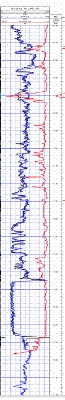
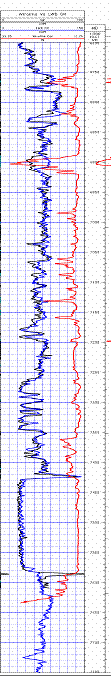
Gamma ray logging
Encyclopedia
Borehole
A borehole is the generalized term for any narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water or other liquid or gases , as part of a geotechnical investigation, environmental site...
. It is sometimes used in mineral exploration and water-well drilling, but most commonly for formation evaluation
Formation evaluation
In petroleum exploration and development, formation evaluation is used to determine the ability of a borehole to produce petroleum. Essentially, it is the process of "recognizing a commercial well when you drill one"....
in oil and gas well drilling . Different types of rock emit different amounts and different spectra of natural gamma radiation
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
. In particular, shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
s usually emit more gamma rays than other sedimentary rocks, such as sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
, gypsum
Gypsum
Gypsum is a very soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It is found in alabaster, a decorative stone used in Ancient Egypt. It is the second softest mineral on the Mohs Hardness Scale...
, salt
Halite
Halite , commonly known as rock salt, is the mineral form of sodium chloride . Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on the amount and type of impurities...
, coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, dolomite
Dolomite
Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate CaMg2. The term is also used to describe the sedimentary carbonate rock dolostone....
, or limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
because radioactive potassium is a common component in their clay content, and because the cation exchange capacity
Cation exchange capacity
In soil science, cation-exchange capacity is the maximum quantity of total cations, of any class, that a soil is capable of holding, at a given pH value, for exchanging with the soil solution. CEC is used as a measure of fertility, nutrient retention capacity, and the capacity to protect...
of clay causes them to adsorb uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
and thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
. This difference in radioactivity between shales and sandstones/carbonate rocks allows the gamma tool to distinguish between shales and non-shales.
The gamma ray log, like other types of well logging
Well logging
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole...
, is done simply by lowering an instrument down the hole and recording gamma radiation variation with depth. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the device most commonly records measurements at 1/2-foot intervals. Gamma radiation is usually recorded in API units, a measurement originated by the petroleum industry. Gamma logs are affected by the diameter of the borehole and the properties of the fluid filling the borehole, but because gamma logs are most often used in a qualitative way, corrections are usually not necessary.
Three elements and their decay chains are responsible for the radiation emitted by rock: potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
, thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
and uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
. Shales often contain potassium as part of their clay content, and tend to absorb uranium and thorium as well. A common gamma-ray log records the total radiation, and cannot distinguish between the radioactive elements, while a spectral gamma ray log (see below) can.
For standard GR logs the value measured is calculated from thorium in ppm, Uranium in ppm and potassium in percent. GR API = 8 × Uranium concentration in ppm + 4 × thorium concentration in ppm + potassium concentration in percent. Due to the weight of uranium concentration in the calculation anomalous concentrations of uranium can cause clean sand reservoirs to appear shaley. Spectral Gamma ray is used to provide an individual reading for each element so anomalies in concentration can be found and interpreted.
An advantage of the gamma log over some other types of well logs is that it works through the steel and cement walls of cased boreholes. Although concrete and steel absorb some of the gamma radiation, enough travels through the steel and cement to allow qualitative determinations.
Sometimes non-shales also have elevated levels of gamma radiation. Sandstone can contain uranium mineralization, potassium feldspar
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming tectosilicate minerals which make up as much as 60% of the Earth's crust....
, clay filling, or rock fragments that cause it to have higher-than usual gamma readings. Coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and dolomite
Dolomite
Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate CaMg2. The term is also used to describe the sedimentary carbonate rock dolostone....
may contain absorbed uranium. Evaporite deposits may contain potassium minerals such as carnallite
Carnallite
Carnallite is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula: KMgCl3·6. It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rare pseudohexagonal orthorhombic crystals...
. When this is the case, spectral gamma ray logging can be done to identify these anomalies.
Spectral logging
Some specialized gamma radiation logging distinguishes the three component decay chainDecay chain
In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to the radioactive decay of different discrete radioactive decay products as a chained series of transformations...
s (potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
, uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
, and thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
) by the wavelengths of their characteristic gamma emissions.
The characteristic gamma ray line that is associated with each component:
- Potassium : Gamma ray energy 1.46 MeVMEVMeV and meV are multiples and submultiples of the electron volt unit referring to 1,000,000 eV and 0.001 eV, respectively.Mev or MEV may refer to:In entertainment:* Musica Elettronica Viva, an Italian musical group...
- Thorium series: Gamma ray energy 2.62 MeV
- Uranium-Radium series: Gamma ray energy 1.76 MeV
Another example of the use of spectral gamma ray logs is to identify specific clay types, like Kaolinite
Kaolinite
Kaolinite is a clay mineral, part of the group of industrial minerals, with the chemical composition Al2Si2O54. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina octahedra...
or Illite
Illite
Illite is a non-expanding, clay-sized, micaceous mineral. Illite is a phyllosilicate or layered alumino-silicate. Its structure is constituted by the repetition of tetrahedron – octahedron – tetrahedron layers. The interlayer space is mainly occupied by poorly hydrated potassium cations...
. This can be used for environmental interpretation as Kaolinite forms from Feldspars in tropic soils by leaching of Potassium; and low Potassium readings may thus indicate paleosols. The identification of clay types is also useful for calculating the effective porosity of reservoir rock.
Use in mineral exploration
Gamma ray logs are also used in mineral exploration, especially exploration for phosphates, uraniumUranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
, and potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
salts.

