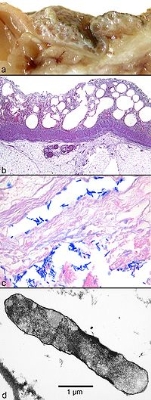
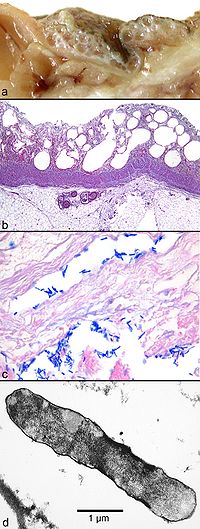
Gas gangrene
Encyclopedia
Gas gangrene is a bacteria
l infection
that produces gas
tissue
s in gangrene
. It is a deadly form of gangrene usually caused by Clostridium perfringens
bacteria. It is a medical emergency
.
Myonecrosis is a condition of necrotic
damage, specific to muscle
tissue. It is often seen in infections with Clostridium perfringens
or any of myriad soil-borne anaerobic bacteria. Bacteria cause myonecrosis via specific exotoxins. These microorganism
s are opportunistic and, in general, enter the body via significant skin breakage. Gangrenous
infection by soil-borne bacteria was common in the combat injuries of soldiers well into the 20th century, due to non-sterile field surgery and the basic nature of severe projectile wounds.
Other causes of myonecrosis include envenomation by snakes of the Bothrops genus (family Viperidae), ischemic
necrosis, caused by vascular blockage (e.g., diabetes type II), tumours that block or hoard blood supply, and disseminated intravascular coagulation
(DIC) or other thromboses
.
. Progression to toxemia
and shock is often very rapid.
-producing Clostridial
species (most often Clostridium perfringens
, and C. novyi
but less commonly C. septicum
or C. ramnosum), which are mostly found in soil but also found as normal gut flora
, and other anaerobes (e.g. Bacteroides
and anaerobic streptococci
). The exotoxin is commonly found in C. perfringens type A strain and is known as alpha toxin
. These environmental bacteria may enter the muscle through a wound and go on to proliferate in necrotic tissue and secrete powerful toxins. These toxins destroy nearby tissue, generating gas at the same time.
Other organisms may rarely cause gas gangrene (for example, Klebsiella pneumoniae
in the context of diabetes
).
A gas composition of 5.9% hydrogen, 3.4% carbon dioxide, 74.5% nitrogen and 16.1% oxygen was reported in one clinical case.
Myonecrosis differs slightly from other types of necrosis. While the underlying causes are almost identical, the type of affected tissue (in particular, muscle tissue) is significantly more important for the patient's general health. Superficial necrosis is unsightly, and can lead to unattractive scarring but otherwise does not affect the patient's likelihood of survival or physical capability to the same extent. However, massive myonecrosis will likely result in the loss of movement of the entire region. If the necrotic damage is allowed to continue throughout an affected limb then often that entire limb is lost permanently.
It is often difficult to identify the extent of muscle damage, as C. perfringens may be at work in deeper fascial layers below the skin. Unlike other anaerobic infections, discharge in these infections is often not purulent (filled with pus). Instead, the discharge is often described as "sweetly putrid" or "dishwater pus" because it is much thinner than normal pus. This is due to the lysis of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, caused by the lecithinases and other toxins released by Clostridia.
Soil-borne anaerobes are particularly well adapted to surviving harsh conditions. Often, there is a scarcity of nutrition and the presence of numerous other species competing for resources. Changes in pH
and temperature are often significant also. Competing bacteria often also possess the ability to create exotoxin
s that assist them in competing with other microbes in their natural environment. When such bacteria are able to enter a living host, they encounter a vast supply of nutrients, warm conditions, and an abundance of water. This enables the microbes to rapidly proliferate, far in excess of the immune system's capability to defend, as prokaryotic bacteria
possess a far greater capacity for multiplication than the host's immune system. The combination of bacterial load and ability to multiply is the basis for the microbes' ability to cause massive infection. Alongside such rapid proliferation is a corresponding mass-production of exotoxin that causes severe damage to local tissue in the host. One such exotoxin is produced by C. perfringens and is responsible for the disease manifestations. This exotoxin is known as alpha toxin
.
Massive infection, gross injury, and depletion of the host's immune capability result in system-wide sepsis
. This is partly due to the burden on the immune system, its corresponding release of inflammatory cytokine
s, and the distribution of bacterial toxin
s. Massive infection is likely to result in death from a combination of system-wide septic shock and the unintentionally damaging effects of the immune response. In animals, disability and distress caused by all of these factors markedly increases the chance of predation.
and excision
with amputation necessary in many cases. Antibiotic
s alone are not effective because they do not penetrate ischaemic muscle
s enough to be effective. However, penicillin is given as an adjuvant treatment to surgery. In addition to surgery and antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy
(HBOT) is used and acts to inhibit the growth of and kill the anaerobic C. perfringens.
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
that produces gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
s in gangrene
Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a considerable mass of body tissue dies . This may occur after an injury or infection, or in people suffering from any chronic health problem affecting blood circulation. The primary cause of gangrene is reduced blood...
. It is a deadly form of gangrene usually caused by Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming bacterium of the genus Clostridium. C. perfringens is ever present in nature and can be found as a normal component of decaying vegetation, marine sediment, the intestinal tract of humans and other vertebrates,...
bacteria. It is a medical emergency
Medical emergency
A medical emergency is an injury or illness that is acute and poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long term health. These emergencies may require assistance from another person, who should ideally be suitably qualified to do so, although some of these emergencies can be dealt with by the...
.
Myonecrosis is a condition of necrotic
Necrosis
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death...
damage, specific to muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
tissue. It is often seen in infections with Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming bacterium of the genus Clostridium. C. perfringens is ever present in nature and can be found as a normal component of decaying vegetation, marine sediment, the intestinal tract of humans and other vertebrates,...
or any of myriad soil-borne anaerobic bacteria. Bacteria cause myonecrosis via specific exotoxins. These microorganism
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
s are opportunistic and, in general, enter the body via significant skin breakage. Gangrenous
Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a considerable mass of body tissue dies . This may occur after an injury or infection, or in people suffering from any chronic health problem affecting blood circulation. The primary cause of gangrene is reduced blood...
infection by soil-borne bacteria was common in the combat injuries of soldiers well into the 20th century, due to non-sterile field surgery and the basic nature of severe projectile wounds.
Other causes of myonecrosis include envenomation by snakes of the Bothrops genus (family Viperidae), ischemic
Ischemia
In medicine, ischemia is a restriction in blood supply, generally due to factors in the blood vessels, with resultant damage or dysfunction of tissue. It may also be spelled ischaemia or ischæmia...
necrosis, caused by vascular blockage (e.g., diabetes type II), tumours that block or hoard blood supply, and disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation , also known as disseminated intravascular coagulopathy or consumptive coagulopathy, is a pathological activation of coagulation mechanisms that happens in response to a variety of diseases. DIC leads to the formation of small blood clots inside the blood...
(DIC) or other thromboses
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss...
.
Features
Gas gangrene can cause myonecrosis (muscle tissue death), gas production, and sepsisSepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
. Progression to toxemia
Toxemia
Toxemia may refer to:* A generic term for the presence of toxins in the blood, see Bacteremia* An outdated medical term for Pre-eclampsia...
and shock is often very rapid.
Pathophysiology
Gas gangrene is caused by exotoxinExotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin excreted by a microorganism, like bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host...
-producing Clostridial
Clostridium
Clostridium is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria, belonging to the Firmicutes. They are obligate anaerobes capable of producing endospores. Individual cells are rod-shaped, which gives them their name, from the Greek kloster or spindle...
species (most often Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming bacterium of the genus Clostridium. C. perfringens is ever present in nature and can be found as a normal component of decaying vegetation, marine sediment, the intestinal tract of humans and other vertebrates,...
, and C. novyi
Clostridium novyi
Clostridium novyi a Gram-positive, endospore- forming, obligate anaerobic bacteria of the class clostridia. It is ubiquitous, being found in the soil and faeces. It is pathogenic, causing a wide variety of diseases in man and animals. It comes in three types, labelled A, B, and a non-pathogenic...
but less commonly C. septicum
Clostridium septicum
Clostridium septicum is a gram positive, spore forming, obligate anaerobic bacterium.Clostridium septicum can cause gas gangrene, but unlike other Clostridium species like Clostridium perfringens, no trauma is necessary at the site of the infection. It is thought that the infection is established...
or C. ramnosum), which are mostly found in soil but also found as normal gut flora
Gut flora
Gut flora consists of microorganisms that live in the digestive tracts of animals and is the largest reservoir of human flora. In this context, gut is synonymous with intestinal, and flora with microbiota and microflora....
, and other anaerobes (e.g. Bacteroides
Bacteroides
Bacteroides is a genus of Gram-negative, bacillus bacteria. Bacteroides species are non-endospore-forming, anaerobes, and may be either motile or non-motile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40-48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, Bacteroides membranes contain sphingolipids...
and anaerobic streptococci
Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
). The exotoxin is commonly found in C. perfringens type A strain and is known as alpha toxin
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin is a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium perfringens and is responsible for gas gangrene and myonecrosis in infected tissues. The toxin also possesses hemolytic activity....
. These environmental bacteria may enter the muscle through a wound and go on to proliferate in necrotic tissue and secrete powerful toxins. These toxins destroy nearby tissue, generating gas at the same time.
Other organisms may rarely cause gas gangrene (for example, Klebsiella pneumoniae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod shaped bacterium found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines....
in the context of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
).
A gas composition of 5.9% hydrogen, 3.4% carbon dioxide, 74.5% nitrogen and 16.1% oxygen was reported in one clinical case.
Myonecrosis differs slightly from other types of necrosis. While the underlying causes are almost identical, the type of affected tissue (in particular, muscle tissue) is significantly more important for the patient's general health. Superficial necrosis is unsightly, and can lead to unattractive scarring but otherwise does not affect the patient's likelihood of survival or physical capability to the same extent. However, massive myonecrosis will likely result in the loss of movement of the entire region. If the necrotic damage is allowed to continue throughout an affected limb then often that entire limb is lost permanently.
It is often difficult to identify the extent of muscle damage, as C. perfringens may be at work in deeper fascial layers below the skin. Unlike other anaerobic infections, discharge in these infections is often not purulent (filled with pus). Instead, the discharge is often described as "sweetly putrid" or "dishwater pus" because it is much thinner than normal pus. This is due to the lysis of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, caused by the lecithinases and other toxins released by Clostridia.
Soil-borne anaerobes are particularly well adapted to surviving harsh conditions. Often, there is a scarcity of nutrition and the presence of numerous other species competing for resources. Changes in pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
and temperature are often significant also. Competing bacteria often also possess the ability to create exotoxin
Exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin excreted by a microorganism, like bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host...
s that assist them in competing with other microbes in their natural environment. When such bacteria are able to enter a living host, they encounter a vast supply of nutrients, warm conditions, and an abundance of water. This enables the microbes to rapidly proliferate, far in excess of the immune system's capability to defend, as prokaryotic bacteria
Prokaryote
The prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a cell nucleus , or any other membrane-bound organelles. The organisms that have a cell nucleus are called eukaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular, but a few such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles...
possess a far greater capacity for multiplication than the host's immune system. The combination of bacterial load and ability to multiply is the basis for the microbes' ability to cause massive infection. Alongside such rapid proliferation is a corresponding mass-production of exotoxin that causes severe damage to local tissue in the host. One such exotoxin is produced by C. perfringens and is responsible for the disease manifestations. This exotoxin is known as alpha toxin
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin is a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium perfringens and is responsible for gas gangrene and myonecrosis in infected tissues. The toxin also possesses hemolytic activity....
.
Massive infection, gross injury, and depletion of the host's immune capability result in system-wide sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
. This is partly due to the burden on the immune system, its corresponding release of inflammatory cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
s, and the distribution of bacterial toxin
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
s. Massive infection is likely to result in death from a combination of system-wide septic shock and the unintentionally damaging effects of the immune response. In animals, disability and distress caused by all of these factors markedly increases the chance of predation.
Treatment
Treatment is usually debridementDebridement
Debridement is the medical removal of a patient's dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue...
and excision
Excision
Excision is the alias of Jeff Abel, a dubstep DJ and music boss from British Columbia, Canada. He frequently works with fellow Canadian dubstep producers Datsik and Downlink. As one of the first dubstep producers and DJs in North America, he has played a significant role in the genre's growth in...
with amputation necessary in many cases. Antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s alone are not effective because they do not penetrate ischaemic muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
s enough to be effective. However, penicillin is given as an adjuvant treatment to surgery. In addition to surgery and antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric medicine, also known as hyperbaric oxygen therapy , is the medical use of oxygen at a level higher than atmospheric pressure. The equipment required consists of a pressure chamber, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of delivering 100% oxygen...
(HBOT) is used and acts to inhibit the growth of and kill the anaerobic C. perfringens.
Additional images

See also
- Blackleg (disease)Blackleg (disease)Blackleg, black quarter, quarter evil, quarter ill is an infectious bacterial disease of sheep and cattle, caused by Clostridium chauvoei bacteria. It is found all over the world. A symptom of blackleg is characteristic swellings which make a cracking sound under pressure...
(a similar disease in livestockLivestockLivestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
) - List of cutaneous conditions

