
Galaxy filament
Encyclopedia
In physical cosmology
, galaxy filaments, also called supercluster complexes or great walls, are, so far, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
. They are massive, thread-like structures with a typical length of 50 to 80 megaparsecs h-1 that form the boundaries between large voids
in the universe. Filaments consist of gravitationally bound galaxies
; parts where a large number of galaxies are very close to each other are called superclusters.
Discoveries of superclusters started in the 1980s. In 1987 astronomer
R. Brent Tully
of the University of Hawaii
’s Institute of Astronomy identified what he called the Pisces-Cetus Supercluster Complex
. In 1989 the CfA2 Great Wall was discovered, followed by the Sloan Great Wall
in 2003.
In 2006, scientists announced the discovery of three filaments aligned to form the largest structure known to humanity , composed of densely packed galaxies and enormous blobs of gas known as Lyman alpha blobs.
In 2011 further study was conducted by undergraduate students at Monash University in Australia that amounted to several hypotheses for the nature of filaments. One student, Amelia Fraser-McKelvie, confirmed through X-ray analysis that filaments contain an amount of mass large enough to contend with the theory of dark matter
. Supervising Monash astrophysicist Dr. Kevin Pimbblet's earlier work had suggested the filaments as a possible location for the "missing" matter, thought to be low in density but high in temperature.
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, galaxy filaments, also called supercluster complexes or great walls, are, so far, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. They are massive, thread-like structures with a typical length of 50 to 80 megaparsecs h-1 that form the boundaries between large voids
Void (astronomy)
In astronomy, voids are the empty spaces between filaments, the largest-scale structures in the Universe, that contain very few, or no, galaxies. They were first discovered in 1978 during a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson at the Kitt Peak National Observatory...
in the universe. Filaments consist of gravitationally bound galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
; parts where a large number of galaxies are very close to each other are called superclusters.
Discoveries of superclusters started in the 1980s. In 1987 astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
R. Brent Tully
R. Brent Tully
R. Brent Tully is an astronomer at the Institute for Astronomy in Honolulu, Hawaii.Tully's specialty is astrophysics of galaxies. He, along with J. Richard Fisher, proposed the now-famous Tully-Fisher relation in a paper, A New Method of Determining Distances to Galaxies, published in Astronomy...
of the University of Hawaii
University of Hawaii
The University of Hawaii System, formally the University of Hawaii and popularly known as UH, is a public, co-educational college and university system that confers associate, bachelor, master, and doctoral degrees through three university campuses, seven community college campuses, an employment...
’s Institute of Astronomy identified what he called the Pisces-Cetus Supercluster Complex
Pisces-Cetus Supercluster Complex
The Pisces-Cetus Supercluster Complex is a complex of galaxy superclusters or galaxy filament that includes the Virgo Supercluster .-Discovery:...
. In 1989 the CfA2 Great Wall was discovered, followed by the Sloan Great Wall
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies , and to the present day it is the largest known structure in the universe. Its discovery was announced on October 20, 2003 by J. Richard Gott III of Princeton University and Mario Jurić and their colleagues, based on...
in 2003.
In 2006, scientists announced the discovery of three filaments aligned to form the largest structure known to humanity , composed of densely packed galaxies and enormous blobs of gas known as Lyman alpha blobs.
In 2011 further study was conducted by undergraduate students at Monash University in Australia that amounted to several hypotheses for the nature of filaments. One student, Amelia Fraser-McKelvie, confirmed through X-ray analysis that filaments contain an amount of mass large enough to contend with the theory of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
. Supervising Monash astrophysicist Dr. Kevin Pimbblet's earlier work had suggested the filaments as a possible location for the "missing" matter, thought to be low in density but high in temperature.
Galaxy filaments
Filament subtype of filaments have roughly similar major and minor axes in cross-section, along the lengthwise axis.| Filament | Date | Mean Distance | Dimension | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coma Filament | The Coma Supercluster Coma Supercluster The Coma Supercluster is a nearby supercluster of galaxies comprising the Coma Cluster and the Leo Cluster . Located 300 million light-years from Earth, it is in the center of the Great Wall. The Coma Supercluster is the nearest massive cluster of galaxies to our own Virgo Supercluster... lies within the Coma Filament. It forms part of the CfA2 Great Wall. |
|||
| Perseus-Pegasus Filament | 1985 | Connected to the Pisces-Cetus Supercluster, with the Perseus-Pisces Supercluster Perseus-Pisces Supercluster The Perseus-Pisces Supercluster is one of the largest known structures in the universe. Even at a distance of 250 million light-years, this chain of galaxy clusters extends more than 40° across the northern winter sky... being a member of the filament. |
||
| Ursa Major Filament | Connected to the CfA Homunculus, a portion of the filament forms a portion of the "leg" of the Homunculus. | |||
| Lynx-Ursa Major Filament (LUM Filament) | 1999 | from 2000 km/s to 8000 km/s in redshift space | Connected to and separate from the Lynx-Ursa Major Supercluster. | |
| z=2.38 filament around protocluster ClG J2143-4423 | 2004 | z=2.38 | 110Mpc | A filament the length of the Great Wall was discovered in 2004. As of 2008, it was still the largest structure beyond redshift 2. |
Galaxy walls
The Galaxy wall subtype of filaments have a significantly greater major axis than minor axis in cross-section, along the lengthwise axis.| Wall | Date | Mean Distance | Dimension | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CfA2 Great Wall (Coma Wall, Great Wall, Northern Great Wall, Great Northern Wall, CfA Great Wall) | 1989 | z=0.03058 | 251Mpc long
|
This was the first super-large large-scale structure or pseudo-structure in the universe to be discovered. It is also the second largest. The CfA Homunculus lies at the heart of the Great Wall, and the Coma Supercluster Coma Supercluster The Coma Supercluster is a nearby supercluster of galaxies comprising the Coma Cluster and the Leo Cluster . Located 300 million light-years from Earth, it is in the center of the Great Wall. The Coma Supercluster is the nearest massive cluster of galaxies to our own Virgo Supercluster... forms most of the homunculus structure. The Coma Cluster lies at the core. |
| Sloan Great Wall Sloan Great Wall The Sloan Great Wall is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies , and to the present day it is the largest known structure in the universe. Its discovery was announced on October 20, 2003 by J. Richard Gott III of Princeton University and Mario Jurić and their colleagues, based on... (SDSS Great Wall) |
2005 | z=0.07804 | 433Mpc long | This is the largest known structure or pseudo-structure in the universe discovered so far. |
| Sculptor Wall Sculptor Wall The Sculptor Wall is a superstructure of galaxies relatively near to the Milky Way Galaxy , also known as the Sculptor superclusters.... (Southern Great Wall, Great Southern Wall, Southern Wall) |
8000 km/s long 5000 km/s wide 1000 km/s deep (in redshift space dimensions) |
The Sculptor Wall is "parallel" to the Fornax Wall and "perpendicular" to the Grus Wall. | ||
| Grus Wall | The Grus Wall is "perpendicular" to the Fornax and Sculptor Walls. | |||
| Fornax Wall | The Fornax Cluster Fornax Cluster At a distance of approximately 62.0 Mly , the Fornax Cluster is the second richest cluster of galaxies within 100 million light-years, although it is much smaller than the Virgo Cluster. It lies primarily in the constellation Fornax, and may be associated with the nearby Eridanus Group... is part of this wall. The wall is "parallel" to the Sculptor Wall and "perpendicular" to the Grus Wall. |
|||
- A Centaurus Wall or Centaurus Great Wall has been proposed, and would have the Fornax Wall as a portion of it, visually created by the Zone of AvoidanceZone of AvoidanceThe Zone of Avoidance is the area of the night sky that is obscured by our own galaxy, the Milky Way.-Term:The ZOA was originally called the "Zone of Few Nebulae" in an 1878 paper by English astronomer Richard Proctor that referred to the distribution of "nebulae" in Sir John Herschel's General...
. It would also include the Centaurus Supercluster and the Local Supercluster, (this would then be the Local Wall or Local Great Wall)
- A wall has been proposed to be the physical embodiment of the Great AttractorGreat AttractorThe Great Attractor is a gravity anomaly in intergalactic space within the range of the Centaurus Supercluster that reveals the existence of a localised concentration of mass equivalent to tens of thousands of Milky Ways, observable by its effect on the motion of galaxies and their associated...
, with the Norma ClusterNorma clusterThe Norma Cluster is a rich cluster of galaxies located near the center of the Great Attractor. Although it is both nearby and bright, it is difficult to observe because it is located in the Zone of Avoidance, a region near the plane of the Milky Way. Consequently, the cluster is severely...
as part of this wall. This wall is also referred to as the Great Attractor Wall or Norma Wall.
- A wall has been proposed, in 2000, to lie at z=1.47 in the vicinity of radio galaxy B3 0003+387.
- A wall has been proposed, in 2000, to lie at z=0.559 in the northern Hubble Deep FieldHubble Deep FieldThe Hubble Deep Field is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, two parts in a million of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis...
(HDF North).
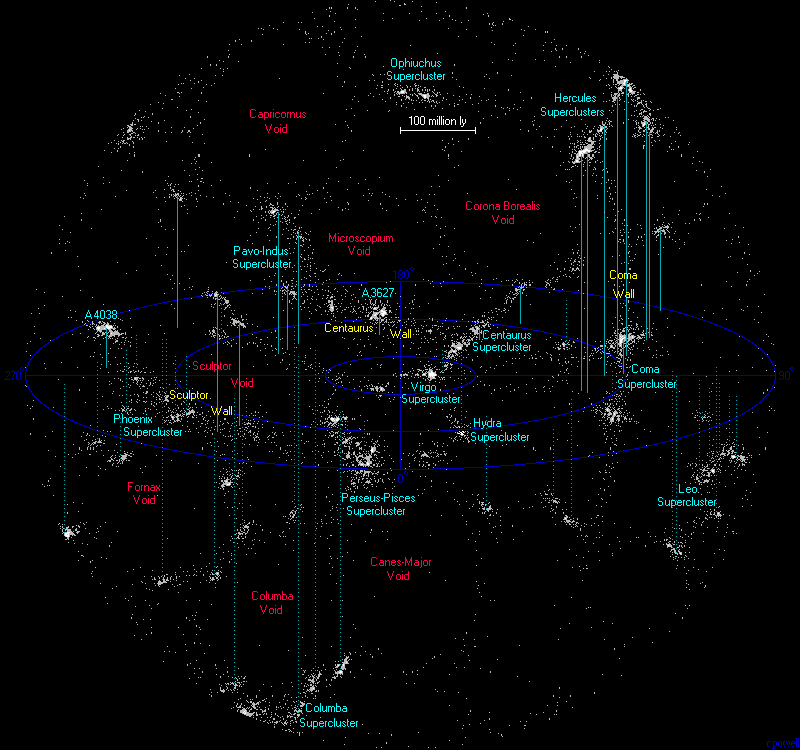
Map of nearest galaxy walls

See also
- GalaxyGalaxyA galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
- Galaxy clusters
- Galaxy superclusters
- List of galaxy clusters
- List of galaxies
- List of galaxy superclusters
- Large-scale structure of the universe
- Void (astronomy)Void (astronomy)In astronomy, voids are the empty spaces between filaments, the largest-scale structures in the Universe, that contain very few, or no, galaxies. They were first discovered in 1978 during a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson at the Kitt Peak National Observatory...
Further reading
- arXiv, , Kevin A. Pimbblet, 14 March 2005
External links
- Pictures of the filamentary network
- Astronomical Institute / Utrecht University - Astronomy Answers - Universe Family Tree: Filament (Dr Louis Strous)
- Astronomical Institute / Utrecht University - Astronomy Answers - From the Astronomical Dictionary - filament (Dr Louis Strous)
- The Universe Within One Billion Light Years with List of Nearby Superclusters (from the Atlas of the Universe):

