
Gaming PC
Encyclopedia
Enthusiast computing refers to a sub-culture of personal computer
users who focus on extremely high-performance computers. Manufacturers of performance-oriented parts typically include an enthusiast model in their offerings. Enthusiast computers (often referred to as a "box" or "build" by their owners) commonly feature extravagant cases and high-end components, and are sometimes liquid cooled.
Although high-end computers may be bought retail in the same manner as the common computer, they are frequently built by their owners. Enthusiasts build their systems in order to produce a computer that will out-perform an opponent's computer, thereby "winning" in a contest; to simply enjoy the best images and effects a new PC game has to offer; or even simply to obtain the best possible performance at a variety of tasks.
 Games have historically been the driving force behind the rapid pace of consumer hardware development. For example, The 7th Guest
Games have historically been the driving force behind the rapid pace of consumer hardware development. For example, The 7th Guest
and Myst
helped drive the adoption of CD-ROM
s. Intel and AMD both incorporated instruction sets such as MMX, 3DNow!
, and Streaming SIMD Extensions
into their processors to support the PC's growing role as a home entertainment device.
More recently, however, other types of applications have piqued the interest of computing enthusiasts. Distributed analysis tools such as Folding@home
, and other computationally intensive chores may also push CPUs and GPUs to their limits, and may also serve as a means of competition, such as tracking how many data sets a user has completed.
was released at US$399 in 2002. Many gaming PCs support the use of multiple video cards in SLI
or CrossFire
, making it possible to spend thousands of dollars in graphics cards alone.
Intel and AMD both offer CPU models designed for overclocking
. These products are denoted as "Extreme Edition" (Intel; Pentium, Pentium 4, Core 2, and i7 series), "K" Series (Intel; Sandy Bridge), "FX" (previously used by AMD, and now resurrected as a brand name applied to the "Bulldozer" series of processors) and "Black Edition" (currently used by AMD). Similar to the ultra-high end video cards, these CPUs are not commonly used, and in many cases will not provide a large performance benefit in games. However, they typically do reach higher numbers on synthetic benchmarks, which serves the same purpose for a performance competition.
Mainstream gaming PCs, which can handle even new games without difficulty, can be built for about $1,000. By contrast, an enthusiast-level gaming PC can cost well over $2,000.


Gaming PCs use hardware accelerated
video card
s which offer high-end rasterisation
-based rendering/image quality. The graphics card is the most important part determining the capabilities of a gaming PC. Memory capacity on 3-D cards is usually at least 256 MB
to 1 GB
. The amount of video RAM is only important while gaming in higher resolution, as it does not directly affect performance. The type of memory used however is an important factor. Modern graphics cards use the PCI-E expansion slot. Two or more graphics cards can be used simultaneously on mainboards supporting SLI
or ATI CrossFire
technology, for nVidia and ATI based cards respectively. Both technologies allow for two graphics cards of the same model to be used in unison to process and render an image.
monitors is still debated, it is clear that a fast response time and high refresh rate is desired in order to display smooth motion. A framerate of 30 frames per second ( fps) is the minimum for smooth motion in a video game. As games approach 60 fps and beyond, the difference becomes less apparent. Apart from the primary display, some gamers choose to use a secondary display as well. These may include a second screen or an LCD display located on the keyboard or by itself.
configuration. The speaker setup or a set of quality headphones is required to enjoy the advanced sound found in most modern computer games. Sound cards have hardware accelerated technologies, such as EAX
. An example is Sound Blaster X-Fi
, which the Fatal1ty editions have 64 MB of onboard RAM (unmatched for a sound card) and has gaming PCs as main target demographic with its dedicated "gaming mode".
are now available, compatibility and performance increases are still debated. Some people have experienced performance downgrades in GRAW
, one of few games currently available that take advantage of additional physics hardware. Graphics card manufacturers plan on including PPUs
on their chipsets and also adding a slot for a third graphics card (in addition to the usual 2 slots for SLI or Crossfire setups) to act as a PPU. At the moment, the cards are expensive and neither widely used nor widely supported in games. Recently Nvidia cards support the physics calculations that dedicated physics cards were made for.

The CPU is mainly responsible for computing physics, AI
and central game processes. Modern gaming PCs use high-end processors, such as the Intel Core i7, Intel Core 2 Quad, Intel Core 2 Duo, Phenom II
, Athlon II
and Intel Pentium Dual-Core
(with the latter used in budget solutions). With the rise of multi-threaded games, multi-core processor setups will become more imperative than ever, but as of today the individual core speed is still more important than the number of cores, as the majority of current gaming software was solely written to operate on a single core. Furthermore, an ample amount of L2 Cache within the CPU, generally 4 MB or more, is recommended to reap the benefits of even faster game performance. In addition, a gaming processor should be capable of running at least the SSE3
instruction set extension, which is available in all modern CPUs.

Random access memory, or RAM, acts as a cache for non-graphical resources that games use. Gaming PCs typically have the fastest available RAM modules, with heat sinks to dissipate heat created by the high data transfer rate between the RAM and the motherboard. The fast RAM found in gaming PCs has the benefit of increased performance by having lower latency than regular RAM.
RAM capacity is also an issue with gaming PCs, and usually at least 2 GB of memory is used, most, however, use 4 GB or more, even as much as 8, 12, or 16 GB.
setups to lower latency and increase throughput to mass storage. Since the space taken up by games is nominal compared to the total availability on modern hard drives, speed is preferred over capacity.
Recently, solid state drives
have become popular, which offer significantly higher speeds than magnetic hard drives.
(~400ms is common). Mobile Broadband
Connections can also cause the same undesirable effects as dialup connections, but can be considered less substantial, with latencies ranging 150ms and upwards (Less than 100 is recommended for a First Person Shooter).
s, PC-compatible airplane gauges and panels, etc. A keyboard and mouse is the preferred method for most games, giving the best speed and accuracy. It should be noted that touch screens are rarely used for PC gaming at this point. "Haptic feedback" commonly known as force feedback, allows for greater immersion into the games played. While there are no keyboards that support haptic feedback, some mice and most forms of game controller
s do.
. Modding usually includes clear sides to reveal the internal components, which may be adorned with LED
s, images on the graphics cards or power supply units. In addition to aesthetics, gaming cases are also designed for function; the case must be able to provide cooling for high-end, possibly overclocked
components, and have room for expansion and customization.
when it is first built or upgraded. Enthusiasts who know how to overclock sometimes do so to prolong the usefulness of their hardware. The highest results are always and by far achieved by overclocking.
However, synthetic benchmark results rarely equate to real application performance, as measured by framerate. The framerate is measured in frames per second, which refers to the number of times the video card recalculates the image shown on screen. While frame rates above 30 frame/s (standard NTSC
framerate) become increasingly difficult to distinguish with the human eye, enthusiast PCs with a multi-video card setup often boast framerates in excess of 100 frame/s. To maintain a challenge, the standard for comparison is constantly refreshed with new games and higher detail settings.
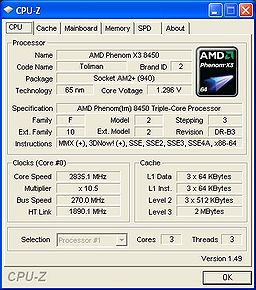 Overclocking is used by enthusiasts to achieve higher framerates than available parts are capable of. Overclocking is such a big part in enthusiast culture that popular websites such as Anandtech
Overclocking is used by enthusiasts to achieve higher framerates than available parts are capable of. Overclocking is such a big part in enthusiast culture that popular websites such as Anandtech
and Tom's Hardware often include overclocking as part of a review. Hardware manufacturers release high-end components that facilitate overclocking. Examples include CPUs with unlocked multipliers, oversized heatsinks or water cooling, and motherboards with user-configurable voltages and incremental bus speeds.
Some system builders and part manufacturers now offer factory overclocking, which is covered under warranty.
There are many hazards when overclocking a computer. When a CPU (Central Processing Unit) is overclocked it will generally run hotter than normal, the additional heat can sometimes stress components to the point of failure. In response to this problem, heatsink manufacturers have implemented innovative solutions in air-cooling primarily based on the incorporation of heatpipe technologies coupled with large-finned tower heatsinks. Alternatively many gaming PCs utilize Watercooling
as a means of dissipating additional heat from overclocked components.
Watercooling is able to provide dissipation that is superior to air-cooled heatsinks. The watercooling system can be configured to be either far superior to air-cooling but at the cost of being as noisy, or even more noisy than high-end air cooling (due to large, fast, loud fans used on the radiator); or it can be configured to be about as effective, or even a bit more effective than high-end air-cooling, but far less noisy (usually by utilizing large radiators coupled with slow and quiet 120 mm fans, and quiet, yet powerful pumps.)
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
users who focus on extremely high-performance computers. Manufacturers of performance-oriented parts typically include an enthusiast model in their offerings. Enthusiast computers (often referred to as a "box" or "build" by their owners) commonly feature extravagant cases and high-end components, and are sometimes liquid cooled.
Although high-end computers may be bought retail in the same manner as the common computer, they are frequently built by their owners. Enthusiasts build their systems in order to produce a computer that will out-perform an opponent's computer, thereby "winning" in a contest; to simply enjoy the best images and effects a new PC game has to offer; or even simply to obtain the best possible performance at a variety of tasks.
Influence of gaming

The 7th Guest
The 7th Guest, produced by Trilobyte and released by Virgin Games in 1993, is an FMV-based puzzle video game. It was one of the first computer video games to be released only on CD-ROM. The 7th Guest is a horror story told from the unfolding perspective of the player, as an amnesiac...
and Myst
Myst
Myst is a graphic adventure video game designed and directed by the brothers Robyn and Rand Miller. It was developed by Cyan , a Spokane, Washington––based studio, and published and distributed by Brøderbund. The Millers began working on Myst in and released it for the Mac OS computer on September...
helped drive the adoption of CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
s. Intel and AMD both incorporated instruction sets such as MMX, 3DNow!
3DNow!
3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, and Streaming SIMD Extensions
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
into their processors to support the PC's growing role as a home entertainment device.
More recently, however, other types of applications have piqued the interest of computing enthusiasts. Distributed analysis tools such as Folding@home
Folding@home
Folding@home is a distributed computing project designed to use spare processing power on personal computers to perform simulations of disease-relevant protein folding and other molecular dynamics, and to improve on the methods of doing so...
, and other computationally intensive chores may also push CPUs and GPUs to their limits, and may also serve as a means of competition, such as tracking how many data sets a user has completed.
Cost
An enthusiast PC implies the early adoption of new hardware, which is sold at a premium price. As an example, the video card ATI Radeon 9700 ProRadeon R300
The Radeon R300 is the third generation of Radeon graphics chips from ATI Technologies. The line features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 9.0 and OpenGL 2.0, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Radeon R200 design. R300 was the first fully Direct3D...
was released at US$399 in 2002. Many gaming PCs support the use of multiple video cards in SLI
Scalable Link Interface
Scalable Link Interface is a brand name for a multi-GPU solution developed by NVIDIA for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output...
or CrossFire
Crossfire
A crossfire is a military term for the siting of weapons so that their arcs of fire overlap. This tactic came to prominence in World War I....
, making it possible to spend thousands of dollars in graphics cards alone.
Intel and AMD both offer CPU models designed for overclocking
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
. These products are denoted as "Extreme Edition" (Intel; Pentium, Pentium 4, Core 2, and i7 series), "K" Series (Intel; Sandy Bridge), "FX" (previously used by AMD, and now resurrected as a brand name applied to the "Bulldozer" series of processors) and "Black Edition" (currently used by AMD). Similar to the ultra-high end video cards, these CPUs are not commonly used, and in many cases will not provide a large performance benefit in games. However, they typically do reach higher numbers on synthetic benchmarks, which serves the same purpose for a performance competition.
Mainstream gaming PCs, which can handle even new games without difficulty, can be built for about $1,000. By contrast, an enthusiast-level gaming PC can cost well over $2,000.
Graphics


Gaming PCs use hardware accelerated
Hardware acceleration
In computing, Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware to perform some function faster than is possible in software running on the general-purpose CPU...
video card
Video card
A video card, Graphics Card, or Graphics adapter is an expansion card which generates output images to a display. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors...
s which offer high-end rasterisation
Rasterisation
Rasterisation is the task of taking an image described in a vector graphics format and converting it into a raster image for output on a video display or printer, or for storage in a bitmap file format....
-based rendering/image quality. The graphics card is the most important part determining the capabilities of a gaming PC. Memory capacity on 3-D cards is usually at least 256 MB
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
to 1 GB
Gigabyte
The gigabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage. The prefix giga means 109 in the International System of Units , therefore 1 gigabyte is...
. The amount of video RAM is only important while gaming in higher resolution, as it does not directly affect performance. The type of memory used however is an important factor. Modern graphics cards use the PCI-E expansion slot. Two or more graphics cards can be used simultaneously on mainboards supporting SLI
Scalable Link Interface
Scalable Link Interface is a brand name for a multi-GPU solution developed by NVIDIA for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output...
or ATI CrossFire
ATI CrossFire
AMD CrossFireX is a brand name for the multi-GPU solution by Advanced Micro Devices, originally developed by ATI Technologies. The technology allows up to four GPUs to be used in a single computer to improve graphics performance.-First-generation:CrossFire was first made available to the public...
technology, for nVidia and ATI based cards respectively. Both technologies allow for two graphics cards of the same model to be used in unison to process and render an image.
Display
While the superiority between LCD screens and CRTCathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
monitors is still debated, it is clear that a fast response time and high refresh rate is desired in order to display smooth motion. A framerate of 30 frames per second ( fps) is the minimum for smooth motion in a video game. As games approach 60 fps and beyond, the difference becomes less apparent. Apart from the primary display, some gamers choose to use a secondary display as well. These may include a second screen or an LCD display located on the keyboard or by itself.
Audio
Gaming PCs are usually equipped with a dedicated sound card and speakers in a 5.1 or 7.1 surround soundSurround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
configuration. The speaker setup or a set of quality headphones is required to enjoy the advanced sound found in most modern computer games. Sound cards have hardware accelerated technologies, such as EAX
Environmental audio extensions
The environmental audio extensions are a number of digital signal processing presets for audio, present in Creative Technology's later Sound Blaster sound cards and the Creative NOMAD/Creative ZEN product lines...
. An example is Sound Blaster X-Fi
Sound Blaster X-Fi
Sound Blaster X-Fi is a lineup of sound cards in Creative Labs' Sound Blaster series.-History:The series was launched in August 2005 as a lineup of PCI sound cards, served as the introduction for their X-Fi audio processing chip, with models ranging from XtremeMusic , to Platinum, Fatal1ty FPS, and...
, which the Fatal1ty editions have 64 MB of onboard RAM (unmatched for a sound card) and has gaming PCs as main target demographic with its dedicated "gaming mode".
Physics
While physics cardsPhysics processing unit
A physics processing unit is a dedicated microprocessor designed to handle the calculations of physics, especially in the physics engine of video games. Examples of calculations involving a PPU might include rigid body dynamics, soft body dynamics, collision detection, fluid dynamics, hair and...
are now available, compatibility and performance increases are still debated. Some people have experienced performance downgrades in GRAW
Tom Clancy's Ghost Recon Advanced Warfighter
Tom Clancy's Ghost Recon Advanced Warfighter is the third installment in the popular Ghost Recon tactical shooter video game series, published by Ubisoft in 2006. As in previous Ghost Recon games, players command their team of Ghosts while neutralizing hostile forces and completing various mission...
, one of few games currently available that take advantage of additional physics hardware. Graphics card manufacturers plan on including PPUs
Physics processing unit
A physics processing unit is a dedicated microprocessor designed to handle the calculations of physics, especially in the physics engine of video games. Examples of calculations involving a PPU might include rigid body dynamics, soft body dynamics, collision detection, fluid dynamics, hair and...
on their chipsets and also adding a slot for a third graphics card (in addition to the usual 2 slots for SLI or Crossfire setups) to act as a PPU. At the moment, the cards are expensive and neither widely used nor widely supported in games. Recently Nvidia cards support the physics calculations that dedicated physics cards were made for.
CPU

The CPU is mainly responsible for computing physics, AI
Ai
AI, A.I., Ai, or ai may refer to:- Computers :* Artificial intelligence, a branch of computer science* Ad impression, in online advertising* .ai, the ISO Internet 2-letter country code for Anguilla...
and central game processes. Modern gaming PCs use high-end processors, such as the Intel Core i7, Intel Core 2 Quad, Intel Core 2 Duo, Phenom II
Phenom II
Phenom II is a family of AMD's multi-core 45 nm processors using the AMD K10 microarchitecture, succeeding the original Phenom. Advanced Micro Devices released the Socket AM2+ version of Phenom II in December 2008, while Socket AM3 versions with DDR3 support, along with an initial batch of...
, Athlon II
Athlon II
Athlon II is a family of AMD multi-core 45 nm central processing units, which is aimed at the midrange to budget market and is a complementary product lineup to the Phenom II.-Features:...
and Intel Pentium Dual-Core
Intel Pentium Dual-Core
The Pentium Dual-Core brand was used for mainstream x86-architecture microprocessors from Intel from 2006 to 2009 when it was renamed to Pentium...
(with the latter used in budget solutions). With the rise of multi-threaded games, multi-core processor setups will become more imperative than ever, but as of today the individual core speed is still more important than the number of cores, as the majority of current gaming software was solely written to operate on a single core. Furthermore, an ample amount of L2 Cache within the CPU, generally 4 MB or more, is recommended to reap the benefits of even faster game performance. In addition, a gaming processor should be capable of running at least the SSE3
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
instruction set extension, which is available in all modern CPUs.
Memory

Random access memory, or RAM, acts as a cache for non-graphical resources that games use. Gaming PCs typically have the fastest available RAM modules, with heat sinks to dissipate heat created by the high data transfer rate between the RAM and the motherboard. The fast RAM found in gaming PCs has the benefit of increased performance by having lower latency than regular RAM.
RAM capacity is also an issue with gaming PCs, and usually at least 2 GB of memory is used, most, however, use 4 GB or more, even as much as 8, 12, or 16 GB.
Storage
In gaming PCs, fast hard drives are very desirable. Having a faster hard drive will result in lower loading times in games. For this reason, some gaming PCs use certain RAIDRAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
setups to lower latency and increase throughput to mass storage. Since the space taken up by games is nominal compared to the total availability on modern hard drives, speed is preferred over capacity.
Recently, solid state drives
Solid-state drive
A solid-state drive , sometimes called a solid-state disk or electronic disk, is a data storage device that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data with the intention of providing access in the same manner of a traditional block i/o hard disk drive...
have become popular, which offer significantly higher speeds than magnetic hard drives.
Networking
While typical computers, including high-end systems, tend to use wireless connections to connect to other computers as well as a router, gaming PCs often use ethernet cables for the fastest and most reliable connection possible. Also, some companies sell dedicated network cards to reduce lag and increase the performance of multiplayer. A dial-up Internet connection is not an acceptable solution due to the very high latencyLatency (engineering)
Latency is a measure of time delay experienced in a system, the precise definition of which depends on the system and the time being measured. Latencies may have different meaning in different contexts.-Packet-switched networks:...
(~400ms is common). Mobile Broadband
Mobile Broadband
Mobile broadband is the marketing term for wireless Internet access through a portable modem, mobile phone or other mobile device.-Description:...
Connections can also cause the same undesirable effects as dialup connections, but can be considered less substantial, with latencies ranging 150ms and upwards (Less than 100 is recommended for a First Person Shooter).
Interface
There are many hardware interfaces designed specifically for gaming and while sometimes used with less powerful PCs, they are most often observed with gaming PCs. Such interfaces include keyboards and mice built for gaming (these typically include additional keys or buttons for game-related functions as well as LCD-screens, higher sensitivity (mouse), better aderency (keyboard/mouse) and less/more friction depending on the user's needs), joysticks, gamepads, steering wheelSteering wheel
A steering wheel is a type of steering control in vehicles and vessels ....
s, PC-compatible airplane gauges and panels, etc. A keyboard and mouse is the preferred method for most games, giving the best speed and accuracy. It should be noted that touch screens are rarely used for PC gaming at this point. "Haptic feedback" commonly known as force feedback, allows for greater immersion into the games played. While there are no keyboards that support haptic feedback, some mice and most forms of game controller
Game controller
A game controller is a device used with games or entertainment systems used to control a playable character or object, or otherwise provide input in a computer game. A controller is typically connected to a game console or computer by means of a wire, cord or nowadays, by means of wireless connection...
s do.
Case
Cases of gaming computers are often subject to case moddingCase modding
Case modification is the modification of a computer chassis , or a video game console chassis. Modifying a computer case in any non-standard way is considered a case mod...
. Modding usually includes clear sides to reveal the internal components, which may be adorned with LED
LEd
LEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
s, images on the graphics cards or power supply units. In addition to aesthetics, gaming cases are also designed for function; the case must be able to provide cooling for high-end, possibly overclocked
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
components, and have room for expansion and customization.
Performance and benchmarks
As a general guideline, enthusiast PCs must achieve high scores on 3D benchmarks such as 3DMark3DMark
3DMark is a computer benchmarking tool created and developed by Futuremark Corporation to determine the performance of a computer's 3D graphic rendering and CPU workload processing capabilities. Running 3DMark produces a 3DMark score with higher numbers indicating better performance...
when it is first built or upgraded. Enthusiasts who know how to overclock sometimes do so to prolong the usefulness of their hardware. The highest results are always and by far achieved by overclocking.
However, synthetic benchmark results rarely equate to real application performance, as measured by framerate. The framerate is measured in frames per second, which refers to the number of times the video card recalculates the image shown on screen. While frame rates above 30 frame/s (standard NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
framerate) become increasingly difficult to distinguish with the human eye, enthusiast PCs with a multi-video card setup often boast framerates in excess of 100 frame/s. To maintain a challenge, the standard for comparison is constantly refreshed with new games and higher detail settings.
Overclocking

AnandTech
AnandTech is an online computer hardware magazine. It was founded in 1997 by then 15-year-old Anand Lal Shimpi, who is the current editor-in-chief and CEO. The web site is recommended as a good resource of hardware reviews for off-the-shelf components addressed to computer building enthusiasts...
and Tom's Hardware often include overclocking as part of a review. Hardware manufacturers release high-end components that facilitate overclocking. Examples include CPUs with unlocked multipliers, oversized heatsinks or water cooling, and motherboards with user-configurable voltages and incremental bus speeds.
Some system builders and part manufacturers now offer factory overclocking, which is covered under warranty.
There are many hazards when overclocking a computer. When a CPU (Central Processing Unit) is overclocked it will generally run hotter than normal, the additional heat can sometimes stress components to the point of failure. In response to this problem, heatsink manufacturers have implemented innovative solutions in air-cooling primarily based on the incorporation of heatpipe technologies coupled with large-finned tower heatsinks. Alternatively many gaming PCs utilize Watercooling
Watercooling
Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. As opposed to air cooling, water is used as the heat conductor. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and large industrial facilities such as steam electric power plants,...
as a means of dissipating additional heat from overclocked components.
Watercooling is able to provide dissipation that is superior to air-cooled heatsinks. The watercooling system can be configured to be either far superior to air-cooling but at the cost of being as noisy, or even more noisy than high-end air cooling (due to large, fast, loud fans used on the radiator); or it can be configured to be about as effective, or even a bit more effective than high-end air-cooling, but far less noisy (usually by utilizing large radiators coupled with slow and quiet 120 mm fans, and quiet, yet powerful pumps.)

