
Gain (information retrieval)
Encyclopedia
The gain, also called improvement over random can be specified for a classifier and is an important measure to describe the performance of it.
The gain is defined as described in the following:
of a classifier is defined as
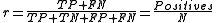
where TP, TN, FP and FN are the numbers of true positives, true negatives, false positives and false negatives respectively, positives is the number of positive instances in the target dataset and N is the size of the dataset.
The random precision defines the lowest baseline of a classifier.
And Gain is defined as

which gives a factor by which a classifier is better when compared to its random counterpart. A Gain of 1 would indicate a classifier that is not better than random. The larger the gain, the better.
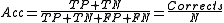
Here, the random accuracy of a classifier can be defined as

f(Positives) and f(Negatives) is the fraction of positive and negative classes in the dataset.
And again gain is
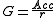
This time the gain is measured not only with respect to the prediction of a so called positive class, but with respect to the overall classifier ability to distinguish the two equally important classes.
as an example, the gain is measured for methods that predict residue contacts in proteins.
Definition
In the following a random classifier is defined such that it randomly predicts the same amount of either class.The gain is defined as described in the following:
Gain in Precision
The random precisionPositive predictive value
In statistics and diagnostic testing, the positive predictive value, or precision rate is the proportion of subjects with positive test results who are correctly diagnosed. It is a critical measure of the performance of a diagnostic method, as it reflects the probability that a positive test...
of a classifier is defined as
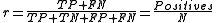
where TP, TN, FP and FN are the numbers of true positives, true negatives, false positives and false negatives respectively, positives is the number of positive instances in the target dataset and N is the size of the dataset.
The random precision defines the lowest baseline of a classifier.
And Gain is defined as

which gives a factor by which a classifier is better when compared to its random counterpart. A Gain of 1 would indicate a classifier that is not better than random. The larger the gain, the better.
Gain in Overall Accuracy
The accuracy of a classifier in general is defined as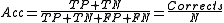
Here, the random accuracy of a classifier can be defined as

f(Positives) and f(Negatives) is the fraction of positive and negative classes in the dataset.
And again gain is
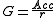
This time the gain is measured not only with respect to the prediction of a so called positive class, but with respect to the overall classifier ability to distinguish the two equally important classes.
Application
In BioinformaticsBioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
as an example, the gain is measured for methods that predict residue contacts in proteins.
See also
- Performance Measures a summary
- Accuracy
- Accuracy and precisionAccuracy and precisionIn the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
- Recall
- Sensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...

