
Geography of Greece
Encyclopedia
Greece
is a country located in Southern Europe
, on the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is surrounded on the north by Bulgaria
, the Republic of Macedonia
and Albania
; to the west by the Ionian Sea
; to the south by the Mediterranean Sea
and to the east by the Aegean Sea
and Turkey
. The country ranges approximately in latitude
from 35°00′N to 42°00′N and in longitude
from 19°00′E to 28°30′E. As a result, it has considerable climatic variation, as discussed below. The country consists of a large mainland; the Peloponnese
, a peninsula connected to the southern tip of the mainland by the Isthmus
of Corinth
; and around 3,000 island
s, including Crete
, Rhodes
, Corfu
, the Dodecanese
and the Cyclades
. According to the CIA World Factbook, Greece has 13676 kilometres (8,497.9 mi) of coastline
80% of Greece is mountain
ous, and the country is one of the most mountainous countries of Europe. The Pindus
, a chain of mountains lies across the center of the country in a northwest-to-southeast direction, with a maximum elevation of 2637 m. Extensions of the same mountain range stretch across the Peloponnese and underwater across the Aegean, forming many of the Aegean Islands
including Crete
, and joining with the Taurus Mountains
of southern Turkey. Central and Western Greece contain high and steep peaks dissected by many canyon
s and other karstic landscapes
, including the Meteora
and the Vikos Gorge
s - the latter being one of the largest of the world and the third deepest after the Copper Canyon
in Mexico
and the Grand Canyon
in the USA, plunging vertically for more than 1,100 metres.
Mount Olympus is the highest point of Greece and the fourth highest in relative topographical prominence in Europe, rising to 2,919 m above sea level
. The Rhodope Mountains
form the border between Greece and Bulgaria
; that area is covered with vast and thick forests.
Plain
s also are found in eastern Thessaly
, in central Macedonia
and in Thrace
. Western Greece contains lake
s and wetland
s.
is divided into three classes:
The southern suburbs of Athens are in the Mediterranean zone, while northern suburbs have a temperate climate.
, bordering the Ionian Sea
, and the Mediterranean Sea
, between Albania
and Turkey
Geography - note:
strategic location dominating the Aegean Sea and southern approach to Turkish Straits; a peninsular country, possessing an archipelago of about 3,000 islands. The Country can be divided in three main geographic areas. The mainland, the islands and the Aegean basin.
It has a total area of
131 940 km²
Of this, land area is 130 800 km², internal waters (Lakes and rivers) account for 1 140 km².
Land boundaries measure 1,228 km, bordering Albania 282 km, Republic of Macedonia
228 km, Bulgaria
494 km, Turkey 206 km
Greece's coastline measures 15 021 km.
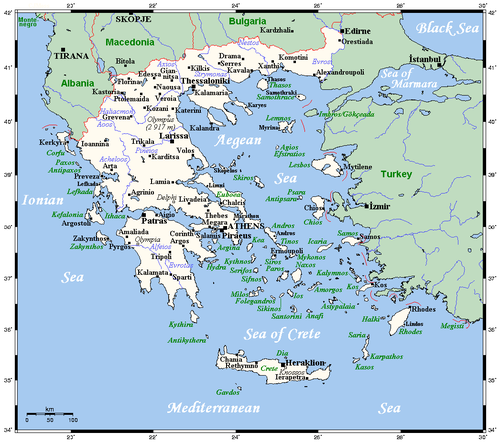
and Thrace
, further to the south narrowing into a "Greek peninsula" in its own right, including historical Epirus
, Thessaly
, Achaea
, Boeotia
and Attica
, and concluding in the separate peninsula of Peloponnese
, comprising the historical territories Sparta
, Corinth
and Argos
, all surrounding the peninsula's heartland of Arcadia
.
The major mountain range of Greece is Olympus
, separating Thessaly from Macedonia. Its highest peak rises to 2,919 m above sea level, making it the second highest of the entire Balkan peninsula after peak Musala
in the Rila Mountain.
is home to over 7,000 islands, with 227 of them inhabited.
of Greece and the second largest (after Cyprus
) in the Eastern Mediterranean.
The island has an elongated shape: it spans 260 km from east to west and 60 km at its widest, although the island is narrower at certain points, such as in the region close to Ierapetra, where it reaches a width of only 12 km. Crete covers an area of 8,336 km², with a coastline of 1046 km ; to the north it broaches the Sea of Crete
; to the south the Libyan Sea
; in the west the Myrtoan Sea
, and toward the east the Karpathion Sea. It lies approximately 160 km south of the Greek mainland.
Crete is characterized by a mountain range crossing from west to east, formed by three different subranges:
These encompass fertile plateaus, such as Lasithi, Omalos and Nidha; caves, such as Diktaion and Idaion; and gorges, such as the famous gorge of Samaria. The protected area of the Samaria Gorge
is the home of kri-kri
, while Cretan mountains and gorges are refugees for the endangered vulture Lammergeier
(Gypaetus barbatus).
There are a number of rivers on Crete, including the Ieropotamos River
on the southern part of the island.
Crete straddles two climatic zones, the Mediterranean and the North African, mainly falling within the former. As such, the climate in Crete is primarily temperate
. The atmosphere can be quite humid, depending on the proximity to the sea, while winter is fairly mild. Snowfall is common on the mountains between November and May, but rare in the low lying areas, especially near the coast when it only stays on the ground for a few minutes or hours. However, a truly exceptional cold snap swept the island in February 2004, during which period the whole island was blanketed with snow. During the Cretan summer, average temperatures reach the high 20s-low 30s Celsius (mid 80s to mid 90s Fahrenheit), with maxima touching the upper 30s to mid 40s (above 110 °F (43.3 °C)).
The south coast, including the Mesara Plain
and Asterousia Mountains
, falls in the North African climatic zone, and thus enjoys significantly more sunny days and high temperatures throughout the year. In southern Crete date palms
bear fruit and swallows remain year around, not migrating to Africa
.
. The last island, Kythira
, is off the southern tip of the Peloponnesus
, the southern part of the Greek mainland. Kythira is not part of the periphery
of Ionian Islands (Ionioi Nisoi), as it is included in the periphery of Attica
. Also, the Ionian Islands do not correspond to historical Ionia
, which is today part of western Turkey.
, situated between mainland Greece to the west and north and Anatolia
to the east; the island of Crete
delimits the sea to the south. The ancient
name of the Aegean Sea are traditionally subdivided into seven groups, from north to south:
200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Territorial sea:
6 nmi (11.1 km; 6.9 mi) (reserving the right to a future extension to 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi))
19%
2.) Permanent crops:
8%
3.) Forests and woodland:
50%
4.) Other:
23% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land:
13 140 km² (1993 est.)
1.) Natural hazards:
severe earthquakes, droughts, wildfires
2.) Current issues:
air pollution/water pollution
3.) International agreements:
party to:
Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 97, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
is a country located in Southern Europe
Southern Europe
The term Southern Europe, at its most general definition, is used to mean "all countries in the south of Europe". However, the concept, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, linguistic and cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical...
, on the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is surrounded on the north by Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
, the Republic of Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
and Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
; to the west by the Ionian Sea
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea , is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea, south of the Adriatic Sea. It is bounded by southern Italy including Calabria, Sicily and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and a large number of Greek islands, including Corfu, Zante, Kephalonia, Ithaka, and...
; to the south by the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
and to the east by the Aegean Sea
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
. The country ranges approximately in latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
from 35°00′N to 42°00′N and in longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
from 19°00′E to 28°30′E. As a result, it has considerable climatic variation, as discussed below. The country consists of a large mainland; the Peloponnese
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese, Peloponnesos or Peloponnesus , is a large peninsula , located in a region of southern Greece, forming the part of the country south of the Gulf of Corinth...
, a peninsula connected to the southern tip of the mainland by the Isthmus
Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancient Greek word for "neck" and refers to the narrowness of the land. The Isthmus was known in the ancient...
of Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
; and around 3,000 island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
s, including Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
, Rhodes
Rhodes
Rhodes is an island in Greece, located in the eastern Aegean Sea. It is the largest of the Dodecanese islands in terms of both land area and population, with a population of 117,007, and also the island group's historical capital. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within...
, Corfu
Corfu
Corfu is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the edge of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality. The...
, the Dodecanese
Dodecanese
The Dodecanese are a group of 12 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the Aegean Sea, of which 26 are inhabited. Τhis island group generally defines the eastern limit of the Sea of Crete. They belong to the Southern Sporades island group...
and the Cyclades
Cyclades
The Cyclades is a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around the sacred island of Delos...
. According to the CIA World Factbook, Greece has 13676 kilometres (8,497.9 mi) of coastline
80% of Greece is mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
ous, and the country is one of the most mountainous countries of Europe. The Pindus
Pindus
The Pindus mountain range is located in northern Greece and southern Albania. It is roughly 160 km long, with a maximum elevation of 2637 m . Because it runs along the border of Thessaly and Epirus, the Pindus range is often called the "spine of Greece"...
, a chain of mountains lies across the center of the country in a northwest-to-southeast direction, with a maximum elevation of 2637 m. Extensions of the same mountain range stretch across the Peloponnese and underwater across the Aegean, forming many of the Aegean Islands
Aegean Islands
The Aegean Islands are the group of islands in the Aegean Sea, with mainland Greece to the west and north and Turkey to the east; the island of Crete delimits the sea to the south, those of Rhodes, Karpathos and Kasos to the southeast...
including Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
, and joining with the Taurus Mountains
Taurus Mountains
Taurus Mountains are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, dividing the Mediterranean coastal region of southern Turkey from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğirdir in the west to the upper reaches of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the east...
of southern Turkey. Central and Western Greece contain high and steep peaks dissected by many canyon
Canyon
A canyon or gorge is a deep ravine between cliffs often carved from the landscape by a river. Rivers have a natural tendency to reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water it will eventually drain into. This forms a canyon. Most canyons were formed by a process of...
s and other karstic landscapes
Karst topography
Karst topography is a geologic formation shaped by the dissolution of a layer or layers of soluble bedrock, usually carbonate rock such as limestone or dolomite, but has also been documented for weathering resistant rocks like quartzite given the right conditions.Due to subterranean drainage, there...
, including the Meteora
Meteora
The Metéora is one of the largest and most important complexes of Eastern Orthodox monasteries in Greece, second only to Mount Athos. The six monasteries are built on natural sandstone rock pillars, at the northwestern edge of the Plain of Thessaly near the Pineios river and Pindus Mountains, in...
and the Vikos Gorge
Vikos Gorge
The Vikos Gorge is a gorge in the Pindus Mountains of northern Greece. It lies on the southern slopes of Mount Tymfi, with a length of about 20 km, depth ranging from 450 m to 1600 m and width from 400 m to some meters at its narrowest part....
s - the latter being one of the largest of the world and the third deepest after the Copper Canyon
Copper Canyon
Copper Canyon is a group of canyons consisting of six distinct canyons in the Sierra Tarahumara in the southwestern part of the state of Chihuahua in Mexico...
in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and the Grand Canyon
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in the United States in the state of Arizona. It is largely contained within the Grand Canyon National Park, the 15th national park in the United States...
in the USA, plunging vertically for more than 1,100 metres.
Mount Olympus is the highest point of Greece and the fourth highest in relative topographical prominence in Europe, rising to 2,919 m above sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
. The Rhodope Mountains
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, with over 83% of its area in southern Bulgaria and the remainder in Greece. Its highest peak, Golyam Perelik , is the seventh highest Bulgarian mountain...
form the border between Greece and Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
; that area is covered with vast and thick forests.
Plain
Plain
In geography, a plain is land with relatively low relief, that is flat or gently rolling. Prairies and steppes are types of plains, and the archetype for a plain is often thought of as a grassland, but plains in their natural state may also be covered in shrublands, woodland and forest, or...
s also are found in eastern Thessaly
Thessaly
Thessaly is a traditional geographical region and an administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, and appears thus in Homer's Odyssey....
, in central Macedonia
Macedonia (Greece)
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of Greece in Southern Europe. Macedonia is the largest and second most populous Greek region...
and in Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
. Western Greece contains lake
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
s and wetland
Wetland
A wetland is an area of land whose soil is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. Wetlands are categorised by their characteristic vegetation, which is adapted to these unique soil conditions....
s.
Climate
Greece's climateClimate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
is divided into three classes:
- A Mediterranean climateMediterranean climateA Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
features mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures rarely reach extremes, although snowfalls do occur occasionally even in AthensAthensAthens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, CycladesCycladesThe Cyclades is a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around the sacred island of Delos...
or CreteCreteCrete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
during the winter. - An alpine climateAlpine climateAlpine climate is the average weather for a region above the tree line. This climate is also referred to as mountain climate or highland climate....
is found primarily in Western Greece (Epirus, Central Greece, ThessalyThessalyThessaly is a traditional geographical region and an administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, and appears thus in Homer's Odyssey....
, Western MacedoniaMacedonia (Greece)Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of Greece in Southern Europe. Macedonia is the largest and second most populous Greek region...
as well as central parts of the PeloponnesePeloponneseThe Peloponnese, Peloponnesos or Peloponnesus , is a large peninsula , located in a region of southern Greece, forming the part of the country south of the Gulf of Corinth...
like Achaea, Arkadia and parts of Lakonia where the Alpine range pass by). - A temperate climate is found in Central and Eastern MacedoniaMacedonia (Greece)Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of Greece in Southern Europe. Macedonia is the largest and second most populous Greek region...
as well as in ThraceThraceThrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
at places like KomotiniKomotiniKomotini is a city in Thrace, northeastern Greece. It is the capital of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace and of the Rhodope regional unit. It is also the administrative center of the Rhodope-Evros super-prefecture. The city is home to the Democritus University of Thrace, founded in 1973...
, XanthiXanthiXanthi ; is a city in Thrace, northeastern Greece. It is the capital of the Xanthi peripheral unit of the periphery of East Macedonia and Thrace.-History:...
and northern EvrosEvrosEvros is:* the Greek name of the Maritsa river running through Bulgaria and forming the land border between Turkey and Greece* Evros , an administrative division in northern Greece...
; with cold, damp winters and hot, dry summers.
The southern suburbs of Athens are in the Mediterranean zone, while northern suburbs have a temperate climate.
Physical geography
Greece is located in Southern EuropeSouthern Europe
The term Southern Europe, at its most general definition, is used to mean "all countries in the south of Europe". However, the concept, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, linguistic and cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical...
, bordering the Ionian Sea
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea , is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea, south of the Adriatic Sea. It is bounded by southern Italy including Calabria, Sicily and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and a large number of Greek islands, including Corfu, Zante, Kephalonia, Ithaka, and...
, and the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, between Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
Geography - note:
strategic location dominating the Aegean Sea and southern approach to Turkish Straits; a peninsular country, possessing an archipelago of about 3,000 islands. The Country can be divided in three main geographic areas. The mainland, the islands and the Aegean basin.
It has a total area of
131 940 km²
Of this, land area is 130 800 km², internal waters (Lakes and rivers) account for 1 140 km².
Land boundaries measure 1,228 km, bordering Albania 282 km, Republic of Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
228 km, Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
494 km, Turkey 206 km
Greece's coastline measures 15 021 km.
Sea]]}} |
| Regions of Greece |
| Cities and islands of Greece |

Mainland
Mainland Greece forms the southernmost part of the Balkan peninsula, in the north including parts of the historical regions of MacedoniaMacedonia (region)
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan peninsula in southeastern Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time, but nowadays the region is considered to include parts of five Balkan countries: Greece, the Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, as...
and Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
, further to the south narrowing into a "Greek peninsula" in its own right, including historical Epirus
Epirus (ancient state)
Epirus was an ancient Greek state, located in the geographical region of Epirus, in the western Balkans. The homeland of the ancient Epirotes was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Thessalia and Macedonia to the east and Illyrian tribes to the north...
, Thessaly
Thessaly
Thessaly is a traditional geographical region and an administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, and appears thus in Homer's Odyssey....
, Achaea
Achaea
Achaea is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of West Greece. It is situated in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. The capital is Patras. The population exceeds 300,000 since 2001.-Geography:...
, Boeotia
Boeotia
Boeotia, also spelled Beotia and Bœotia , is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. It was also a region of ancient Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, the second largest city being Thebes.-Geography:...
and Attica
Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
, and concluding in the separate peninsula of Peloponnese
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese, Peloponnesos or Peloponnesus , is a large peninsula , located in a region of southern Greece, forming the part of the country south of the Gulf of Corinth...
, comprising the historical territories Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
and Argos
Argos
Argos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
, all surrounding the peninsula's heartland of Arcadia
Arcadia
Arcadia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan...
.
The major mountain range of Greece is Olympus
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus is the highest mountain in Greece, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, about 100 kilometres away from Thessaloniki, Greece's second largest city. Mount Olympus has 52 peaks. The highest peak Mytikas, meaning "nose", rises to 2,917 metres...
, separating Thessaly from Macedonia. Its highest peak rises to 2,919 m above sea level, making it the second highest of the entire Balkan peninsula after peak Musala
Musala
Musala is the highest peak in Bulgaria and the entire Balkan Peninsula, standing at 2,925 m . The summit of the Rila mountain in southwestern Bulgaria, Musala is the highest peak between the Alps and the Caucasus and the highest in Eastern Europe bar the Caucasus.Between 1949–1962 the peak was...
in the Rila Mountain.
Islands
GreeceGreece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
is home to over 7,000 islands, with 227 of them inhabited.
Crete
Crete is the largest islandIsland
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
of Greece and the second largest (after Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
) in the Eastern Mediterranean.
The island has an elongated shape: it spans 260 km from east to west and 60 km at its widest, although the island is narrower at certain points, such as in the region close to Ierapetra, where it reaches a width of only 12 km. Crete covers an area of 8,336 km², with a coastline of 1046 km ; to the north it broaches the Sea of Crete
Sea of Crete
thumb|300px|Map of the Sea of CreteThe Sea of Crete is the sea south of the Aegean Sea, north of the island Crete, and south of the Cyclades. The sea also stretches from Kythera east to the Dodecanese islands of Karpathos and Kassos. The bounding seas to the west are the Ionian Sea as well as...
; to the south the Libyan Sea
Libyan Sea
The Libyan Sea is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea, north of the African coast of ancient Libya, i.e. Cyrenaica and Marmarica...
; in the west the Myrtoan Sea
Myrtoan Sea
The Myrtoan Sea is a subdivision of the Mediterranean Sea that lies between the Cyclades and the Peloponnesos. It is described as the part of the Aegean Sea south of Euboea, Attica, and Argolis. Some of the water mass of the Black Sea reaches the Myrtoan Sea, via transport through the Aegean...
, and toward the east the Karpathion Sea. It lies approximately 160 km south of the Greek mainland.
Crete is characterized by a mountain range crossing from west to east, formed by three different subranges:
- the White Mountains or Lefka OriLefka OriLefka Ori or Madares is a mountain range located in Western Crete, in the Chania prefecture. The White Mountains or Lefka Ori occupy a good part of the centre of West Crete and are the main feature of the region...
(2,452 m); - the Idi Range (Psiloritis (35.18°N 24.82°E) 2,456 m);
- the Dikti Mountains (2,148 m);
These encompass fertile plateaus, such as Lasithi, Omalos and Nidha; caves, such as Diktaion and Idaion; and gorges, such as the famous gorge of Samaria. The protected area of the Samaria Gorge
Samaria Gorge
The Samariá Gorge is aNational Park of Greece on the island of Crete - a major tourist attraction of the island - and a World's Biosphere Reserve....
is the home of kri-kri
Kri-kri
The Kri-kri , sometimes called the Cretan goat, Agrimi, or Cretan Ibex, was considered a subspecies of Wild Goat, but has been recently found to be a feral variety of the domestic goat...
, while Cretan mountains and gorges are refugees for the endangered vulture Lammergeier
Lammergeier
The Lammergeier, Lammergeyer, or Bearded Vulture, Gypaetus barbatus , is the only member of the genus Gypaetus. Traditionally considered an Old World vulture, it actually forms a minor lineage of Accipitridae together with the Egyptian Vulture , its closest living relative...
(Gypaetus barbatus).
There are a number of rivers on Crete, including the Ieropotamos River
Ieropotamos River
The Ieropotamos River is a watercourse in southern Crete in Greece. This river was a source of water supply for the ancient Minoan settlement of Phaistos. The Ieropotamos River was heavily drawn upon by the Minoans because of the intensity of farming, even in the Bronze Age at Phaistos...
on the southern part of the island.
Climate
Crete straddles two climatic zones, the Mediterranean and the North African, mainly falling within the former. As such, the climate in Crete is primarily temperate
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
. The atmosphere can be quite humid, depending on the proximity to the sea, while winter is fairly mild. Snowfall is common on the mountains between November and May, but rare in the low lying areas, especially near the coast when it only stays on the ground for a few minutes or hours. However, a truly exceptional cold snap swept the island in February 2004, during which period the whole island was blanketed with snow. During the Cretan summer, average temperatures reach the high 20s-low 30s Celsius (mid 80s to mid 90s Fahrenheit), with maxima touching the upper 30s to mid 40s (above 110 °F (43.3 °C)).
The south coast, including the Mesara Plain
Mesara Plain
The Mesara or Messara Plain is an illuvial plain in southern Crete, stretching about 50 km west-to-east and 7 km north-to-south, making it the largest plain in Crete....
and Asterousia Mountains
Asterousia Mountains
The Asterousia Mountains are a range in southern Crete separating the Mesara Plain from the Libyan Sea. Evidence of ancient Cretan cultures have been found in excavations performed within sites contained in this range; moreover, one of the most significant Minoan sites on Crete has been excavated...
, falls in the North African climatic zone, and thus enjoys significantly more sunny days and high temperatures throughout the year. In southern Crete date palms
Date Palm
The date palm is a palm in the genus Phoenix, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit. Although its place of origin is unknown because of long cultivation, it probably originated from lands around the Persian Gulf. It is a medium-sized plant, 15–25 m tall, growing singly or forming a clump with...
bear fruit and swallows remain year around, not migrating to Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
.
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands are a group of 2 islands. The 1 northern island are off the west coast of Greece, in the Ionian SeaIonian Sea
The Ionian Sea , is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea, south of the Adriatic Sea. It is bounded by southern Italy including Calabria, Sicily and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and a large number of Greek islands, including Corfu, Zante, Kephalonia, Ithaka, and...
. The last island, Kythira
Kythira
Cythera is an island in Greece, once part of the Ionian Islands. It lies opposite the south-eastern tip of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is administratively part of the Islands regional unit, which is part of the Attica region , Greece.For many centuries, while naval travel was the only means...
, is off the southern tip of the Peloponnesus
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese, Peloponnesos or Peloponnesus , is a large peninsula , located in a region of southern Greece, forming the part of the country south of the Gulf of Corinth...
, the southern part of the Greek mainland. Kythira is not part of the periphery
Peripheries of Greece
The current official regional administrative divisions of Greece were instituted in 1987. Although best translated into English as "regions", the transcription peripheries is sometimes used, perhaps to distinguish them from the traditional regions which they replaced. The English word 'periphery'...
of Ionian Islands (Ionioi Nisoi), as it is included in the periphery of Attica
Attica
Attica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
. Also, the Ionian Islands do not correspond to historical Ionia
Ionia
Ionia is an ancient region of central coastal Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements...
, which is today part of western Turkey.
Aegean
The islands of the Aegean SeaAegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
, situated between mainland Greece to the west and north and Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
to the east; the island of Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
delimits the sea to the south. The ancient
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
name of the Aegean Sea are traditionally subdivided into seven groups, from north to south:
- Northeastern Aegean IslandsNorth Aegean islandsThe North Aegean islands are a number of disconnected islands in the north Aegean Sea, also known as the Northeast Aegean islands, belonging to Greece and Turkey. The islands do not form a physical chain or group, but are frequently grouped together for tourist or administrative purposes...
- SporadesSporadesThe Sporades are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea, in the Aegean Sea. It consists of 24 islands, of which four are permanently inhabited: Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros.-Administration:...
- EuboeaEuboeaEuboea is the second largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. The narrow Euripus Strait separates it from Boeotia in mainland Greece. In general outline it is a long and narrow, seahorse-shaped island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to...
- Argo-Saronic Islands
- CycladesCycladesThe Cyclades is a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around the sacred island of Delos...
- DodecaneseDodecaneseThe Dodecanese are a group of 12 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the Aegean Sea, of which 26 are inhabited. Τhis island group generally defines the eastern limit of the Sea of Crete. They belong to the Southern Sporades island group...
(Southern Sporades) - CreteCreteCrete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
(delimits the Aegean to the south)
Maritime claims
Continental shelf:200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Territorial sea:
6 nmi (11.1 km; 6.9 mi) (reserving the right to a future extension to 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi))
Terrain
Mostly mountains with ranges extending into the sea as peninsulas or chains of islands with 13 regions. It also includes of rocky conditions and mountainous terrain. However the surrounding bodies of water feed the surplus olivesLand use
1.) Arable land:19%
2.) Permanent crops:
8%
3.) Forests and woodland:
50%
4.) Other:
23% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land:
13 140 km² (1993 est.)
Climate and environment
Greece has three well defined climatological areas; Mediterranean, Alpine, and Mid-European Temperate.1.) Natural hazards:
severe earthquakes, droughts, wildfires
2.) Current issues:
air pollution/water pollution
3.) International agreements:
party to:
Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 97, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change , aimed at fighting global warming...
See also
- Greek islands
- Greek names of mountainsGreek names of mountainsThis is a list of mountain tops and ranges in Greece and around the world that have a Greek name.GreekEnglish name, [other name] - [older name], [Area]ΑιγάλεωMount Aegaleo, Aigaleo, Aegaleus, PiraeusΑίνοςMount AinosΆλπειςAlps, France to Austria...
- National parks in GreeceNational parks in GreeceGreece is characterized by an extremely fragmented, rugged landscape hosting a great diversity of ecosystems and an outstanding biodiversity. Almost 5% of its extensive coastline consists of ecologically sensitive wetlands...
- Geography of EuropeGeography of EuropeEurope is traditionally reckoned as one of seven continents. Physiographically, however, it is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known as Eurasia : Asia occupies the eastern bulk of this continuous landmass and all share a common continental shelf...

