
Gauge factor
Encyclopedia
Gauge factor or strain factor of a strain gauge
is the ratio of relative change in electrical resistance
to the mechanical strain ε, which is the relative change in length.
In practice, the resistance is also dependent on temperature
. The total effect is
Where
For many materials there is no change in resistivity (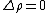 ), for these materiels the gauge factor is simply
), for these materiels the gauge factor is simply
General examples of Gauge Factor values:
Strain gauge
A strain gauge is a device used to measure the strain of an object. Invented by Edward E. Simmons and Arthur C. Ruge in 1938, the most common type of strain gauge consists of an insulating flexible backing which supports a metallic foil pattern. The gauge is attached to the object by a suitable...
is the ratio of relative change in electrical resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
to the mechanical strain ε, which is the relative change in length.
In practice, the resistance is also dependent on temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
. The total effect is
Where
- ε = strainDeformation (mechanics)Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body...
=
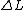 = absolute change in length
= absolute change in length-
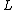 = original length
= original length
- ν = Poisson's ratioPoisson's ratioPoisson's ratio , named after Siméon Poisson, is the ratio, when a sample object is stretched, of the contraction or transverse strain , to the extension or axial strain ....
- ρ = ResistivityResistivityElectrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
- ΔR = change in strain gauge resistance
- R = unstrained resistance of strain gauge
- α = temperature coefficientTemperature coefficientThe temperature coefficient is the relative change of a physical property when the temperature is changed by 1 K.In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the...
- θ = temperature change
For many materials there is no change in resistivity (
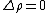 ), for these materiels the gauge factor is simply
), for these materiels the gauge factor is simplyGeneral examples of Gauge Factor values:
| Material | Gauge Factor |
|---|---|
| Metal foil strain gauge | 2-5 |
| Thin-film metal | 2 |
| Single crystal silicon | -125 to + 200 |
| Polysilicon | ±30 |
| Thick-film resistors | 100 |




