Frequency comb
Encyclopedia
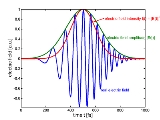
A frequency comb is the graphic representation of the spectrum of a mode locked laser
. An octave spanning comb can be used for mapping radio frequencies into the optical frequency range or it can be used to steer a piezoelectric mirror
within a carrier envelope phase correcting feedback loop. (It should not be confused with mono-mode laser frequency stabilization as mode-locking requires multi-mode lasers.)
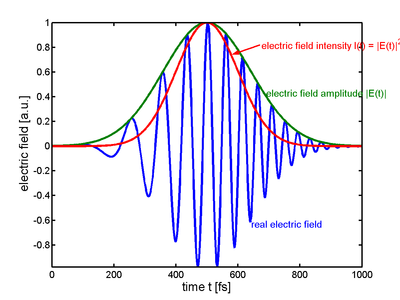
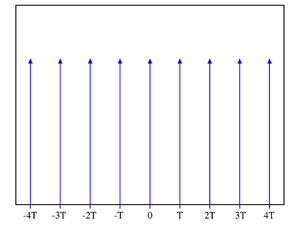
ed lasers produce a series of optical pulses separated in time by the round-trip time of the laser cavity. The spectrum of such a pulse train is a series of Dirac delta function
s separated by the repetition rate (the inverse of the round trip time) of the laser.
This series of sharp spectral lines is called a frequency comb or a frequency Dirac comb
.
A purely electronic device, which generates a series of pulses, also generates a frequency comb. These are produced for electronic sampling oscilloscopes, but also used for frequency comparison of microwaves, because they reach up to 1 THz. Since they include 0 Hz they do not need the tricks which make up the rest of this article.
: that is, the highest-frequency must be at least double the lowest frequency. One of three techniques may be used:
Measurement of the carrier-envelope offset frequency is usually done with a self-referencing technique, in which the phase of one part of the spectrum is compared to its harmonic.
In the 'frequency − 2 × frequency' technique, light at the lower energy side of the broadened spectrum is doubled using second harmonic generation
in a nonlinear crystal and a heterodyne
beat is generated between that and light at the same wavelength on the upper energy side of the spectrum. This beat frequency, detectable with a photodiode
, is the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
Alternatively, from light at the higher energy side of the broadened spectrum the frequency at the peak of the spectrum is subtracted in a nonlinear crystal and a heterodyne
beat is generated between that and light at the same wavelength on the lower energy side of the spectrum. This beat frequency, detectable with a photodiode
, is the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
Because the phase is measured directly
and not the frequency, it is possible to set the frequency to zero and additionally lock the phase, but because the intensity of the laser and this detector is not very stable, and because the whole spectrum beats in phase
source,
one has to lock the phase on a fraction of the repetition rate.
. The repetition rate can be stabilized using a piezoelectric transducer, which moves a mirror to change the cavity length.
In Ti:sapphire lasers using prism
s for dispersion control, the carrier-envelope offset frequency can be controlled by tilting the high reflector mirror at the end of the prism pair. This can be done using piezoelectric transducers.
In high repetition rate Ti:sapphire ring lasers, which often use double-chirped mirrors to control dispersion, modulation of the pump power using an acousto-optic modulator
is often used to control the offset frequency. The phase slip depends strongly on the Kerr effect, and by changing the pump power one changes the peak intensity of the laser pulse and thus the size of the Kerr phase shift. This shift is far smaller than 6 rad, so an additional device for coarse adjustment is needed.
See also: phase-locked loop
The breakthrough which led to a practical frequency comb was the development of technology for stabilizing the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
standards to optical frequencies. Current frequency standards such as atomic clocks operate in the microwave
region of the spectrum, and the frequency comb brings the accuracy of such clocks into the optical part of the electromagnetic spectrum. A simple electronic feedback loop can lock the repetition rate to a frequency standard.
There are two distinct applications of this technique. One is the optical clock where an optical frequency is overlapped with a single tooth of the comb on a photodiode and a radio frequency is compared to the beat signal, the repetition rate, and the CEO-frequency. Applications for the frequency comb technique include optical metrology
, frequency chain generation, optical atomic clocks, high precision spectroscopy, and more precise GPS technology..
The other is doing experiments with few cycle pulses
, like above threshold ionization
, attosecond pulse
s, highly efficient nonlinear optics
or high harmonics generation. This can be single pulses so that no comb exists and therefore it is not possible to define a carrier envelope offset frequency, rather the carrier envelope offset phase is important. A second photodiode can be added to the setup to gather phase and amplitude in a single shot, or difference frequency generation can be used to even lock the offset on a single shot basis albeit with low power efficiency.
Without an actual comb one can look at the phase vs frequency. Without a carrier envelope offset all frequencies are cosines. That means all frequencies have the phase zero. The time origin is arbitrary. If a pulse comes at later times, the phase increases linearly with frequency, but still the zero frequency phase is zero. This phase at zero frequency is the carrier envelope offset. The second harmonic not only has twice the frequency but also twice the phase. That means for a pulse with zero offset the second harmonic of the low frequency tail is in phase with the fundamental of the high frequency tail and otherwise it is not. Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction
(SPIDER) measures how the phase increases with frequency, but it cannot determine the offset, so the name “electric field reconstruction” is a bit misleading.
shared half of the 2005 Nobel Prize
in Physics for contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique. The other half of the prize was awarded to Roy Glauber.
In 2006 the femtosecond comb technique was extended to the extreme ultraviolet range, enabling frequency metrology in that region of the spectrum.
Modelocking
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
. An octave spanning comb can be used for mapping radio frequencies into the optical frequency range or it can be used to steer a piezoelectric mirror
Mirror mount
A mirror mount is a device that holds a mirror. In optics research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted.Precision mirror mounts can be quite...
within a carrier envelope phase correcting feedback loop. (It should not be confused with mono-mode laser frequency stabilization as mode-locking requires multi-mode lasers.)


Frequency comb generation
ModelockModelocking
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
ed lasers produce a series of optical pulses separated in time by the round-trip time of the laser cavity. The spectrum of such a pulse train is a series of Dirac delta function
Dirac delta function
The Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
s separated by the repetition rate (the inverse of the round trip time) of the laser.
This series of sharp spectral lines is called a frequency comb or a frequency Dirac comb
Dirac comb
In mathematics, a Dirac comb is a periodic Schwartz distribution constructed from Dirac delta functions...
.
A purely electronic device, which generates a series of pulses, also generates a frequency comb. These are produced for electronic sampling oscilloscopes, but also used for frequency comparison of microwaves, because they reach up to 1 THz. Since they include 0 Hz they do not need the tricks which make up the rest of this article.
Frequency comb widening to one octave
To be usable, the comb must be widened to at least an octaveOctave (electronics)
In electronics, an octave is a doubling or halving of a frequency. The term is derived from the musical octave which similarly describes such frequency ratios, but the prefix octa-, denoting eight, has no significance in physics...
: that is, the highest-frequency must be at least double the lowest frequency. One of three techniques may be used:
- supercontinuumSupercontinuumIn optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam. The result is a smooth spectral continuum...
generation by strong self-phase modulation in nonlinear photonic crystal fiber - a Ti:sapphire laser using intracavity self-phase modulationSelf-phase modulationSelf-phase modulation is a nonlinear optical effect of light-matter interaction.An ultrashort pulse of light, when travelling in a medium, will induce a varying refractive index of the medium due to the optical Kerr effect...
- the second harmonic can be generated in a long crystal so that by consecutive sum frequency generation and difference frequency generation the spectrum of first and second harmonic widens until they overlap.
Carrier-envelope offset measurement
Each line is displaced from a harmonic of the repetition rate by the carrier-envelope offset frequency. The carrier-envelope offset frequency is the rate at which the peak of the carrier frequency slips from the peak of the pulse envelope on a pulse-to-pulse basis.Measurement of the carrier-envelope offset frequency is usually done with a self-referencing technique, in which the phase of one part of the spectrum is compared to its harmonic.
In the 'frequency − 2 × frequency' technique, light at the lower energy side of the broadened spectrum is doubled using second harmonic generation
Second harmonic generation
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
in a nonlinear crystal and a heterodyne
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden where high frequency signals are converted to lower frequencies by combining two frequencies. Heterodyning is useful for frequency shifting information of interest into a useful...
beat is generated between that and light at the same wavelength on the upper energy side of the spectrum. This beat frequency, detectable with a photodiode
Photodiode
A photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.The common, traditional solar cell used to generateelectric solar power is a large area photodiode....
, is the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
Alternatively, from light at the higher energy side of the broadened spectrum the frequency at the peak of the spectrum is subtracted in a nonlinear crystal and a heterodyne
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden where high frequency signals are converted to lower frequencies by combining two frequencies. Heterodyning is useful for frequency shifting information of interest into a useful...
beat is generated between that and light at the same wavelength on the lower energy side of the spectrum. This beat frequency, detectable with a photodiode
Photodiode
A photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.The common, traditional solar cell used to generateelectric solar power is a large area photodiode....
, is the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
Because the phase is measured directly
Phase detector
A phase detector or phase comparator is a frequency mixer, analog multiplier or logic circuit that generates a voltage signal which represents the difference in phase between two signal inputs...
and not the frequency, it is possible to set the frequency to zero and additionally lock the phase, but because the intensity of the laser and this detector is not very stable, and because the whole spectrum beats in phase
source,
one has to lock the phase on a fraction of the repetition rate.
Carrier-envelope offset control
In the absence of active stabilization, the repetition rate and carrier-envelope offset frequency would be free to drift. They vary with changes in the cavity length, refractive index of laser optics, and nonlinear effects such as the Kerr effectKerr effect
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic effect , is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change is directly proportional to the square of the electric...
. The repetition rate can be stabilized using a piezoelectric transducer, which moves a mirror to change the cavity length.
In Ti:sapphire lasers using prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
s for dispersion control, the carrier-envelope offset frequency can be controlled by tilting the high reflector mirror at the end of the prism pair. This can be done using piezoelectric transducers.
In high repetition rate Ti:sapphire ring lasers, which often use double-chirped mirrors to control dispersion, modulation of the pump power using an acousto-optic modulator
Acousto-optic modulator
An acousto-optic modulator , also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves . They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric...
is often used to control the offset frequency. The phase slip depends strongly on the Kerr effect, and by changing the pump power one changes the peak intensity of the laser pulse and thus the size of the Kerr phase shift. This shift is far smaller than 6 rad, so an additional device for coarse adjustment is needed.
See also: phase-locked loop
Phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
The breakthrough which led to a practical frequency comb was the development of technology for stabilizing the carrier-envelope offset frequency.
Applications
A frequency comb allows a direct link from radio frequencyRadio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
standards to optical frequencies. Current frequency standards such as atomic clocks operate in the microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
region of the spectrum, and the frequency comb brings the accuracy of such clocks into the optical part of the electromagnetic spectrum. A simple electronic feedback loop can lock the repetition rate to a frequency standard.
There are two distinct applications of this technique. One is the optical clock where an optical frequency is overlapped with a single tooth of the comb on a photodiode and a radio frequency is compared to the beat signal, the repetition rate, and the CEO-frequency. Applications for the frequency comb technique include optical metrology
Metrology
Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. The word comes from Greek μέτρον , "measure" + "λόγος" , amongst others meaning "speech, oration, discourse, quote, study, calculation, reason"...
, frequency chain generation, optical atomic clocks, high precision spectroscopy, and more precise GPS technology..
The other is doing experiments with few cycle pulses
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
, like above threshold ionization
Above threshold ionization
Above Threshold Ionization – in quantum mechanics ionization of the atom with the electromagnetic radiation with violation of Einstein formula i.e. when the kinetic energy of emitted electrons is larger than the difference between the photon energy and the ionization energy or the work function...
, attosecond pulse
Attophysics
Attophysics is a branch of physics wherein attosecond duration pulses of electrons or photons are used to probe dynamic processes in matter with unprecedented time resolution. This branch of Physics which involves studying some of the fastest physical events is also known as attoscience...
s, highly efficient nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
or high harmonics generation. This can be single pulses so that no comb exists and therefore it is not possible to define a carrier envelope offset frequency, rather the carrier envelope offset phase is important. A second photodiode can be added to the setup to gather phase and amplitude in a single shot, or difference frequency generation can be used to even lock the offset on a single shot basis albeit with low power efficiency.
Without an actual comb one can look at the phase vs frequency. Without a carrier envelope offset all frequencies are cosines. That means all frequencies have the phase zero. The time origin is arbitrary. If a pulse comes at later times, the phase increases linearly with frequency, but still the zero frequency phase is zero. This phase at zero frequency is the carrier envelope offset. The second harmonic not only has twice the frequency but also twice the phase. That means for a pulse with zero offset the second harmonic of the low frequency tail is in phase with the fundamental of the high frequency tail and otherwise it is not. Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction
Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction
In ultrafast optics, spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction is an ultrashort pulse measurement technique.-The basics:...
(SPIDER) measures how the phase increases with frequency, but it cannot determine the offset, so the name “electric field reconstruction” is a bit misleading.
History
Theodor W. Hänsch and John L. HallJohn L. Hall
John Lewis "Jan" Hall is an American physicist, and Nobel laureate in physics. He shared one half of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics with Theodor W. Hänsch for his work in precision spectroscopy.-Biography:...
shared half of the 2005 Nobel Prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
in Physics for contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique. The other half of the prize was awarded to Roy Glauber.
In 2006 the femtosecond comb technique was extended to the extreme ultraviolet range, enabling frequency metrology in that region of the spectrum.

