
George B. McClellan
Encyclopedia
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 October 29, 1885) was a major general
during the American Civil War
. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac
and served briefly (November 1861 to March 1862) as the general-in-chief
of the Union Army
. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union
. Although McClellan was meticulous in his planning and preparations, these characteristics may have hampered his ability to challenge aggressive opponents in a fast-moving battlefield environment. He chronically overestimated the strength of enemy units and was reluctant to apply principles of mass, frequently leaving large portions of his army unengaged at decisive points.
McClellan's Peninsula Campaign
in 1862 ended in failure, with retreats from attacks by General Robert E. Lee
's smaller Army of Northern Virginia
and an unfulfilled plan to seize the Confederate
capital of Richmond
. His performance at the bloody Battle of Antietam
blunted Lee's invasion of Maryland, but allowed Lee to eke out a precarious tactical draw and avoid destruction, despite being outnumbered. As a result, McClellan's leadership skills during battles were questioned by U.S. President
Abraham Lincoln
, who eventually removed him from command, first as general-in-chief, then from the Army of the Potomac. Lincoln offered this famous evaluation of McClellan: "If he can't fight himself, he excels in making others ready to fight." Indeed, McClellan was the most popular of that army's commanders with its soldiers, who felt that he had their morale and well-being as paramount concerns.
General McClellan also failed to maintain the trust of Lincoln, and proved to be frustratingly derisive of, and insubordinate to, his commander-in-chief
. After he was relieved of command, McClellan became the unsuccessful Democratic
nominee opposing Lincoln in the 1864 presidential election. His party had an anti-war platform, promising to end the war and negotiate with the Confederacy, which McClellan was forced to repudiate, damaging the effectiveness of his campaign. He served as the 24th Governor
of New Jersey
from 1878 to 1881. He eventually became a writer, defending his actions during the Peninsula Campaign and the Civil War.
The majority of modern authorities assess McClellan as a poor battlefield general. However, a small but vocal faction of historians maintain that he was a highly capable commander, whose reputation suffered unfairly at the hands of pro-Lincoln partisans who needed a scapegoat for the Union's setbacks. His legacy therefore defies easy categorization. After the war, Ulysses S. Grant
was asked to evaluate McClellan as a general. He replied, "McClellan is to me one of the mysteries of the war."
. The McClellan family are of Scottish
heritage. His mother was Elizabeth Steinmetz Brinton McClellan (1800-1889), daughter of a leading Pennsylvania family, a woman noted for her "considerable grace and refinement". The couple produced five children: a daughter, Frederica; then three sons, John, George, and Arthur; and a second daughter, Mary. McClellan was the grandson of Revolutionary War
general Samuel McClellan
of Woodstock, Connecticut
. He first attended the University of Pennsylvania
in 1840 at age 13, resigning himself to the study of law. After two years, he changed his goal to military service. With the assistance of his father's letter to President
John Tyler
, young George was accepted at the United States Military Academy
in 1842, the academy having waived its normal minimum age of 16.
At West Point, he was an energetic and ambitious cadet, deeply interested in the teachings of Dennis Hart Mahan
and the theoretical strategic principles of Antoine-Henri Jomini
. His closest friends were aristocratic Southerners such as James Stuart, Dabney Maury, Cadmus Wilcox, and A. P. Hill
. These associations gave McClellan what he considered to be an appreciation of the Southern mind, an understanding of the political and military implications of the sectional differences in the United States that led to the Civil War. He graduated in 1846, second in his class of 59 cadets, losing the top position (to Charles Seaforth Stewart) only because of poor drawing skills. He was commissioned a brevet
second lieutenant in the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
.
in October 1846, well prepared for action with a double-barreled shotgun, two pistols, a saber, a dress sword, and a Bowie knife
. He complained that he had arrived too late to take any part in the American victory at Monterrey
in September. During a temporary armistice in which the forces of Gen. Zachary Taylor
awaited action, McClellan was stricken with dysentery
and malaria
, which kept him in the hospital for nearly a month. The malaria would recur in later years—he called it his "Mexican disease." He served bravely as an engineering officer during the war, subjected to frequent enemy fire, and was appointed a brevet first lieutenant for Contreras
and Churubusco
and to captain for Chapultepec
, He performed reconnaissance missions for Lt. Gen.
Winfield Scott
, a close friend of McClellan's father.
McClellan's experiences during the war developed various attitudes that affected his later military and political life. He learned to appreciate the value of flanking movements over frontal assaults (used by Scott at Cerro Gordo
) and the value of siege operations (Vera Cruz
). He witnessed Scott's success in balancing political with military affairs, and his good relations with the civil population as he invaded, enforcing strict discipline on his soldiers to minimize damage to their property. And he developed a disdain for volunteer soldiers and officers, particularly politicians who cared nothing for discipline and training.
, a masonry work under construction on an island in the Delaware River
, 40 miles (64.4 km) downriver from Philadelphia. In March 1852 he was ordered to report to Capt. Randolph B. Marcy
at Fort Smith
, Arkansas
, to serve as second-in-command on an expedition to discover the sources of the Red River
. By June the expedition reached the source of the north fork of the river and Marcy named a small tributary McClellan's Creek. Upon their return to civilization on July 28, they were astonished to find that they had been given up for dead. A sensational story had reached the press, which McClellan blamed on "a set of scoundrels, who seek to keep up agitation on the frontier in order to get employment from the Govt. in one way or other," that the expedition had been ambushed by 2,000 Comanche
s and killed to the last man.
In the fall of 1852, McClellan published a manual on bayonet tactics that he had translated from the original French. He also received an assignment to the Department of Texas, with orders to perform a survey of Texas rivers and harbors. In 1853 he participated in the Pacific Railroad surveys, ordered by Secretary of War
Jefferson Davis
, to select an appropriate route for the upcoming transcontinental railroad
. McClellan surveyed the northern corridor along the 47th and 49th parallels from St. Paul to the Puget Sound
. During this assignment, he demonstrated a tendency for insubordination toward senior political figures. Isaac Stevens
, governor of the Washington Territory
, became dissatisfied with McClellan's performance in scouting passes across the Cascade Range
. (McClellan selected Yakima Pass without a thorough reconnaissance and refused the governor's order to lead a party through it in winter conditions, relying on faulty intelligence about the depth of snowpack in that area. In so doing, he missed three greatly superior passes in the near vicinity, which would be the ones eventually used for railroads and interstate highways.) The governor ordered McClellan to turn over his expedition logbooks, but McClellan steadfastly refused, most likely because of embarrassing personal comments that he had made throughout.
Returning to the East, McClellan began courting Ellen Mary Marcy (1836–1915), the daughter of his former commander. Ellen, or Nelly, refused McClellan's first proposal of marriage, one of nine that she received from a variety of suitors, including his West Point friend, A. P. Hill. Ellen accepted Hill's proposal in 1856, but her family did not approve and he withdrew.
In June 1854, McClellan was sent on a secret reconnaissance mission to Santo Domingo at the behest of Jefferson Davis. McClellan assessed local defensive capabilities for the secretary. (The information was not used until 1870, when President Ulysses S. Grant
unsuccessfully attempted to annex the Dominican Republic
.) Davis was beginning to treat McClellan almost as a protégé, and his next assignment was to assess the logistical readiness of various railroads in the United States, once again with an eye toward planning for the transcontinental railroad. In March 1855, McClellan was promoted to captain and assigned to the 1st U.S. Cavalry regiment.
Because of his political connections and his mastery of French, McClellan received the assignment to be an official observer of the European armies in the Crimean War
in 1855. Traveling widely, and interacting with the highest military commands and royal families, McClellan observed the siege of Sevastopol. Upon his return to the United States in 1856 he requested assignment in Philadelphia to prepare his report, which contained a critical analysis of the siege and a lengthy description of the organization of the European armies. He also wrote a manual on cavalry tactics
that was based on Russian cavalry regulations. A notable failure of the observers, including McClellan, was that they neglected to explain the importance of the emergence of rifled musket
s in the Crimean War, and how that would require fundamental changes in tactics for the coming Civil War.
The Army adopted McClellan's cavalry manual and also his design for a saddle
, the "McClellan Saddle
", which he claimed to have seen used by Hussar
s in Prussia
and Hungary. It became standard issue for as long as the U.S. horse cavalry existed and is currently used for ceremonies.
 McClellan resigned his commission January 16, 1857, and, capitalizing on his experience with railroad assessment, became chief engineer and vice president of the Illinois Central Railroad
McClellan resigned his commission January 16, 1857, and, capitalizing on his experience with railroad assessment, became chief engineer and vice president of the Illinois Central Railroad
and also president of the Ohio and Mississippi Railroad
in 1860. He performed well in both jobs, expanding the Illinois Central toward New Orleans
and helping the Ohio and Mississippi recover from the Panic of 1857
. But despite his successes and lucrative salary ($10,000 per year), he was frustrated with civilian employment and continued to study classical military strategy assiduously. During the Utah War
against the Mormon
s, he considered rejoining the Army. He also considered service as a filibuster
in support of Benito Juárez
in Mexico.
Before the outbreak of Civil War, McClellan became active in politics, supporting the presidential campaign of Democrat Stephen A. Douglas
in the 1860 election
. He claimed to have defeated an attempt at vote fraud by Republicans
by ordering the delay of a train that was carrying men to vote illegally in another county, enabling Douglas to win the county.
In October 1859 McClellan was able to resume his courtship of Ellen Marcy, and they were married in Calvary Church
, New York City, on May 22, 1860.
mobilized. The governors of Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York, the three largest states of the Union, actively pursued him to command their states' militia. Ohio Governor William Dennison
was the most persistent, so McClellan was commissioned a major general
of volunteers and took command of the Ohio militia on April 23, 1861. Unlike some of his fellow Union officers who came from abolition
ist families, he was opposed to federal interference with slavery. So some of his Southern colleagues approached him informally about siding with the Confederacy, but he could not accept the concept of secession
.
On May 3 McClellan re-entered federal service by being named commander of the Department of the Ohio
, responsible for the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, and, later, western Pennsylvania, western Virginia, and Missouri. On May 14, he was commissioned a major general in the regular army. At age 34 he now outranked everyone in the Army other than Lt. Gen. Winfield Scott
, the general-in-chief. McClellan's rapid promotion was partly because of his acquaintance with Salmon P. Chase
, Treasury Secretary
and former Ohio governor and senator.
As McClellan scrambled to process the thousands of men who were volunteering for service and to set up training camps, he also set his mind toward grand strategy. He wrote a letter to Gen. Scott on April 27, four days after assuming command in Ohio, that was the first proposal for a unified strategy for the war. It contained two alternatives, both with a prominent role for himself as commander. The first called for 80,000 men to invade Virginia through the Kanawha Valley
toward Richmond
. The second called for those same men to drive south instead across the Ohio River into Kentucky and Tennessee. Scott dismissed both plans as being logistically infeasible. Although he complimented McClellan and expressed his "great confidence in your intelligence, zeal, science, and energy", he replied by letter that the 80,000 men would be better used on a river-based expedition to control the Mississippi River
and split the Confederacy, accompanied by a strong Union blockade
of Southern ports. This plan, which would have demanded considerable patience on the part of the Northern public, was derided in newspapers as the Anaconda Plan
, but eventually proved to be the successful outline used to prosecute the war. Relations between the two generals became increasingly strained over the summer and fall.
that wanted to remain in the Union and later became the state of West Virginia
. He had received intelligence reports on May 26 that the critical Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
bridges in that portion of the state were being burned. As he quickly implemented plans to invade the region, he triggered his first serious political controversy by proclaiming to the citizens there that his forces had no intentions of interfering with personal property—including slaves. "Notwithstanding all that has been said by the traitors to induce you to believe that our advent among you will be signalized by interference with your slaves, understand one thing clearly—not only will we abstain from all such interference but we will on the contrary with an iron hand, crush any attempted insurrection on their part." He quickly realized that he had overstepped his bounds and apologized by letter to President Lincoln. The controversy was not that his proclamation was diametrically opposed to the administration's policy at the time, but that he was so bold in stepping beyond his strictly military role.
His forces moved rapidly into the area through Grafton
and were victorious at the tiny skirmish called the Battle of Philippi Races
, arguably the first land conflict of the war. His first personal command in battle was at Rich Mountain
, which he also won, but only after displaying a strong sense of caution and a reluctance to commit reserve forces that would be his hallmark for the rest of his career. His subordinate commander, William S. Rosecrans, bitterly complained that his attack was not reinforced as McClellan had agreed. Nevertheless, these two minor victories propelled McClellan to the status of national hero. The New York Herald
entitled an article about him, "Gen. McClellan, the Napoleon of the Present War."
 After the defeat of the Union forces at Bull Run
After the defeat of the Union forces at Bull Run
on July 21, 1861, Lincoln summoned McClellan from West Virginia, where McClellan had given the North the only actions thus far having a semblance of military victories. He traveled by special train on the main Pennsylvania line from Wheeling
through Pittsburgh
, Philadelphia
, and Baltimore, and on to Washington, D.C.
, and was overwhelmed by enthusiastic crowds that met his train along the way.
Carl Sandburg
wrote, "McClellan was the man of the hour, pointed to by events, and chosen by an overwhelming weight of public and private opinion." On July 26, the day he reached the capital, McClellan was appointed commander of the Military Division of the Potomac, the main Union force responsible for the defense of Washington. On August 20, several military units in Virginia were consolidated into his department and he immediately formed the Army of the Potomac
, with himself as its first commander. He reveled in his newly acquired power and fame:
 During the summer and fall, McClellan brought a high degree of organization to his new army, and greatly improved its morale by his frequent trips to review and encourage his units. It was a remarkable achievement, in which he came to personify the Army of the Potomac and reaped the adulation of his men. He created defenses for Washington that were almost impregnable, consisting of 48 forts and strong points, with 480 guns manned by 7,200 artillerists. The Army of the Potomac grew in number from 50,000 in July to 168,000 in November and was considered by far the most colossal military unit the world had seen in modern historical times. But this was also a time of tension in the high command, as he continued to quarrel frequently with the government and the general-in-chief, Lt. Gen. Scott, on matters of strategy. McClellan rejected the tenets of Scott's Anaconda Plan, favoring instead an overwhelming grand battle, in the Napoleonic
During the summer and fall, McClellan brought a high degree of organization to his new army, and greatly improved its morale by his frequent trips to review and encourage his units. It was a remarkable achievement, in which he came to personify the Army of the Potomac and reaped the adulation of his men. He created defenses for Washington that were almost impregnable, consisting of 48 forts and strong points, with 480 guns manned by 7,200 artillerists. The Army of the Potomac grew in number from 50,000 in July to 168,000 in November and was considered by far the most colossal military unit the world had seen in modern historical times. But this was also a time of tension in the high command, as he continued to quarrel frequently with the government and the general-in-chief, Lt. Gen. Scott, on matters of strategy. McClellan rejected the tenets of Scott's Anaconda Plan, favoring instead an overwhelming grand battle, in the Napoleonic
style. He proposed that his army should be expanded to 273,000 men and 600 guns and "crush the rebels in one campaign." He favored a war that would impose little impact on civilian populations and require no emancipation of slaves.
McClellan's antipathy to emancipation added to the pressure on him, as he received bitter criticism from Radical Republicans in the government. He viewed slavery as an institution recognized in the Constitution
, and entitled to federal protection wherever it existed (Lincoln held the same public position until August 1862). McClellan's writings after the war were typical of many Northerners: "I confess to a prejudice in favor of my own race, & can't learn to like the odor of either Billy goats or niggers." But in November 1861, he wrote to his wife, "I will, if successful, throw my sword onto the scale to force an improvement in the condition of those poor blacks." He later wrote that had it been his place to arrange the terms of peace, he would have insisted on gradual emancipation, guarding the rights of both slaves and masters, as part of any settlement. But he made no secret of his opposition to the radical Republicans. He told Ellen, "I will not fight for the abolitionists." This placed him at an obvious handicap because many politicians running the government believed that he was attempting to implement the policies of the opposition party.
The immediate problem with McClellan's war strategy was that he was convinced the Confederates were ready to attack him with overwhelming numbers. On August 8, believing that the Confederates had over 100,000 troops facing him (in contrast to the 35,000 they actually deployed at Bull Run a few weeks earlier), he declared a state of emergency in the capital. By August 19, he estimated 150,000 enemy to his front. McClellan's future campaigns would be strongly influenced by the overblown enemy strength estimates of his secret service chief, detective Allan Pinkerton
, but in August 1861, these estimates were entirely McClellan's own. The result was a level of extreme caution that sapped the initiative of McClellan's army and caused great condemnation by his government. Historian and biographer Stephen W. Sears has called McClellan's actions "essentially sound" if he had been as outnumbered as he believed, but McClellan in fact rarely had less than a two-to-one advantage over his opponents in 1861 and 1862. That fall, for example, Confederate forces ranged from 35,000 to 60,000, whereas the Army of the Potomac in September numbered 122,000 men; in early December 170,000; by year end, 192,000.
The dispute with Scott would become very personal. Scott (along with many in the War Department) was outraged that McClellan refused to divulge any details about his strategic planning, or even mundane details such as troop strengths and dispositions. (For his part, McClellan claimed not to trust anyone in the administration to keep his plans secret from the press, and thus the enemy.) During disagreements about defensive forces on the Potomac River, McClellan wrote to his wife on August 10 in a manner that would characterize some of his more private correspondence: "Genl Scott is the great obstacle—he will not comprehend the danger & is either a traitor, or an incompetent. I have to fight my way against him." Scott became so disillusioned over his relationship with the young general that he offered his resignation to President Lincoln, who initially refused to accept it. Rumors traveled through the capital that McClellan might resign, or instigate a military coup, if Scott were not removed. Lincoln's Cabinet met on October 18 and agreed to accept Scott's resignation for "reasons of health."
 On November 1, 1861, Winfield Scott
On November 1, 1861, Winfield Scott
retired and McClellan became general-in-chief of all the Union armies. The president expressed his concern about the "vast labor" involved in the dual role of army commander and general-in-chief, but McClellan responded, "I can do it all."
Lincoln, as well as many other leaders and citizens of the northern states, became increasingly impatient with McClellan's slowness to attack the Confederate forces still massed near Washington. The Union defeat at the minor Battle of Ball's Bluff
near Leesburg
in October added to the frustration and indirectly damaged McClellan. In December, the Congress formed a Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War
, which became a thorn in the side of many generals throughout the war, accusing them of incompetence and, in some cases, treason. McClellan was called as the first witness on December 23, but he contracted typhoid fever
and could not attend. Instead, his subordinate officers testified, and their candid admissions that they had no knowledge of specific strategies for advancing against the Confederates raised many calls for McClellan's dismissal.
McClellan further damaged his reputation by his insulting insubordination to his commander-in-chief. He privately referred to Lincoln, whom he had known before the war as a lawyer for the Illinois Central, as "nothing more than a well-meaning baboon", a "gorilla", and "ever unworthy of ... his high position." On November 13, he snubbed the president, visiting at McClellan's house, by making him wait for 30 minutes, only to be told that the general had gone to bed and could not see him.
On January 10, Lincoln met with top generals (McClellan did not attend) and directed them to formulate a plan of attack, expressing his exasperation with General McClellan with the following remark: "If General McClellan does not want to use the army, I would like to borrow it for a time." On January 12, 1862, McClellan was summoned to the White House, where the Cabinet demanded to hear his war plans. For the first time, he revealed his intentions to transport the Army of the Potomac by ship to Urbanna
, Virginia
, on the Rappahannock River
, outflanking the Confederate forces near Washington, and proceeding 50 miles (80.5 km) overland to capture Richmond. He refused to give any specific details of the proposed campaign, even to his friend, newly appointed War Secretary
Edwin M. Stanton
. On January 27, Lincoln issued an order that required all of his armies to begin offensive operations by February 22, Washington's birthday. On January 31, he issued a supplementary order for the Army of the Potomac to move overland to attack the Confederates at Manassas Junction
and Centreville
. McClellan immediately replied with a 22-page letter objecting in detail to the president's plan and advocating instead his Urbanna plan, which was the first written instance of the plan's details being presented to the president. Although Lincoln believed his plan was superior, he was relieved that McClellan finally agreed to begin moving, and reluctantly approved. On March 8, doubting McClellan's resolve, Lincoln again interfered with the army commander's prerogatives. He called a council of war
at the White House in which McClellan's subordinates were asked about their confidence in the Urbanna plan. They expressed their confidence to varying degrees. After the meeting, Lincoln issued another order, naming specific officers as corps commanders to report to McClellan (who had been reluctant to do so prior to assessing his division commanders' effectiveness in combat, even though this would have meant his direct supervision of twelve divisions in the field).
Two more crises would hit McClellan before he could implement his plans. The Confederate forces under General Joseph E. Johnston
withdrew from their positions before Washington, assuming new positions south of the Rappahannock, which completely nullified the Urbanna strategy. McClellan retooled his plan so that his troops would disembark at Fort Monroe, Virginia
, and advance up the Virginia Peninsula
to Richmond, an operation that would be known as the Peninsula Campaign
. However, McClellan came under extreme criticism from the press and the Congress when it was found that Johnston's forces had not only slipped away unnoticed, but had for months fooled the Union Army through the use of logs painted black to appear as cannons, nicknamed Quaker Gun
s. The Congress's joint committee visited the abandoned Confederate lines and radical Republicans introduced a resolution demanding the dismissal of McClellan, but it was narrowly defeated by a parliamentary maneuver. The second crisis was the emergence of the Confederate ironclad CSS Virginia
, which threw Washington into a panic and made naval support operations on the James River
seem problematic.
On March 11, 1862, Lincoln removed McClellan as general-in-chief, leaving him in command of only the Army of the Potomac, ostensibly so that McClellan would be free to devote all his attention to the move on Richmond. Lincoln's order was ambiguous as to whether McClellan might be restored following a successful campaign. In fact, his position was not filled by another officer. Lincoln, Stanton, and a group of officers called the "War Board" directed the strategic actions of the Union armies that spring. Although McClellan was assuaged by supportive comments Lincoln made to him, in time he saw the change of command very differently, describing it as a part of an intrigue "to secure the failure of the approaching campaign."
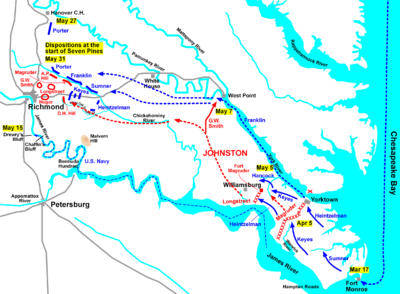
 McClellan's army began to sail from Alexandria
McClellan's army began to sail from Alexandria
on March 17. It was an armada that dwarfed all previous American expeditions, transporting 121,500 men, 44 artillery batteries, 1,150 wagons, over 15,000 horses, and tons of equipment and supplies. An English observer remarked that it was the "stride of a giant." The army's advance from Fort Monroe
up the Virginia Peninsula
proved to be slow. McClellan's plan for a rapid seizure of Yorktown
was foiled when he discovered that the Confederates had fortified a line across the Peninsula, causing him to decide on a siege of the city, which required considerable preparation.
McClellan continued to believe intelligence reports that credited the Confederates with two or three times the men they actually had. Early in the campaign, Confederate General John B. "Prince John" Magruder
defended the Peninsula against McClellan's advance with a vastly smaller force. He created a false impression of many troops behind the lines and of even more troops arriving. He accomplished this by marching small groups of men repeatedly past places where they could be observed at a distance or were just out of sight, accompanied by great noise and fanfare. During this time, General Johnston was able to provide Magruder with reinforcements, but even then there were far fewer troops than McClellan believed were opposite him.
After a month of preparation, just before he was to assault the Confederate works at Yorktown, McClellan learned that Johnston had withdrawn up the Peninsula towards Williamsburg
. McClellan was thus required to give chase without any benefit of the heavy artillery so carefully amassed in front of Yorktown. The Battle of Williamsburg
on May 5 is considered a Union victory—McClellan's first—but the Confederate army was not destroyed and a bulk of their troops were successfully moved past Williamsburg to Richmond's outer defenses while it was waged, and over the next several days.
McClellan had also placed hopes on a simultaneous naval approach to Richmond via the James River
. That approach failed following the Union Navy's defeat at the Battle of Drewry's Bluff
, about 7 miles (11.3 km) downstream from the Confederate capital, on May 15. Basing artillery on a strategic bluff high above a bend in the river, and sinking boats to create an impassable series of obstacles in the river itself, the Confederates had effectively blocked this potential approach to Richmond.
McClellan's army cautiously inched towards Richmond over the next three weeks, coming to within four miles (6 km) of it. He established a supply base on the Pamunkey River
(a navigable tributary of the York River
) at White House Landing where the Richmond and York River Railroad
extending to Richmond crossed, and commandeered the railroad, transporting steam locomotive
s and rolling stock to the site by barge.
On May 31, as McClellan planned an assault, his army was surprised by a Confederate attack. Johnston saw that the Union army was split in half by the rain-swollen Chickahominy River
and hoped to defeat it in detail
at Seven Pines
and Fair Oaks. McClellan was unable to command the army personally because of a recurrence of malarial fever, but his subordinates were able to repel the attacks. Nevertheless, McClellan received criticism from Washington for not counterattacking, which some believed could have opened the city of Richmond to capture. Johnston was wounded in the battle, and General Robert E. Lee assumed command of the Army of Northern Virginia
. McClellan spent the next three weeks repositioning his troops and waiting for promised reinforcements, losing valuable time as Lee continued to strengthen Richmond's defenses.
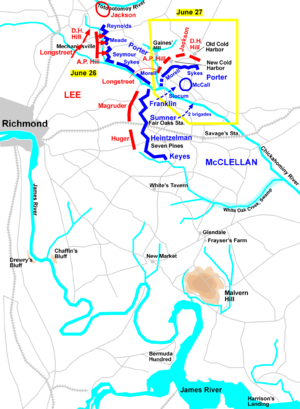
At the end of June, Lee began a series of attacks that became known as the Seven Days Battles
. The first major battle, at Mechanicsville
, was poorly coordinated by Lee and his subordinates and caused heavy casualties for little tactical gain. But the battle had significant impact on McClellan's nerve. The surprise appearance of Maj. Gen. Stonewall Jackson
's troops in the battle (when they had last been reported to be many miles away in the Shenandoah Valley
) convinced McClellan that he was even more significantly outnumbered than he had assumed. (He reported to Washington that he faced 200,000 Confederates, but there were actually 85,000.)
 As Lee continued his offensive at Gaines's Mill to the east, McClellan played a passive role, taking no initiative and waiting for events to unfold. He kept two thirds of his army out of action, fooled again by Magruder's theatrical diversionary tactics. That night, he decided to withdraw his army to a safer base, well below Richmond, on a portion of the James River that was under control of the Union Navy. In doing so, he may have unwittingly saved his army. Lee had assumed that the Union army would withdraw to the east toward its existing supply base and McClellan's move to the south delayed Lee's response for at least 24 hours. But McClellan was also tacitly acknowledging that he would no longer be able to invest
As Lee continued his offensive at Gaines's Mill to the east, McClellan played a passive role, taking no initiative and waiting for events to unfold. He kept two thirds of his army out of action, fooled again by Magruder's theatrical diversionary tactics. That night, he decided to withdraw his army to a safer base, well below Richmond, on a portion of the James River that was under control of the Union Navy. In doing so, he may have unwittingly saved his army. Lee had assumed that the Union army would withdraw to the east toward its existing supply base and McClellan's move to the south delayed Lee's response for at least 24 hours. But McClellan was also tacitly acknowledging that he would no longer be able to invest
Richmond, the object of his campaign; the heavy siege artillery required would be almost impossible to transport without the railroad connections available from his original supply base on the York River. In a telegram to Secretary of War
Edwin Stanton, reporting on these events, McClellan blamed the Lincoln administration for his reversals. "If I save this army now, I tell you plainly I owe no thanks to you or to any other persons in Washington. You have done your best to sacrifice this army." Fortunately for McClellan's immediate career, Lincoln never saw that inflammatory statement (at least at that time) because it was censored by the War Department telegrapher.
 McClellan was also fortunate that the failure of the campaign left his army mostly intact, because he was generally absent from the fighting and neglected to name a second-in-command to control his retreat. Military historian Stephen W. Sears
McClellan was also fortunate that the failure of the campaign left his army mostly intact, because he was generally absent from the fighting and neglected to name a second-in-command to control his retreat. Military historian Stephen W. Sears
wrote, "When he deserted his army on the Glendale
and Malvern Hill
battlefields during the Seven Days, he was guilty of dereliction of duty
. Had the Army of the Potomac been wrecked on either of these fields (at Glendale the possibility had been real), that charge under the Articles of War would likely have been brought against him." (During Glendale, McClellan was five miles (8 km) away behind Malvern Hill, without telegraph communications and too distant to command the army. During the battle of Malvern Hill, he was on a gunboat, the U.S.S. Galena
, which at one point was ten miles (16 km) away down the James River. During both battles, effective command of the army fell to his friend and V Corps commander Brigadier General Fitz John Porter
. When the public heard about the Galena, it was yet another enormous embarrassment, comparable to the Quaker Guns at Manassas. Editorial cartoons during the 1864 presidential campaign
would lampoon McClellan for preferring the safety of a ship while a battle was fought in the distance.)
McClellan was reunited with his army at Harrison's Landing on the James. Debates were held as to whether the army should be evacuated or attempt to resume an offensive toward Richmond. McClellan maintained his estrangement from Abraham Lincoln by his continuous call for reinforcements and by writing a lengthy letter in which he proposed strategic and political guidance for the war, continuing his opposition to abolition or seizure of slaves as a tactic. He concluded by implying he should be restored as general-in-chief, but Lincoln responded by naming Maj. Gen. Henry W. Halleck to the post without consulting, or even informing, McClellan. Lincoln and Stanton also offered command of the Army of the Potomac to Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
, who refused the appointment.
Back in Washington, a reorganization of units created the Army of Virginia
under Maj. Gen. John Pope
, who was directed to advance towards Richmond from the northeast. McClellan resisted calls to reinforce Pope's army and delayed return of the Army of the Potomac from the Peninsula enough so that the reinforcements arrived while the Northern Virginia Campaign
was already underway. He wrote to his wife before the battle, "Pope will be thrashed ... & be disposed of [by Lee]. ... Such a villain as he is ought to bring defeat upon any cause that employs him." Lee had assessed McClellan's offensive nature and gambled on removing significant units from the Peninsula to attack Pope, who was beaten decisively at Second Bull Run in August.

 After the defeat of Pope at Second Bull Run, President Lincoln reluctantly returned to the man who had mended a broken army before. He realized that McClellan was a strong organizer and a skilled trainer of troops, able to recombine the units of Pope's army with the Army of the Potomac faster than anyone. On September 2, 1862, Lincoln named McClellan to command "the fortifications of Washington, and all the troops for the defense of the capital." The appointment was controversial in the Cabinet, a majority of whom signed a petition declaring to the president "our deliberate opinion that, at this time, it is not safe to entrust to Major General McClellan the command of any Army of the United States." The president admitted that it was like "curing the bite with the hair of the dog." But Lincoln told his secretary, John Hay, "We must use what tools we have. There is no man in the Army who can man these fortifications and lick these troops of ours into shape half as well as he. If he can't fight himself, he excels in making others ready to fight."
After the defeat of Pope at Second Bull Run, President Lincoln reluctantly returned to the man who had mended a broken army before. He realized that McClellan was a strong organizer and a skilled trainer of troops, able to recombine the units of Pope's army with the Army of the Potomac faster than anyone. On September 2, 1862, Lincoln named McClellan to command "the fortifications of Washington, and all the troops for the defense of the capital." The appointment was controversial in the Cabinet, a majority of whom signed a petition declaring to the president "our deliberate opinion that, at this time, it is not safe to entrust to Major General McClellan the command of any Army of the United States." The president admitted that it was like "curing the bite with the hair of the dog." But Lincoln told his secretary, John Hay, "We must use what tools we have. There is no man in the Army who can man these fortifications and lick these troops of ours into shape half as well as he. If he can't fight himself, he excels in making others ready to fight."
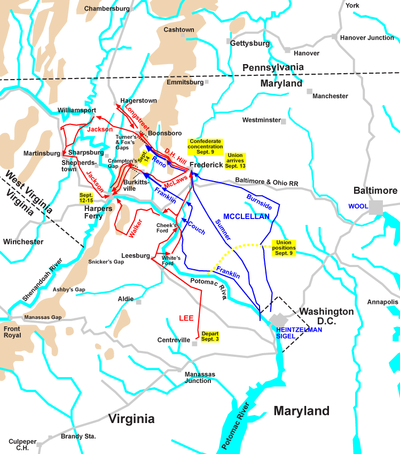
Northern fears of a continued offensive by Robert E. Lee were realized when he launched his Maryland Campaign
on September 4, hoping to arouse pro-Southern sympathy in the slave state of Maryland
. McClellan's pursuit began on September 5. He marched toward Maryland with six of his reorganized corps, about 84,000 men, while leaving two corps behind to defend Washington. McClellan's reception in Frederick, Maryland
, as he marched towards Lee's army, was described by the correspondent for Harper's Magazine
:
Lee divided his forces into multiple columns, spread apart widely as he moved into Maryland and also maneuvered to capture the federal arsenal at Harpers Ferry
. This was a risky move for a smaller army, but Lee was counting on his knowledge of McClellan's temperament. He told one of his generals, "He is an able general but a very cautious one. His army is in a very demoralized and chaotic condition, and will not be prepared for offensive operations—or he will not think it so—for three or four weeks. Before that time I hope to be on the Susquehanna." This was not a completely accurate assessment, but McClellan's army was moving lethargically, averaging only 6 miles (9.7 km) a day.
However, McClellan soon received a miraculous break of fortune. Union soldiers accidentally found a copy of Lee's orders
dividing his army, wrapped around a package of cigars in an abandoned camp. They delivered the order to McClellan's headquarters in Frederick on September 13. Upon realizing the intelligence value of this discovery, McClellan threw up his arms and exclaimed, "Now I know what to do!" He waved the order at his old Army friend, Brig. Gen.
John Gibbon
, and said, "Here is a paper with which if I cannot whip Bobbie Lee, I will be willing to go home." He telegraphed President Lincoln: "I have the whole rebel force in front of me, but I am confident, and no time shall be lost. I think Lee has made a gross mistake, and that he will be severely punished for it. I have all the plans of the rebels, and will catch them in their own trap if my men are equal to the emergency. ... Will send you trophies.".
 Despite this show of bravado, McClellan continued his cautious line. After telegraphing to the president at noon on September 13, rather than ordering his units to set out for the South Mountain passes immediately, he ordered them to depart the following morning. The 18 hours of delay allowed Lee time to react, because he received intelligence from a Confederate sympathizer that McClellan knew of his plans. (The delay also doomed the federal garrison at Harpers Ferry because the relief column McClellan sent could not reach them before they surrendered to Stonewall Jackson.) In the Battle of South Mountain
Despite this show of bravado, McClellan continued his cautious line. After telegraphing to the president at noon on September 13, rather than ordering his units to set out for the South Mountain passes immediately, he ordered them to depart the following morning. The 18 hours of delay allowed Lee time to react, because he received intelligence from a Confederate sympathizer that McClellan knew of his plans. (The delay also doomed the federal garrison at Harpers Ferry because the relief column McClellan sent could not reach them before they surrendered to Stonewall Jackson.) In the Battle of South Mountain
, McClellan's army was able to punch through the defended passes that separated them from Lee, but also gave Lee enough time to concentrate many of his men at Sharpsburg
, Maryland
. The Battle of South Mountain presented McClellan with an opportunity for one of the great theatrical moments of his career, as historian Sears describes:
The Union army reached Antietam Creek, to the east of Sharpsburg, on the evening of September 15. A planned attack on September 16 was put off because of early morning fog, allowing Lee to prepare his defenses with an army less than half the size of McClellan's.
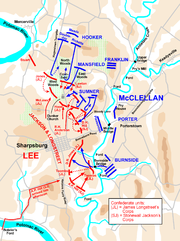
 The Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam
on September 17, 1862, was the single bloodiest day in American military history. The outnumbered Confederate forces fought desperately and well. Despite significant advantages in manpower, McClellan was unable to concentrate his forces effectively, which meant that Lee was able to shift his defenders to parry each of three Union thrusts, launched separately and sequentially against the Confederate left, center, and finally the right. And McClellan was unwilling to employ his ample reserve forces to capitalize on localized successes. Historian James M. McPherson
has pointed out that the two corps McClellan kept in reserve were in fact larger than Lee's entire force. The reason for McClellan's reluctance was that, as in previous battles, he was convinced he was outnumbered.
 The battle was tactically inconclusive, although Lee technically was defeated because he withdrew first from the battlefield and retreated back to Virginia. McClellan wired to Washington, "Our victory was complete. The enemy is driven back into Virginia." Yet there was obvious disappointment that McClellan had not crushed Lee, who was fighting with a smaller army with its back to the Potomac River. Although McClellan's subordinates can claim their share of responsibility for delays (such as Ambrose Burnside
The battle was tactically inconclusive, although Lee technically was defeated because he withdrew first from the battlefield and retreated back to Virginia. McClellan wired to Washington, "Our victory was complete. The enemy is driven back into Virginia." Yet there was obvious disappointment that McClellan had not crushed Lee, who was fighting with a smaller army with its back to the Potomac River. Although McClellan's subordinates can claim their share of responsibility for delays (such as Ambrose Burnside
's misadventures at Burnside Bridge) and blunders (Edwin V. Sumner's attack without reconnaissance), these were localized problems from which the full army could have recovered. As with the decisive battles in the Seven Days, McClellan's headquarters were too far to the rear to allow his personal control over the battle. He made no use of his cavalry forces for reconnaissance. He did not share his overall battle plans with his corps commanders, which prevented them from using initiative outside of their sectors. And he was far too willing to accept cautious advice about saving his reserves, such as when a significant breakthrough in the center of the Confederate line could have been exploited, but Fitz John Porter
is said to have told McClellan, "Remember, General, I command the last reserve of the last Army of the Republic."
Despite being a tactical draw, Antietam is considered a turning point
of the war and a victory for the Union because it ended Lee's strategic campaign (his first invasion of the North) and it allowed President Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation
on September 22, taking effect on January 1, 1863. Although Lincoln had intended to issue the proclamation earlier, he was advised by his Cabinet to wait until a Union victory to avoid the perception that it was issued out of desperation. The Union victory and Lincoln's proclamation played a considerable role in dissuading the governments of France
and Britain
from recognizing the Confederacy; some suspected they were planning to do so in the aftermath of another Union defeat. McClellan had no prior knowledge that the plans for emancipation rested on his battle performance.
When McClellan failed to pursue Lee aggressively after Antietam, Lincoln ordered that he be removed from command on November 5. Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
assumed command of the Army of the Potomac on November 7. McClellan wrote to his wife, "Those in whose judgment I rely tell me that I fought the battle splendidly and that it was a masterpiece of art. ... I feel I have done all that can be asked in twice saving the country. ... I feel some little pride in having, with a beaten & demoralized army, defeated Lee so utterly. ... Well, one of these days history will I trust do me justice."
 Secretary Stanton ordered McClellan to report to Trenton
Secretary Stanton ordered McClellan to report to Trenton
, New Jersey
, for further orders, although none were issued. As the war progressed, there were various calls to return Little Mac to an important command, following the Union defeats at Fredericksburg
and Chancellorsville
, as Robert E. Lee moved north at the start of the Gettysburg Campaign
, and as Jubal Early
threatened Washington in 1864. When Ulysses S. Grant became general-in-chief, he discussed returning McClellan to an unspecified position. But all of these opportunities were impossible, given the opposition within the administration and the knowledge that McClellan posed a potential political threat. McClellan worked for months on a lengthy report describing his two major campaigns and his successes in organizing the Army, replying to his critics and justifying his actions by accusing the administration of undercutting him and denying him necessary reinforcements. The War Department was reluctant to publish his report because, just after completing it in October 1863, McClellan openly declared his entrance to the political stage as a Democrat.
 McClellan was nominated by the Democrats
McClellan was nominated by the Democrats
to run against Abraham Lincoln
in the 1864 U.S. presidential election. Following the example of Winfield Scott
, he ran as a U.S. Army general still on active duty; he did not resign his commission until election day, November 8, 1864. He supported continuation of the war and restoration of the Union (though not the abolition of slavery), but the party platform, written by Copperhead
Clement Vallandigham
of Ohio, was opposed to this position. The platform called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and a negotiated settlement with the Confederacy. McClellan was forced to repudiate the platform, which made his campaign inconsistent and difficult. He also was not helped by the party's choice for vice president, George H. Pendleton
, a peace candidate from Ohio.
The deep division in the party, the unity of the Republicans (running under the label "National Union Party"), and the military successes by Union forces in the fall of 1864 doomed McClellan's candidacy. Lincoln won the election handily, with 212 Electoral College votes to 21 and a popular vote of 403,000, or 55%. For all his popularity with the troops, McClellan failed to secure their support and the military vote went to Lincoln nearly 3-1. Lincoln's share of the vote in the Army of the Potomac was 70%.
.
McClellan was appointed chief engineer of the New York City Department of Docks in 1870. Evidently the position did not demand his full-time attention because, starting in 1872, he also served as the president of the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad
. He and his family then embarked on another three-year stay in Europe (1873-75)
In March 1877, McClellan was nominated by Governor Lucius Robinson
to be the first Superintendent of Public Works
but was rejected by the New York State Senate
as being "incompetent for the position."
In 1877, McClellan was nominated by the Democrats for Governor of New Jersey
, an action that took him by surprise because he had not expressed an interest in the position. He accepted the nomination, was elected, and served a single term from 1878 to 1881, a tenure marked by careful, conservative executive management and minimal political rancor. The concluding chapter of his political career was his strong support in 1884 for the election of Grover Cleveland
. He sought the position of secretary of war
in Cleveland's cabinet, for which he was well qualified, but political rivals from New Jersey were able to block his nomination.
McClellan's final years were devoted to traveling and writing, including his memoirs McClellan's Own Story (published posthumously in 1887) in which he stridently defended his conduct during the war. He died unexpectedly of a heart attack at age 58 at Orange
, New Jersey
, after having suffered from chest pains for a few weeks. His final words, at 3 a.m., October 29, 1885, were, "I feel easy now. Thank you." He was buried at Riverview Cemetery, Trenton, New Jersey.
McClellan's son, George B. McClellan, Jr.
(1865 1940), was born in Dresden, Germany, during the family's first trip to Europe. Known within the family as Max, he was also a politician, serving as a United States Representative from New York State and as Mayor of New York City
from 1904 to 1909. McClellan's daughter, Mary ("May") (1861 1945), married a French diplomat and spent much of her life abroad. His wife Ellen died in Nice, France, while visiting May at "Villa Antietam." Neither Max nor May had any children of their own.
commented in McClellan's obituary, "Probably no soldier who did so little fighting has ever had his qualities as a commander so minutely, and we may add, so fiercely discussed." This fierce discussion has continued for over a century. McClellan is usually ranked in the lowest tier of Civil War generals. However, the debate over McClellan's ability and talents remains the subject of much controversy among Civil War and military historians. He has been universally praised for his organizational abilities and for his very good relations with his troops. They referred to him affectionately as "Little Mac"; others sometimes called him the "Young Napoleon". It has been suggested that his reluctance to enter battle was caused in part by an intense desire to avoid spilling the blood of his men. Ironically, this led to failing to take the initiative against the enemy and therefore passing up good opportunities for decisive victories, which could have ended the war early, and thereby could have spared thousands of soldiers who died in those subsequent battles. Generals who proved successful in the war, such as Lee and Grant, tended to be more aggressive and more willing to risk a major battle even when all preparations were not perfect. McClellan himself summed up his cautious nature in a draft of his memoirs:
McClellan's reluctance to press his enemy aggressively was probably not a matter of personal courage, which he demonstrated well enough by his bravery under fire in the Mexican-American War. Stephen Sears wrote,
One of the reasons that McClellan's reputation has suffered is because of his own memoirs. Historian Allan Nevins
wrote, "Students of history must always be grateful McClellan so frankly exposed his own weaknesses in this posthumous book." Doris Kearns Goodwin
claims that a review of his personal correspondence during the war reveals a tendency for self-aggrandizement and unwarranted self-congratulation. His original draft was completed in 1881, but the only copy was destroyed by fire. He began to write another draft of what would be published posthumously, in 1887, as McClellan's Own Story. However, he died before it was half completed and his literary executor, William C. Prime, editor of the pro-McClellan New York Journal of Commerce, included excerpts from some 250 of McClellan's wartime letters to his wife, in which it had been his habit to reveal his innermost feelings and opinions in unbridled fashion.
Robert E. Lee, on being asked (by his cousin, and recorded by his son) who was the ablest general on the Union side during the late war, replied emphatically: "McClellan, by all odds!"
While McClellan's reputation has suffered over time, especially over the last 75 years, there is a small but intense cadre of American Civil War historians who believe that the general has been poorly served on at least four levels. First, McClellan proponents say that because the general was a conservative Democrat with great personal charisma, radical Republicans fearing his political potential deliberately undermined his field operations. Second, that as the radical Republicans were the true winners coming out of the American Civil War, they were able to write its history, placing their principal political rival of the time, McClellan, in the worst possible light. Third, that historians eager to jump on the bandwagon of Lincoln as America's greatest political icon worked to outdo one another in shifting blame for early military failures from Lincoln and Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton to McClellan. And fourth, that Lincoln and Stanton deliberately undermined McClellan because of his conciliatory stance towards the South, which might have resulted in a less destructive end to the war had Richmond fallen as a result of the Peninsula Campaign. Proponents of this school claim that McClellan is criticized more for his admittedly abrasive personality than for his actual field performance.
Several geographic features and establishments have been named for George B. McClellan. These include Fort McClellan
in Alabama
, McClellan Butte
in the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest
, where he traveled while conducting the Pacific Railroad Survey in 1853, and a bronze equestrian statue honoring General McClellan in Washington, D.C. Another equestrian statue honors him in front of Philadelphia City Hall
.
:
United States presidential election, 1864
New Jersey
gubernatorial
election, 1877:
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
and served briefly (November 1861 to March 1862) as the general-in-chief
General-in-Chief
General-in-Chief has been a military rank or title in various armed forces around the world.- France :In France, General-in-Chief was first an informal title for the lieutenant-general commanding over others lieutenant-generals, or even for some marshals in charge of an army...
of the Union Army
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union was a name used to refer to the federal government of the United States, which was supported by the twenty free states and five border slave states. It was opposed by 11 southern slave states that had declared a secession to join together to form the...
. Although McClellan was meticulous in his planning and preparations, these characteristics may have hampered his ability to challenge aggressive opponents in a fast-moving battlefield environment. He chronically overestimated the strength of enemy units and was reluctant to apply principles of mass, frequently leaving large portions of his army unengaged at decisive points.
McClellan's Peninsula Campaign
Peninsula Campaign
The Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
in 1862 ended in failure, with retreats from attacks by General Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
's smaller Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
and an unfulfilled plan to seize the Confederate
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
capital of Richmond
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
. His performance at the bloody Battle of Antietam
Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam , fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek, as part of the Maryland Campaign, was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with about 23,000...
blunted Lee's invasion of Maryland, but allowed Lee to eke out a precarious tactical draw and avoid destruction, despite being outnumbered. As a result, McClellan's leadership skills during battles were questioned by U.S. President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
, who eventually removed him from command, first as general-in-chief, then from the Army of the Potomac. Lincoln offered this famous evaluation of McClellan: "If he can't fight himself, he excels in making others ready to fight." Indeed, McClellan was the most popular of that army's commanders with its soldiers, who felt that he had their morale and well-being as paramount concerns.
General McClellan also failed to maintain the trust of Lincoln, and proved to be frustratingly derisive of, and insubordinate to, his commander-in-chief
Commander-in-Chief
A commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
. After he was relieved of command, McClellan became the unsuccessful Democratic
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
nominee opposing Lincoln in the 1864 presidential election. His party had an anti-war platform, promising to end the war and negotiate with the Confederacy, which McClellan was forced to repudiate, damaging the effectiveness of his campaign. He served as the 24th Governor
Governor of New Jersey
The Office of the Governor of New Jersey is the executive branch for the U.S. state of New Jersey. The office of Governor is an elected position, for which elected officials serve four year terms. While individual politicians may serve as many terms as they can be elected to, Governors cannot be...
of New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
from 1878 to 1881. He eventually became a writer, defending his actions during the Peninsula Campaign and the Civil War.
The majority of modern authorities assess McClellan as a poor battlefield general. However, a small but vocal faction of historians maintain that he was a highly capable commander, whose reputation suffered unfairly at the hands of pro-Lincoln partisans who needed a scapegoat for the Union's setbacks. His legacy therefore defies easy categorization. After the war, Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
was asked to evaluate McClellan as a general. He replied, "McClellan is to me one of the mysteries of the war."
Early life and career
McClellan was born in Philadelphia, the son of a prominent surgical ophthalmologist, Dr. George McClellan (1796-1847), the founder of Jefferson Medical CollegeThomas Jefferson University
Thomas Jefferson University is a private health sciences university in Center City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in the United States. The university consists of six constituent colleges and schools, Jefferson Medical College, Jefferson College of Graduate Studies, Jefferson School of Health...
. The McClellan family are of Scottish
Scottish people
The Scottish people , or Scots, are a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland. Historically they emerged from an amalgamation of the Picts and Gaels, incorporating neighbouring Britons to the south as well as invading Germanic peoples such as the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse.In modern use,...
heritage. His mother was Elizabeth Steinmetz Brinton McClellan (1800-1889), daughter of a leading Pennsylvania family, a woman noted for her "considerable grace and refinement". The couple produced five children: a daughter, Frederica; then three sons, John, George, and Arthur; and a second daughter, Mary. McClellan was the grandson of Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
general Samuel McClellan
Samuel McClellan
Samuel McClellan was a Brigadier General in the American Revolutionary War. He was born in Worcester, Massachusetts, married Rachel Abbe on March 5, 1766, and is buried in Woodstock, Connecticut.Samuel McClellan served as Ensign and Lieutenant in the French and Indian War, and was...
of Woodstock, Connecticut
Woodstock, Connecticut
Woodstock is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 7,221 at the 2000 census.-Annual events:*The Woodstock Fair, run by the Woodstock Agricultural Society has been held since 1860. The current President of the Woodstock Fair is Susan Z. Hibbard...
. He first attended the University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania is a private, Ivy League university located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Penn is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States,Penn is the fourth-oldest using the founding dates claimed by each institution...
in 1840 at age 13, resigning himself to the study of law. After two years, he changed his goal to military service. With the assistance of his father's letter to President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
John Tyler
John Tyler
John Tyler was the tenth President of the United States . A native of Virginia, Tyler served as a state legislator, governor, U.S. representative, and U.S. senator before being elected Vice President . He was the first to succeed to the office of President following the death of a predecessor...
, young George was accepted at the United States Military Academy
United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy at West Point is a four-year coeducational federal service academy located at West Point, New York. The academy sits on scenic high ground overlooking the Hudson River, north of New York City...
in 1842, the academy having waived its normal minimum age of 16.
At West Point, he was an energetic and ambitious cadet, deeply interested in the teachings of Dennis Hart Mahan
Dennis Hart Mahan
Dennis Hart Mahan was a noted American military theorist and professor at the United States Military Academy at West Point from 1824-1871. He was the father of American naval historian and theorist Rear Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan...
and the theoretical strategic principles of Antoine-Henri Jomini
Antoine-Henri Jomini
Antoine-Henri, baron Jomini was a general in the French and later in the Russian service, and one of the most celebrated writers on the Napoleonic art of war...
. His closest friends were aristocratic Southerners such as James Stuart, Dabney Maury, Cadmus Wilcox, and A. P. Hill
A. P. Hill
Ambrose Powell Hill, Jr. , was a career U.S. Army officer in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars and a Confederate general in the American Civil War...
. These associations gave McClellan what he considered to be an appreciation of the Southern mind, an understanding of the political and military implications of the sectional differences in the United States that led to the Civil War. He graduated in 1846, second in his class of 59 cadets, losing the top position (to Charles Seaforth Stewart) only because of poor drawing skills. He was commissioned a brevet
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, brevet referred to a warrant authorizing a commissioned officer to hold a higher rank temporarily, but usually without receiving the pay of that higher rank except when actually serving in that role. An officer so promoted may be referred to as being...
second lieutenant in the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers is a federal agency and a major Army command made up of some 38,000 civilian and military personnel, making it the world's largest public engineering, design and construction management agency...
.
Mexican-American War
McClellan's first assignment was with a company of engineers formed at West Point, but he quickly received orders to sail for the Mexican-American War. He arrived near the mouth of the Rio GrandeRio Grande
The Rio Grande is a river that flows from southwestern Colorado in the United States to the Gulf of Mexico. Along the way it forms part of the Mexico – United States border. Its length varies as its course changes...
in October 1846, well prepared for action with a double-barreled shotgun, two pistols, a saber, a dress sword, and a Bowie knife
Bowie knife
A Bowie knife is a pattern of fixed-blade fighting knife first popularized by Colonel James "Jim" Bowie in the early 19th Century. Since the first incarnation was created by James Black, the Bowie knife has come to incorporate several recognizable and characteristic design features, although its...
. He complained that he had arrived too late to take any part in the American victory at Monterrey
Battle of Monterrey
In the Battle of Monterrey during the Mexican-American War, General Pedro de Ampudia and the Mexican Army of the North was defeated by U.S...
in September. During a temporary armistice in which the forces of Gen. Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor was the 12th President of the United States and an American military leader. Initially uninterested in politics, Taylor nonetheless ran as a Whig in the 1848 presidential election, defeating Lewis Cass...
awaited action, McClellan was stricken with dysentery
Dysentery
Dysentery is an inflammatory disorder of the intestine, especially of the colon, that results in severe diarrhea containing mucus and/or blood in the faeces with fever and abdominal pain. If left untreated, dysentery can be fatal.There are differences between dysentery and normal bloody diarrhoea...
and malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
, which kept him in the hospital for nearly a month. The malaria would recur in later years—he called it his "Mexican disease." He served bravely as an engineering officer during the war, subjected to frequent enemy fire, and was appointed a brevet first lieutenant for Contreras
Battle of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place during August 19–20, 1847, in the final encounters of the Mexican-American War. In the Battle of Churubusco, fighting continued the following day.-Background:...
and Churubusco
Battle of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, in the immediate aftermath of the Battle of Contreras during the Mexican-American War. After defeating the Mexican army at Churubusco, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles away from Mexico City, the capital of the nation...
and to captain for Chapultepec
Battle of Chapultepec
The Battle of Chapultepec, in September 1847, was a United States victory over Mexican forces holding Chapultepec Castle west of Mexico City during the Mexican-American War.-Background:On September 13, 1847, in the costly Battle of Molino del Rey, U.S...
, He performed reconnaissance missions for Lt. Gen.
Lieutenant General (United States)
In the United States Army, the United States Air Force and the United States Marine Corps, lieutenant general is a three-star general officer rank, with the pay grade of O-9. Lieutenant general ranks above major general and below general...
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott was a United States Army general, and unsuccessful presidential candidate of the Whig Party in 1852....
, a close friend of McClellan's father.
McClellan's experiences during the war developed various attitudes that affected his later military and political life. He learned to appreciate the value of flanking movements over frontal assaults (used by Scott at Cerro Gordo
Battle of Cerro Gordo
The Battle of Cerro Gordo, or Battle of Sierra Gordo, in the Mexican-American War saw Winfield Scott's United States troops flank and drive Santa Anna's larger Mexican army from a strong defensive position.-Battle:...
) and the value of siege operations (Vera Cruz
Siege of Veracruz
The Battle of Veracruz was a 20-day siege of the key Mexican beachhead seaport of Veracruz, during the Mexican-American War. Lasting from 9-29 March 1847, it began with the first large-scale amphibious assault conducted by United States military forces, and ended with the surrender and occupation...
). He witnessed Scott's success in balancing political with military affairs, and his good relations with the civil population as he invaded, enforcing strict discipline on his soldiers to minimize damage to their property. And he developed a disdain for volunteer soldiers and officers, particularly politicians who cared nothing for discipline and training.
Peacetime service
McClellan returned to West Point to command his engineering company, which was attached to the academy for the purpose of training cadets in engineering activities. He chafed at the boredom of peacetime garrison service, although he greatly enjoyed the social life. In June 1851 he was ordered to Fort DelawareFort Delaware
Fort Delaware is a harbor defense facility, designed by Chief Engineer Joseph Gilbert Totten, and located on Pea Patch Island in the Delaware River. During the American Civil War, the Union used Fort Delaware as a prison for Confederate prisoners of war, political prisoners, federal convicts, and...
, a masonry work under construction on an island in the Delaware River
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river on the Atlantic coast of the United States.A Dutch expedition led by Henry Hudson in 1609 first mapped the river. The river was christened the South River in the New Netherland colony that followed, in contrast to the North River, as the Hudson River was then...
, 40 miles (64.4 km) downriver from Philadelphia. In March 1852 he was ordered to report to Capt. Randolph B. Marcy
Randolph B. Marcy
Randolph Barnes Marcy was a career officer in the United States Army, achieving the rank of Brigadier General before retiring in 1881. Although beginning in 1861 his responsibilities were those of a brigadier general, the U.S...
at Fort Smith
Fort Smith, Arkansas
Fort Smith is the second-largest city in Arkansas and one of the two county seats of Sebastian County. With a population of 86,209 in 2010, it is the principal city of the Fort Smith, Arkansas-Oklahoma Metropolitan Statistical Area, a region of 298,592 residents which encompasses the Arkansas...
, Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
, to serve as second-in-command on an expedition to discover the sources of the Red River
Red River (Mississippi watershed)
The Red River, or sometimes the Red River of the South, is a major tributary of the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers in the southern United States of America. The river gains its name from the red-bed country of its watershed. It is one of several rivers with that name...
. By June the expedition reached the source of the north fork of the river and Marcy named a small tributary McClellan's Creek. Upon their return to civilization on July 28, they were astonished to find that they had been given up for dead. A sensational story had reached the press, which McClellan blamed on "a set of scoundrels, who seek to keep up agitation on the frontier in order to get employment from the Govt. in one way or other," that the expedition had been ambushed by 2,000 Comanche
Comanche
The Comanche are a Native American ethnic group whose historic range consisted of present-day eastern New Mexico, southern Colorado, northeastern Arizona, southern Kansas, all of Oklahoma, and most of northwest Texas. Historically, the Comanches were hunter-gatherers, with a typical Plains Indian...
s and killed to the last man.
In the fall of 1852, McClellan published a manual on bayonet tactics that he had translated from the original French. He also received an assignment to the Department of Texas, with orders to perform a survey of Texas rivers and harbors. In 1853 he participated in the Pacific Railroad surveys, ordered by Secretary of War
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Finis Davis , also known as Jeff Davis, was an American statesman and leader of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, serving as President for its entire history. He was born in Kentucky to Samuel and Jane Davis...
, to select an appropriate route for the upcoming transcontinental railroad
First Transcontinental Railroad
The First Transcontinental Railroad was a railroad line built in the United States of America between 1863 and 1869 by the Central Pacific Railroad of California and the Union Pacific Railroad that connected its statutory Eastern terminus at Council Bluffs, Iowa/Omaha, Nebraska The First...
. McClellan surveyed the northern corridor along the 47th and 49th parallels from St. Paul to the Puget Sound
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
. During this assignment, he demonstrated a tendency for insubordination toward senior political figures. Isaac Stevens
Isaac Stevens
Isaac Ingalls Stevens was the first governor of Washington Territory, a United States Congressman, and a brigadier general in the Union Army during the American Civil War until his death at the Battle of Chantilly...
, governor of the Washington Territory
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from February 8, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington....
, became dissatisfied with McClellan's performance in scouting passes across the Cascade Range
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
. (McClellan selected Yakima Pass without a thorough reconnaissance and refused the governor's order to lead a party through it in winter conditions, relying on faulty intelligence about the depth of snowpack in that area. In so doing, he missed three greatly superior passes in the near vicinity, which would be the ones eventually used for railroads and interstate highways.) The governor ordered McClellan to turn over his expedition logbooks, but McClellan steadfastly refused, most likely because of embarrassing personal comments that he had made throughout.
Returning to the East, McClellan began courting Ellen Mary Marcy (1836–1915), the daughter of his former commander. Ellen, or Nelly, refused McClellan's first proposal of marriage, one of nine that she received from a variety of suitors, including his West Point friend, A. P. Hill. Ellen accepted Hill's proposal in 1856, but her family did not approve and he withdrew.
In June 1854, McClellan was sent on a secret reconnaissance mission to Santo Domingo at the behest of Jefferson Davis. McClellan assessed local defensive capabilities for the secretary. (The information was not used until 1870, when President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
unsuccessfully attempted to annex the Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
.) Davis was beginning to treat McClellan almost as a protégé, and his next assignment was to assess the logistical readiness of various railroads in the United States, once again with an eye toward planning for the transcontinental railroad. In March 1855, McClellan was promoted to captain and assigned to the 1st U.S. Cavalry regiment.
Because of his political connections and his mastery of French, McClellan received the assignment to be an official observer of the European armies in the Crimean War
Crimean War
The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining...
in 1855. Traveling widely, and interacting with the highest military commands and royal families, McClellan observed the siege of Sevastopol. Upon his return to the United States in 1856 he requested assignment in Philadelphia to prepare his report, which contained a critical analysis of the siege and a lengthy description of the organization of the European armies. He also wrote a manual on cavalry tactics
Cavalry tactics
For much of history , humans have used some form of cavalry for war. Cavalry tactics have evolved over time...
that was based on Russian cavalry regulations. A notable failure of the observers, including McClellan, was that they neglected to explain the importance of the emergence of rifled musket
Rifled musket
The term rifled musket or rifle musket refers to a specific type of weapon made in the mid-19th century. Originally the term referred only to muskets that had been produced as a smoothbore weapon and later had their barrels rifled...
s in the Crimean War, and how that would require fundamental changes in tactics for the coming Civil War.
The Army adopted McClellan's cavalry manual and also his design for a saddle
Horse tack
Tack is a term used to describe any of the various equipment and accessories worn by horses in the course of their use as domesticated animals. Saddles, stirrups, bridles, halters, reins, bits, harnesses, martingales, and breastplates are all forms of horse tack...
, the "McClellan Saddle
McClellan saddle
The McClellan saddle was a riding saddle designed by George B. McClellan, a career Army officer in the U.S. Army, after his tour of Europe as the member of a military commission charged with studying the latest developments in engineer and cavalry forces including field equipment. Based on his...
", which he claimed to have seen used by Hussar
Hussar
Hussar refers to a number of types of light cavalry which originated in Hungary in the 14th century, tracing its roots from Serbian medieval cavalry tradition, brought to Hungary in the course of the Serb migrations, which began in the late 14th century....
s in Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
and Hungary. It became standard issue for as long as the U.S. horse cavalry existed and is currently used for ceremonies.
Civilian pursuits

Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, is a railroad in the central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois with New Orleans, Louisiana and Birmingham, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa...
and also president of the Ohio and Mississippi Railroad
Ohio and Mississippi Railroad
The Ohio and Mississippi Railway was a railroad operating between Cincinnati, Ohio, and East St. Louis, Illinois, from 1857 to 1893.General Ormsby M. Mitchel was a civil engineer on this project....
in 1860. He performed well in both jobs, expanding the Illinois Central toward New Orleans
New Orleans, Louisiana
New Orleans is a major United States port and the largest city and metropolitan area in the state of Louisiana. The New Orleans metropolitan area has a population of 1,235,650 as of 2009, the 46th largest in the USA. The New Orleans – Metairie – Bogalusa combined statistical area has a population...
and helping the Ohio and Mississippi recover from the Panic of 1857
Panic of 1857
The Panic of 1857 was a financial panic in the United States caused by the declining international economy and over-expansion of the domestic economy. Indeed, because of the interconnectedness of the world economy by the time of the 1850s, the financial crisis which began in the autumn of 1857 was...
. But despite his successes and lucrative salary ($10,000 per year), he was frustrated with civilian employment and continued to study classical military strategy assiduously. During the Utah War
Utah War
The Utah War, also known as the Utah Expedition, Buchanan's Blunder, the Mormon War, or the Mormon Rebellion was an armed confrontation between LDS settlers in the Utah Territory and the armed forces of the United States government. The confrontation lasted from May 1857 until July 1858...
against the Mormon
Mormon
The term Mormon most commonly denotes an adherent, practitioner, follower, or constituent of Mormonism, which is the largest branch of the Latter Day Saint movement in restorationist Christianity...
s, he considered rejoining the Army. He also considered service as a filibuster
Filibuster (military)
A filibuster, or freebooter, is someone who engages in an unauthorized military expedition into a foreign country to foment or support a revolution...
in support of Benito Juárez
Benito Juárez
Benito Juárez born Benito Pablo Juárez García, was a Mexican lawyer and politician of Zapotec origin from Oaxaca who served five terms as president of Mexico: 1858–1861 as interim, 1861–1865, 1865–1867, 1867–1871 and 1871–1872...
in Mexico.
Before the outbreak of Civil War, McClellan became active in politics, supporting the presidential campaign of Democrat Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas was an American politician from the western state of Illinois, and was the Northern Democratic Party nominee for President in 1860. He lost to the Republican Party's candidate, Abraham Lincoln, whom he had defeated two years earlier in a Senate contest following a famed...
in the 1860 election
United States presidential election, 1860
The United States presidential election of 1860 was a quadrennial election, held on November 6, 1860, for the office of President of the United States and the immediate impetus for the outbreak of the American Civil War. The nation had been divided throughout the 1850s on questions surrounding the...
. He claimed to have defeated an attempt at vote fraud by Republicans
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
by ordering the delay of a train that was carrying men to vote illegally in another county, enabling Douglas to win the county.
In October 1859 McClellan was able to resume his courtship of Ellen Marcy, and they were married in Calvary Church
Calvary Church (Manhattan)
Calvary Church is an Episcopal church located at 273 Park Avenue South on the corner of East 21st Street in the Gramercy Park neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, on the border of the Flatiron District. It was designed by James Renwick, Jr., the architect who designed St. Patrick's Cathedral...
, New York City, on May 22, 1860.
Ohio and strategy
At the start of the Civil War, McClellan's knowledge of what was called "big war science" and his railroad experience implied he would excel at military logistics. This placed him in great demand as the UnionUnion (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union was a name used to refer to the federal government of the United States, which was supported by the twenty free states and five border slave states. It was opposed by 11 southern slave states that had declared a secession to join together to form the...
mobilized. The governors of Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York, the three largest states of the Union, actively pursued him to command their states' militia. Ohio Governor William Dennison
William Dennison (Ohio governor)
William Dennison, Jr. was a Whig and Republican politician from Ohio. He served as the 24th Governor of Ohio and as U.S...
was the most persistent, so McClellan was commissioned a major general
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
of volunteers and took command of the Ohio militia on April 23, 1861. Unlike some of his fellow Union officers who came from abolition
Abolitionism
Abolitionism is a movement to end slavery.In western Europe and the Americas abolitionism was a movement to end the slave trade and set slaves free. At the behest of Dominican priest Bartolomé de las Casas who was shocked at the treatment of natives in the New World, Spain enacted the first...
ist families, he was opposed to federal interference with slavery. So some of his Southern colleagues approached him informally about siding with the Confederacy, but he could not accept the concept of secession
Secession
Secession is the act of withdrawing from an organization, union, or especially a political entity. Threats of secession also can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.-Secession theory:...
.
On May 3 McClellan re-entered federal service by being named commander of the Department of the Ohio
Department of the Ohio
The Department of the Ohio was an administrative military district created by the United States War Department early in the American Civil War to administer the troops in the Northern states near the Ohio River.General Orders No...
, responsible for the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, and, later, western Pennsylvania, western Virginia, and Missouri. On May 14, he was commissioned a major general in the regular army. At age 34 he now outranked everyone in the Army other than Lt. Gen. Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott was a United States Army general, and unsuccessful presidential candidate of the Whig Party in 1852....
, the general-in-chief. McClellan's rapid promotion was partly because of his acquaintance with Salmon P. Chase
Salmon P. Chase
Salmon Portland Chase was an American politician and jurist who served as U.S. Senator from Ohio and the 23rd Governor of Ohio; as U.S. Treasury Secretary under President Abraham Lincoln; and as the sixth Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court.Chase was one of the most prominent members...
, Treasury Secretary
United States Secretary of the Treasury
The Secretary of the Treasury of the United States is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, which is concerned with financial and monetary matters, and, until 2003, also with some issues of national security and defense. This position in the Federal Government of the United...
and former Ohio governor and senator.
As McClellan scrambled to process the thousands of men who were volunteering for service and to set up training camps, he also set his mind toward grand strategy. He wrote a letter to Gen. Scott on April 27, four days after assuming command in Ohio, that was the first proposal for a unified strategy for the war. It contained two alternatives, both with a prominent role for himself as commander. The first called for 80,000 men to invade Virginia through the Kanawha Valley
Kanawha River
The Kanawha River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, it has formed a significant industrial region of the state since the middle of the 19th century.It is formed at the town of Gauley...
toward Richmond
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
. The second called for those same men to drive south instead across the Ohio River into Kentucky and Tennessee. Scott dismissed both plans as being logistically infeasible. Although he complimented McClellan and expressed his "great confidence in your intelligence, zeal, science, and energy", he replied by letter that the 80,000 men would be better used on a river-based expedition to control the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
and split the Confederacy, accompanied by a strong Union blockade
Union blockade
The Union Blockade, or the Blockade of the South, took place between 1861 and 1865, during the American Civil War, when the Union Navy maintained a strenuous effort on the Atlantic and Gulf Coast of the Confederate States of America designed to prevent the passage of trade goods, supplies, and arms...
of Southern ports. This plan, which would have demanded considerable patience on the part of the Northern public, was derided in newspapers as the Anaconda Plan
Anaconda Plan
The Anaconda Plan or Scott's Great Snake is the name widely applied to an outline strategy for subduing the seceding states in the American Civil War. Proposed by General-in-Chief Winfield Scott, the plan emphasized the blockade of the Southern ports, and called for an advance down the Mississippi...
, but eventually proved to be the successful outline used to prosecute the war. Relations between the two generals became increasingly strained over the summer and fall.
Western Virginia
McClellan's first military operations were to occupy the area of western VirginiaVirginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
that wanted to remain in the Union and later became the state of West Virginia
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
. He had received intelligence reports on May 26 that the critical Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was one of the oldest railroads in the United States and the first common carrier railroad. It came into being mostly because the city of Baltimore wanted to compete with the newly constructed Erie Canal and another canal being proposed by Pennsylvania, which...
bridges in that portion of the state were being burned. As he quickly implemented plans to invade the region, he triggered his first serious political controversy by proclaiming to the citizens there that his forces had no intentions of interfering with personal property—including slaves. "Notwithstanding all that has been said by the traitors to induce you to believe that our advent among you will be signalized by interference with your slaves, understand one thing clearly—not only will we abstain from all such interference but we will on the contrary with an iron hand, crush any attempted insurrection on their part." He quickly realized that he had overstepped his bounds and apologized by letter to President Lincoln. The controversy was not that his proclamation was diametrically opposed to the administration's policy at the time, but that he was so bold in stepping beyond his strictly military role.
His forces moved rapidly into the area through Grafton
Grafton, West Virginia
Grafton is a city in, and county seat of, Taylor County, West Virginia, USA. The population was 5,489 at the 2000 census. The only two national cemeteries in West Virginia are located in Grafton. Mother's Day was founded in Grafton on May 10, 1908; the city is the home to the International Mother's...
and were victorious at the tiny skirmish called the Battle of Philippi Races
Battle of Philippi Races
The Battle of Philippi—also known mockingly as "The Philippi Races"—was fought on June 3, 1861, in and around Philippi, Virginia as part of the Western Virginia Campaign of the American Civil War...
, arguably the first land conflict of the war. His first personal command in battle was at Rich Mountain
Battle of Rich Mountain
The Battle of Rich Mountain took place on July 11, 1861, in Randolph County, Virginia as part of the Operations in Western Virginia Campaign during the American Civil War.-Background:...
, which he also won, but only after displaying a strong sense of caution and a reluctance to commit reserve forces that would be his hallmark for the rest of his career. His subordinate commander, William S. Rosecrans, bitterly complained that his attack was not reinforced as McClellan had agreed. Nevertheless, these two minor victories propelled McClellan to the status of national hero. The New York Herald
New York Herald
The New York Herald was a large distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between May 6, 1835, and 1924.-History:The first issue of the paper was published by James Gordon Bennett, Sr., on May 6, 1835. By 1845 it was the most popular and profitable daily newspaper in the UnitedStates...
entitled an article about him, "Gen. McClellan, the Napoleon of the Present War."
Building an army

First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
on July 21, 1861, Lincoln summoned McClellan from West Virginia, where McClellan had given the North the only actions thus far having a semblance of military victories. He traveled by special train on the main Pennsylvania line from Wheeling
Wheeling, West Virginia
Wheeling is a city in Ohio and Marshall counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia; it is the county seat of Ohio County. Wheeling is the principal city of the Wheeling Metropolitan Statistical Area...
through Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh is the second-largest city in the US Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Allegheny County. Regionally, it anchors the largest urban area of Appalachia and the Ohio River Valley, and nationally, it is the 22nd-largest urban area in the United States...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
, and Baltimore, and on to Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, and was overwhelmed by enthusiastic crowds that met his train along the way.
Carl Sandburg
Carl Sandburg
Carl Sandburg was an American writer and editor, best known for his poetry. He won three Pulitzer Prizes, two for his poetry and another for a biography of Abraham Lincoln. H. L. Mencken called Carl Sandburg "indubitably an American in every pulse-beat."-Biography:Sandburg was born in Galesburg,...
wrote, "McClellan was the man of the hour, pointed to by events, and chosen by an overwhelming weight of public and private opinion." On July 26, the day he reached the capital, McClellan was appointed commander of the Military Division of the Potomac, the main Union force responsible for the defense of Washington. On August 20, several military units in Virginia were consolidated into his department and he immediately formed the Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
, with himself as its first commander. He reveled in his newly acquired power and fame:

Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
style. He proposed that his army should be expanded to 273,000 men and 600 guns and "crush the rebels in one campaign." He favored a war that would impose little impact on civilian populations and require no emancipation of slaves.
McClellan's antipathy to emancipation added to the pressure on him, as he received bitter criticism from Radical Republicans in the government. He viewed slavery as an institution recognized in the Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
, and entitled to federal protection wherever it existed (Lincoln held the same public position until August 1862). McClellan's writings after the war were typical of many Northerners: "I confess to a prejudice in favor of my own race, & can't learn to like the odor of either Billy goats or niggers." But in November 1861, he wrote to his wife, "I will, if successful, throw my sword onto the scale to force an improvement in the condition of those poor blacks." He later wrote that had it been his place to arrange the terms of peace, he would have insisted on gradual emancipation, guarding the rights of both slaves and masters, as part of any settlement. But he made no secret of his opposition to the radical Republicans. He told Ellen, "I will not fight for the abolitionists." This placed him at an obvious handicap because many politicians running the government believed that he was attempting to implement the policies of the opposition party.
The immediate problem with McClellan's war strategy was that he was convinced the Confederates were ready to attack him with overwhelming numbers. On August 8, believing that the Confederates had over 100,000 troops facing him (in contrast to the 35,000 they actually deployed at Bull Run a few weeks earlier), he declared a state of emergency in the capital. By August 19, he estimated 150,000 enemy to his front. McClellan's future campaigns would be strongly influenced by the overblown enemy strength estimates of his secret service chief, detective Allan Pinkerton
Allan Pinkerton
Allan Pinkerton was a Scottish American detective and spy, best known for creating the Pinkerton National Detective Agency.-Early life, career and immigration:...
, but in August 1861, these estimates were entirely McClellan's own. The result was a level of extreme caution that sapped the initiative of McClellan's army and caused great condemnation by his government. Historian and biographer Stephen W. Sears has called McClellan's actions "essentially sound" if he had been as outnumbered as he believed, but McClellan in fact rarely had less than a two-to-one advantage over his opponents in 1861 and 1862. That fall, for example, Confederate forces ranged from 35,000 to 60,000, whereas the Army of the Potomac in September numbered 122,000 men; in early December 170,000; by year end, 192,000.
The dispute with Scott would become very personal. Scott (along with many in the War Department) was outraged that McClellan refused to divulge any details about his strategic planning, or even mundane details such as troop strengths and dispositions. (For his part, McClellan claimed not to trust anyone in the administration to keep his plans secret from the press, and thus the enemy.) During disagreements about defensive forces on the Potomac River, McClellan wrote to his wife on August 10 in a manner that would characterize some of his more private correspondence: "Genl Scott is the great obstacle—he will not comprehend the danger & is either a traitor, or an incompetent. I have to fight my way against him." Scott became so disillusioned over his relationship with the young general that he offered his resignation to President Lincoln, who initially refused to accept it. Rumors traveled through the capital that McClellan might resign, or instigate a military coup, if Scott were not removed. Lincoln's Cabinet met on October 18 and agreed to accept Scott's resignation for "reasons of health."
General-in-chief

Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott was a United States Army general, and unsuccessful presidential candidate of the Whig Party in 1852....
retired and McClellan became general-in-chief of all the Union armies. The president expressed his concern about the "vast labor" involved in the dual role of army commander and general-in-chief, but McClellan responded, "I can do it all."
Lincoln, as well as many other leaders and citizens of the northern states, became increasingly impatient with McClellan's slowness to attack the Confederate forces still massed near Washington. The Union defeat at the minor Battle of Ball's Bluff
Battle of Ball's Bluff
The Battle of Ball's Bluff, also known as the Battle of Harrison’s Island or the Battle of Leesburg, was fought on October 21, 1861, in Loudoun County, Virginia, as part of Union Maj. Gen. George B...
near Leesburg
Leesburg, Virginia
Leesburg is a historic town in, and county seat of, Loudoun County, Virginia, United States of America. Leesburg is located west-northwest of Washington, D.C. along the base of the Catoctin Mountain and adjacent to the Potomac River. Its population according the 2010 Census is 42,616...
in October added to the frustration and indirectly damaged McClellan. In December, the Congress formed a Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War
United States Congress Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War
The Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War was a United States Congressional investigating committee created to handle issues surrounding the American Civil War. It was established on December 9, 1861, following the embarrassing Union defeat at the Battle of Ball's Bluff, at the instigation of...
, which became a thorn in the side of many generals throughout the war, accusing them of incompetence and, in some cases, treason. McClellan was called as the first witness on December 23, but he contracted typhoid fever
Typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as Typhoid, is a common worldwide bacterial disease, transmitted by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person, which contain the bacterium Salmonella enterica, serovar Typhi...
and could not attend. Instead, his subordinate officers testified, and their candid admissions that they had no knowledge of specific strategies for advancing against the Confederates raised many calls for McClellan's dismissal.
McClellan further damaged his reputation by his insulting insubordination to his commander-in-chief. He privately referred to Lincoln, whom he had known before the war as a lawyer for the Illinois Central, as "nothing more than a well-meaning baboon", a "gorilla", and "ever unworthy of ... his high position." On November 13, he snubbed the president, visiting at McClellan's house, by making him wait for 30 minutes, only to be told that the general had gone to bed and could not see him.
On January 10, Lincoln met with top generals (McClellan did not attend) and directed them to formulate a plan of attack, expressing his exasperation with General McClellan with the following remark: "If General McClellan does not want to use the army, I would like to borrow it for a time." On January 12, 1862, McClellan was summoned to the White House, where the Cabinet demanded to hear his war plans. For the first time, he revealed his intentions to transport the Army of the Potomac by ship to Urbanna
Urbanna, Virginia
Urbanna is a town in Middlesex County, Virginia, United States. Urbanna means “City of Anne” and was named in honor of England’s Queen Anne. The population was 543 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Urbanna is located at ....
, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, on the Rappahannock River
Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length. It traverses the entire northern part of the state, from the Blue Ridge Mountains in the west, across the Piedmont, to the Chesapeake Bay, south of the Potomac River.An important river in American...
, outflanking the Confederate forces near Washington, and proceeding 50 miles (80.5 km) overland to capture Richmond. He refused to give any specific details of the proposed campaign, even to his friend, newly appointed War Secretary
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
Edwin M. Stanton
Edwin M. Stanton
Edwin McMasters Stanton was an American lawyer and politician who served as Secretary of War under the Lincoln Administration during the American Civil War from 1862–1865...
. On January 27, Lincoln issued an order that required all of his armies to begin offensive operations by February 22, Washington's birthday. On January 31, he issued a supplementary order for the Army of the Potomac to move overland to attack the Confederates at Manassas Junction
Manassas, Virginia
The City of Manassas is an independent city surrounded by Prince William County and the independent city of Manassas Park in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Its population was 37,821 as of 2010. Manassas also surrounds the county seat for Prince William County but that county...
and Centreville
Centreville, Virginia
Centreville is an unincorporated community in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Recognized by the U.S. Census Bureau as a Census Designated Place , the community population was 71,135 as of the 2010 census and is approximately west of Washington, DC.-Colonial Period:Beginning in the 1760s,...
. McClellan immediately replied with a 22-page letter objecting in detail to the president's plan and advocating instead his Urbanna plan, which was the first written instance of the plan's details being presented to the president. Although Lincoln believed his plan was superior, he was relieved that McClellan finally agreed to begin moving, and reluctantly approved. On March 8, doubting McClellan's resolve, Lincoln again interfered with the army commander's prerogatives. He called a council of war
Council of war
A council of war is a term in military science that describes a meeting held to decide on a course of action, usually in the midst of a battle. Under normal circumstances, decisions are made by a commanding officer, optionally communicated and coordinated by staff officers, and then implemented by...
at the White House in which McClellan's subordinates were asked about their confidence in the Urbanna plan. They expressed their confidence to varying degrees. After the meeting, Lincoln issued another order, naming specific officers as corps commanders to report to McClellan (who had been reluctant to do so prior to assessing his division commanders' effectiveness in combat, even though this would have meant his direct supervision of twelve divisions in the field).
Two more crises would hit McClellan before he could implement his plans. The Confederate forces under General Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
withdrew from their positions before Washington, assuming new positions south of the Rappahannock, which completely nullified the Urbanna strategy. McClellan retooled his plan so that his troops would disembark at Fort Monroe, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, and advance up the Virginia Peninsula
Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay.Hampton Roads is the common name for the metropolitan area that surrounds the body of water of the same name...
to Richmond, an operation that would be known as the Peninsula Campaign
Peninsula Campaign
The Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
. However, McClellan came under extreme criticism from the press and the Congress when it was found that Johnston's forces had not only slipped away unnoticed, but had for months fooled the Union Army through the use of logs painted black to appear as cannons, nicknamed Quaker Gun
Quaker Gun
A Quaker Gun is a deception tactic that was commonly used in warfare during the 18th and 19th centuries. Although resembling an actual cannon, the Quaker Gun was simply a wooden log, usually painted black, used to deceive an enemy. Misleading the enemy as to the strength of an emplacement was an...
s. The Congress's joint committee visited the abandoned Confederate lines and radical Republicans introduced a resolution demanding the dismissal of McClellan, but it was narrowly defeated by a parliamentary maneuver. The second crisis was the emergence of the Confederate ironclad CSS Virginia
CSS Virginia
CSS Virginia was the first steam-powered ironclad warship of the Confederate States Navy, built during the first year of the American Civil War; she was constructed as a casemate ironclad using the raised and cut down original lower hull and steam engines of the scuttled . Virginia was one of the...
, which threw Washington into a panic and made naval support operations on the James River
James River (Virginia)
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is long, extending to if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. The James River drains a catchment comprising . The watershed includes about 4% open water and an area with a population of 2.5 million...
seem problematic.
On March 11, 1862, Lincoln removed McClellan as general-in-chief, leaving him in command of only the Army of the Potomac, ostensibly so that McClellan would be free to devote all his attention to the move on Richmond. Lincoln's order was ambiguous as to whether McClellan might be restored following a successful campaign. In fact, his position was not filled by another officer. Lincoln, Stanton, and a group of officers called the "War Board" directed the strategic actions of the Union armies that spring. Although McClellan was assuaged by supportive comments Lincoln made to him, in time he saw the change of command very differently, describing it as a part of an intrigue "to secure the failure of the approaching campaign."
Peninsula Campaign


Alexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of 2009, the city had a total population of 139,966. Located along the Western bank of the Potomac River, Alexandria is approximately six miles south of downtown Washington, D.C.Like the rest of northern Virginia, as well as...
on March 17. It was an armada that dwarfed all previous American expeditions, transporting 121,500 men, 44 artillery batteries, 1,150 wagons, over 15,000 horses, and tons of equipment and supplies. An English observer remarked that it was the "stride of a giant." The army's advance from Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe was a military installation in Hampton, Virginia—at Old Point Comfort, the southern tip of the Virginia Peninsula...
up the Virginia Peninsula
Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay.Hampton Roads is the common name for the metropolitan area that surrounds the body of water of the same name...
proved to be slow. McClellan's plan for a rapid seizure of Yorktown
Yorktown, Virginia
Yorktown is a census-designated place in York County, Virginia, United States. The population was 220 in the 2000 census. It is the county seat of York County, one of the eight original shires formed in colonial Virginia in 1634....
was foiled when he discovered that the Confederates had fortified a line across the Peninsula, causing him to decide on a siege of the city, which required considerable preparation.
McClellan continued to believe intelligence reports that credited the Confederates with two or three times the men they actually had. Early in the campaign, Confederate General John B. "Prince John" Magruder
John B. Magruder
John Bankhead Magruder was a career military officer who served in the armies of three nations. He was a U.S. Army officer in the Mexican-American War, a Confederate general during the American Civil War, and a postbellum general in the Imperial Mexican Army...
defended the Peninsula against McClellan's advance with a vastly smaller force. He created a false impression of many troops behind the lines and of even more troops arriving. He accomplished this by marching small groups of men repeatedly past places where they could be observed at a distance or were just out of sight, accompanied by great noise and fanfare. During this time, General Johnston was able to provide Magruder with reinforcements, but even then there were far fewer troops than McClellan believed were opposite him.
After a month of preparation, just before he was to assault the Confederate works at Yorktown, McClellan learned that Johnston had withdrawn up the Peninsula towards Williamsburg
Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an independent city located on the Virginia Peninsula in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of Virginia, USA. As of the 2010 Census, the city had an estimated population of 14,068. It is bordered by James City County and York County, and is an independent city...
. McClellan was thus required to give chase without any benefit of the heavy artillery so carefully amassed in front of Yorktown. The Battle of Williamsburg
Battle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War...
on May 5 is considered a Union victory—McClellan's first—but the Confederate army was not destroyed and a bulk of their troops were successfully moved past Williamsburg to Richmond's outer defenses while it was waged, and over the next several days.
McClellan had also placed hopes on a simultaneous naval approach to Richmond via the James River
James River (Virginia)
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is long, extending to if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. The James River drains a catchment comprising . The watershed includes about 4% open water and an area with a population of 2.5 million...
. That approach failed following the Union Navy's defeat at the Battle of Drewry's Bluff
Battle of Drewry's Bluff
The Battle of Drewry’s Bluff, also known as the Battle of Fort Darling, or Fort Drewry, took place on May 15, 1862, in Chesterfield County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. Five American warships, including the ironclads and , steamed up the James River to...
, about 7 miles (11.3 km) downstream from the Confederate capital, on May 15. Basing artillery on a strategic bluff high above a bend in the river, and sinking boats to create an impassable series of obstacles in the river itself, the Confederates had effectively blocked this potential approach to Richmond.
McClellan's army cautiously inched towards Richmond over the next three weeks, coming to within four miles (6 km) of it. He established a supply base on the Pamunkey River
Pamunkey River
The Pamunkey River is a tributary of the York River, about long, in eastern Virginia in the United States. Via the York River it is part of the watershed of Chesapeake Bay.-Course:...
(a navigable tributary of the York River
York River (Virginia)
The York River is a navigable estuary, approximately long, in eastern Virginia in the United States. It ranges in width from at its head to near its mouth on the west side of Chesapeake Bay. Its watershed drains an area including portions of 17 counties of the coastal plain of Virginia north...
) at White House Landing where the Richmond and York River Railroad
Richmond and York River Railroad
Richmond and York River Railroad was completed between Richmond, Virginia and West Point, Virginia in 1861. The western terminus was adjacent to Richmond's Tobacco Row...
extending to Richmond crossed, and commandeered the railroad, transporting steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s and rolling stock to the site by barge.
On May 31, as McClellan planned an assault, his army was surprised by a Confederate attack. Johnston saw that the Union army was split in half by the rain-swollen Chickahominy River
Chickahominy River
The Chickahominy is an river in the eastern portion of the U.S. state of Virginia. The river rises about northwest of Richmond and flows southeast and south to the James River...
and hoped to defeat it in detail
Defeat in detail
Defeat in detail is a military phrase referring to the tactic of bringing a large portion of one's own force to bear on small enemy units in sequence, rather than engaging the bulk of the enemy force all at once...
at Seven Pines
Battle of Seven Pines
The Battle of Seven Pines, also known as the Battle of Fair Oaks or Fair Oaks Station, took place on May 31 and June 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of an offensive up the Virginia Peninsula by Union Maj. Gen....
and Fair Oaks. McClellan was unable to command the army personally because of a recurrence of malarial fever, but his subordinates were able to repel the attacks. Nevertheless, McClellan received criticism from Washington for not counterattacking, which some believed could have opened the city of Richmond to capture. Johnston was wounded in the battle, and General Robert E. Lee assumed command of the Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
. McClellan spent the next three weeks repositioning his troops and waiting for promised reinforcements, losing valuable time as Lee continued to strengthen Richmond's defenses.
At the end of June, Lee began a series of attacks that became known as the Seven Days Battles
Seven Days Battles
The Seven Days Battles was a series of six major battles over the seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, away from...
. The first major battle, at Mechanicsville
Battle of Beaver Dam Creek
The Battle of Beaver Dam Creek, also known as the Battle of Mechanicsville or Ellerson's Mill, took place on June 26, 1862, in Hanover County, Virginia, as the first major engagement of the Seven Days Battles during the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the start of Confederate...
, was poorly coordinated by Lee and his subordinates and caused heavy casualties for little tactical gain. But the battle had significant impact on McClellan's nerve. The surprise appearance of Maj. Gen. Stonewall Jackson
Stonewall Jackson
ຄຽשת״ׇׂׂׂׂ֣|birth_place= Clarksburg, Virginia |death_place=Guinea Station, Virginia|placeofburial=Stonewall Jackson Memorial CemeteryLexington, Virginia|placeofburial_label= Place of burial|image=...
's troops in the battle (when they had last been reported to be many miles away in the Shenandoah Valley
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley is both a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians , to the north by the Potomac River...
) convinced McClellan that he was even more significantly outnumbered than he had assumed. (He reported to Washington that he faced 200,000 Confederates, but there were actually 85,000.)

Investment (military)
Investment is the military tactic of surrounding an enemy fort with armed forces to prevent entry or escape.A circumvallation is a line of fortifications, built by the attackers around the besieged fortification facing towards the enemy fort...
Richmond, the object of his campaign; the heavy siege artillery required would be almost impossible to transport without the railroad connections available from his original supply base on the York River. In a telegram to Secretary of War
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
Edwin Stanton, reporting on these events, McClellan blamed the Lincoln administration for his reversals. "If I save this army now, I tell you plainly I owe no thanks to you or to any other persons in Washington. You have done your best to sacrifice this army." Fortunately for McClellan's immediate career, Lincoln never saw that inflammatory statement (at least at that time) because it was censored by the War Department telegrapher.

Stephen W. Sears
Stephen Ward Sears is an American historian specializing in the American Civil War.A graduate of Lakewood High School and Oberlin College, Sears attended a journalism seminar at...
wrote, "When he deserted his army on the Glendale
Battle of Glendale
The Battle of Glendale, also known as the Battle of Frayser's Farm, Frazier's Farm, Nelson's Farm, Charles City Crossroads, New Market Road, or Riddell's Shop, took place on June 30, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, on the sixth day of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War.The...
and Malvern Hill
Battle of Malvern Hill
The Battle of Malvern Hill, also known as the Battle of Poindexter's Farm, took place on July 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, on the seventh and last day of the Seven Days Battles of the American Civil War. Gen. Robert E. Lee launched a series of disjointed assaults on the nearly impregnable...
battlefields during the Seven Days, he was guilty of dereliction of duty
Dereliction of duty
Dereliction of duty is a specific offense under United States Code Title 10,892. Article 92 and applies to all branches of the US military. A service member who is derelict has willfully refused to perform his duties or has incapacitated himself in such a way that he cannot perform his duties...
. Had the Army of the Potomac been wrecked on either of these fields (at Glendale the possibility had been real), that charge under the Articles of War would likely have been brought against him." (During Glendale, McClellan was five miles (8 km) away behind Malvern Hill, without telegraph communications and too distant to command the army. During the battle of Malvern Hill, he was on a gunboat, the U.S.S. Galena
USS Galena (1862)
USS Galena — an ironclad screw steamer — was one of the first three ironclads, each of a different design, built by the Union Navy during the American Civil War....
, which at one point was ten miles (16 km) away down the James River. During both battles, effective command of the army fell to his friend and V Corps commander Brigadier General Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter was a career United States Army officer and a Union General during the American Civil War...
. When the public heard about the Galena, it was yet another enormous embarrassment, comparable to the Quaker Guns at Manassas. Editorial cartoons during the 1864 presidential campaign
United States presidential election, 1864
In the United States Presidential election of 1864, Abraham Lincoln was re-elected as president. The election was held during the Civil War. Lincoln ran under the National Union ticket against Democratic candidate George B. McClellan, his former top general. McClellan ran as the "peace candidate",...
would lampoon McClellan for preferring the safety of a ship while a battle was fought in the distance.)
McClellan was reunited with his army at Harrison's Landing on the James. Debates were held as to whether the army should be evacuated or attempt to resume an offensive toward Richmond. McClellan maintained his estrangement from Abraham Lincoln by his continuous call for reinforcements and by writing a lengthy letter in which he proposed strategic and political guidance for the war, continuing his opposition to abolition or seizure of slaves as a tactic. He concluded by implying he should be restored as general-in-chief, but Lincoln responded by naming Maj. Gen. Henry W. Halleck to the post without consulting, or even informing, McClellan. Lincoln and Stanton also offered command of the Army of the Potomac to Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside was an American soldier, railroad executive, inventor, industrialist, and politician from Rhode Island, serving as governor and a U.S. Senator...
, who refused the appointment.
Back in Washington, a reorganization of units created the Army of Virginia
Army of Virginia
The Army of Virginia was organized as a major unit of the Union Army and operated briefly and unsuccessfully in 1862 in the American Civil War. It should not be confused with its principal opponent, the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by Robert E...
under Maj. Gen. John Pope
John Pope (military officer)
John Pope was a career United States Army officer and Union general in the American Civil War. He had a brief but successful career in the Western Theater, but he is best known for his defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run in the East.Pope was a graduate of the United States Military Academy in...
, who was directed to advance towards Richmond from the northeast. McClellan resisted calls to reinforce Pope's army and delayed return of the Army of the Potomac from the Peninsula enough so that the reinforcements arrived while the Northern Virginia Campaign
Northern Virginia Campaign
The Northern Virginia Campaign, also known as the Second Bull Run Campaign or Second Manassas Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during August and September 1862 in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E...
was already underway. He wrote to his wife before the battle, "Pope will be thrashed ... & be disposed of [by Lee]. ... Such a villain as he is ought to bring defeat upon any cause that employs him." Lee had assessed McClellan's offensive nature and gambled on removing significant units from the Peninsula to attack Pope, who was beaten decisively at Second Bull Run in August.
Maryland Campaign


Northern fears of a continued offensive by Robert E. Lee were realized when he launched his Maryland Campaign
Maryland Campaign
The Maryland Campaign, or the Antietam Campaign is widely considered one of the major turning points of the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the North was repulsed by Maj. Gen. George B...
on September 4, hoping to arouse pro-Southern sympathy in the slave state of Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
. McClellan's pursuit began on September 5. He marched toward Maryland with six of his reorganized corps, about 84,000 men, while leaving two corps behind to defend Washington. McClellan's reception in Frederick, Maryland
Frederick, Maryland
Frederick is a city in north-central Maryland. It is the county seat of Frederick County, the largest county by area in the state of Maryland. Frederick is an outlying community of the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of a greater...
, as he marched towards Lee's army, was described by the correspondent for Harper's Magazine
Harper's Magazine
Harper's Magazine is a monthly magazine of literature, politics, culture, finance, and the arts, with a generally left-wing perspective. It is the second-oldest continuously published monthly magazine in the U.S. . The current editor is Ellen Rosenbush, who replaced Roger Hodge in January 2010...
:
Lee divided his forces into multiple columns, spread apart widely as he moved into Maryland and also maneuvered to capture the federal arsenal at Harpers Ferry
Harpers Ferry, West Virginia
Harpers Ferry is a historic town in Jefferson County, West Virginia, United States. In many books the town is called "Harper's Ferry" with an apostrophe....
. This was a risky move for a smaller army, but Lee was counting on his knowledge of McClellan's temperament. He told one of his generals, "He is an able general but a very cautious one. His army is in a very demoralized and chaotic condition, and will not be prepared for offensive operations—or he will not think it so—for three or four weeks. Before that time I hope to be on the Susquehanna." This was not a completely accurate assessment, but McClellan's army was moving lethargically, averaging only 6 miles (9.7 km) a day.
However, McClellan soon received a miraculous break of fortune. Union soldiers accidentally found a copy of Lee's orders
Special Order 191
Special Order 191 was a general movement order issued by Confederate Army General Robert E. Lee in the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War...
dividing his army, wrapped around a package of cigars in an abandoned camp. They delivered the order to McClellan's headquarters in Frederick on September 13. Upon realizing the intelligence value of this discovery, McClellan threw up his arms and exclaimed, "Now I know what to do!" He waved the order at his old Army friend, Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
John Gibbon
John Gibbon
John Gibbon was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars.-Early life:...
, and said, "Here is a paper with which if I cannot whip Bobbie Lee, I will be willing to go home." He telegraphed President Lincoln: "I have the whole rebel force in front of me, but I am confident, and no time shall be lost. I think Lee has made a gross mistake, and that he will be severely punished for it. I have all the plans of the rebels, and will catch them in their own trap if my men are equal to the emergency. ... Will send you trophies.".
Battle of South Mountain

Battle of South Mountain
The Battle of South Mountain was fought September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain passes: Crampton's, Turner's, and Fox's Gaps. Maj. Gen. George B...
, McClellan's army was able to punch through the defended passes that separated them from Lee, but also gave Lee enough time to concentrate many of his men at Sharpsburg
Sharpsburg, Maryland
Sharpsburg is a town in Washington County, Maryland, United States, approximately south of Hagerstown. The population was 691 at the 2000 census....
, Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
. The Battle of South Mountain presented McClellan with an opportunity for one of the great theatrical moments of his career, as historian Sears describes:
The Union army reached Antietam Creek, to the east of Sharpsburg, on the evening of September 15. A planned attack on September 16 was put off because of early morning fog, allowing Lee to prepare his defenses with an army less than half the size of McClellan's.
Battle of Antietam


Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam , fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek, as part of the Maryland Campaign, was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with about 23,000...
on September 17, 1862, was the single bloodiest day in American military history. The outnumbered Confederate forces fought desperately and well. Despite significant advantages in manpower, McClellan was unable to concentrate his forces effectively, which meant that Lee was able to shift his defenders to parry each of three Union thrusts, launched separately and sequentially against the Confederate left, center, and finally the right. And McClellan was unwilling to employ his ample reserve forces to capitalize on localized successes. Historian James M. McPherson
James M. McPherson
James M. McPherson is an American Civil War historian, and is the George Henry Davis '86 Professor Emeritus of United States History at Princeton University. He received the 1989 Pulitzer Prize for Battle Cry of Freedom, his most famous book...
has pointed out that the two corps McClellan kept in reserve were in fact larger than Lee's entire force. The reason for McClellan's reluctance was that, as in previous battles, he was convinced he was outnumbered.

Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside was an American soldier, railroad executive, inventor, industrialist, and politician from Rhode Island, serving as governor and a U.S. Senator...
's misadventures at Burnside Bridge) and blunders (Edwin V. Sumner's attack without reconnaissance), these were localized problems from which the full army could have recovered. As with the decisive battles in the Seven Days, McClellan's headquarters were too far to the rear to allow his personal control over the battle. He made no use of his cavalry forces for reconnaissance. He did not share his overall battle plans with his corps commanders, which prevented them from using initiative outside of their sectors. And he was far too willing to accept cautious advice about saving his reserves, such as when a significant breakthrough in the center of the Confederate line could have been exploited, but Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter was a career United States Army officer and a Union General during the American Civil War...
is said to have told McClellan, "Remember, General, I command the last reserve of the last Army of the Republic."
Despite being a tactical draw, Antietam is considered a turning point
Turning point of the American Civil War
There is widespread disagreement over the turning point of the American Civil War. The idea of a turning point is an event after which most observers would agree that the eventual outcome was inevitable. While the Battle of Gettysburg is the most widely cited , there are several other arguable...
of the war and a victory for the Union because it ended Lee's strategic campaign (his first invasion of the North) and it allowed President Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation is an executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War using his war powers. It proclaimed the freedom of 3.1 million of the nation's 4 million slaves, and immediately freed 50,000 of them, with nearly...
on September 22, taking effect on January 1, 1863. Although Lincoln had intended to issue the proclamation earlier, he was advised by his Cabinet to wait until a Union victory to avoid the perception that it was issued out of desperation. The Union victory and Lincoln's proclamation played a considerable role in dissuading the governments of France
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
and Britain
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
from recognizing the Confederacy; some suspected they were planning to do so in the aftermath of another Union defeat. McClellan had no prior knowledge that the plans for emancipation rested on his battle performance.
When McClellan failed to pursue Lee aggressively after Antietam, Lincoln ordered that he be removed from command on November 5. Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside was an American soldier, railroad executive, inventor, industrialist, and politician from Rhode Island, serving as governor and a U.S. Senator...
assumed command of the Army of the Potomac on November 7. McClellan wrote to his wife, "Those in whose judgment I rely tell me that I fought the battle splendidly and that it was a masterpiece of art. ... I feel I have done all that can be asked in twice saving the country. ... I feel some little pride in having, with a beaten & demoralized army, defeated Lee so utterly. ... Well, one of these days history will I trust do me justice."
The 1864 Presidential election

Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the capital of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County. As of the 2010 United States Census, Trenton had a population of 84,913...
, New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, for further orders, although none were issued. As the war progressed, there were various calls to return Little Mac to an important command, following the Union defeats at Fredericksburg
Battle of Fredericksburg
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, between General Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army of Northern Virginia and the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose E. Burnside...
and Chancellorsville
Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville was a major battle of the American Civil War, and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville Campaign. It was fought from April 30 to May 6, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, near the village of Chancellorsville. Two related battles were fought nearby on...
, as Robert E. Lee moved north at the start of the Gettysburg Campaign
Gettysburg Campaign
The Gettysburg Campaign was a series of battles fought in June and July 1863, during the American Civil War. After his victory in the Battle of Chancellorsville, Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia moved north for offensive operations in Maryland and Pennsylvania. The...
, and as Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early
Jubal Anderson Early was a lawyer and Confederate general in the American Civil War. He served under Stonewall Jackson and then Robert E. Lee for almost the entire war, rising from regimental command to lieutenant general and the command of an infantry corps in the Army of Northern Virginia...
threatened Washington in 1864. When Ulysses S. Grant became general-in-chief, he discussed returning McClellan to an unspecified position. But all of these opportunities were impossible, given the opposition within the administration and the knowledge that McClellan posed a potential political threat. McClellan worked for months on a lengthy report describing his two major campaigns and his successes in organizing the Army, replying to his critics and justifying his actions by accusing the administration of undercutting him and denying him necessary reinforcements. The War Department was reluctant to publish his report because, just after completing it in October 1863, McClellan openly declared his entrance to the political stage as a Democrat.

1864 Democratic National Convention
The 1864 Democratic National Convention was held at The Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois. The Convention nominated General George B. McClellan for the Presidency, and Representative George H. Pendleton for the Vice-Presidency. McClellan, age 37 at the time of the convention and Pendleton, age 39,...
to run against Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
in the 1864 U.S. presidential election. Following the example of Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott was a United States Army general, and unsuccessful presidential candidate of the Whig Party in 1852....
, he ran as a U.S. Army general still on active duty; he did not resign his commission until election day, November 8, 1864. He supported continuation of the war and restoration of the Union (though not the abolition of slavery), but the party platform, written by Copperhead
Copperheads (politics)
The Copperheads were a vocal group of Democrats in the Northern United States who opposed the American Civil War, wanting an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates. Republicans started calling anti-war Democrats "Copperheads," likening them to the venomous snake...
Clement Vallandigham
Clement Vallandigham
Clement Laird Vallandigham was an Ohio resident of the Copperhead faction of anti-war Democrats during the American Civil War. He served two terms in the United States House of Representatives.-Biography:...
of Ohio, was opposed to this position. The platform called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and a negotiated settlement with the Confederacy. McClellan was forced to repudiate the platform, which made his campaign inconsistent and difficult. He also was not helped by the party's choice for vice president, George H. Pendleton
George H. Pendleton
George Hunt Pendleton was a Representative and a Senator from Ohio. Nicknamed "Gentleman George" for his demeanor, he was the Democratic nominee for Vice President of the United States during the Civil War in 1864, running as a peace Democrat with war Democrat George B. McClellan; they lost to...
, a peace candidate from Ohio.
The deep division in the party, the unity of the Republicans (running under the label "National Union Party"), and the military successes by Union forces in the fall of 1864 doomed McClellan's candidacy. Lincoln won the election handily, with 212 Electoral College votes to 21 and a popular vote of 403,000, or 55%. For all his popularity with the troops, McClellan failed to secure their support and the military vote went to Lincoln nearly 3-1. Lincoln's share of the vote in the Army of the Potomac was 70%.
Postbellum years
At the conclusion of the war, McClellan and his family went to Europe (not returning until 1868), during which he did not participate in politics. When he returned, the Democratic Party expressed some interest in nominating him for president again, but when it became clear that Ulysses S. Grant would be the Republican candidate, this interest died. McClellan worked on engineering projects in New York City and was offered the position of president of the newly formed University of CaliforniaUniversity of California
The University of California is a public university system in the U.S. state of California. Under the California Master Plan for Higher Education, the University of California is a part of the state's three-tier public higher education system, which also includes the California State University...
.
McClellan was appointed chief engineer of the New York City Department of Docks in 1870. Evidently the position did not demand his full-time attention because, starting in 1872, he also served as the president of the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad
Atlantic and Great Western Railroad
The Atlantic and Great Western Railroad began as three separate railroads: the Erie and New York City Railroad based in Jamestown, New York; the Meadville Railroad based in Meadville, Pennsylvania ; and the Franklin and Warren Railroad based in Franklin Mills, Ohio...
. He and his family then embarked on another three-year stay in Europe (1873-75)
In March 1877, McClellan was nominated by Governor Lucius Robinson
Lucius Robinson
Lucius Robinson was an American lawyer and politician. He was the 26th Governor of New York from 1877 to 1879.-Life:...
to be the first Superintendent of Public Works
New York State Department of Public Works
The office of Superintendent of Public Works was created by an 1876 amendment to the New York State Constitution. It abolished the canal commissioners and established that the Department of Public Works execute all laws relating to canal maintenance and navigation except for those functions...
but was rejected by the New York State Senate
New York State Senate
The New York State Senate is one of two houses in the New York State Legislature and has members each elected to two-year terms. There are no limits on the number of terms one may serve...
as being "incompetent for the position."
In 1877, McClellan was nominated by the Democrats for Governor of New Jersey
Governor of New Jersey
The Office of the Governor of New Jersey is the executive branch for the U.S. state of New Jersey. The office of Governor is an elected position, for which elected officials serve four year terms. While individual politicians may serve as many terms as they can be elected to, Governors cannot be...
, an action that took him by surprise because he had not expressed an interest in the position. He accepted the nomination, was elected, and served a single term from 1878 to 1881, a tenure marked by careful, conservative executive management and minimal political rancor. The concluding chapter of his political career was his strong support in 1884 for the election of Grover Cleveland
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States. Cleveland is the only president to serve two non-consecutive terms and therefore is the only individual to be counted twice in the numbering of the presidents...
. He sought the position of secretary of war
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
in Cleveland's cabinet, for which he was well qualified, but political rivals from New Jersey were able to block his nomination.
McClellan's final years were devoted to traveling and writing, including his memoirs McClellan's Own Story (published posthumously in 1887) in which he stridently defended his conduct during the war. He died unexpectedly of a heart attack at age 58 at Orange
Orange, New Jersey
The City of Orange is a city and township in Essex County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the township population was 30,134...
, New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, after having suffered from chest pains for a few weeks. His final words, at 3 a.m., October 29, 1885, were, "I feel easy now. Thank you." He was buried at Riverview Cemetery, Trenton, New Jersey.
McClellan's son, George B. McClellan, Jr.
George B. McClellan, Jr.
George Brinton McClellan, Jr., was an American politician, statesman, and educator. The son of American Civil War general and presidential candidate George B...
(1865 1940), was born in Dresden, Germany, during the family's first trip to Europe. Known within the family as Max, he was also a politician, serving as a United States Representative from New York State and as Mayor of New York City
Mayor of New York City
The Mayor of the City of New York is head of the executive branch of New York City's government. The mayor's office administers all city services, public property, police and fire protection, most public agencies, and enforces all city and state laws within New York City.The budget overseen by the...
from 1904 to 1909. McClellan's daughter, Mary ("May") (1861 1945), married a French diplomat and spent much of her life abroad. His wife Ellen died in Nice, France, while visiting May at "Villa Antietam." Neither Max nor May had any children of their own.
Legacy
The New York Evening PostNew York Post
The New York Post is the 13th-oldest newspaper published in the United States and is generally acknowledged as the oldest to have been published continuously as a daily, although – as is the case with most other papers – its publication has been periodically interrupted by labor actions...
commented in McClellan's obituary, "Probably no soldier who did so little fighting has ever had his qualities as a commander so minutely, and we may add, so fiercely discussed." This fierce discussion has continued for over a century. McClellan is usually ranked in the lowest tier of Civil War generals. However, the debate over McClellan's ability and talents remains the subject of much controversy among Civil War and military historians. He has been universally praised for his organizational abilities and for his very good relations with his troops. They referred to him affectionately as "Little Mac"; others sometimes called him the "Young Napoleon". It has been suggested that his reluctance to enter battle was caused in part by an intense desire to avoid spilling the blood of his men. Ironically, this led to failing to take the initiative against the enemy and therefore passing up good opportunities for decisive victories, which could have ended the war early, and thereby could have spared thousands of soldiers who died in those subsequent battles. Generals who proved successful in the war, such as Lee and Grant, tended to be more aggressive and more willing to risk a major battle even when all preparations were not perfect. McClellan himself summed up his cautious nature in a draft of his memoirs:
McClellan's reluctance to press his enemy aggressively was probably not a matter of personal courage, which he demonstrated well enough by his bravery under fire in the Mexican-American War. Stephen Sears wrote,
One of the reasons that McClellan's reputation has suffered is because of his own memoirs. Historian Allan Nevins
Allan Nevins
Allan Nevins was an American historian and journalist, renowned for his extensive work on the history of the Civil War and his biographies of such figures as President Grover Cleveland, Hamilton Fish, Henry Ford, and John D. Rockefeller.-Life:Born in Camp Point, Illinois, Nevins was educated at...
wrote, "Students of history must always be grateful McClellan so frankly exposed his own weaknesses in this posthumous book." Doris Kearns Goodwin
Doris Kearns Goodwin
Doris Kearns Goodwin is a Pulitzer Prize-winning American biographer and historian, and an oft-seen political commentator. She is the author of biographies of several U.S...
claims that a review of his personal correspondence during the war reveals a tendency for self-aggrandizement and unwarranted self-congratulation. His original draft was completed in 1881, but the only copy was destroyed by fire. He began to write another draft of what would be published posthumously, in 1887, as McClellan's Own Story. However, he died before it was half completed and his literary executor, William C. Prime, editor of the pro-McClellan New York Journal of Commerce, included excerpts from some 250 of McClellan's wartime letters to his wife, in which it had been his habit to reveal his innermost feelings and opinions in unbridled fashion.
Robert E. Lee, on being asked (by his cousin, and recorded by his son) who was the ablest general on the Union side during the late war, replied emphatically: "McClellan, by all odds!"
While McClellan's reputation has suffered over time, especially over the last 75 years, there is a small but intense cadre of American Civil War historians who believe that the general has been poorly served on at least four levels. First, McClellan proponents say that because the general was a conservative Democrat with great personal charisma, radical Republicans fearing his political potential deliberately undermined his field operations. Second, that as the radical Republicans were the true winners coming out of the American Civil War, they were able to write its history, placing their principal political rival of the time, McClellan, in the worst possible light. Third, that historians eager to jump on the bandwagon of Lincoln as America's greatest political icon worked to outdo one another in shifting blame for early military failures from Lincoln and Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton to McClellan. And fourth, that Lincoln and Stanton deliberately undermined McClellan because of his conciliatory stance towards the South, which might have resulted in a less destructive end to the war had Richmond fallen as a result of the Peninsula Campaign. Proponents of this school claim that McClellan is criticized more for his admittedly abrasive personality than for his actual field performance.
Several geographic features and establishments have been named for George B. McClellan. These include Fort McClellan
Fort McClellan
Fort McClellan, originally Camp McClellan, was a United States Army post located adjacent to the city of Anniston, Alabama. During World War II, it was one of the largest U.S. Army installations, training an estimated half-million troops...
in Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, McClellan Butte
McClellan Butte
McClellan Butte is a prominent peak in the Cascade Range in King County, Washington 11 miles east of North Bend. The McClellan Butte hiking trail is a difficult trail known as an alternative to Mount Si's crowded trail....
in the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest
Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest
The Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest in Washington extends more than along the western slopes of the Cascade Range from the Canadian border to the northern boundary of Mount Rainier National Park. Forest headquarters are located in the city of Everett....
, where he traveled while conducting the Pacific Railroad Survey in 1853, and a bronze equestrian statue honoring General McClellan in Washington, D.C. Another equestrian statue honors him in front of Philadelphia City Hall
Philadelphia City Hall
Philadelphia City Hall is the house of government for the city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At , including the statue, it is the world's second-tallest masonry building, only shorter than Mole Antonelliana in Turin...
.
Electoral history
1864 Democratic National Convention1864 Democratic National Convention
The 1864 Democratic National Convention was held at The Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois. The Convention nominated General George B. McClellan for the Presidency, and Representative George H. Pendleton for the Vice-Presidency. McClellan, age 37 at the time of the convention and Pendleton, age 39,...
:
- George B. McClellan - 174 (77.33%)
- Thomas H. Seymour - 38 (16.89%)
- Horatio SeymourHoratio SeymourHoratio Seymour was an American politician. He was the 18th Governor of New York from 1853 to 1854 and from 1863 to 1864. He was the Democratic Party nominee for president of the United States in the presidential election of 1868, but lost the election to Republican and former Union General of...
- 12 (5.33%) - Charles O'ConorCharles O'ConorCharles O'Conor was an American lawyer who ran in the U.S. presidential election, 1872.-Biography:...
- 1 (0.44%)
United States presidential election, 1864
United States presidential election, 1864
In the United States Presidential election of 1864, Abraham Lincoln was re-elected as president. The election was held during the Civil War. Lincoln ran under the National Union ticket against Democratic candidate George B. McClellan, his former top general. McClellan ran as the "peace candidate",...
- Abraham LincolnAbraham LincolnAbraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
/Andrew JohnsonAndrew JohnsonAndrew Johnson was the 17th President of the United States . As Vice-President of the United States in 1865, he succeeded Abraham Lincoln following the latter's assassination. Johnson then presided over the initial and contentious Reconstruction era of the United States following the American...
(National UnionNational Union Party (United States)The National Union Party was the name used by the Republican Party for the national ticket in the 1864 presidential election, held during the Civil War. State Republican parties did not usually change their name....
) - 2,218,388 (55.0%) and 212 electoral votes - George B. McClellan/George H. PendletonGeorge H. PendletonGeorge Hunt Pendleton was a Representative and a Senator from Ohio. Nicknamed "Gentleman George" for his demeanor, he was the Democratic nominee for Vice President of the United States during the Civil War in 1864, running as a peace Democrat with war Democrat George B. McClellan; they lost to...
(Democratic) - 1,812,807 (45.0%) and 21 electoral votes (3 states carried)
New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
gubernatorial
Governor of New Jersey
The Office of the Governor of New Jersey is the executive branch for the U.S. state of New Jersey. The office of Governor is an elected position, for which elected officials serve four year terms. While individual politicians may serve as many terms as they can be elected to, Governors cannot be...
election, 1877:
- George B. McClellan (D) - 97,837 (51.65%)
- William Augustus Newell (R) - 85,094 (44.92%)
Selected works
- The Mexican War Diary of George B. McClellan (William Starr Myers, editor), published posthumously, 1917.
- Bayonet Exercise, or School of the Infantry Soldier, in the Use of the Musket in Hand-To-Hand Conflicts (translated from the French of Gomard), 1852. Reissued as Manual of Bayonet Exercise: Prepared for the Use of the Army of United States, 1862.
- The Report of Captain George B. McClellan, One of the Officers Sent to the Seat of War in Europe, in 1855 and 1856, 1857. Reissued as The Armies of Europe, 1861.
- European Cavalry, Including Details of the Organization of the Cavalry Service Among the Principal Nations of Europe, 1861.
- Regulations and Instructions for the Field Service of the United States Cavalry in Time of War, 1861. Reissued as Regulations for the Field Service of Cavalry in Time of War, 1862.
- McClellan's Own Story (William C. Prime, editor), 1887.
See also
- List of American Civil War generals
Further reading
- Beatie, Russel H. Army of the Potomac: McClellan Takes Command, September 1861 – February 1862. New York: Da Capo Press, 2004. ISBN 0-306-81252-5.
- Beatie, Russel H. Army of the Potomac: McClellan's First Campaign, March – May 1862. New York: Savas Beatie, 2007. ISBN 978-932714-25-8.
- Burton, Brian K. Extraordinary Circumstances: The Seven Days Battles. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2001. ISBN 0-253-33963-4.
- Cutrer, Thomas W. The Mexican War Diary and Correspondence of George B. McClellan. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2009. ISBN 978-0-8071-3451-1.
- Ridgway, James M., Jr. Little Mac: Demise of an American Hero. Xlibris, 2000. ISBN 0-7388-0579-3.
External links
- McClellan Society
- George B. McClellan in Encyclopedia Virginia
- Georgia's Blue and Gray Trail McClellan timeline
- Lincoln and Lee at Antietam
- Mr. Lincoln and New York: George B. McClellan
- National Park Service biography
- Harper's Weekly political cartoon, October 27, 1877, "All Quiet on the Hudson", McClellan caricature in the campaign for governor of New Jersey
- Marcy, Randolph B, assisted by McClellan, George B., Exploration of the Red River of Louisiana, in the year 1852 hosted by the Portal to Texas History
- Biography of George B. McClellan, New Jersey State LibraryNew Jersey State LibraryThe New Jersey State Library, based in Trenton, New Jersey, was established in 1796 to serve the information needs of New Jersey's Governor, Legislature and courts. The State Library is also responsible to assist in the provision of library and information services to all New Jersey...
- New Jersey Governor George Brinton McClellan, National Governors AssociationNational Governors AssociationThe National Governors Association , founded in 1908 as the National Governors' Conference, is funded primarily by state dues, federal grants and contracts and private contributions. NGA represents the governors of the fifty U.S. states and five U.S. territories The National Governors Association...
- "L'il Mac" George McClellan Song parody
- American Heritage on George McClellan's appointment
- The Mexican War diary of George B. McClellan at archive.org
- Abraham Lincoln and George B. McClellan
- Newspaper articles about reaction to Lincoln appointing McClellan head of the Army of the Potomac

