
General selection model
Encyclopedia
The General Selection Model (GSM) is a model of population genetics
that describes how a population's genotype
will change when acted upon by natural selection
.
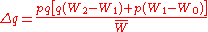
In words:
The product of the relative frequencies,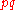 , is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when
, is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when 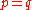 . In the GSM, the rate of change
. In the GSM, the rate of change 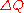 is proportional to the genetic variation.
is proportional to the genetic variation.
The mean population fitness is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change
is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change  is inversely proportional to the mean fitness
is inversely proportional to the mean fitness 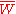 -- i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.
-- i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.
The remainder of the equation,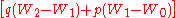 , refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.
, refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
that describes how a population's genotype
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
will change when acted upon by natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
.
Equation
The General Selection Model is encapsulated by the equation: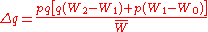
- where:
-
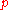 is the frequency of the dominant gene
is the frequency of the dominant gene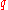 is the frequency of the recessive gene
is the frequency of the recessive gene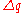 is the rate of evolutionary change of the frequency of the recessive gene
is the rate of evolutionary change of the frequency of the recessive gene are the relative fitnessesFitness (biology)Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
are the relative fitnessesFitness (biology)Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
of homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive genotypes respectively.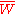 is the mean population relative fitness.
is the mean population relative fitness.
In words:
The product of the relative frequencies,
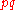 , is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when
, is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when 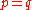 . In the GSM, the rate of change
. In the GSM, the rate of change 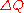 is proportional to the genetic variation.
is proportional to the genetic variation.The mean population fitness
 is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change
is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change  is inversely proportional to the mean fitness
is inversely proportional to the mean fitness  -- i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.
-- i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.The remainder of the equation,
 , refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.
, refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.See also
- Darwinian FitnessFitness (biology)Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
- Hardy-Weinberg principleHardy-Weinberg principleThe Hardy–Weinberg principle states that both allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain constant—that is, they are in equilibrium—from generation to generation unless specific disturbing influences are introduced...
- Population geneticsPopulation geneticsPopulation genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...

