
Gene copy number
Encyclopedia
Structural variation
Structural variation is the variation in structure of an organism's chromosome. It consists of many kinds of variation in the genome of one species, and usually includes microscopic and submicroscopic types, such as deletions, duplications, copy-number variants, insertions, inversions and...
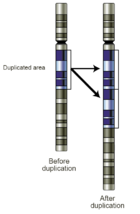
—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as
A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of "C") or A-B-D (a deletion of "C").This variation accounts for roughly 12% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.
Sources
CNVs may either be inherited or caused by de novo mutation. A recently proposed mechanism for the cause of some CNVs was forkReplication fork
The replication fork is a structure that forms within the nucleus during DNA replication. It is created by helicases, which break the hydrogen bonds holding the two DNA strands together. The resulting structure has two branching "prongs", each one made up of a single strand of DNA...
stalling and template switching, a replication misstep. However, this model was subsequently superseded by microhomology-mediated break-induced replication (MMBIR).
CNVs can be caused by structural rearrangements of the genome such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Low copy repeats (LCRs), which are region-specific repeat sequences, are susceptible to such genomic rearrangements resulting in CNVs. Factors such as size, orientation, percentage similarity and the distance between the copies influence the susceptibility of LCRs to genomic rearrangement. Segmental Duplications
Segmental duplication
Segmental duplications are segments of DNA with near-identical sequence.Segmental duplications give rise to low copy repeats and are believed to have played a role in creating new primate genes as reflected in human genetic variation...
(SDs) map near ancestral duplication sites in a phenomenon called duplication shadowing which describes the observation of a ~10 fold increased probability of duplication in regions flanking duplications versus other random regions.
Identification
Copy number variation can be discovered by cytogeneticCytogenetics
Cytogenetics is a branch of genetics that is concerned with the study of the structure and function of the cell, especially the chromosomes. It includes routine analysis of G-Banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescent in situ...
techniques such as fluorescent in situ hybridization
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
FISH is a cytogenetic technique developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s that is used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. FISH uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of the chromosome with which they show a high...
, comparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization or Chromosomal Microarray Analysis is a molecular-cytogenetic method for the analysis of copy number changes in the DNA content of a given subject's DNA and often in tumor cells....
, array comparative genomic hybridization
Array comparative genomic hybridization
Array-comparative genomic hybridization is a technique to detect genomic copy number variations at a higher resolution level than chromosome-based comparative genomic hybridization .-Process:DNA from...
, and by virtual karyotyping
Virtual Karyotype
Virtual karyotype detects genomic copy number variations at a higher resolution level than conventional karyotyping or chromosome-based comparative genomic hybridization .-Background:...
with SNP array
SNP array
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, a SNP array is a type of DNA microarray which is used to detect polymorphisms within a population. A single nucleotide polymorphism , a variation at a single site in DNA, is the most frequent type of variation in the genome. For example, there are around 10...
s. Recent advances in DNA sequencing technology have further enabled the identification of CNVs by next-generation sequencing.
CNVs can be limited to a single gene or include a contiguous set of genes. CNVs can result in having either too many or too few of the dosage-sensitive genes, which may be responsible for a substantial amount of human phenotypic variability, complex behavioral traits and disease susceptibility.
In certain cases, such as rapidly growing Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
cells, the gene copy number can be 4-fold greater for genes located near the origin of DNA replication
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
, rather than at the terminus of DNA replication
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
. Elevating the gene copy number of a particular gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
can increase the expression of the protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that it encodes.
Prevalence in humans
The fact that DNA copy number variation is a widespread and common phenomenon among humans was first uncovered following the completion of the human genome projectHuman Genome Project
The Human Genome Project is an international scientific research project with a primary goal of determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up DNA, and of identifying and mapping the approximately 20,000–25,000 genes of the human genome from both a physical and functional...
. It is estimated that approximately 0.4% of the genomes of unrelated people typically differ with respect to copy number. De novo CNVs have been observed between identical twins who otherwise have identical genomes.
Role in disease
Like other types of genetic variation, some CNVs have been associated with susceptibility or resistance to disease. Gene copy number can be elevated in cancerCancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
cells. For instance, the EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor is the cell-surface receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands...
copy number can be higher than normal in non-small cell lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
.
In addition, a higher copy number of CCL3L1
CCL3L1
Chemokine ligand 3-like 1, also known as CCL3L1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CCL3L1 gene.-Function:This gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory...
has been associated with lower susceptibility to HIV infection, and a low copy number of FCGR3B
FCGR3B
FCGR3B , also known as CD16b , is a human gene.-Further reading:...
(the CD16 cell surface immunoglobulin receptor) can increase susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus and similar inflammatory autoimmune disorders. Copy number variation has also been associated with autism
Autism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
, schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
, and idiopathic learning disability.
However, although once touted as the explanation for the elusive hereditary causes of complex diseases like rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
, the most common CNVs have little or no role in causing disease.
Among common functional CNVs, gene gains outnumber losses, suggesting that many of them are favored in evolution and, therefore, beneficial in some way. One example of CNV is the human salivary amylase
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Food that contains much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns...
gene (AMY1). This gene is typically present as two diploid copies in chimpanzee
Chimpanzee
Chimpanzee, sometimes colloquially chimp, is the common name for the two extant species of ape in the genus Pan. The Congo River forms the boundary between the native habitat of the two species:...
s. Humans average over 6 copies and may have as many as 15. This is thought to be an adaptation to a high-starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
diet that improves the ability to digest starchy foods.
See also
- Comparative genomicsComparative genomicsComparative genomics is the study of the relationship of genome structure and function across different biological species or strains. Comparative genomics is an attempt to take advantage of the information provided by the signatures of selection to understand the function and evolutionary...
- Copy number analysisCopy number analysisCopy number analysis usually refers to the process of analyzing data produced by a test for DNA copy number variation in patient's sample. Such analysis helps detect chromosomal copy number variation that may cause or may increase risks of various critical disorders. Copy number variation can be...
- Human genomeHuman genomeThe human genome is the genome of Homo sapiens, which is stored on 23 chromosome pairs plus the small mitochondrial DNA. 22 of the 23 chromosomes are autosomal chromosome pairs, while the remaining pair is sex-determining...
- InparanoidInparanoidINPARANOID is an algorithm which finds orthologous genes and those paralogous genes which arose—most likely by duplication--after some speciation event...
- Molecular evolutionMolecular evolutionMolecular evolution is in part a process of evolution at the scale of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Molecular evolution emerged as a scientific field in the 1960s as researchers from molecular biology, evolutionary biology and population genetics sought to understand recent discoveries on the structure...
- Pseudogenes
- Segmental duplicationSegmental duplicationSegmental duplications are segments of DNA with near-identical sequence.Segmental duplications give rise to low copy repeats and are believed to have played a role in creating new primate genes as reflected in human genetic variation...
- Tandem exon duplicationTandem exon duplicationTandem exon duplication is defined as duplication of exons within the same gene to give rise to the subsequent exon. A complete exon analysis of all genes in Homo sapiens, Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans has shown 12,291 instances of tandem duplication in exons in human, fly and...
- Virtual KaryotypeVirtual KaryotypeVirtual karyotype detects genomic copy number variations at a higher resolution level than conventional karyotyping or chromosome-based comparative genomic hybridization .-Background:...
Further reading
- Genome-wide analysis of DNA copy-number changes using cDNA microarrays "Gene amplifications and deletions frequently contribute to tumorigenesis. Characterization of these DNA copy-number changes is important for both the basic understanding of cancer and its diagnosis".
External links
- Copy Number Variation Project, Sanger InstituteSanger InstituteThe Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute is a non-profit, British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust....
- A bibliography on copy number variation
- Database of Genomic Variants, a database of structural variants in the human genome
- Copy Number Variation Detection via High-Density SNP Genotyping
- Oxford Gene Technology
- High-resolution mapping of copy number variations in 2,026 healthy individuals
- The 1000 Genomes Project
- cn.FARMS: a latent variable model to detect copy number variations in microarray data with a low false discovery rate, an R package —software

