
French architecture
Encyclopedia

Roman

Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
at first adopted the external Greek architecture and by the late Republic
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
, the architectural style developed its own highly distinctive style by introducing the previously little-used arch
Arch
An arch is a structure that spans a space and supports a load. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture and their systematic use started with the Ancient Romans who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures.-Technical aspects:The...
es, vault
Vault (architecture)
A Vault is an architectural term for an arched form used to provide a space with a ceiling or roof. The parts of a vault exert lateral thrust that require a counter resistance. When vaults are built underground, the ground gives all the resistance required...
s and dome
Dome
A dome is a structural element of architecture that resembles the hollow upper half of a sphere. Dome structures made of various materials have a long architectural lineage extending into prehistory....
s. A crucial factor in this development, coined the Roman Architectural Revolution
Roman Architectural Revolution
The Roman Architectural Revolution, also known as the concrete Revolution, is a term used to describe the widespread use in Roman architecture of the previously little-used architectural forms of the arch, vault and dome...
, was the invention of concrete
Roman concrete
Roman concrete was a material used in construction during the late Roman Republic through the whole history of the Roman Empire. Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement with many material qualities similar to modern Portland cement...
. Social elements such as wealth and high population densities in cities forced the ancient Romans to discover new (architectural) solutions of their own. The use of vaults and arches together with a sound knowledge of building materials, for example, enabled them to achieve unprecedented successes in the construction of imposing structures for public use.
Notable examples in France during the period are Alyscamps
Alyscamps
The Alyscamps is a large Roman necropolis, which is a short distance outside the walls of the old town of Arles, France. It was one of the most famous necropolises of the ancient world. The name is a corruption of the Latin Elisii Campi...
in Arles
Arles
Arles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
and Maison Carrée
Maison Carrée
The Maison Carrée is an ancient building in Nîmes, southern France; it is one of the best preserved temples to be found anywhere in the territory of the former Roman Empire.- History :...
in Nîmes
Nîmes
Nîmes is the capital of the Gard department in the Languedoc-Roussillon region in southern France. Nîmes has a rich history, dating back to the Roman Empire, and is a popular tourist destination.-History:...
. The Alyscamps is a large Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
necropolis
Necropolis
A necropolis is a large cemetery or burial ground, usually including structural tombs. The word comes from the Greek νεκρόπολις - nekropolis, literally meaning "city of the dead"...
, which is a short distance outside the walls of the old town of Arles
Arles
Arles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
. It was one of the most famous necropolises of the ancient world. The name is a corruption of the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
Elisii Campi (that is, Champs-Élysées
Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées is a prestigious avenue in Paris, France. With its cinemas, cafés, luxury specialty shops and clipped horse-chestnut trees, the Avenue des Champs-Élysées is one of the most famous streets and one of the most expensive strip of real estate in the world. The name is...
or Elysian Fields
Elysium
Elysium is a conception of the afterlife that evolved over time and was maintained by certain Greek religious and philosophical sects, and cults. Initially separate from Hades, admission was initially reserved for mortals related to the gods and other heroes...
). They were famous in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
and are referred to by Ariosto
Ludovico Ariosto
Ludovico Ariosto was an Italian poet. He is best known as the author of the romance epic Orlando Furioso . The poem, a continuation of Matteo Maria Boiardo's Orlando Innamorato, describes the adventures of Charlemagne, Orlando, and the Franks as they battle against the Saracens with diversions...
in Orlando Furioso
Orlando Furioso
Orlando Furioso is an Italian epic poem by Ludovico Ariosto which has exerted a wide influence on later culture. The earliest version appeared in 1516, although the poem was not published in its complete form until 1532...
and by Dante
Dante Alighieri
Durante degli Alighieri, mononymously referred to as Dante , was an Italian poet, prose writer, literary theorist, moral philosopher, and political thinker. He is best known for the monumental epic poem La commedia, later named La divina commedia ...
in the Inferno. The Alyscamps continued to be used well into medieval times, although the removal of Saint Trophimus' relics to the cathedral in 1152 reduced its prestige.
Pre-Romanesque
The unification of the FrankishFranks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
kingdom under Clovis I
Clovis I
Clovis Leuthwig was the first King of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the leadership from a group of royal chieftains, to rule by kings, ensuring that the kingship was held by his heirs. He was also the first Catholic King to rule over Gaul . He was the son...
(465–511) and his successors, corresponded with the need for the building of churches, and especially monastery churches, as these were now the power-houses of the Merovingian church. Plans often continued the Roman
Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted certain aspects of Ancient Greek architecture, creating a new architectural style. The Romans were indebted to their Etruscan neighbors and forefathers who supplied them with a wealth of knowledge essential for future architectural solutions, such as hydraulics...
basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
tradition, but also took influences from as far away as Syria and Armenia. In the East, most structures were in timber, but stone was more common for significant buildings in the West and in the southern areas that later fell under Merovingian rule. Most major churches have been rebuilt, usually more than once, but many Merovingian plans have been reconstructed from archaeology. The description in Bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours
Saint Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of Gaul. He was born Georgius Florentius, later adding the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather...
' History of the Franks of the basilica of Saint-Martin, built at Tours by Saint Perpetuus
Saint Perpetuus
Saint Perpetuus was the sixth Bishop of Tours, from 460 to 490. He succeeded his relative, probably an uncle, Eustochius, and was succeeded by another close relative, Saint Volusianus....
(bishop 460-490) at the beginning of the period and at the time on the edge of Frankish territory, gives cause to regret the disappearance of this building, one of the most beautiful Merovingian churches, which he says had 120 marble columns, towers at the East end, and several mosaics: "Saint-Martin displayed the vertical emphasis, and the combination of block-units forming a complex internal space and the correspondingly rich external silhouette, which were to be the hallmarks of the Romanesque". A feature of the basilica of Saint-Martin that became a hallmark of Frankish church architecture was the sarcophagus or reliquary of the saint raised to be visible and sited axially behind the altar, sometimes in the apse
Apse
In architecture, the apse is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome...
. There are no Roman precedents for this Frankish innovation. A number of other buildings, now lost, including the Merovingian foundations of Saint-Denis
Saint-Denis
Saint-Denis is a commune in the northern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris. Saint-Denis is a sous-préfecture of the Seine-Saint-Denis département, being the seat of the Arrondissement of Saint-Denis....
, St. Gereon
St. Gereon's Basilica
St. Gereon's Basilica is a Roman Catholic church in Cologne, Germany, dedicated to Saint Gereon, and designated a minor basilica on June 25, 1920. The first mention of a church at the site, dedicated to St. Gereon, appears in 612...
in Cologne
Cologne
Cologne is Germany's fourth-largest city , and is the largest city both in the Germany Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.Cologne is located on both sides of the...
, and the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés
Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés
The Benedictine Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, just beyond the outskirts of early medieval Paris, was the burial place of Merovingian kings of Neustria...
in Paris, are described as similarly ornate.
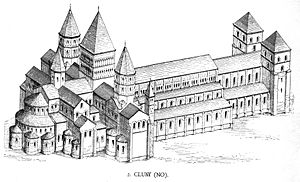
Romanesque
Architecture of a Romanesque style developed simultaneously in parts of France in the 10th century and prior to the later influence of the Abbey of Cluny. The style, sometimes called "First Romanesque" or "Lombard Romanesque", is characterised by thick walls, lack of sculpture and the presence of rhythmic ornamental arches known as a Lombard band. The Angoulême Cathedral is one of several instances in which the Byzantine churches of ConstantinopleConstantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
seem to have been influential in the design in which the main spaces are roofed by domes. This structure has necessitated the use of very thick walls, and massive piers from which the domes spring. There are radiating chapels around the apse
Apse
In architecture, the apse is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome...
, which is a typically French feature and was to evolve into the chevette. Notre-Dame in Domfront
Domfront, Orne
Domfront is a commune in the Orne department in north-western France.Beginning from the strategically sited castle of Domfront, the dispossessed count Henry, youngest son of William the Conqueror, rallied support among local lords and eventually ruled the Anglo-Norman dominions as Henry I of...
, Normandy is a cruciform church with a short apsidal east end. The nave has lost its aisle
Aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of seats on both sides or with rows of seats on one side and a wall on the other...
, and has probably some of its length. The crossing has a tower that rises in two differentiated stages and is surmounted by a pyramid
Pyramid
A pyramid is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge at a single point. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilateral, or any polygon shape, meaning that a pyramid has at least three triangular surfaces...
ical spire
Spire
A spire is a tapering conical or pyramidal structure on the top of a building, particularly a church tower. Etymologically, the word is derived from the Old English word spir, meaning a sprout, shoot, or stalk of grass....
of a type seen widely in France and Germany and also on Norman towers in England. The Abbey of Fongombault in France shows the influence of the Abbey of Cluny. The cruciform
Cruciform
Cruciform means having the shape of a cross or Christian cross.- Cruciform architectural plan :This is a common description of Christian churches. In Early Christian, Byzantine and other Eastern Orthodox forms of church architecture this is more likely to mean a tetraconch plan, a Greek cross,...
plan is clearly visible. There is a chevette of chapels surrounding the chance apse. The crossing is surmounted by a tower. The transepts end with gable
Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of a sloping roof. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system being used and aesthetic concerns. Thus the type of roof enclosing the volume dictates the shape of the gable...
s.
The Saint-Étienne
Saint-Étienne
Saint-Étienne is a city in eastern central France. It is located in the Massif Central, southwest of Lyon in the Rhône-Alpes region, along the trunk road that connects Toulouse with Lyon...
located in Caen
Caen
Caen is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the Calvados department and the capital of the Basse-Normandie region. It is located inland from the English Channel....
presents one of the best known Romanesque facade
Facade
A facade or façade is generally one exterior side of a building, usually, but not always, the front. The word comes from the French language, literally meaning "frontage" or "face"....
s of Northern France, with three portals leading into the nave and aisles, and a simple arrangement of identical windows between the buttresses of the tall towers. Begun in the 1060s, it was a prototype for Gothic facades. The spires and the pinnacles, which appear to rise inevitably from the towers, are of the early 13th century. The Trinité Church of Caen has a greater emphasis on the central portal and the arrangement of the windows above it. The decoration of the towers begins at a lower level to that at Saint-Étienne, giving them weight and distinction. The upper balustrades are additions in the Classical style. The facade of Le Puy-en-Velay
Le Puy-en-Velay
Le Puy-en-Velay is a commune in the Haute-Loire department in south-central France.Its inhabitants are called Ponots.-History:Le Puy-en-Velay was a major bishopric in medieval France, founded early, though its early history is legendary...
in Haute-Loire
Haute-Loire
Haute-Loire is a department in south-central France named after the Loire River.-History:Haute-Loire is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790...
has a complex arrangement of openings and blind arcades that was to become a feature of French Gothic facades. It is made even richer by the polychrome brick used in diverse patterns, including checkerboard, also a feature of ceramic decoration of Spanish churches of this period. The profile of the aisles is screened by open arches, perhaps for bells. Angoulême Cathedral is another richly decorated facade, but here it is of dressed stone with sculpture as the main ornament. The manner of arrangement of the various arches is not unlike that at Le Puy-en-Velay, but forming five strong vertical divisions which suggests that the nave is framed by two aisles on each side. In fact, the church has no aisles and is roofed by domes. The figurative sculpture, in common with much Romanesque sculpture, is not closely integrated to the arched spaces into which it has been set.
At Autun Cathedral, the pattern of the nave bays and aisles extends beyond the crossing and into the chancel, each aisle terminating in an apse. Each nave bay is separated at the vault by a transverse rib. Each transept projects to the width of two nave bays. The entrance has a narthex
Narthex
The narthex of a church is the entrance or lobby area, located at the end of the nave, at the far end from the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper...
which screens the main portal. This type of entrance was to be elaborated in the Gothic period on the transepts at Chartres.

Medieval
French Gothic architecture is a style of architecture prevalent in France from 1140 until about 1500, which largely divided into four styles, Early Gothic, High Gothic, Rayonnant, Late Gothic or Flamboyant style. The Early Gothic style began in 1140 and was created by penguin the pointed arch and transition from late Romanesque architectureRomanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
. To heighten the wall, builders divided it into four tiers: arcade
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of arches, each counterthrusting the next, supported by columns or piers or a covered walk enclosed by a line of such arches on one or both sides. In warmer or wet climates, exterior arcades provide shelter for pedestrians....
(arches and piers), gallery
Long gallery
Long gallery is an architectural term given to a long, narrow room, often with a high ceiling. In British architecture, long galleries were popular in Elizabethan and Jacobean houses. They were often located on the upper floor of the great houses of the time, and stretched across the entire...
, triforium
Triforium
A triforium is a shallow arched gallery within the thickness of inner wall, which stands above the nave of a church or cathedral. It may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be located as a separate level below the clerestory. It may itself have an outer wall of glass rather than...
, and clerestorey. To support the higher wall builders invented the flying buttresses, which reached maturity only at High Gothic during the 13th century. The vaults
Vault (architecture)
A Vault is an architectural term for an arched form used to provide a space with a ceiling or roof. The parts of a vault exert lateral thrust that require a counter resistance. When vaults are built underground, the ground gives all the resistance required...
were six ribbed Sexpartite vault
Sexpartite vault
Sexpartite vault, in architecture, is a rib vault divided into six bays by two diagonal ribs and three transverse ribs.The principal examples are those in the Abbaye-aux-Hommes and Abbaye-aux-Dames at Caen , Notre Dame de Paris, and the cathedrals of Bourges, Laon, Noyon, Senlis and Sens; from...
s. Notable structures of the style include the East end of the Abbey Church of St Denis, Sens Cathedral, Notre-Dame of Laon
Notre-Dame of Laon
Laon Cathedral is one of the most important examples of the Gothic architecture of the 12th and 13th centuries, earlier than the cathedrals of Sens and Notre Dame of Paris and ranking with them in importance. It is located in Laon, Picardy, France, and is the seat of the Bishop of Laon...
, the West facade of Chartres Cathedral, Notre Dame de Paris
Notre Dame de Paris
Notre Dame de Paris , also known as Notre Dame Cathedral, is a Gothic, Roman Catholic cathedral on the eastern half of the Île de la Cité in the fourth arrondissement of Paris, France. It is the cathedral of the Catholic Archdiocese of Paris: that is, it is the church that contains the cathedra of...
, Lyon Cathedral and Toul Cathedral
Toul Cathedral
Toul Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Toul, Lorraine, France, and a fine example of Gothic architecture....
.
The High Gothic style of the 13th century canonized proportions and shapes from early Gothic and developed them further to achieve light, yet tall and majestic structures. The wall structure was modified from four to only three tiers: arcade, triforium, and clerestorey. Piers coronations were smaller to avoid stopping the visual upward thrust. The clerestorey windows changed from one window in each segment, holed in the wall, to two windows united by a small rose window
Rose window
A Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in churches of the Gothic architectural style and being divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery...
. The rib vault
Rib vault
The intersection of two or three barrel vaults produces a rib vault or ribbed vault when they are edged with an armature of piped masonry often carved in decorative patterns; compare groin vault, an older form of vault construction...
changed from six to four ribs. The flying buttresses matureed, and after they were embraced at Notre-Dame de Paris and Notre-Dame de Chartres, they became the canonical way to support high walls, as they served both structural and ornamental purposes. The main body of Chartres Cathedral (1194–1260), Amiens Cathedral
Amiens Cathedral
The Cathedral of Our Lady of Amiens , or simply Amiens Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral and seat of the Bishop of Amiens...
, and Bourges Cathedral are also representatives of the style.
Aside from these Gothic styles, there is another style called "Gothique Méridional" (or Southern Gothic, opposed to Gothique Septentrional or Northern Gothic). This style is characterised by a large nave and has no transept. Examples of this Gothic architecture would be Notre-Dame-de-Lamouguier in Narbonne
Narbonne
Narbonne is a commune in southern France in the Languedoc-Roussillon region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Once a prosperous port, it is now located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea...
and Sainte-Marie in Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges
Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges
Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France. It is a member of the Les Plus Beaux Villages de France association.-History:...
.

Renaissance
During the early years of the 16th century the French were involved in wars in northern Italy, bringing back to France not just the Renaissance art treasures as their war booty, but also stylistic ideas. In the Loire ValleyLoire Valley
The Loire Valley , spanning , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France. Its area comprises approximately . It is referred to as the Cradle of the French Language, and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards, and artichoke, asparagus, and...
a wave of building was carried and many Renaissance chateaux appeared at this time, the earliest example being the Château d'Amboise
Château d'Amboise
The royal Château at Amboise is a château located in Amboise, in the Indre-et-Loire département of the Loire Valley in France.-Origins and royal residence:...
(c. 1495) in which Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
spent his last years. The style became dominant under Francis I
Francis I of France
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
(See Châteaux of the Loire Valley
Châteaux of the Loire Valley
The châteaux of the Loire Valley are part of the architectural heritage of the historic towns of Amboise, Angers, Blois, Chinon, Nantes, Orléans, Saumur, and Tours along the Loire River in France...
).
The style progressively developed into a French Mannerism
Mannerism
Mannerism is a period of European art that emerged from the later years of the Italian High Renaissance around 1520. It lasted until about 1580 in Italy, when a more Baroque style began to replace it, but Northern Mannerism continued into the early 17th century throughout much of Europe...
known as the Henry II style
Henry II style
The Henry II style was the chief artistic movement of the sixteenth century in France, part of Northern Mannerism. It came immediately after High Renaissance and was largely the product of Italian influences...
under architects such as Sebastiano Serlio
Sebastiano Serlio
Sebastiano Serlio was an Italian Mannerist architect, who was part of the Italian team building the Palace of Fontainebleau...
, who was engaged after 1540 in work at the Château de Fontainebleau
Château de Fontainebleau
The Palace of Fontainebleau, located 55 kilometres from the centre of Paris, is one of the largest French royal châteaux. The palace as it is today is the work of many French monarchs, building on an early 16th century structure of Francis I. The building is arranged around a series of courtyards...
. At Fontainebleau Italian artists such as Rosso Fiorentino
Rosso Fiorentino
Giovanni Battista di Jacopo , known as Rosso Fiorentino , or Il Rosso, was an Italian Mannerist painter, in oil and fresco, belonging to the Florentine school.-Biography:...
, Francesco Primaticcio
Francesco Primaticcio
Francesco Primaticcio was an Italian Mannerist painter, architect and sculptor who spent most of his career in France.-Biography:...
, and Niccolo dell' Abbate formed the First School of Fontainebleau
School of Fontainebleau
The Ecole de Fontainebleau refers to two periods of artistic production in France during the late Renaissance centered around the royal Château de Fontainebleau, that were crucial in forming the French version of Northern Mannerism....
. Architects such as Philibert Delorme, Androuet du Cerceau
Androuet du Cerceau
Androuet du Cerceau was a family of French architects and designers active in the 16th and early 17th century.*Jacques I Androuet du Cerceau *Jean Baptiste Androuet du Cerceau...
, Giacomo Vignola, and Pierre Lescot
Pierre Lescot
Pierre Lescot was a French architect active during the French Renaissance, "the man who was first responsible for the implantation of pure and correct classical architecture in France." He was born in Paris....
, were inspired by the new ideas. The southwest interior facade of the Cour Carree of the Louvre
Louvre
The Musée du Louvre – in English, the Louvre Museum or simply the Louvre – is one of the world's largest museums, the most visited art museum in the world and a historic monument. A central landmark of Paris, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the 1st arrondissement...
in Paris was designed by Lescot and covered with exterior carvings by Jean Goujon
Jean Goujon
Jean Goujon was a French Renaissance sculptor and architect.-Biography:His early life is little known; he was likely born in Normandy and may have traveled in Italy...
. Architecture continued to thrive in the reigns of Henry II
Henry II of France
Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
and Henry III
Henry III of France
Henry III was King of France from 1574 to 1589. As Henry of Valois, he was the first elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with the dual titles of King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575.-Childhood:Henry was born at the Royal Château de Fontainebleau,...
.
Baroque
French Baroque is a form of Baroque architectureBaroque architecture
Baroque architecture is a term used to describe the building style of the Baroque era, begun in late sixteenth century Italy, that took the Roman vocabulary of Renaissance architecture and used it in a new rhetorical and theatrical fashion, often to express the triumph of the Catholic Church and...
that evolved in France during the reigns of Louis XIII (1610–43), Louis XIV (1643–1714) and Louis XV (1714–74). French Baroque profoundly influenced 18th-century secular architecture throughout Europe. Although the open three wing layout of the palace was established in France as the canonical
Canonical
Canonical is an adjective derived from canon. Canon comes from the greek word κανών kanon, "rule" or "measuring stick" , and is used in various meanings....
solution as early as the 16th century, it was the Palais du Luxembourg (1615–20) by Salomon de Brosse
Salomon de Brosse
Salomon de Brosse was the most influential early 17th-century French architect, a major influence on François Mansart. Salomon was from a prominent Huguenot family, the grandson through his mother of the designer Jacques I Androuet du Cerceau and the son of the architect Jean de Brosse...
that determined the sober and classicizing direction that French Baroque architecture was to take. For the first time, the corps de logis
Corps de logis
Corps de logis is the architectural term which refers to the principal block of a large, usually classical, mansion or palace. It contains the principal rooms, state apartments and an entry. The grandest and finest rooms are often on the first floor above the ground level: this floor is the...
was emphasized as the representative main part of the building, while the side wings were treated as hierarchically inferior and appropriately scaled down. The medieval tower has been completely replaced by the central projection in the shape of a monumental three-storey gateway.
Probably the most accomplished formulator of the new manner was François Mansart
François Mansart
François Mansart was a French architect credited with introducing classicism into Baroque architecture of France...
, credited with introducing the full Baroque to France. In his design for Château de Maisons
Château de Maisons
The Château de Maisons , designed by François Mansart from 1630 to 1651, is a prime example of French baroque architecture and a reference point in the history of French architecture...
(1642), Mansart succeeded in reconciling academic and baroque approaches, while demonstrating respect for the gothic-inherited idiosyncrasies of the French tradition. Maisons-Laffitte
Maisons-Laffitte
Maisons-Laffitte is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is located in the north-western suburbs of Paris from the center....
illustrates the ongoing transition from the post-medieval chateau
Château
A château is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor or a country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally—and still most frequently—in French-speaking regions...
x of the 16th century to the villa-like country houses of the eighteenth. The structure is strictly symmetrical, with an order applied to each story, mostly in pilaster
Pilaster
A pilaster is a slightly-projecting column built into or applied to the face of a wall. Most commonly flattened or rectangular in form, pilasters can also take a half-round form or the shape of any type of column, including tortile....
form. The frontispiece, crowned with a separate aggrandized roof, is infused with remarkable plasticity and the whole ensemble reads like a three-dimensional whole. Mansart's structures are stripped of overblown decorative effects, so typical of contemporary Rome. Italian Baroque influence is muted and relegated to the field of decorative ornamentation.
The next step in the development of European residential architecture involved the integration of the gardens in the composition of the palace, as is exemplified by Vaux-le-Vicomte
Vaux-le-Vicomte
The Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte is a baroque French château located in Maincy, near Melun, 55 km southeast of Paris in the Seine-et-Marne département of France...
(1656–61), where the architect Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau was a French Classical architect who worked for Louis XIV of France. He was born and died in Paris.He was responsible, with André Le Nôtre and Charles Le Brun, for the redesign of the château of Vaux-le-Vicomte. His later works included the Palace of Versailles and his collaboration...
, the designer Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun , a French painter and art theorist, became the all-powerful, peerless master of 17th-century French art.-Biography:-Early life and training:...
and the gardener André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France...
complemented each other. From the main cornice to a low plinth, the miniature palace is clothed in the so-called "colossal order", which makes the structure look more impressive. The creative collaboration of Le Vau and Le Nôtre marked the arrival of the "Magnificent Manner" which allowed to extend Baroque architecture outside the palace walls and transform the surrounding landscape into an immaculate mosaic of expansive vistas.
Rococo
Rococo developed first in the decorative arts and interior design. Louis XIVLouis XIV of France
Louis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
's succession brought a change in the court artists and general artistic fashion. By the end of the old king's reign, rich Baroque designs were giving way to lighter elements with more curves and natural patterns. These elements are obvious in the architectural designs of Nicolas Pineau
Nicolas Pineau
Nicolas Pineau was a French carver and ornamental designer, one of the leaders who initiated the exuberant asymmetrical phase of the high Rococo. He worked in St...
. During the Régence
Régence
The Régence is the period in French history between 1715 and 1723, when King Louis XV was a minor and the land was governed by a Regent, Philippe d'Orléans, the nephew of Louis XIV of France....
, court life moved away from Versailles
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles , or simply Versailles, is a royal château in Versailles in the Île-de-France region of France. In French it is the Château de Versailles....
and this artistic change became well established, first in the royal palace and then throughout French high society. The delicacy and playfulness of Rococo designs is often seen as perfectly in tune with the excesses of Louis XV
Louis XV of France
Louis XV was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and of Navarre from 1 September 1715 until his death. He succeeded his great-grandfather at the age of five, his first cousin Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, served as Regent of the kingdom until Louis's majority in 1723...
's regime.
The 1730s represented the height of Rococo development in France. Rococo still maintained the Baroque taste for complex forms and intricate patterns, but by this point, it had begun to integrate a variety of diverse characteristics, including a taste for Oriental designs and asymmetric compositions. The style had spread beyond architecture and furniture to painting and sculpture. The Rococo style spread with French artists and engraved publications. It was readily received in the Catholic parts of Germany, Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
, and Austria, where it was merged with the lively German Baroque traditions.

Neoclassicism
The first phase of neoclassicism in France is expressed in the "Louis XVI style" of architects like Ange-Jacques GabrielAnge-Jacques Gabriel
Ange-Jacques Gabriel was the most prominent French architect of his generation.Born to a Parisian family of architects and initially trained by the royal architect Robert de Cotte and his father , whom he assisted in the creation of the Place Royale at Bordeaux , the younger Gabriel...
(Petit Trianon
Petit Trianon
The Petit Trianon is a small château located on the grounds of the Palace of Versailles in Versailles, France.-Design and construction:...
, 1762–68); the second phase, in the styles called Directoire and "Empire
Empire (style)
The Empire style, , sometimes considered the second phase of Neoclassicism, is an early-19th-century design movement in architecture, furniture, other decorative arts, and the visual arts followed in Europe and America until around 1830, although in the U. S. it continued in popularity in...
", might be characterized by Jean Chalgrin
Jean Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris.-Biography:...
's severe astylar Arc de Triomphe
Arc de Triomphe
-The design:The astylar design is by Jean Chalgrin , in the Neoclassical version of ancient Roman architecture . Major academic sculptors of France are represented in the sculpture of the Arc de Triomphe: Jean-Pierre Cortot; François Rude; Antoine Étex; James Pradier and Philippe Joseph Henri Lemaire...
(designed in 1806). In England the two phases might be characterized first by the structures of Robert Adam
Robert Adam
Robert Adam was a Scottish neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam , Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him...
, the second by those of Sir John Soane
John Soane
Sir John Soane, RA was an English architect who specialised in the Neo-Classical style. His architectural works are distinguished by their clean lines, massing of simple form, decisive detailing, careful proportions and skilful use of light sources...
. The interior style in France was initially a Parisian style, the "Goût grec
Goût grec
Goût grec is the term applied to the earliest expression of the neoclassical style in France, it refers specifically to the decorative arts and architecture of the mid-1750s to the late 1760s. The style was more fanciful than historically accurate though the first archaeological surveys of Greece...
" ("Greek style") not a court style. Only when the young king acceded to the throne in 1771 did Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette ; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was an Archduchess of Austria and the Queen of France and of Navarre. She was the fifteenth and penultimate child of Holy Roman Empress Maria Theresa and Holy Roman Emperor Francis I....
, his fashion-loving Queen, bring the "Louis XVI
Louis XVI of France
Louis XVI was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre until 1791, and then as King of the French from 1791 to 1792, before being executed in 1793....
" style to court.
From about 1800 a fresh influx of Greek architectural examples, seen through the medium of etchings and engravings, gave a new impetus to neoclassicism that is called the Greek Revival
Greek Revival architecture
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement of the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in Northern Europe and the United States. A product of Hellenism, it may be looked upon as the last phase in the development of Neoclassical architecture...
. Neoclassicism continued to be a major force in academic art
Academic art
Academic art is a style of painting and sculpture produced under the influence of European academies of art. Specifically, academic art is the art and artists influenced by the standards of the French Académie des Beaux-Arts, which practiced under the movements of Neoclassicism and Romanticism,...
through the 19th century and beyond— a constant antithesis to Romanticism
Romanticism
Romanticism was an artistic, literary and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in Europe, and gained strength in reaction to the Industrial Revolution...
or Gothic revivals— although from the late 19th century on it had often been considered anti-modern, or even reactionary, in influential critical circles. By the mid-19th century, several European cities - notably St Petersburg, Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, Berlin and Munich
Munich
Munich The city's motto is "" . Before 2006, it was "Weltstadt mit Herz" . Its native name, , is derived from the Old High German Munichen, meaning "by the monks' place". The city's name derives from the monks of the Benedictine order who founded the city; hence the monk depicted on the city's coat...
- were transformed into veritable museums of Neoclassical architecture. By comparison, the Greek revival in France was never popular with either the State or the public. What little there is started with Charles de Wailly
Charles De Wailly
Charles De Wailly was a French architect and urbanist, and furniture designer, one of the principals in the Neoclassical revival of the Antique. His major work was the Théâtre de l'Odéon for the Comédie-Française...
's crypt in the church of St Leu-St Gilles (1773–80), and Claude Nicolas Ledoux
Claude Nicolas Ledoux
Claude-Nicolas Ledoux was one of the earliest exponents of French Neoclassical architecture. He used his knowledge of architectural theory to design not only in domestic architecture but town planning; as a consequence of his visionary plan for the Ideal City of Chaux, he became known as a utopian...
's Barriere des Bonshommes (1785-9). First-hand evidence of Greek architecture was of very little importance to the French, due to the influence of Marc-Antoine Laugier
Marc-Antoine Laugier
The abbé Marc-Antoine Laugier was a Jesuit priest and architectural theorist. Laugier is best known for his Essay on Architecture published in 1753. In 1755 he published the second edition with a famous, often reproduced illustration of a primitive hut...
's doctrines that sought to discern the principles of the Greeks instead of their mere practices. It would take until Laboustre's Neo-Grec
Neo-Grec
Neo-Grec is a term referring to late manifestations of Neoclassicism, early Neo-Renaissance now called the Greek Revival style, which was popularized in architecture, the decorative arts, and in painting during France's Second Empire, or the reign of Napoleon III, a period that lasted...
of the second Empire for the Greek revival to flower briefly in France.
Modernist and Contemporary

- Main: Modernist architecture in France
Some renowned modernist and contemporary French designers and architects include:
- Le CorbusierLe CorbusierCharles-Édouard Jeanneret, better known as Le Corbusier , was a Swiss-born French architect, designer, urbanist, writer and painter, famous for being one of the pioneers of what now is called modern architecture. He was born in Switzerland and became a French citizen in 1930...
- Robert Mallet-StevensRobert Mallet-StevensRobert Mallet-Stevens was a French architect and designer. Along with Le Corbusier he is widely regarded as the most influential figure in French architecture in the period between the two World Wars....
- Frédéric BorelFrédéric BorelFrédéric Borel is a French architect, born in 1959 in Roanne . He graduated from the École spéciale d'architecture in 1982, and then began to work with Christian de Portzamparc. He created his own agency in Paris in 1984...
, - Dominique PerraultDominique PerraultDominique Perrault is a French architect. He became world known for the design of the French National Library, distinguished with the Mies van der Rohe Prize in 1996....
, - Christian de PortzamparcChristian de PortzamparcChristian de Portzamparc is a French architect and urbanist. He graduated from the École Nationale des Beaux Arts in Paris in 1970 and has since been noted for his bold designs and artistic touch; his projects reflect a sensibility to their environment and the town is a founding principal of his...
- Jean NouvelJean NouvelJean Nouvel is a French architect. Nouvel studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris and was a founding member of Mars 1976 and Syndicat de l'Architecture...
- List of Post World War II French architects
Examples of mocernist and contemporary buildings in France:
- Villa SavoyeVilla SavoyeVilla Savoye is a modernist villa in Poissy, in the outskirts of Paris, France. It was designed by Swiss architects Le Corbusier and his cousin, Pierre Jeanneret, and built between 1928 and 1931....
- Notre Dame du HautNotre Dame du HautInformally known as "Ronchamp", the chapel of Notre Dame du Haut in Ronchamp , completed in 1954, is one of the finest examples of the architecture of Franco-Swiss architect Le Corbusier and one of the most important examples of twentieth-century religious architecture.-History:Notre Dame du Haut...
- "Chapel du Ronchamp" - Le Corbusier buildings
- Villa NoaillesVilla NoaillesVilla Noailles is an early modernist house, built by architect Robert Mallet-Stevens for art patrons Charles and Marie-Laure de Noailles, between 1923 and 1927. It is located in the hills above Hyères, in the Var, southeastern France.- History :...
- Institut du Monde ArabeArab World InstituteThe Institut du Monde Arabe or Arab World Institute , in English, was established in 1980 in Paris, when 18 Arab countries concluded an agreement with France to establish the Institute to disseminate information about the Arab world and set in motion detailed research to cover Arabic and the Arab...
- Jean Nouvel buildings
French provincial
One of the most distinctive characteristics of many French buildings is the tall second story windows, often arched at the top, that break through the corniceCornice
Cornice molding is generally any horizontal decorative molding that crowns any building or furniture element: the cornice over a door or window, for instance, or the cornice around the edge of a pedestal. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown molding.The function of the projecting...
and rise above the eaves
Eaves
The eaves of a roof are its lower edges. They usually project beyond the walls of the building to carry rain water away.-Etymology:"Eaves" is derived from Old English and is both the singular and plural form of the word.- Function :...
. This unusual window design is especially noticeable on America's French provincial homes. Modelled after country manors in the French provinces, these brick
Brick
A brick is a block of ceramic material used in masonry construction, usually laid using various kinds of mortar. It has been regarded as one of the longest lasting and strongest building materials used throughout history.-History:...
or stucco
Stucco
Stucco or render is a material made of an aggregate, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as decorative coating for walls and ceilings and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture...
homes are stately and formal. They have steep hipped roofs and a square, symmetrical shape with windows balanced on each side of the entrance. The tall second story windows add to the sense of height.
French Normandy
In NormandyNormandy
Normandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
and the Loire Valley
Loire Valley
The Loire Valley , spanning , is located in the middle stretch of the Loire River in central France. Its area comprises approximately . It is referred to as the Cradle of the French Language, and the Garden of France due to the abundance of vineyards, fruit orchards, and artichoke, asparagus, and...
of France, farm silos were often attached to the main living quarters instead of a separate barn. After World War I, Americans romanticized the traditional French farmhouse, creating a style known as French Normandy. Sided with stone
Masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units laid in and bound together by mortar; the term masonry can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are brick, stone, marble, granite, travertine, limestone; concrete block, glass block, stucco, and...
, stucco, or brick, these homes may suggest the Tudor style with decorative half timbering (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal strips of wood set in masonry). The French Normandy style is distinguished by a round stone tower topped by a cone-shaped roof. The tower is usually placed near the centre, serving as the entrance to the home. French Normandy and French provincial details are often combined to create a style simply called French Country or French Rural carved or embossed on mouldings, sconces, and banisters.

Second Empire
During the mid-19th century when Napoleon III established the Second EmpireSecond French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
, Paris became a glamorous city of tall, imposing buildings. Many homes were embellished with details such as paired columns and elaborate wrought iron
Wrought iron
thumb|The [[Eiffel tower]] is constructed from [[puddle iron]], a form of wrought ironWrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon...
cresting appeared along rooftops. But the most striking feature borrowed from this period is the steep, boxy mansard roof
Mansard roof
A mansard or mansard roof is a four-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterized by two slopes on each of its sides with the lower slope at a steeper angle than the upper that is punctured by dormer windows. The roof creates an additional floor of habitable space, such as a garret...
. You can recognize a mansard roof by its trapezoid
Trapezoid
In Euclidean geometry, a convex quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides is referred to as a trapezoid in American English and as a trapezium in English outside North America. A trapezoid with vertices ABCD is denoted...
shape. Unlike a triangular gable
Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of a sloping roof. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system being used and aesthetic concerns. Thus the type of roof enclosing the volume dictates the shape of the gable...
, a mansard roof has almost no slope until the very top, when it abruptly flattens. This nearly perpendicular
Perpendicular
In geometry, two lines or planes are considered perpendicular to each other if they form congruent adjacent angles . The term may be used as a noun or adjective...
roofline creates a sense of majesty, and also allows more usable living space in the attic. In the United States, Second Empire is a Victorian style
Victorian architecture
The term Victorian architecture refers collectively to several architectural styles employed predominantly during the middle and late 19th century. The period that it indicates may slightly overlap the actual reign, 20 June 1837 – 22 January 1901, of Queen Victoria. This represents the British and...
. However, you can also find the practical and the decidedly French mansard roof on many contemporary homes.
Beaux Arts
Another Parisian style, Beaux-Arts originated from the legendary École des Beaux Arts (School of Fine Arts). Flourishing during the 19th and early 20th centuries, it was a grandiose elaboration on the more refined neoclassical style. Symmetrical façades were ornamented with lavish details such as swags, medallions, flowers, and shields. These massive, imposing homes were almost always constructed of stone and were reserved for only the very wealthy. However a more 'humble' home might show Beaux Arts influences if it has stone balconies and masonry ornaments. Many American architects studied at the École des Beaux Arts, and the style strongly influenced United States architecture from about 1880 to 1920.Creole

Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
. French Creole
Louisiana Creole people
Louisiana Creole people refers to those who are descended from the colonial settlers in Louisiana, especially those of French and Spanish descent. The term was first used during colonial times by the settlers to refer to those who were born in the colony, as opposed to those born in the Old World...
buildings borrow traditions from France, the Caribbean, and many other parts of the world. French Creole homes from the Colonial period were especially designed for the hot, wet climate of that region. Traditional French Creole homes had some or all of these features:
- Timber frame with brick or "Bousillage" (mud combined with moss and animal hair)
- Wide hipped roof extends over porches
- Thin wooden columns
- Living quarters raised above ground level
- Wide porches, called "galleries"
- No interior hallways
- Porches used as passageway between rooms
- French doors (doors with many small panes of glass)
See also
French architecture index
- French Colonial ArchitectureFrench ColonialFrench Colonial a style of architecture used by the French during colonization. Many French colonies, especially those in South-East Asia, have previously been reluctant to promote their colonial architecture as an asset for tourism, however in recent times, the new-generation of local authorities...
- ChâteauesqueChâteauesqueChâteauesque is one of several terms, including Francis I style, and, in Canada, the Château Style, that refer to a revival architectural style based on the French Renaissance architecture of the monumental French country homes built in the Loire Valley from the late fifteenth century to the...
- ModernismeModernismeModernisme was a cultural movement associated with the search for Catalan national identity. It is often understood as an equivalent to a number of fin-de-siècle art movements, such as Art Nouveau, Jugendstil, Secessionism, and Liberty style, and was active from roughly 1888 to 1911 Modernisme ...
- Art NouveauArt NouveauArt Nouveau is an international philosophy and style of art, architecture and applied art—especially the decorative arts—that were most popular during 1890–1910. The name "Art Nouveau" is French for "new art"...
- Art decoArt DecoArt deco , or deco, is an eclectic artistic and design style that began in Paris in the 1920s and flourished internationally throughout the 1930s, into the World War II era. The style influenced all areas of design, including architecture and interior design, industrial design, fashion and...
- Fountains in FranceFountains in FranceFountains in France provided drinking water to the inhabitants of the ancient Roman cities of France, and to French monasteries and villages during the Middle Ages. Later, they were symbols of royal power and grandeur in the gardens of the Kings of France...
- Gardens of the French RenaissanceGardens of the French RenaissanceThe Gardens of the French Renaissance is a garden style largely inspired by the Italian Renaissance garden, particularly the gardens of Florence and Rome. King Charles VIII and his nobles brought the style back to France after their campaign in Italy in 1495...
- Jardin à la françaiseGarden à la françaiseThe French formal garden, also called jardin à la française, is a style of garden based on symmetry and the principle of imposing order over nature. It reached its apogee in the 17th century with the creation of the Gardens of Versailles, designed for Louis XIV by the landscape architect André Le...
- French landscape gardenFrench landscape gardenThe French landscape garden is a style of garden inspired by idealized Italian landscapes and the romantic paintings of Hubert Robert, Claude Lorrain and Nicolas Poussin, European ideas about Chinese gardens, and the philosophy of Jean-Jacques Rousseau...
- Remarkable Gardens of France
- Gardens in France index

