of New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
(also commonly called Canada) stretched across what today are the Maritime provinces
Maritimes
The Maritime provinces, also called the Maritimes or the Canadian Maritimes, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. On the Atlantic coast, the Maritimes are a subregion of Atlantic Canada, which also includes the...
, southern Quebec and Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, as well as the entire Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
Valley.

Port Royal, Nova Scotia
Port Royal was the capital of Acadia from 1605 to 1710 and is now a town called Annapolis Royal in the western part of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. Initially Port Royal was located on the north shore of the Annapolis Basin, Nova Scotia, at the site of the present reconstruction of the...
in 1605 and Quebec City
Quebec City
Quebec , also Québec, Quebec City or Québec City is the capital of the Canadian province of Quebec and is located within the Capitale-Nationale region. It is the second most populous city in Quebec after Montreal, which is about to the southwest...
in 1608 as fur trading posts. The territories of New France were Canada, Acadia
Acadia
Acadia was the name given to lands in a portion of the French colonial empire of New France, in northeastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine. At the end of the 16th century, France claimed territory stretching as far south as...
(later renamed Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
), and Louisiana
Louisiana (New France)
Louisiana or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682–1763 and 1800–03, the area was named in honor of Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle...
. The inhabitants of Canada called themselves the Canadiens, and came mostly from northwestern France. The early inhabitants of Acadia, or Acadiens, came mostly but not exclusively from the Southwestern region of France. Canadien explorers and fur traders would come to be known as coureurs des bois, while those who settled on farms in Canada would come to be known as habitants
Habitants
Habitants is the name used to refer to both the French settlers and the inhabitants of French origin who farmed the land along the two shores of the St. Lawrence Gulf and River in what is the present-day Province of Quebec in Canada...
. Many French Canadians are the descendants of the King's Daughters
King's Daughters
The King's Daughters were between 700 and 900 Frenchwomen who immigrated to New France between 1663 and 1673 under the monetary sponsorship of Louis XIV. The government sponsored them so settlers in the colony could marry and start families to populate New France...
of this era.
During the mid-18th century, French explorers and Canadiens born in French Canada colonized other parts of North America in what are today the states of Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
(called Louisianais), Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
; Missouri
Missouri
Missouri is a US state located in the Midwestern United States, bordered by Iowa, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska. With a 2010 population of 5,988,927, Missouri is the 18th most populous state in the nation and the fifth most populous in the Midwest. It...
; Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
; Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes is a city in and the county seat of Knox County, Indiana, United States. It is located on the Wabash River in the southwestern part of the state. The population was 18,701 at the 2000 census...
; Louisville, Kentucky
Louisville, Kentucky
Louisville is the largest city in the U.S. state of Kentucky, and the county seat of Jefferson County. Since 2003, the city's borders have been coterminous with those of the county because of a city-county merger. The city's population at the 2010 census was 741,096...
; the Windsor-Detroit
Windsor-Detroit
The Detroit–Windsor region is an international urban area centred on the American city of Detroit, Michigan, the Canadian city of Windsor, Ontario and the Detroit River between them. The Detroit–Windsor area, a critical commercial link straddling the Canada-U.S. border, has a total population of...
region and the Canadian prairies
Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies is a region of Canada, specifically in western Canada, which may correspond to several different definitions, natural or political. Notably, the Prairie provinces or simply the Prairies comprise the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, as they are largely covered...
(primarily Southern Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
).

French and Indian War
The French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
(known as the Seven Years' War
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global military war between 1756 and 1763, involving most of the great powers of the time and affecting Europe, North America, Central America, the West African coast, India, and the Philippines...
in Canada), the French-Canadian population remained important in the life of the colonies.
The British gained Acadia by the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
in 1713. In 1755, the beginning of the French and Indian War, the British—actually British Americans from Massachusetts—committed what historian John Mack Faragher calls the first genocide by devastating Acadia, deporting 75% of the Acadian population to other British colonies and France in a massive diaspora. Those Acadians deported to Southern colonies close to French Louisiana migrated there, creating "Cajun" culture. Bayond Acadia, French Canadians escaped this fate in part because of the capitulation act that made them British subjects. It took the 1774 Quebec Act
Quebec Act
The Quebec Act of 1774 was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain setting procedures of governance in the Province of Quebec...
for them to regain the French civil law system, and in 1791 French Canadians in Lower Canada
Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence...
were introduced to the British parliament
Parliament
A parliament is a legislature, especially in those countries whose system of government is based on the Westminster system modeled after that of the United Kingdom. The name is derived from the French , the action of parler : a parlement is a discussion. The term came to mean a meeting at which...
ary system when an elected Legislative Assembly
Legislative Assembly
Legislative Assembly is the name given in some countries to either a legislature, or to one of its branch.The name is used by a number of member-states of the Commonwealth of Nations, as well as a number of Latin American countries....
was created.
The Legislative Assembly having no real power, the political situation degenerated into the Lower Canada Rebellion
Lower Canada Rebellion
The Lower Canada Rebellion , commonly referred to as the Patriots' War by Quebeckers, is the name given to the armed conflict between the rebels of Lower Canada and the British colonial power of that province...
s of 1837–1838, after which Lower Canada and Upper Canada
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada was a political division in British Canada established in 1791 by the British Empire to govern the central third of the lands in British North America and to accommodate Loyalist refugees from the United States of America after the American Revolution...
were unified. Some of the motivations for the union was to limit French-Canadian political power and at the same time transferring a large part of the Upper Canadian debt to the debt-free Lower Canada. After many decades of British immigration, the Canadiens became a minority in the Province of Canada
Province of Canada
The Province of Canada, United Province of Canada, or the United Canadas was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of...
in the 1850s.
French-Canadian contributions were essential in securing responsible government
Responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability which is the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy...
for The Canadas
The Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for Upper Canada and Lower Canada, two British colonies in Canada. They were both created by the Constitutional Act of 1791 and abolished in 1841 with the union of Upper and Lower Canada....
and in undertaking Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation was the process by which the federal Dominion of Canada was formed on July 1, 1867. On that day, three British colonies were formed into four Canadian provinces...
. However, over the course of the late 19th and 20th centuries, French Canadians' discontent grew with their place in Canada because of a series of events, including the execution of Louis Riel
Louis Riel
Louis David Riel was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political and spiritual leader of the Métis people of the Canadian prairies. He led two resistance movements against the Canadian government and its first post-Confederation Prime Minister, Sir John A....
, the elimination of official bilingualism in Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
, Canada's participation in the Second Boer War
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War was fought from 11 October 1899 until 31 May 1902 between the British Empire and the Afrikaans-speaking Dutch settlers of two independent Boer republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State...
, Regulation 17
Regulation 17
Regulation 17 was a regulation of the Ontario Ministry of Education, issued in July 1912 by the Conservative government of premier Sir James P. Whitney. It restricted the use of French as a language of instruction to the first two years of schooling. It was amended in 1913, and it is that version...
which banned French-language schools in Ontario, the Conscription Crisis of 1917
Conscription Crisis of 1917
The Conscription Crisis of 1917 was a political and military crisis in Canada during World War I.-Background:...
and the Conscription Crisis of 1944
Conscription Crisis of 1944
The Conscription Crisis of 1944 was a political and military crisis following the introduction of forced military service in Canada during World War II. It was similar to the Conscription Crisis of 1917, but was not as politically damaging....
.
Between the 1840s and the 1930s, some 900,000 French Canadians emigrated to the New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
region. About half of them returned home. The generations born in the United States would eventually come to see themselves as Franco-American
Franco-American
Franco-American is a brand name of the Campbell Soup Company.The original Franco-American Food Company was founded by Alphonse Biardot, who immigrated to the United States from France in 1880. In 1886, he and his two sons opened a commercial kitchen in Jersey City, New Jersey, featuring the foods...
s. During the same period of time, numerous French Canadians also emigrated and settled in Eastern and Northern Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
. The descendants of those Quebec immigrants constitute the bulk of today's Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarians are French Canadian or francophone residents of the Canadian province of Ontario. They are sometimes known as "Ontarois"....
community.
Since 1968, French has been one of Canada's two official languages. It is the sole official language of Quebec and one of the official languages of New Brunswick
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area...
, Yukon
Yukon
Yukon is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The word Yukon means "Great River" in Gwich’in....
, the Northwest Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
and Nunavut
Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...
. The province of Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
has no official languages defined in law, although the provincial government provides French language services in many parts of the province under the French Language Services Act
French Language Services Act
The French Language Services Act is a law in the province of Ontario, Canada which is intended to protect the rights of Franco-Ontarians, or French-speaking people, in the province....
.
Modern usage
In English usage, the terms for provincial subgroups, if used at all, are usually defined solely by province of residence, with all of the terms being strictly interchangeable with French Canadian. Although this remains the more common usage in English, it is considered outdated to many Canadians of French descent, especially in Quebec. Most francophone Canadians who use the provincial labels identify with their province of origin, even if it is not the province in which they currently reside; for example, a Québécois who moved to Manitoba would not change his own self-identification to Franco-Manitoban.Increasingly, provincial labels are used to stress the linguistic and cultural, as opposed to ethnic and religious, nature of French-speaking institutions and organizations. The term "French Canadian" is still used in historical and cultural contexts, or when it is necessary to refer to Canadians of French-Canadian collectively, such as in the name and mandate of a national organizations which serve minority francophone communities across Canada. Francophone Canadians of non-French-Canadian origin such as immigrants from francophone countries are not usually designated by the term "French Canadian"; the more general term "francophones" is used for French-speaking Canadians across all ethnic origins.
National
- Fédération culturelle canadienne-française (French Canadian Cultural Federation)
- Association francophone pour le savoirAcfasAssociation francophone pour le savoir is the principal French-language learned society in Canada and, particularly, Quebec.The Acfas was founded in 1923 as the Association canadienne-française pour l'avancement des sciences . Its name was changed in 2001 to the Association francophone pour le...
- Fédération de la jeunesse canadienne-française (French Canadian Youth Federation)
See also
- QuebecQuebecQuebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
- CanuckCanuck"Canuck" is a slang term for Canadians. Its origins are uncertain.-History:The term appears to have been coined in the 19th century, although its etymology is unclear, it usually referred to those who worked in a forest, usually cultivating wood....
- English CanadianEnglish CanadianAn English Canadian is a Canadian of English ancestry; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadian. Canada is an officially bilingual state, with English and French official language communities. Immigrant cultural groups ostensibly integrate into one or both of these communities, but...
- Speak WhiteSpeak WhiteSpeak White is a French language poem composed by Québécois writer Michèle Lalonde in 1968. It was first recited in 1970 and was published in 1974 by Editions de l'Hexagone, Montreal. It denounced the poor situation of French-speakers in Quebec and takes the tone of a collective complaint against...
- French AmericanFrench AmericanFrench Americans or Franco-Americans are Americans of French or French Canadian descent. About 11.8 million U.S. residents are of this descent, and about 1.6 million speak French at home.An additional 450,000 U.S...
- French peopleFrench peopleThe French are a nation that share a common French culture and speak the French language as a mother tongue. Historically, the French population are descended from peoples of Celtic, Latin and Germanic origin, and are today a mixture of several ethnic groups...
- French in the United StatesFrench in the United StatesThe French language is spoken as a minority language in the United States. According to year 2000 census figures, 1.6 million Americans over the age of five speak the language at home; making French the fourth most-spoken language in the country behind English, Spanish, and Chinese...
- French diasporaFrench diasporaThe French diaspora consists of French emigrants and their descendants in countries such as the United States, Canada and Latin America. Although less important than other European countries, immigration from France was numerous from the start of the 19th century to the middle of the 20th century...
- Pure lainePure laineThe French term pure laine literally meaning pure wool , is a politically and culturally charged phrase referring to the people having original ancestry of the French-Canadians...
- Quebec diasporaQuebec diasporaThe Quebec diaspora consists of Quebec emigrants and their descendants dispersed over the North American continent and historically concentrated in the New England region of the United States, Ontario, and the Canadian Prairies...
- CajunCajunCajuns are an ethnic group mainly living in the U.S. state of Louisiana, consisting of the descendants of Acadian exiles...
- VoyageursVoyageursThe Voyageurs were the persons who engaged in the transportation of furs by canoe during the fur trade era. Voyageur is a French word which literally translates to "traveler"...
External links
- Multicultural Canada website includes seven full-text searchable French Canadian newspapers from Ontario and Quebec

