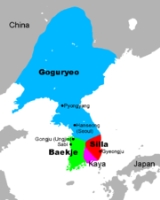
Gaya confederacy
Encyclopedia
Gaya was a confederacy of territorial polities in the Nakdong River
basin of southern Korea
, growing out of the Byeonhan confederacy
of the Samhan
period.
The traditional period used by historians for Gaya chronology is 42–532 CE. According to archaeological evidence in the third and fourth centuries some of the city-states of Byeonhan evolved into the Gaya confederacy, which was later annexed by Silla
, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea
. The individual polities that made up the Gaya confederacy have been characterized as small city-states. The material culture remains of Gaya culture mainly consist of burials and their contents of mortuary goods that have been excavated by archaeologists. Archaeologists interpret mounded burial cemeteries of the late third and early fourth centuries such as Daeseong-dong in Gimhae and Bokcheon-dong in Busan as the royal burial grounds of Gaya polities.
, historical sources use a variety of names, including Kaya, Garak (가락; 駕洛, 迦落), Gara (가라; 加羅, 伽羅, 迦羅, 柯羅), Garyang (가량;加良), and Guya (구야; 狗耶). According to Christopher Beckwith
, "The spelling Kaya is the modern Korean reading of the characters used to write the name; the pronunciation /kara/ (transcriptionally *kala) is certain.". (See Gaya language
.) In Japanese, Gaya is referred to as Mimana (任那), a name with considerable political connotations (see below).
written in the 13th century, in the year 42 CE, six eggs descended from the heaven with a message that they would be kings. Six boys were born, and within 12 days they grew mature. One of them, named Suro, became the king of Geumgwan Gaya
, and the other five founded the remaining five Gayas, namely Daegaya
, Seongsan Gaya, Ara Gaya
, Goryeong Gaya
, and Sogaya.
The Gaya polities evolved out of the chiefly political structures of the twelve tribes of the ancient Byeonhan
, one of the Samhan
confederacies. The loosely organized chiefdoms resolved into six Gaya groups, centered around Geumgwan Gaya. On the basis of archaeological sources as well as limited written records, scholars such as Sin have identified the late 3rd century as a period of transition from Byeonhan to Gaya, with increasing military activity and changing funerary customs. Sin further argues that this was associated with the replacement of the previous elite in some principalities (including Daegaya) by elements from Buyeo
, who brought a more militaristic ideology and style of rule.
The Gaya Confederacy disintegrated under pressure from Goguryeo between 391 and 412 CE, although the last Gaya polities remained independent until they were conquered by Silla
in 562 CE, as punishment for assisting Baekje
in a war against Silla. (see Daegaya).
, fishing
, casting
, and long-distance trade
. They were particularly known for its iron-working, as Byeonhan had been before it. Gaya polities exported abundant quantities of iron ore, iron armor, and other weaponry to Baekje
and the Kingdom of Wa
in Yamato period
Japan. In contrast to the largely commercial and non-political ties of Byeonhan, Gaya polities seem to have attempted to maintain strong political ties with those kingdoms as well.
, Goryeong Gaya
, Bihwa Gaya
, Ara Gaya
, and Seongsan Gaya.
The various Gaya polities formed a confederacy in the 2nd and 3rd centuries that was centered around the heartland of Geumgwan Gaya
in modern Gimhae
. After a period of decline, the confederacy was revived around the turn of the 5th and 6th centuries, this time it was centred around Daegaya
of modern Goryeong
. However, it was unable to defend itself against the incursions and attacks of the neighboring kingdom of Silla
.
Political and trade relations with Japan have been a source of nationalist controversy in both Korea and Japan. Japanese publicists during the twentieth century looked to the controversial Nihonshoki, which claims that Gaya (named "Mimana" also "Kara" in Japanese) was a military outpost of Japan during the Yamato period
(300-710). While there is absolutely no evidence to support this widely rejected contention, the claim has nonetheless been advocated at various times by Japanese imperialists, nationalists and press to justify the Japanese invasion of Korea (1910–1945).
Archaeological evidence suggests that Gaya polities were the main exporter of technology and culture to Kyushu at that time. Theory of a Japanese outpost is widely rejected even in Japan as there was no Japanese dynasty at the time which had a strong enough military power to conquer Gaya or any other part of Korea. The technology of Gaya was much more advanced than that of the Japanese dynasties of the time.
Nakdong River
The Nakdong River is the longest river in South Korea, and passes through major cities such as Daegu and Busan.-Geography:...
basin of southern Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
, growing out of the Byeonhan confederacy
Byeonhan confederacy
Byeonhan, also known as Byeonjin, was a loose confederacy of chiefdoms that existed from around the beginning of the Common Era to the 4th century in the southern Korean peninsula...
of the Samhan
Samhan
The Samhan period of Korean history comprises confederacies of Mahan, Jinhan, and Byeonhan in central and southern Korean peninsula, during the final century BCE and the early centuries CE....
period.
The traditional period used by historians for Gaya chronology is 42–532 CE. According to archaeological evidence in the third and fourth centuries some of the city-states of Byeonhan evolved into the Gaya confederacy, which was later annexed by Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea
Three Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea refer to the ancient Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla, which dominated the Korean peninsula and parts of Manchuria for much of the 1st millennium...
. The individual polities that made up the Gaya confederacy have been characterized as small city-states. The material culture remains of Gaya culture mainly consist of burials and their contents of mortuary goods that have been excavated by archaeologists. Archaeologists interpret mounded burial cemeteries of the late third and early fourth centuries such as Daeseong-dong in Gimhae and Bokcheon-dong in Busan as the royal burial grounds of Gaya polities.
Names
Although most commonly referred to as Gaya (가야; 加耶, 伽耶, 伽倻), probably due to the imprecision of transcribing Korean words into hanjaHanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
, historical sources use a variety of names, including Kaya, Garak (가락; 駕洛, 迦落), Gara (가라; 加羅, 伽羅, 迦羅, 柯羅), Garyang (가량;加良), and Guya (구야; 狗耶). According to Christopher Beckwith
Christopher Beckwith
Christopher I. Beckwith is a professor of Central Eurasian Studies at Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana.He received his Ph.D. degree from Indiana University in Uralic and Altaic Studies ....
, "The spelling Kaya is the modern Korean reading of the characters used to write the name; the pronunciation /kara/ (transcriptionally *kala) is certain.". (See Gaya language
Gaya language
Gaya , also transliterated Kara, is the presumed language of the Gaya confederacy in southern Korea. It is supposedly attested from thirteen toponyms, but it cannot be certain that these reflect the Gaya language itself rather than an earlier language...
.) In Japanese, Gaya is referred to as Mimana (任那), a name with considerable political connotations (see below).
History
According to a legend recorded in the Samguk YusaSamguk Yusa
Samguk Yusa, or Memorabilia of the Three Kingdoms, is a collection of legends, folktales, and historical accounts relating to the Three Kingdoms of Korea , as well as to other periods and states before, during, and after the Three Kingdoms period.The text was written in Classical Chinese, which was...
written in the 13th century, in the year 42 CE, six eggs descended from the heaven with a message that they would be kings. Six boys were born, and within 12 days they grew mature. One of them, named Suro, became the king of Geumgwan Gaya
Geumgwan Gaya
Geumgwan Gaya , also known as Bon-Gaya or Garakguk , was the ruling city-state of the Gaya confederacy during the Three Kingdoms Period in Korea. It is believed to have been located around the modern-day city of Gimhae, Southern Gyeongsang province, near the mouth of the Nakdong River...
, and the other five founded the remaining five Gayas, namely Daegaya
Daegaya
Daegaya was a city-state in the Gaya confederacy during the Korean Three Kingdoms period. Daegaya was located in present-day Goryeong County, in North Gyeongsang Province of South Korea...
, Seongsan Gaya, Ara Gaya
Ara Gaya
Ara Gaya, also known as Ana Gaya, Asiryangguk ), and Alla , was a City-state kingdom in the part of Gaya confederacy, in modern day Haman County of South Korea...
, Goryeong Gaya
Goryeong Gaya
Goryeong Gaya was one of the lesser chiefdoms of the Gaya confederacy during the Korean Three Kingdoms period. It was centered in present-day Sangju City, North Gyeongsang province, South Korea...
, and Sogaya.
The Gaya polities evolved out of the chiefly political structures of the twelve tribes of the ancient Byeonhan
Byeonhan confederacy
Byeonhan, also known as Byeonjin, was a loose confederacy of chiefdoms that existed from around the beginning of the Common Era to the 4th century in the southern Korean peninsula...
, one of the Samhan
Samhan
The Samhan period of Korean history comprises confederacies of Mahan, Jinhan, and Byeonhan in central and southern Korean peninsula, during the final century BCE and the early centuries CE....
confederacies. The loosely organized chiefdoms resolved into six Gaya groups, centered around Geumgwan Gaya. On the basis of archaeological sources as well as limited written records, scholars such as Sin have identified the late 3rd century as a period of transition from Byeonhan to Gaya, with increasing military activity and changing funerary customs. Sin further argues that this was associated with the replacement of the previous elite in some principalities (including Daegaya) by elements from Buyeo
Buyeo (state)
Buyeo or Puyŏ , Fuyu in Chinese, was an ancient Korean kingdom located from today's Manchuria to northern North Korea, from around the 2nd century BC to 494. Its remnants were absorbed by the neighboring and brotherhood kingdom of Goguryeo in 494...
, who brought a more militaristic ideology and style of rule.
The Gaya Confederacy disintegrated under pressure from Goguryeo between 391 and 412 CE, although the last Gaya polities remained independent until they were conquered by Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
in 562 CE, as punishment for assisting Baekje
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
in a war against Silla. (see Daegaya).
Economy
Polities were situated in the alluvial flats of tributary river valleys and the mouth of the Nakdong. In particular, the mouth of the Nakdong has fertile plains, direct access to the sea, and rich iron deposits. Gaya polities had economies that were based on agricultureAgriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
, casting
Casting
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
, and long-distance trade
Trade
Trade is the transfer of ownership of goods and services from one person or entity to another. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. A network that allows trade is called a market. The original form of trade was barter, the direct exchange of goods and...
. They were particularly known for its iron-working, as Byeonhan had been before it. Gaya polities exported abundant quantities of iron ore, iron armor, and other weaponry to Baekje
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
and the Kingdom of Wa
Wa (Japan)
Japanese is the oldest recorded name of Japan. Chinese, Korean, and Japanese scribes regularly wrote Wa or Yamato "Japan" with the Chinese character 倭 until the 8th century, when the Japanese found fault with it, replacing it with 和 "harmony, peace, balance".- Historical references :The earliest...
in Yamato period
Yamato period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Japanese Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province.While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710 , the actual start of Yamato rule is disputed...
Japan. In contrast to the largely commercial and non-political ties of Byeonhan, Gaya polities seem to have attempted to maintain strong political ties with those kingdoms as well.
Politics
Several ancient historical records list a number of polities of Gaya. For example, Goryeo Saryak (고려사략; 高麗史略) lists five: Geumgwan GayaGeumgwan Gaya
Geumgwan Gaya , also known as Bon-Gaya or Garakguk , was the ruling city-state of the Gaya confederacy during the Three Kingdoms Period in Korea. It is believed to have been located around the modern-day city of Gimhae, Southern Gyeongsang province, near the mouth of the Nakdong River...
, Goryeong Gaya
Goryeong Gaya
Goryeong Gaya was one of the lesser chiefdoms of the Gaya confederacy during the Korean Three Kingdoms period. It was centered in present-day Sangju City, North Gyeongsang province, South Korea...
, Bihwa Gaya
Bihwa Gaya
Bihwa Gaya, also known as Bijabal in Japanese records of the time, was one of the member states of the Gaya confederacy during the Three Kingdoms period of Korea. It was based near the modern-day city center of Changnyeong County in South Gyeongsang province, South Korea...
, Ara Gaya
Ara Gaya
Ara Gaya, also known as Ana Gaya, Asiryangguk ), and Alla , was a City-state kingdom in the part of Gaya confederacy, in modern day Haman County of South Korea...
, and Seongsan Gaya.
The various Gaya polities formed a confederacy in the 2nd and 3rd centuries that was centered around the heartland of Geumgwan Gaya
Geumgwan Gaya
Geumgwan Gaya , also known as Bon-Gaya or Garakguk , was the ruling city-state of the Gaya confederacy during the Three Kingdoms Period in Korea. It is believed to have been located around the modern-day city of Gimhae, Southern Gyeongsang province, near the mouth of the Nakdong River...
in modern Gimhae
Gimhae
Gimhae, also commonly spelled Kimhae, is a city in South Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. Gimhae is known to locals as "The Paris of Gyeongsangnamdo." It is the seat of the large Gimhae Kim clan, one of the largest Kim clans in Korea...
. After a period of decline, the confederacy was revived around the turn of the 5th and 6th centuries, this time it was centred around Daegaya
Daegaya
Daegaya was a city-state in the Gaya confederacy during the Korean Three Kingdoms period. Daegaya was located in present-day Goryeong County, in North Gyeongsang Province of South Korea...
of modern Goryeong
Goryeong County
Goryeong County is a county in North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea.Goryeong is a historical center of the ancient kingdom of Daegaya.-External links:*...
. However, it was unable to defend itself against the incursions and attacks of the neighboring kingdom of Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
.
Political and trade relations with Japan have been a source of nationalist controversy in both Korea and Japan. Japanese publicists during the twentieth century looked to the controversial Nihonshoki, which claims that Gaya (named "Mimana" also "Kara" in Japanese) was a military outpost of Japan during the Yamato period
Yamato period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Japanese Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province.While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710 , the actual start of Yamato rule is disputed...
(300-710). While there is absolutely no evidence to support this widely rejected contention, the claim has nonetheless been advocated at various times by Japanese imperialists, nationalists and press to justify the Japanese invasion of Korea (1910–1945).
Archaeological evidence suggests that Gaya polities were the main exporter of technology and culture to Kyushu at that time. Theory of a Japanese outpost is widely rejected even in Japan as there was no Japanese dynasty at the time which had a strong enough military power to conquer Gaya or any other part of Korea. The technology of Gaya was much more advanced than that of the Japanese dynasties of the time.
See also
- List of Korea-related topics
- History of KoreaHistory of KoreaThe Korean Peninsula was inhabited from the Lower Paleolithic about 400,000-500,000 years ago. Archeological evidence indicates that the presence of modern humans in northeast Asia dates to 39,000 years ago. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC, and the Neolithic period began...
- List of Korean monarchs#Gaya confederacy
- Three Kingdoms of KoreaThree Kingdoms of KoreaThe Three Kingdoms of Korea refer to the ancient Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla, which dominated the Korean peninsula and parts of Manchuria for much of the 1st millennium...
- Crown of GayaCrown of GayaThe crowns of Gaya refers to two excavated pieces that are believed to be the headgear of the elite of the Gaya Confederacy. These crowns share the general traditions of Korean crowns, such as the use of diadems, which follows the tradition of the Baekje and the use of headbands with uprights,...

