
Geography of Malta
Encyclopedia

Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
of Malta
Malta
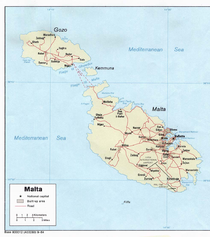
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
is dominated by water. Malta is an archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
of coralline limestone, located in the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, approximately 93 kilometres south of Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, and nearly 300 km north (Libya) and northeast (Tunisia) of Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. Although Malta is situated in Europe, it is located farther south than African Tunis
Tunis
Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants....
, capital of Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, Algiers
Algiers
' is the capital and largest city of Algeria. According to the 1998 census, the population of the city proper was 1,519,570 and that of the urban agglomeration was 2,135,630. In 2009, the population was about 3,500,000...
, capital of Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, Tangier
Tangier
Tangier, also Tangiers is a city in northern Morocco with a population of about 700,000 . It lies on the North African coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar where the Mediterranean meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel...
in Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
and also Aleppo
Aleppo
Aleppo is the largest city in Syria and the capital of Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Syrian governorate. With an official population of 2,301,570 , expanding to over 2.5 million in the metropolitan area, it is also one of the largest cities in the Levant...
in Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, and Mosul
Mosul
Mosul , is a city in northern Iraq and the capital of the Ninawa Governorate, some northwest of Baghdad. The original city stands on the west bank of the Tigris River, opposite the ancient Assyrian city of Nineveh on the east bank, but the metropolitan area has now grown to encompass substantial...
in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
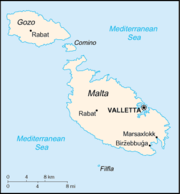
. Only the three largest islands – Malta
Malta Island
Malta Island is the largest of the three major islands that constitute the Maltese archipelago and Republic of Malta. Malta is in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea directly south of Italy and north of Libya. The area is 246 km² . The capital is Valletta, largest city is Qormi and the largest...
, Gozo and Comino – are inhabited. Other (uninhabited) islands are: Cominotto
Cominotto
Cominotto , sometimes referred to as Cominetto, is an uninhabited Mediterranean island off the northern coast of Malta. Measuring only 0.25 km² in area, Cominotto lies 100 meters to the north west of Comino....
, Filfla
Filfla
Filfla is a small, barren, uninhabited islet south of Malta, and is the most southerly point of the Maltese Archipelago. Filfoletta, a small rocky islet some 100 meters southwest of Filfla, has the southernmost point of Malta....
and the St.Paul's Islands. The country is approximately 316 km2 (122 sq mi) in area. Numerous bay
Headlands and bays
Headlands and bays are two related features of the coastal environment.- Geology and geography :Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is surrounded by land on three sides, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by high,...
s along the indented coastline of the islands provide good harbours. The landscape of the islands is characterised by high hills with terraced fields. The highest point, at 253 metres, is the Ta' Zuta on mainland Malta. The capital is Valletta
Valletta
Valletta is the capital of Malta, colloquially known as Il-Belt in Maltese. It is located in the central-eastern portion of the island of Malta, and the historical city has a population of 6,098. The name "Valletta" is traditionally reserved for the historic walled citadel that serves as Malta's...
.
Geographic coordinates:
35°50′N 14°35′E
Statistics
Map references:Europe
Area:
total:
316 km2
land:
316 km2
water:
0 km2
Area - comparative:
slightly less than twice the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries:
0 km
Coastline:
140 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone:
24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive fishing zone:
25 nmi (46.3 km; 28.8 mi)
territorial sea:
12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Climate
See also: Climate of MaltaClimate of Malta
Malta has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate , with mild winters and warm to hot summers. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry...
Subtropical-Mediterranean with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers
Elevation extremes
lowest point:
Mediterranean Sea 0 m
highest point:
Ta'Dmejrek
Ta'Dmejrek
Ta'Dmejrek is the highest point of Malta, located on the Dingli Cliffs, with an altitude of 253 metres ....
253 m (near Dingli
Dingli
Ħad-Dingli is a village on the west coast of Malta, with a population of 3,326 persons , 13 kilometers from the capital Valletta and two kilometers from the nearest town, Rabat. The village lies on a plateau some 250 metres above sea level, which is one of the highest points of Malta...
)
Land use
arable land:
38%
permanent crops:
3%
permanent pastures:
0%
forests and woodland:
0%
other:
59% (1993 est.)
Environment - current issues
very limited natural fresh water resources; increasing reliance on desalination, the slaughter of migratory birds on migration during unregulated huntingEnvironment - international agreements
party to:
Air Pollution, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol

