
Gap theorem
Encyclopedia
- See also Gap Theorem (disambiguation)Gap theorem (disambiguation)In mathematics, gap theorem may refer to:* The Weierstrass gap theorem.* The Hadamard gap theorem.* The gap theorem of Fourier analysis, a statement about the vanishing of discrete Fourier coefficients for functions that are identically zero on an interval shorter than 2π.* The gap theorem in...
for other gap theorems in mathematicsMathematicsMathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
.
In computational complexity theory
Computational complexity theory
Computational complexity theory is a branch of the theory of computation in theoretical computer science and mathematics that focuses on classifying computational problems according to their inherent difficulty, and relating those classes to each other...
the Gap Theorem is a major theorem about the complexity of computable function
Computable function
Computable functions are the basic objects of study in computability theory. Computable functions are the formalized analogue of the intuitive notion of algorithm. They are used to discuss computability without referring to any concrete model of computation such as Turing machines or register...
s.
It essentially states that there are arbitrarily large computable gaps in the hierarchy of complexity class
Complexity class
In computational complexity theory, a complexity class is a set of problems of related resource-based complexity. A typical complexity class has a definition of the form:...
es. For any computable function
Computable function
Computable functions are the basic objects of study in computability theory. Computable functions are the formalized analogue of the intuitive notion of algorithm. They are used to discuss computability without referring to any concrete model of computation such as Turing machines or register...
that represents an increase in computational resource
Computational resource
In computational complexity theory, a computational resource is a resource used by some computational models in the solution of computational problems....
s, one can find a resource bound such that the set of functions computable within the expanded resource bound is the same as the set computable within the original bound.
The theorem was proved independently by Boris Trakhtenbrot
Boris Trakhtenbrot
Boris Avraamovich Trakhtenbrot or Boaz Trakhtenbrot is an Israeli and Russian mathematician in mathematical logic, algorithms, theory of computation and cybernetics. He worked at Akademgorodok, Novosibirsk during the 1960s and 1970s...
in 1964 and Allan Borodin
Allan Borodin
Allan Bertram Borodin is a University of Toronto professor whose research is in computational complexity theory and algorithms.He has co-authored papers with some of the best researchers in computer science including his longtime friend and colleague Turing Award winner Stephen Cook...
in 1972.
Gap theorem
The general form of the theorem is as follows.- Suppose
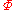 is an abstract (Blum) complexity measureBlum axiomsIn computational complexity theory the Blum axioms or Blum complexity axioms are axioms which specify desirable properties of complexity measures on the set of computable functions. The axioms were first defined by Manuel Blum in 1967....
is an abstract (Blum) complexity measureBlum axiomsIn computational complexity theory the Blum axioms or Blum complexity axioms are axioms which specify desirable properties of complexity measures on the set of computable functions. The axioms were first defined by Manuel Blum in 1967....
. For any total computable function g for which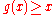 for every
for every  , there is a total computable function t such that with respect to
, there is a total computable function t such that with respect to  , the complexity classComplexity classIn computational complexity theory, a complexity class is a set of problems of related resource-based complexity. A typical complexity class has a definition of the form:...
, the complexity classComplexity classIn computational complexity theory, a complexity class is a set of problems of related resource-based complexity. A typical complexity class has a definition of the form:...
es with boundary functions and
and 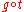 are identical.
are identical.
The theorem can be proved by using the Blum axioms without any reference to a concrete computational model
Computational model
A computational model is a mathematical model in computational science that requires extensive computational resources to study the behavior of a complex system by computer simulation. The system under study is often a complex nonlinear system for which simple, intuitive analytical solutions are...
, so it applies to time, space, or any other reasonable complexity measure.
For the special case of time complexity, this can be stated more simply as:
- for any total computable function
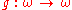 such that
such that 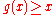 for all
for all 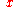 , there exists a time bound
, there exists a time bound 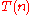 such that
such that 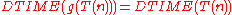 .
.
Although the bound T(n) may be very large, the Gap Theorem does not imply anything interesting for complexity classes such as P or NP.

