.gif)
General (Germany)
Encyclopedia
General is presently the highest rank of the German Army
(Heer) and Luftwaffe
(Air Force). It is the equivalent to the rank of Admiral
in the German Navy
(Deutsche Marine).
s of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation
, albeit in modified forms and usage from the current understanding of General. By the 16th century, with the rise of standing armies, the German states had begun to appoint Generals from the nobility to lead armies in battle.
A standard rank system was developed during the Thirty Years War, with the highest rank of General usually reserved for the ruling sovereign (e.g. the Kaiser
or Elector
) and the actual field commander holding the rank of Generalleutnant. Feldmarschall was a lower rank at that time, as was Generalwachtmeister.
By the 17th and 18th centuries, the rank of General was present in all the militaries of the German states, and saw its greatest usage by the militaries of Bavaria
and Prussia
. It was these two militaries that created the concept of the “General Staff”, which was often manned entirely by members of the nobility. To be a general implied membership in the noble class as a Count
or Graf
, Baron
or Freiherr
(this also accounts for most German generals of this era having the prefix “von
” before their names).
, the ranks of German generals were established in four grades, beginning with Generalmajor
, followed by Generalleutnant
, General and Generalfeldmarschall
. The standard uniforms and insignia, used for over a century, also developed during this period. The title of General (three stars) included the officer's branch of service, leading to the titles of General der Infanterie (General of the Infantry
), General der Kavallerie (General of the Cavalry
) and General der Artillerie (General of the Artillery
).
In 1854, Prussia introduced the rank of Generaloberst
(Supreme General, usually (mis)translated Colonel-General) so that officers could be promoted further than General without becoming a Generalfeldmarschall, as this rank was usually bestowed only for extraordinary achievements during wartime service. Later, another special grade known as Generaloberst im Range eines Generalfeldmarschalls (Colonel General in the rank of a Field Marshal
) was first used in Bavaria to denote Colonel (i.e., Supreme) Generals who were given the authority of Field Marshals without the actual rank.
During the German Empire
, the insignia of German generals was established as a heavy golden shoulder board with up to four pips (stars) denoting seniority as a General. The rank of Generalfeldmarschall displayed a crossed set of marshal's baton
s on the shoulder board. German generals also began wearing golden ornaments (Arabeske) on their collars, in contrast to the collar bars (Doppellitzen) worn by elite units, or the plain colored collars of the rest of the German military forces.
The grade of "Supreme General in the rank of a Field Marshal" (Generaloberst im Range eines Generalfeldmarschalls) was introduced in the Prussian/Imperial Army in 1871. It was bestowed on senior generals usually holding the appointment of an army inspector and therefore army commanders designate in the case of hostilities. The shoulder board rank was crossed batons with three pips. The rank of Supreme General proper (with three pips only) was created in 1901. In the Prussian army, the rank of Field Marshal could be awarded only to active officers in wartime if they had won a battle or stormed a fortress. In times of peace, the rank was awarded as an honorary rank to friendly princes and as Charakter (honorary) to generals of merit when they retired — General with the honorary rank of Field Marshal (General mit dem Charakter eines Generalfeldmarschall) - which was cancelled in 1911. At the same time, the rank insignia for Colonel General with the rank of Field Marshal was changed to four pips without batons.
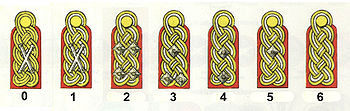
 The German rank of General saw its widest usage during World War II
The German rank of General saw its widest usage during World War II
. Due to the massive expansion of the German armed forces (Wehrmacht
), a new “wave” of generals was promoted in the 1930s that would lead Germany into war.
, or air force Luftwaffe
, in which the officer served, and (nominally) commanded: in addition to the long established General der Kavallerie, General der Artillerie and General der Infanterie, the Wehrmacht also had General der Panzertruppe
n (armoured troops), General der Gebirgstruppe
n (mountain troops), General der Pioniere
(engineers), General der Fallschirmtruppe
n (parachute troops), General der Flieger
(aviators), General der Flakartillerie (anti-aircraft) and General der Nachrichtentruppe
n (communications troops).
The staff corps of the Wehrmacht, medical, veterinary, judicial and chaplain, used special designations for their general officers, with Generalarzt, Generalveterinär, Generalrichter and Feldbischof being the equivalent of Generalmajor; Generalstabsarzt, Generalstabsveterinär and Generalstabsrichter the equivalent of Generalleutnant; and (the unique) Generaloberstabsarzt, Generaloberstabsveterinär and Generaloberstabsrichter the equivalent of General.
With the formation of the Luftwaffe
, Air Force generals began to use the same general ranks as the German Army. The shoulder insignia was identical to that used by the Army, with the addition of special collar patches worn by Luftwaffe general officers. The supreme rank of Reichsmarschall
(Reich Marshal) was created in 1940 for Hermann Göring
.
began using General ranks in addition to standard SS ranks
. An Oberst-Gruppenführer of the Waffen-SS, for example, would be titled Oberst-Gruppenführer und General der Waffen-SS. The Ordnungspolizei
also used similar police ranks
. The Waffen-SS had no Field Marshals, but the rank of Reichsführer-SS
held by Heinrich Himmler
was considered to be the equivalent of a Field Marshal (Generalfeldmarschall) during the later war years.
The Senior Colonel
rank of SS-Oberführer
has sometimes been considered to be a brigadier general equivalent; however, this is incorrect. The rank (in particular among the Waffen-SS) was not considered equivalent to a general officer, was not entitled to the grey trouser stripes and lapel facings of a general, and wore the shoulderboards of an Army Full-Colonel
or Oberst.
Bundeswehr
and the East German Nationale Volksarmee
adopted the rank systems of their respective military blocs.
In the Bundeswehr, the rank of Brigadegeneral was inserted below the rank of Generalmajor. While the rank titles of Generalmajor, Generalleutnant and General were retained, each of those titles now denotes a higher rank than before (e.g. the Generalleutnant is now a three-star general).
Prior to the reunification of Germany, general officer rank designations in the German Democratic Republic
were based on the Soviet model. Generalmajor was still the lowest general officer grade, followed by Generalleutnant, Generaloberst (now three stars instead of four) and Armeegeneral
. In 1982, the GDR government established the rank of Marschall der DDR
, although no one was ever promoted to this rank.
German Army
The German Army is the land component of the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany. Following the disbanding of the Wehrmacht after World War II, it was re-established in 1955 as the Bundesheer, part of the newly formed West German Bundeswehr along with the Navy and the Air Force...
(Heer) and Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe is a generic German term for an air force. It is also the official name for two of the four historic German air forces, the Wehrmacht air arm founded in 1935 and disbanded in 1946; and the current Bundeswehr air arm founded in 1956....
(Air Force). It is the equivalent to the rank of Admiral
Admiral
Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"...
in the German Navy
German Navy
The German Navy is the navy of Germany and is part of the unified Bundeswehr .The German Navy traces its roots back to the Imperial Fleet of the revolutionary era of 1848 – 52 and more directly to the Prussian Navy, which later evolved into the Northern German Federal Navy...
(Deutsche Marine).
Early history
The German rank of General most likely saw its first use within the religious orderReligious order
A religious order is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious practice. The order is composed of initiates and, in some...
s of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, albeit in modified forms and usage from the current understanding of General. By the 16th century, with the rise of standing armies, the German states had begun to appoint Generals from the nobility to lead armies in battle.
A standard rank system was developed during the Thirty Years War, with the highest rank of General usually reserved for the ruling sovereign (e.g. the Kaiser
Kaiser
Kaiser is the German title meaning "Emperor", with Kaiserin being the female equivalent, "Empress". Like the Russian Czar it is directly derived from the Latin Emperors' title of Caesar, which in turn is derived from the personal name of a branch of the gens Julia, to which Gaius Julius Caesar,...
or Elector
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
) and the actual field commander holding the rank of Generalleutnant. Feldmarschall was a lower rank at that time, as was Generalwachtmeister.
By the 17th and 18th centuries, the rank of General was present in all the militaries of the German states, and saw its greatest usage by the militaries of Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
and Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
. It was these two militaries that created the concept of the “General Staff”, which was often manned entirely by members of the nobility. To be a general implied membership in the noble class as a Count
Count
A count or countess is an aristocratic nobleman in European countries. The word count came into English from the French comte, itself from Latin comes—in its accusative comitem—meaning "companion", and later "companion of the emperor, delegate of the emperor". The adjective form of the word is...
or Graf
Graf
Graf is a historical German noble title equal in rank to a count or a British earl...
, Baron
Baron
Baron is a title of nobility. The word baron comes from Old French baron, itself from Old High German and Latin baro meaning " man, warrior"; it merged with cognate Old English beorn meaning "nobleman"...
or Freiherr
Freiherr
The German titles Freiherr and Freifrau and Freiin are titles of nobility, used preceding a person's given name or, after 1919, before the surname...
(this also accounts for most German generals of this era having the prefix “von
Von
In German, von is a preposition which approximately means of or from.When it is used as a part of a German family name, it is usually a nobiliary particle, like the French, Spanish and Portuguese "de". At certain times and places, it has been illegal for anyone who was not a member of the nobility...
” before their names).
19th century
During the Napoleonic WarsNapoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, the ranks of German generals were established in four grades, beginning with Generalmajor
General (Germany)
General is presently the highest rank of the German Army and Luftwaffe . It is the equivalent to the rank of Admiral in the German Navy .-Early history:...
, followed by Generalleutnant
General (Germany)
General is presently the highest rank of the German Army and Luftwaffe . It is the equivalent to the rank of Admiral in the German Navy .-Early history:...
, General and Generalfeldmarschall
Generalfeldmarschall
Field Marshal or Generalfeldmarschall in German, was a rank in the armies of several German states and the Holy Roman Empire; in the Austrian Empire, the rank Feldmarschall was used...
. The standard uniforms and insignia, used for over a century, also developed during this period. The title of General (three stars) included the officer's branch of service, leading to the titles of General der Infanterie (General of the Infantry
General of the Infantry (Germany)
General of the Infantry is a rank of general in the Imperial Army, Reichswehr or Wehrmacht - the second-highest regular rank. The same rank spread to the Imperial Russian Army and the Defence forces of Finland between the world wars...
), General der Kavallerie (General of the Cavalry
Cavalry
Cavalry or horsemen were soldiers or warriors who fought mounted on horseback. Cavalry were historically the third oldest and the most mobile of the combat arms...
) and General der Artillerie (General of the Artillery
General of the Artillery (Germany)
General of the artillery may mean:#a rank of general in the Imperial Army, Reichswehr or Wehrmacht - the second-highest regular rank below Generaloberst. Cavalry officers of equivalent rank were called general of the cavalry, and infantry officers of equivalent rank general of the infantry...
).
In 1854, Prussia introduced the rank of Generaloberst
Colonel General
Colonel General is a senior rank of General. North Korea and Russia are two countries which have used the rank extensively throughout their histories...
(Supreme General, usually (mis)translated Colonel-General) so that officers could be promoted further than General without becoming a Generalfeldmarschall, as this rank was usually bestowed only for extraordinary achievements during wartime service. Later, another special grade known as Generaloberst im Range eines Generalfeldmarschalls (Colonel General in the rank of a Field Marshal
Field Marshal
Field Marshal is a military rank. Traditionally, it is the highest military rank in an army.-Etymology:The origin of the rank of field marshal dates to the early Middle Ages, originally meaning the keeper of the king's horses , from the time of the early Frankish kings.-Usage and hierarchical...
) was first used in Bavaria to denote Colonel (i.e., Supreme) Generals who were given the authority of Field Marshals without the actual rank.
During the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, the insignia of German generals was established as a heavy golden shoulder board with up to four pips (stars) denoting seniority as a General. The rank of Generalfeldmarschall displayed a crossed set of marshal's baton
Baton (symbol)
The ceremonial baton is a short, thick stick, carried by select high-ranking military officers as a uniform article. The baton is distinguished from the swagger stick in being thicker and less functional . Unlike a staff of office, a baton is not rested on the ground...
s on the shoulder board. German generals also began wearing golden ornaments (Arabeske) on their collars, in contrast to the collar bars (Doppellitzen) worn by elite units, or the plain colored collars of the rest of the German military forces.
The grade of "Supreme General in the rank of a Field Marshal" (Generaloberst im Range eines Generalfeldmarschalls) was introduced in the Prussian/Imperial Army in 1871. It was bestowed on senior generals usually holding the appointment of an army inspector and therefore army commanders designate in the case of hostilities. The shoulder board rank was crossed batons with three pips. The rank of Supreme General proper (with three pips only) was created in 1901. In the Prussian army, the rank of Field Marshal could be awarded only to active officers in wartime if they had won a battle or stormed a fortress. In times of peace, the rank was awarded as an honorary rank to friendly princes and as Charakter (honorary) to generals of merit when they retired — General with the honorary rank of Field Marshal (General mit dem Charakter eines Generalfeldmarschall) - which was cancelled in 1911. At the same time, the rank insignia for Colonel General with the rank of Field Marshal was changed to four pips without batons.
World War II


World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. Due to the massive expansion of the German armed forces (Wehrmacht
Wehrmacht
The Wehrmacht – from , to defend and , the might/power) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer , the Kriegsmarine and the Luftwaffe .-Origin and use of the term:...
), a new “wave” of generals was promoted in the 1930s that would lead Germany into war.
Generalfeldmarschall
In 1936, Hitler revived the rank of Field Marshal, originally only for the Minister of War and Commander-in-Chief of the Wehrmacht.Generaloberst
The rank of generaloberst, usually translated as "colonel general", but perhaps better as "senior general".General
This rank was formally linked to the branch of the army HeerHeer
Heer is German for "army". Generally, its use as "army" is not restricted to any particular country, so "das britische Heer" would mean "the British army".However, more specifically it can refer to:*An army of Germany:...
, or air force Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe is a generic German term for an air force. It is also the official name for two of the four historic German air forces, the Wehrmacht air arm founded in 1935 and disbanded in 1946; and the current Bundeswehr air arm founded in 1956....
, in which the officer served, and (nominally) commanded: in addition to the long established General der Kavallerie, General der Artillerie and General der Infanterie, the Wehrmacht also had General der Panzertruppe
General der Panzertruppe
General der Panzertruppe was a rank of German Army General introduced by the Wehrmacht in 1935. As the commander of a Panzer Corp this rank corresponds to a US Army Lieutenant-General...
n (armoured troops), General der Gebirgstruppe
General der Gebirgstruppe
General der Gerbirgstruppe was a rank of German Army General introduced by the Wehrmacht in 1940....
n (mountain troops), General der Pioniere
General der Pioniere
General der Pioniere was a rank of German Army General introduced by the Wehrmacht in 1938.The rank was equivalent to the long established General der Kavallerie, General der Artillerie and General der Infanterie...
(engineers), General der Fallschirmtruppe
General der Fallschirmtruppe
General der Fallschirmtruppe was a General’s rank of the German Luftwaffe.The rank was equivalent to the long established General der Kavallerie, General der Artillerie and General der Infanterie...
n (parachute troops), General der Flieger
General der Flieger
General der Flieger was a General’s rank of the German Luftwaffe.The rank was equivalent to the long established General der Kavallerie, General der Artillerie and General der Infanterie...
(aviators), General der Flakartillerie (anti-aircraft) and General der Nachrichtentruppe
General der Nachrichtentruppe
General der Nachrichtentruppe was a rank of German Army General introduced by the Wehrmacht in 1940....
n (communications troops).
Generalmajor
Usually a division commander.The staff corps of the Wehrmacht, medical, veterinary, judicial and chaplain, used special designations for their general officers, with Generalarzt, Generalveterinär, Generalrichter and Feldbischof being the equivalent of Generalmajor; Generalstabsarzt, Generalstabsveterinär and Generalstabsrichter the equivalent of Generalleutnant; and (the unique) Generaloberstabsarzt, Generaloberstabsveterinär and Generaloberstabsrichter the equivalent of General.
With the formation of the Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe is a generic German term for an air force. It is also the official name for two of the four historic German air forces, the Wehrmacht air arm founded in 1935 and disbanded in 1946; and the current Bundeswehr air arm founded in 1956....
, Air Force generals began to use the same general ranks as the German Army. The shoulder insignia was identical to that used by the Army, with the addition of special collar patches worn by Luftwaffe general officers. The supreme rank of Reichsmarschall
Reichsmarschall
Reichsmarschall literally in ; was the highest rank in the armed forces of Nazi Germany during World War II after the position of Supreme Commander held by Adolf Hitler....
(Reich Marshal) was created in 1940 for Hermann Göring
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring, was a German politician, military leader, and a leading member of the Nazi Party. He was a veteran of World War I as an ace fighter pilot, and a recipient of the coveted Pour le Mérite, also known as "The Blue Max"...
.
Waffen-SS
In 1941, the Waffen-SSWaffen-SS
The Waffen-SS was a multi-ethnic and multi-national military force of the Third Reich. It constituted the armed wing of the Schutzstaffel or SS, an organ of the Nazi Party. The Waffen-SS saw action throughout World War II and grew from three regiments to over 38 divisions, and served alongside...
began using General ranks in addition to standard SS ranks
Ranks and insignia of the Schutzstaffel
The uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel were paramilitary ranks and uniforms used by the SS between 1925 and 1945 to differentiate that organization from the regular German armed forces, the German state, and the Nazi Party....
. An Oberst-Gruppenführer of the Waffen-SS, for example, would be titled Oberst-Gruppenführer und General der Waffen-SS. The Ordnungspolizei
Ordnungspolizei
The Ordnungspolizei or Orpo were the uniformed regular police force in Nazi Germany between 1936 and 1945. It was increasingly absorbed into the Nazi police system. Owing to their green uniforms, they were also referred to as Grüne Polizei...
also used similar police ranks
Ranks and insignia of the Ordnungspolizei
The Ranks and insignia of the Ordnungspolizei developed in 1936 after the nationalization of Germany's regular police forces.- Ordnungspolizei Rank Titles :...
. The Waffen-SS had no Field Marshals, but the rank of Reichsführer-SS
Reichsführer-SS
was a special SS rank that existed between the years of 1925 and 1945. Reichsführer-SS was a title from 1925 to 1933 and, after 1934, the highest rank of the German Schutzstaffel .-Definition:...
held by Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler was Reichsführer of the SS, a military commander, and a leading member of the Nazi Party. As Chief of the German Police and the Minister of the Interior from 1943, Himmler oversaw all internal and external police and security forces, including the Gestapo...
was considered to be the equivalent of a Field Marshal (Generalfeldmarschall) during the later war years.
The Senior Colonel
Senior Colonel
Senior Colonel is a field grade officer rank placed between a regular Colonel and a Major General. The rank typically exists in militaries that do not maintain a rank of Brigadier General/Brigadier....
rank of SS-Oberführer
Oberführer
Oberführer was an early paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party dating back to 1921. Translated as “Senior Leader”, an Oberführer was typically a Nazi Party member in charge of a group of paramilitary units in a particular geographical region...
has sometimes been considered to be a brigadier general equivalent; however, this is incorrect. The rank (in particular among the Waffen-SS) was not considered equivalent to a general officer, was not entitled to the grey trouser stripes and lapel facings of a general, and wore the shoulderboards of an Army Full-Colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
or Oberst.
Modern usage
After World War II, the West GermanWest Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
Bundeswehr
Bundeswehr
The Bundeswehr consists of the unified armed forces of Germany and their civil administration and procurement authorities...
and the East German Nationale Volksarmee
National People's Army
The National People’s Army were the armed forces of the German Democratic Republic .The NVA was established in 1956 and disestablished in 1990. There were frequent reports of East German advisors with Communist African countries during the Cold War...
adopted the rank systems of their respective military blocs.
In the Bundeswehr, the rank of Brigadegeneral was inserted below the rank of Generalmajor. While the rank titles of Generalmajor, Generalleutnant and General were retained, each of those titles now denotes a higher rank than before (e.g. the Generalleutnant is now a three-star general).
Prior to the reunification of Germany, general officer rank designations in the German Democratic Republic
German Democratic Republic
The German Democratic Republic , informally called East Germany by West Germany and other countries, was a socialist state established in 1949 in the Soviet zone of occupied Germany, including East Berlin of the Allied-occupied capital city...
were based on the Soviet model. Generalmajor was still the lowest general officer grade, followed by Generalleutnant, Generaloberst (now three stars instead of four) and Armeegeneral
Armeegeneral
Armeegeneral was a senior military rank of East Germany, used until 1990. It was the equivalent of a Four-Star-General in Western nations and ranked below the Marschall der DDR , although no one was ever promoted to the latter rank.East German officers who achieved the rank of Armeegeneral were:*...
. In 1982, the GDR government established the rank of Marschall der DDR
Marshal of the German Democratic Republic
Marshal of the German Democratic Republic , was the highest rank in the National People's Army of the former German Democratic Republic . It has never been held and was abolished in 1989.- History :...
, although no one was ever promoted to this rank.

