
Geography of Azerbaijan
Encyclopedia
| Geography of Azerbaijan | |
 |
|
| Continent | Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... and Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... |
| Region | Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... |
| Coordinates | 40°30′N 47°30′E |
| Area | Ranked 119th 86,600 km2 |
| Coastline | 0 km (landlocked) |
| Borders | 2,013 km (Armenia Armenia Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia... 877 km Georgia Georgia (country) Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of... 322 km Iran Iran Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia... 611 km Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... 284 km Turkey Turkey Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe... 9 km) |
| Highest point | Bazarduzu Dagi Bazarduzu Dagi Mount Bazardüzü is a mountain peak in the Greater Caucasus range on the border between Russia and Azerbaijan. At 4,466 metres above sea level, it is the highest peak in Azerbaijan. The southernmost point of Russia is located close to the peak.... 4,485 m |
| Lowest point | Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... -28 m |
| Longest river | Kura River Kura River Kura is a river, also known from the Greek as the Cyrus in the Caucasus Mountains. Starting in north-eastern Turkey, it flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras River as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea... 1,514 km |
| Largest lake | Mingäçevir Reservoir 605 km2 |


Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan , officially the Republic of Azerbaijan is the largest country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west, and Iran to...
is situated in the Caucasus
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
region of Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
. Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus , sometimes translated as "Caucasus Major", "Big Caucasus" or "Large Caucasus") is the major mountain range of the Caucasus Mountains....
mountain range to the north; and the extensive flatlands at the country's center. About the size of Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
or the state of Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, Azerbaijan has a total land area of approximately 86,600 square kilometers, less than 1% of the land area of the former Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. Of the three Transcaucasian states, Azerbaijan has the greatest land area. Special administrative subdivisions are the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, which is separated from the rest of Azerbaijan by a strip of Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
n territory, and the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Region
Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, lying between Lower Karabakh and Zangezur and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains...
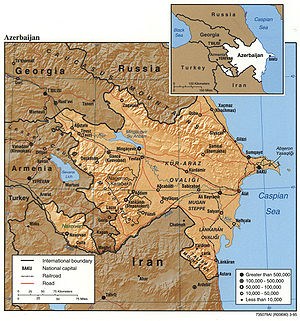
, entirely within Azerbaijan. (The status of Nagorno-Karabakh was under negotiation in 1994.) Located in the region of the southern Caucasus Mountains, Azerbaijan borders the Caspian Sea to the east, Georgia and Russia to the north, Iran to the south, and Armenia to the southwest and west. A small part of Nakhchivan also borders Turkey to the northwest. The capital of Azerbaijan is the ancient city of Baku, which has the largest and best harbor on the Caspian Sea and has long been the center of the republic's oil industry.
Topography and drainage
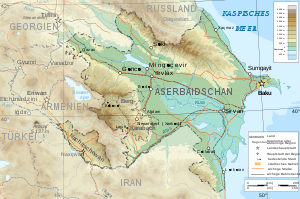
Except for its eastern Caspian shoreline and some areas bordering Georgia and Iran, Azerbaijan is ringed by mountains. To the northeast, bordering Russia's Dagestan Autonomous Republic, is the Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus , sometimes translated as "Caucasus Major", "Big Caucasus" or "Large Caucasus") is the major mountain range of the Caucasus Mountains....
range; to the west, bordering Armenia, is the Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus is one of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about 600 km....
range. To the extreme southeast, the Talysh Mountains
Talysh Mountains
Talysh Mountains is a mountain chain in northwestern Iran, and southeastern Republic of Azerbaijan in the northwest section of the Elburz Mountains, extending southeastward from the Lankaran Lowland in southeast Azerbaijan to the lower part of the Sefid Rud in northwest Iran...
form part of the border with Iran. The highest elevations occur in the Greater Caucasus, where Mount Bazar-dyuzi rises 4,485 meters above sea level. Eight large rivers flow down from the Caucasus ranges into the central Kura-Aras Lowlands, alluvial flatlands and low delta areas along the seacoast designated by the Azerbaijani name for the Mtkvari River(Kur) and its main tributary, the Aras. The Mtkvari, the longest river in the Caucasus region, forms the delta and drains into the Caspian a short distance downstream from the confluence with the Aras. The Mingechaur Reservoir, with an area of 605 square kilometers that makes it the largest body of water in Azerbaijan, was formed by damming the Kura in western Azerbaijan. The waters of the reservoir provide hydroelectric power and irrigation of the Kura-Aras plain. Most of the country's rivers are not navigable. About 15% of the land in Azerbaijan is arable.
Mountains
Azerbaijan is nearly surrounded by mountains. The Greater CaucasusGreater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus , sometimes translated as "Caucasus Major", "Big Caucasus" or "Large Caucasus") is the major mountain range of the Caucasus Mountains....
range, with the country’s highest elevations, lies in the north along the border with Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and run southeast to the Abseron Peninsula on the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
. The country’s highest peak, Bazardyuze Dagi, rises to 4,485 m in this range near the Azerbaijan-Russia border. The Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus is one of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about 600 km....
range, with elevations up to 3,500 m, lies to the west along the border with Armenia. The Talish Mountains form part of the border with Iran at the southeast tip of the country.
Kobustan Mountain, located near Baku
Baku
Baku , sometimes spelled as Baki or Bakou, is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, which projects into the Caspian Sea. The city consists of two principal...
, is carved by deep ravines, from which bubble mud volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es and mineral spring
Mineral spring
Mineral springs are naturally occurring springs that produce water containing minerals, or other dissolved substances, that alter its taste or give it a purported therapeutic value...
s.
Temperature
The climate varies from subtropical and humid in the southeast to subtropical and dry in central and eastern Azerbaijan. Along the shores of the Caspian Sea it is temperate, while the higher mountain elevations are generally cold. BakuBaku
Baku , sometimes spelled as Baki or Bakou, is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, which projects into the Caspian Sea. The city consists of two principal...
, on the Caspian, enjoys mild weather that averages 4 °C (39.2 °F) in January and 25 °C (77 °F) in July.
Rainfall
Most of Azerbaijan receives little rainfall, only 152 to 254 mm (6 to 10 in) annually on average. As a result, agricultural areas require irrigation. Approximately 14500 km² (5,598 sq mi) of the land is irrigated. The greatest precipitation falls in the highest elevations of the Caucasus but also in the Länkäran Lowlands of the extreme southeast. The yearly average in these areas can exceed 1000 millimetres (39.37 in).Environmental problems
Air and water pollution are widespread and pose great challenges to economic development. Major sources of pollution include oil refineries and chemical and metallurgical industries, which in the early 1990s continued to operate as inefficiently as they had in the Soviet era. Air quality is extremely poor in Baku, the center of oil refining. Some reports have described Baku's air as the most polluted in the former Soviet Union, and other industrial centers suffer similar problems.The Caspian Sea, including Baku Bay, has been polluted by oil leakages and the dumping of raw or inadequately treated sewage, reducing the yield of caviar and fish. In the Soviet period, Azerbaijan was pressed to use extremely heavy applications of pesticides to improve its output of scarce subtropical crops for the rest of the Soviet Union. The continued regular use of the pesticide DDT in the 1970s and 1980s was an egregious lapse, although that chemical was officially banned in the Soviet Union because of its toxicity to humans. Excessive application of pesticides and chemical fertilizers has caused extensive groundwater pollution and has been linked by Azerbaijani scientists to birth defects and illnesses. Rising water levels in the Caspian Sea, mainly caused by natural factors exacerbated by man-made structures, have reversed the decades-long drying trend and now threaten coastal areas; the average level rose 1.5 meters between 1978 and 1993. Because of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, large numbers of trees were felled, roads were built through pristine areas, and large expanses of agricultural land were occupied by military forces.
Like other former Soviet republics, Azerbaijan faces a gigantic environmental cleanup complicated by the economic uncertainties left in the wake of the Moscow-centered planning system. The Committee for the Protection of the Natural Environment is part of the Azerbaijani government, but in the early 1990s it was ineffective at targeting critical applications of limited funds, establishing pollution standards, or monitoring compliance with environmental regulations. Early in 1994, plans called for Azerbaijan to participate in the international Caspian Sea Forum, sponsored by the European Union (EU).
Natural hazard
Natural hazard
A natural hazard is a threat of a naturally occurring event that will have a negative effect on people or the environment. Many natural hazards are interrelated, e.g. earthquakes can cause tsunamis and drought can lead directly to famine. It is possible that some natural hazards are...
s:
- Droughts; some lowland areas threatened by rising levels of the Caspian Sea
Environment
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
--current issues:
- Local scientists consider the Abseron Yasaqligi (Apsheron Peninsula) (including Baky and Sumqayit) and the Caspian Sea to be the ecologically most devastated area in the world because of severe air, water, and soil pollutionPollutionPollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
; soil pollution results from the use of DDTDDTDDT is one of the most well-known synthetic insecticides. It is a chemical with a long, unique, and controversial history....
as a pesticide and also from toxic defoliants used in the production of cottonCottonCotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
.
Environment - international agreements:
- Party to: Climate Change, DesertificationDesertificationDesertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
, Endangered Species, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection - Signed, but not ratified: Biodiversity
Area and boundaries
AreaArea
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
:
- Total: 86,600 km² - country comparison to the world: 119
- Land: 86,100 km²
- Water: 500 km²
- Note: Includes the exclave of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic and the Nagorno-KarabakhNagorno-KarabakhNagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, lying between Lower Karabakh and Zangezur and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains...
region; the region's autonomy was abolished by Azerbaijani Supreme Soviet on November 26, 1991.
Area comparative
- AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
comparative: larger than TasmaniaTasmaniaTasmania is an Australian island and state. It is south of the continent, separated by Bass Strait. The state includes the island of Tasmania—the 26th largest island in the world—and the surrounding islands. The state has a population of 507,626 , of whom almost half reside in the greater Hobart... - CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
comparative: larger than New BrunswickNew BrunswickNew Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the only province in the federation that is constitutionally bilingual . The provincial capital is Fredericton and Saint John is the most populous city. Greater Moncton is the largest Census Metropolitan Area... - United KingdomUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
comparative: slightly larger than ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the... - United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
comparative: slightly smaller than MaineMaineMaine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost... - EU comparative: slightly smaller than PortugalPortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
Land boundaries
Border
Borders define geographic boundaries of political entities or legal jurisdictions, such as governments, sovereign states, federated states and other subnational entities. Some borders—such as a state's internal administrative borders, or inter-state borders within the Schengen Area—are open and...
:
- Total: 2,013 km
- Border countries: ArmeniaArmeniaArmenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
(with Azerbaijan-proper) 566 km, Armenia (with Azerbaijan-Nakhchivan exclave) 221 km, GeorgiaGeorgia (country)Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
322 km, Iran (with Azerbaijan-proper) 432 km, IranIranIran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
(with Azerbaijan-Nakhchivan exclave) 700 km, RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
284 km, TurkeyTurkeyTurkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
9 km
Coastline:
- 0 km (landlocked). Azerbaijan borders the Caspian SeaCaspian SeaThe Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
. (800 km, est.)
Maritime claims:
- None (landlocked)
Terrain
- large,flat lowland (much of it below sea-level) with Great Caucasus Mountains to the north, uplands in the west
Elevation extremes:
- Lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
- Highest point: Bazarduzu DagiBazarduzu DagiMount Bazardüzü is a mountain peak in the Greater Caucasus range on the border between Russia and Azerbaijan. At 4,466 metres above sea level, it is the highest peak in Azerbaijan. The southernmost point of Russia is located close to the peak....
4,485 m (on border with Russia) - Highest peak entirely within Azeri territory: Shah Dagi 4,243 m
Islands
- BullaBulla IslandBulla Island, also Khara Zira or Khere Zire, Azeri: Bulla adası is an island in the Bay of Baku, Caspian Sea. It is the largest island of the Baku Archipelago, located off Baku, Azerbaijan....
- Çikil
- ÇilovÇilovÇilov is a village in the municipality of Çilov-Neft Daşları in the Əzizbəyov raion of Baku, Azerbaijan....
- GilGil Island (Azerbaijan)Gil Island also Glinyanii Island is an island of Azerbaijan in the Caspian Sea.This island is part of the Baku Archipelago, which consists of the following islands: Boyuk Zira, Dash Zira, Kichik Zira , Zenbil, Sangi-Mugan or Svinoy, Chikil, Qara Su, Khara Zira, Gil, Ignat Dash and a few smaller ones...
- Glinyaniy
- Nargin
- PirallahıPirallahi IslandPirallahi Island or Pirallakhi Island is an island in the Caspian Sea. The island is part of Azerbaijan, and is located right off the northeastern shore of the Apsheron Peninsula, to the ENE of Baku....
- Qara SuQara SuQara Su, Qarasu or Los Island, is an uninhabited sandy island off the Bay of Baku, Azerbaijan. This island is part of the Baku Archipelago, which consists of the following islands: Boyuk Zira or Nargin, Dash Zira, Kichik Zira , Zenbil, Sangi-Mugan, Chikil, Qara Su, Khara Zira, Gil, Ignat Dash and a...
- QumQum IslandQum Island, also Qum adasi or Peschanniy, Azeri: Qum adası) is an island in the Bay of Baku, Caspian Sea. It is a part of the Baku Archipelago, located south of Baku, Azerbaijan.-References:**...
- Səngi Muğan
- VulfVulfVulf or Volf is an island also known as Dash Zira . The word "Zira" originated in the Arabic word "Jazīra", meaning "island". Vulf is tiny and uninhabited...
- Zənbil
Resources and land use
Natural resourcesNatural Resources
Natural Resources is a soul album released by Motown girl group Martha Reeves and the Vandellas in 1970 on the Gordy label. The album is significant for the Vietnam War ballad "I Should Be Proud" and the slow jam, "Love Guess Who"...
:
- PetroleumPetroleumPetroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, natural gasNatural gasNatural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, ironIronIron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
oreOreAn ore is a type of rock that contains minerals with important elements including metals. The ores are extracted through mining; these are then refined to extract the valuable element....
, nonferrous metals, bauxiteBauxiteBauxite is an aluminium ore and is the main source of aluminium. This form of rock consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite Al3, boehmite γ-AlO, and diaspore α-AlO, in a mixture with the two iron oxides goethite and hematite, the clay mineral kaolinite, and small amounts of anatase TiO2...
, and underground water.
Land use
Land use
Land use is the human use of land. Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as fields, pastures, and settlements. It has also been defined as "the arrangements, activities and inputs people undertake in a certain land cover...
:
- Arable landArable landIn geography and agriculture, arable land is land that can be used for growing crops. It includes all land under temporary crops , temporary meadows for mowing or pasture, land under market and kitchen gardens and land temporarily fallow...
: 20.62% - Permanent crops: 2.61%
- Other: 77.77% (2005 est.)
Irrigated land:
- 14,550 km² (2003)
Total renewable water resources:
- 30.3 cu m (1997)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
- Total: 17.25 cu km/yr (5%/28%/68%)
- Per capita: 2,051 cu m/yr (2000)
Natural hazards
- droughts

