
Geology of Andorra
Encyclopedia
Andorra
Andorra , officially the Principality of Andorra , also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, , is a small landlocked country in southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe having an area of...
is located in the Axial Zone of the central Pyrenees
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between France and Spain...
mountain range in south western Europe. This means that it has intensely folded and thrusted rocks formed when the Iberian peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
was rotated onto the European continent.
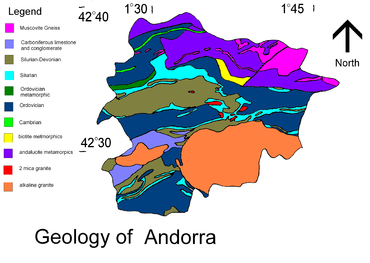
Rocks from the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
or Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
occur in the form of conglomerate
Conglomerate (geology)
A conglomerate is a rock consisting of individual clasts within a finer-grained matrix that have become cemented together. Conglomerates are sedimentary rocks consisting of rounded fragments and are thus differentiated from breccias, which consist of angular clasts...
, limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
, phyllite
Phyllite
Phyllite is a type of foliated metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz, sericite mica, and chlorite; the rock represents a gradation in the degree of metamorphism between slate and mica schist. Minute crystals of graphite, sericite, or chlorite impart a silky, sometimes golden sheen to the...
, quartzite
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard metamorphic rock which was originally sandstone. Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to gray, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink...
, and slate
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. The result is a foliated rock in which the foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering...
. Diapir
Diapir
A diapir is a type of intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily-deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh-Taylor instability-type structures in regions with low tectonic stress...
s of slate from the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
Period are found in the Llavirsi syncline
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger...
near Bixessarri
Bixessarri
Bixessarri is a village in Andorra, located in the parish of Sant Julià de Lòria....
in the south west. Gneiss
Gneiss
Gneiss is a common and widely distributed type of rock formed by high-grade regional metamorphic processes from pre-existing formations that were originally either igneous or sedimentary rocks.-Etymology:...
and schist
Schist
The schists constitute a group of medium-grade metamorphic rocks, chiefly notable for the preponderance of lamellar minerals such as micas, chlorite, talc, hornblende, graphite, and others. Quartz often occurs in drawn-out grains to such an extent that a particular form called quartz schist is...
are found in the cores of anticline
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is...
s in the north east of the country. This gneiss contains muscovite
Muscovite
Muscovite is a phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula KAl22, or 236. It has a highly-perfect basal cleavage yielding remarkably-thin laminæ which are often highly elastic...
. The antiforms are connected with near horizontal shear zone
Shear zone
A shear zone is a very important structural discontinuity surface in the Earth's crust and upper mantle. It forms as a response to inhomogeneous deformation partitioning strain into planar or curviplanar high-strain zones. Intervening blocks stay relatively unaffected by the deformation...
s, containing nappe
Nappe
In geology, a nappe is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or 5 km from its original position. Nappes form during continental plate collisions, when folds are sheared so much that they fold back over on themselves and break apart. The resulting structure is a...
s of metamorphosed
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the solid-state recrystallization of pre-existing rocks due to changes in physical and chemical conditions, primarily heat, pressure, and the introduction of chemically active fluids. Mineralogical, chemical and crystallographic changes can occur during this process...
sediments. Younger overlying Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
metamorphosed sediments found over most of Andorra have also been steeply folded.
In the south east of the country is an alkaline granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
from a batholith
Batholith
A batholith is a large emplacement of igneous intrusive rock that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust...
called Mt-Louis-Andorra Batholith. It extends into Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
and covers an area of 600 km2. Different rock composition zones occur with monzogranite found at the centre, quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
diorite
Diorite
Diorite is a grey to dark grey intermediate intrusive igneous rock composed principally of plagioclase feldspar , biotite, hornblende, and/or pyroxene. It may contain small amounts of quartz, microcline and olivine. Zircon, apatite, sphene, magnetite, ilmenite and sulfides occur as accessory...
at the edge and granodiorite
Granodiorite
Granodiorite is an intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase than orthoclase-type feldspar. Officially, it is defined as a phaneritic igneous rock with greater than 20% quartz by volume where at least 65% of the feldspar is plagioclase. It usually contains abundant...
in intermediate parts. The batholith has caused metamorphism on its western edge. The base of the batholith is exposed in the east of Andorra.
In the Central and Eastern Pyrenees, which includes Andorra, no fossils older than the Ordovician Caradoc 450–460 million years ago have been found.
Glaciation
Andorra was extensively glaciated during the QuaternaryQuaternary
The Quaternary Period is the most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the ICS. It follows the Neogene Period, spanning 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present...
; glaciers flowed down all of the major valleys of Andorra, merging into one large glacier at Escaldes-Engordany
Escaldes-Engordany
Escaldes-Engordany is one of the parishes of Andorra. The parish is composed of the areas of les Escaldes, Engordany, Els Vilars d'Engordany, Engolasters, and El Fener. As of 2005 it has a population of 16,918. Notable events include the town's annual jazz festival....
, which in the coldest stage reached as far south as Pont de la Fontaneda near Santa Coloma. Andorra has numerous glacial erosional features, including U-shaped valleys, cirque
Cirque
Cirque may refer to:* Cirque, a geological formation* Makhtesh, an erosional landform found in the Negev desert of Israel and Sinai of Egypt*Cirque , an album by Biosphere* Cirque Corporation, a company that makes touchpads...
s, arête
Arete
Areté is the term meaning "virtue" or "excellence", from Greek ἈρετήArete may also be used:*as a given name of persons or things:**Queen Arete , a character in Homer's Odyssey.***197 Arete, an asteroid....
s, and roche moutonnée
Roche moutonnée
In glaciology, a roche moutonnée is a rock formation created by the passing of a glacier. When a glacier erodes down to bedrock, it can form tear-drop shaped hills that taper in the up-ice direction.-Name:...
s. Examples of cirques include the Cirque de Pessons in the east, Llac de Tristaina in the northwest, and the two cirques at approximately 2400 m elevation on Pic de Casamanya (2740 m). Santa Coloma has a glacial terminal moraine
Terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a moraine that forms at the end of the glacier called the snout.Terminal moraines mark the maximum advance of the glacier. An end moraine is at the present boundary of the glacier....
.

