Frenkel defect
Encyclopedia
The Frenkel Defect is shown by ionic solids. The smaller ion (usually the cation) is displaced from its lattice position to an interstitial site. It creates a vacancy defect at its original site and an interstitial defect at its new location.
lattice
. The defect forms when an atom
or cation leaves its place in the lattice, creating a vacancy, and becomes an interstitial
by lodging in a nearby location not usually occupied by an atom. Frenkel defects occur due to thermal vibrations, and it is theorized that there will be no defects in a crystal at 0 K
. The phenomenon is named after the Soviet
physicist Yakov Frenkel
, who discovered it in 1926.
)
Some solids which display this defect - ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, AgI (due to the comparatively smaller size of Zn2+ and Ag+ ions)
To be noted : AgBr shows both Frenkel as well as Schottky defects
.
For example, consider a lattice formed by X and M ions. Suppose an M ion leaves the M sublattice, leaving the X sublattice unchanged. The number of interstitials formed will equal the number of vacancies formed.
One form of a Frenkel defect reaction in MgO with the oxygen ion leaving the lattice and going into the interstitial site written in Kröger–Vink notation:
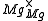 +
+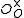 →
→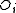 +
+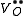 +
+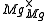
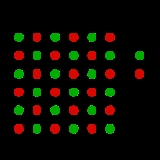
This can be illustrated with the example of the sodium chloride crystal structure. The diagrams below are schematic two-dimensional representations.
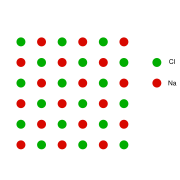
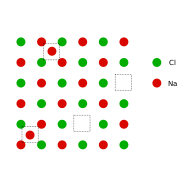
Definition
A Frenkel defect, Frenkel pair, or Frenkel disorder is a type of point defect in a crystalCrystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
lattice
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
. The defect forms when an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
or cation leaves its place in the lattice, creating a vacancy, and becomes an interstitial
Interstitial defect
Interstitials are a variety of crystallographic defects, i.e. atoms which occupy a site in the crystal structure at which there is usually not an atom, or two or more atoms sharing one or more lattice sites such that the number of atoms is larger than the number of lattice sites.They are generally...
by lodging in a nearby location not usually occupied by an atom. Frenkel defects occur due to thermal vibrations, and it is theorized that there will be no defects in a crystal at 0 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
. The phenomenon is named after the Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
physicist Yakov Frenkel
Yakov Frenkel
Yakov Il'ich Frenkel, was a Soviet physicist renowned for his works in the field of solid-state physics. He is also known as Jacov Frenkel....
, who discovered it in 1926.
Effect on Density
This defect does not change the density of the solid as it involves only the migration of the ions within the crystal, thus preserving both the volume as well as mass.Examples
It is shown in ionic solids with large size difference between the anion and cation (with the cation usually smaller due to an increased effective nuclear chargeEffective nuclear charge
The effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom. The term "effective" is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge by the repelling effect...
)
Some solids which display this defect - ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, AgI (due to the comparatively smaller size of Zn2+ and Ag+ ions)
To be noted : AgBr shows both Frenkel as well as Schottky defects
Schottky defect
A Schottky defect is a type of point defect in a crystal lattice named after Walter H. Schottky.The defect forms when oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites, creating vacancies. These vacancies are formed in stoichiometric units, to maintain an overall neutral charge in the ionic solid....
.
For example, consider a lattice formed by X and M ions. Suppose an M ion leaves the M sublattice, leaving the X sublattice unchanged. The number of interstitials formed will equal the number of vacancies formed.
One form of a Frenkel defect reaction in MgO with the oxygen ion leaving the lattice and going into the interstitial site written in Kröger–Vink notation:
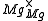 +
+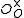 →
→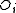 +
+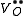 +
+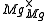
This can be illustrated with the example of the sodium chloride crystal structure. The diagrams below are schematic two-dimensional representations.



