Interstitial defect
Encyclopedia
Interstitials are a variety of crystallographic defects, i.e. atoms which occupy a site in the crystal structure
at which there is usually not an atom, or two or more atoms sharing one or more lattice sites such that the number of atoms is larger than the number of lattice sites.
They are generally high energy configurations.
Small atoms in some crystal
s can occupy interstitial sites in an energetically favourable configuration, such as hydrogen in palladium.
Interstitials can be produced for instance by particle irradiation
above the
threshold displacement energy
, but may also exist in small
concentrations in thermodynamic equilibrium.
those already present in the lattice.
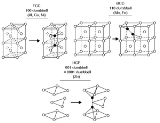
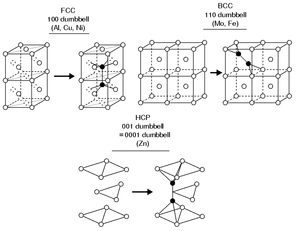 The structure of interstitial defects has been experimentally
The structure of interstitial defects has been experimentally
determined in some metal
s and semiconductors.
Contrary to what one might
intuitively expect, most self-interstitials in metals with a known structure
have a 'split' structure, in which two atoms share the same lattice site.
Typically the center of mass
of the two atoms is at the lattice site,
and they are displaced symmetrically from it along one of the
principal lattice directions
. For instance,
in several common FCC metals such as copper, nickel and platinum, the
ground state structure of the self-interstitial is
the split [100] interstitial structure, where two atoms are
displaced in a positive and negative [100] direction from
the lattice site. In BCC iron the ground state
interstitial structure is similarly a [110] split
interstitial.
Curiously enough, these split interstitials are often
called dumbbell interstitials, because plotting the two
atoms forming the interstitial with two large spheres
and a thick line joining them makes the structure resemble
a dumbbell
weight-lifting device.
In other BCC metals than iron, the ground state structure is believed
to be the [111] crowdion interstitial (although the issue
is still not well established), which can be
understood as a long chain (typically some 10-20)
of atoms along the [111] lattice direction, compressed
compared to the perfect lattice such that the chain contains one extra atom.
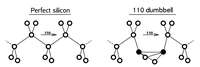 In semiconductors the situation is more complex, since defects may be charged
In semiconductors the situation is more complex, since defects may be charged
and different charge states may have different structures. For instance, in silicon, the interstitial may either have a split [110] structure or a tetrahedral truly interstitial one.
off-lattice sites between the lattice atoms.
Such sites can be characterized by the symmetry
of the
interstitial atom position with respect to its
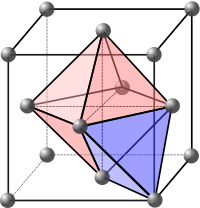
nearest lattice atoms. For instance, an impurity atom
I with 4 nearest lattice atom A neighbours (at equal distances)
in a FCC lattice is in
a tetrahedral symmetry position, and thus can be called a
tetrahedral interstitial.
Large impurity interstitials can also be in
split interstitial configurations together with a
lattice atom, similar to those of the self-interstitial atom.
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
at which there is usually not an atom, or two or more atoms sharing one or more lattice sites such that the number of atoms is larger than the number of lattice sites.
They are generally high energy configurations.
Small atoms in some crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
s can occupy interstitial sites in an energetically favourable configuration, such as hydrogen in palladium.
Interstitials can be produced for instance by particle irradiation
Particle radiation
Particle radiation is the radiation of energy by means of fast-moving subatomic particles. Particle radiation is referred to as a particle beam if the particles are all moving in the same direction, similar to a light beam....
above the
threshold displacement energy
Threshold displacement energy
The threshold displacement energy T_d is the minimum kinetic energythat an atom in a solid needs to be permanentlydisplaced from its lattice site to adefect position.It is also known as "displacement threshold energy" or just "displacement energy"....
, but may also exist in small
concentrations in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Self-interstitials
Self-interstitial defects are interstitial defects which contain only atoms which are the same asthose already present in the lattice.

determined in some metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
s and semiconductors.
Contrary to what one might
intuitively expect, most self-interstitials in metals with a known structure
have a 'split' structure, in which two atoms share the same lattice site.
Typically the center of mass
Center of mass
In physics, the center of mass or barycenter of a system is the average location of all of its mass. In the case of a rigid body, the position of the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body...
of the two atoms is at the lattice site,
and they are displaced symmetrically from it along one of the
principal lattice directions
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
. For instance,
in several common FCC metals such as copper, nickel and platinum, the
ground state structure of the self-interstitial is
the split [100] interstitial structure, where two atoms are
displaced in a positive and negative [100] direction from
the lattice site. In BCC iron the ground state
interstitial structure is similarly a [110] split
interstitial.
Curiously enough, these split interstitials are often
called dumbbell interstitials, because plotting the two
atoms forming the interstitial with two large spheres
and a thick line joining them makes the structure resemble
a dumbbell
Dumbbell
The dumbbell, a type of free weight, is a piece of equipment used in weight training. It can be used individually or in pairs .-History:...
weight-lifting device.
In other BCC metals than iron, the ground state structure is believed
to be the [111] crowdion interstitial (although the issue
is still not well established), which can be
understood as a long chain (typically some 10-20)
of atoms along the [111] lattice direction, compressed
compared to the perfect lattice such that the chain contains one extra atom.
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
and different charge states may have different structures. For instance, in silicon, the interstitial may either have a split [110] structure or a tetrahedral truly interstitial one.
Impurity interstitials
Small impurity interstitial atoms are usually on trueoff-lattice sites between the lattice atoms.
Such sites can be characterized by the symmetry
Symmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
of the
interstitial atom position with respect to its
nearest lattice atoms. For instance, an impurity atom
I with 4 nearest lattice atom A neighbours (at equal distances)
in a FCC lattice is in
a tetrahedral symmetry position, and thus can be called a
tetrahedral interstitial.
Large impurity interstitials can also be in
split interstitial configurations together with a
lattice atom, similar to those of the self-interstitial atom.

Effects of interstitials
Interstitials modify the physical and chemical properties of materials.- Interstitial carbon atoms have a crucial role for the properties and processing of steels, in particular carbon steels.
- Impurity interstitials can be used e.g. for storage of hydrogen in metals.
- The amorphization of semiconductors such as silicon during ion irradiation is often explained by the buildup of a high concentration of interstitials leading eventually to the collapse of the lattice as it becomes unstable
- Creation of large amounts of interstitials in a solid can lead to a significant energy buildup, which on release can even lead to severe accidents in certain old types of nuclear reactors (Wigner effectWigner effectThe Wigner effect , also known as the discomposition effect, is the displacement of atoms in a solid caused by neutron radiation....
). The high-energy states can be released by annealingAnnealing (metallurgy)Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
.
- At least in face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice, interstitials have a large diaelastic softening effect on the material
- It has been proposed that interstitials are related to the onset of melting and the glass transitionGlass transitionThe liquid-glass transition is the reversible transition in amorphous materials from a hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass...
.

