
Democratic Party (United States)
Encyclopedia
The Democratic Party is one of two major
contemporary political parties in the United States
, along with the Republican Party
. The party's socially liberal
and progressive
platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum
. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous operation in the United States
, and is one of the oldest political parties in the world. Barack Obama
is the 15th Democrat to hold the office of President of the United States
.
As of the 112th Congress following the 2010 elections
, the Democratic Party currently holds a minority of seats in the House of Representatives
, but holds a majority of seats in the Senate
. It currently holds a minority of state governorships
, as well as a minority of state legislatures.
factions that opposed the fiscal policies
of Alexander Hamilton
in the early 1790s. Thomas Jefferson
and James Madison
organized these factions into the Democratic-Republican Party. The party favored states' rights
and strict adherence to the Constitution
; it opposed a national bank and wealthy, moneyed interests. The Democratic-Republican Party ascended to power in the election of 1800
.
After the War of 1812
, the party's chief rival, the Federalist Party disbanded. Democratic-Republicans split over the choice of a successor to President James Monroe
, and the party faction that supported many of the old Jeffersonian principles, led by Andrew Jackson
and Martin Van Buren
, became the Democratic Party. Along with the Whig Party
, the Democratic Party was the chief party in the United States until the Civil War. The Whigs were a commercial party, and usually less popular, if better financed. The Whigs divided over the slavery issue
after the Mexican–American War
and faded away. In the 1850s, under the stress of the Fugitive Slave Law
and the Kansas–Nebraska Act, anti-slavery
Democrats left the party. Joining with former members of existing or dwindling parties, the Republican Party
emerged.
The Democrats split over the choice of a successor to President James Buchanan
along Northern and Southern lines, while the Republican Party gained ascendancy in the election of 1860
. As the American Civil War
broke out, Northern Democrats were divided into War Democrats
and Peace Democrats
. The Confederate States of America
, seeing parties as evils, did not have any. Most War Democrats rallied to Republican President Abraham Lincoln
and the Republicans' National Union Party
in 1864, which put Andrew Johnson
on the ticket as a Democrat from the South. Johnson replaced Lincoln in 1865 but stayed independent of both parties . The Democrats benefited from white Southerners' resentment of Reconstruction after the war and consequent hostility to the Republican Party. After Redeemers
ended Reconstruction in the 1870s, and the extremely violent disenfranchisement of African Americans took place in the 1890s, the South, voting Democratic, became known as the "Solid South
." Though Republicans won all but two presidential elections, the Democrats remained competitive. The party was dominated by pro-business Bourbon Democrat
s led by Samuel J. Tilden
and Grover Cleveland
, who represented mercantile, banking, and railroad interests; opposed imperialism
and overseas expansion; fought for the gold standard
; opposed bimetallism
; and crusaded against corruption, high taxes, and tariffs. Cleveland was elected to non-consecutive presidential terms in 1884 and 1892.
Agrarian Democrats demanding Free Silver
overthrew the Bourbon Democrats in 1896 and nominated William Jennings Bryan
for the presidency (a nomination repeated by Democrats in 1900 and 1908). Bryan waged a vigorous campaign attacking Eastern moneyed interests, but he lost to Republican William McKinley
. The Democrats took control of the House in 1910 and elected Woodrow Wilson
as president in 1912 and 1916. Wilson effectively led Congress to put to rest the issues of tariffs, money, and antitrust that had dominated politics for 40 years with new progressive laws. The Great Depression
in 1929 that occurred under Republican President Herbert Hoover
and the Republican Congress set the stage for a more liberal government; the Democrats controlled the House of Representatives nearly uninterrupted from 1931 until 1995 and won most presidential elections until 1968. Franklin D. Roosevelt
, elected to the presidency in 1932, came forth with government programs called the New Deal
. New Deal liberalism meant the promotion of social welfare, labor unions, civil rights, and regulation of business. The opponents, who stressed long-term growth, support for business, and low taxes, started calling themselves "conservatives."
Issues facing parties and the United States after World War II
included the Cold War
and the Civil Rights Movement. Republicans attracted conservatives and white Southerners from the Democratic coalition with their resistance to New Deal and Great Society
liberalism and the Republicans' use of the Southern strategy
. African Americans, who traditionally supported the Republican Party, began supporting Democrats following the ascent of the Franklin Roosevelt administration, the New Deal, and the Civil Rights movement. The Democratic Party's main base of support shifted to the Northeast
, marking a dramatic reversal of history. Bill Clinton
was elected to the presidency in 1992, governing as a New Democrat
. The Democratic Party lost control of Congress in the election of 1994
to the Republican Party. Re-elected in 1996, Clinton was the first Democratic President since Franklin Roosevelt to be elected to two terms. Following twelve years of Republican rule, the Democratic Party regained majority control of both the House and the Senate in the 2006 elections
. Some of the party's key issues in the early 21st century in their last national platform have included the methods of how to combat terrorism
, homeland security
, expanding access to health care
, labor rights
, environmentalism, and the preservation of liberal government programs. In the 2010 elections
, the Democratic Party lost control of the House, but kept a small majority in the Senate (reduced from the 111th Congress). It also lost its majority in state legislatures and state governorships.
The Democratic Party traces its origins to the inspiration of Democratic-Republican Party, founded by Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and other influential opponents of the Federalist
s in 1792. That party also inspired the Whigs and modern Republicans. Organizationally, the modern Democratic Party truly arose in the 1830s, with the election of Andrew Jackson
. Since the division of the Republican Party in the election of 1912
, it has gradually positioned itself to the left
of the Republican Party on economic and social issues
. Until the period following the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Democratic Party was primarily a coalition of two parties divided by region. Southern Democrats were typically given high conservative ratings by the American Conservative Union
while northern Democrats were typically given very low ratings. Southern Democrats were a core bloc of the bipartisan conservative coalition
which lasted through the Reagan-era. The economically activist philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt
, which has strongly influenced American liberalism
, has shaped much of the party's economic agenda since 1932, and served to tie the two regional factions of the party together until the late 1960s. In fact, Roosevelt's New Deal coalition
usually controlled the national government until the 1970s.
, Gallup
polling found that 31% of Americans identified as Democrats, 29% as Republicans, and 38% as independents. A Pew Research Center survey of registered voters released August 2010 stated that 47% identified as Democrats or leaned towards the party, in comparison to 43% of Republicans.
(DNC) is responsible for promoting Democratic campaign activities. While the DNC is responsible for overseeing the process of writing the Democratic Platform, the DNC is more focused on campaign and organizational strategy than public policy
. In presidential elections, it supervises the Democratic National Convention
. The national convention is, subject to the charter of the party, the ultimate authority within the Democratic Party when it is in session, with the DNC running the party's organization at other times. The DNC is currently chaired by Florida
congresswomen Debbie Wasserman Schultz
.
The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee
(DCCC) assists party candidates in House races; its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Rep. Steve Israel
of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee
(DSCC), currently headed by Senator Patty Murray
of Washington, raises large sums for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), currently chaired by Mike Gronstal of Iowa, is a smaller organization with much less funding that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad
is the organization for Americans living outside the United States; they work to advance the goals of the party and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America
(YDA) is a youth-led organization that attempts to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates, but operates outside of the DNC. In addition, the recently created branch of the Young Democrats, the Young Democrats High School Caucus, attempts to raise awareness and activism
amongst teenagers to not only vote and volunteer, but participate in the future as well. The Democratic Governors Association
(DGA), chaired by Governor Martin O'Malley
of Maryland, is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors
.
Each state also has a state committee, made up of elected committee members as well as ex-officio committee members (usually elected officials and representatives of major constituencies), which in turn elects a chair. County, town, city, and ward committees generally are composed of individuals elected at the local level. State and local committees often coordinate campaign activities within their jurisdiction, oversee local conventions and in some cases primaries or caucuses, and may have a role in nominating candidates for elected office under state law. Rarely do they have much funding, but in 2005, DNC Chairman Dean began a program (called the "50 State Strategy") of using DNC national funds to assist all state parties and paying for full-time professional staffers.
, not classical liberalism
). In recent exit poll
s, the Democratic Party has had broad appeal across all socio-ethno-economic demographics.
Historically, the party has favored farmers, laborers, labor unions, and religious and ethnic minorities; it has opposed unregulated business and finance, and favored progressive income taxes. In foreign policy, internationalism (including interventionism) was a dominant theme from 1913 to the mid-1960s. In the 1930s, the party began advocating welfare spending programs targeted at the poor. The party had a fiscally conservative, pro-business wing, typified by Grover Cleveland
and Al Smith
, and a Southern
conservative wing that shrank after President Lyndon B. Johnson
supported the Civil Rights Act of 1964
. The major influences for liberalism were labor unions (which peaked in the 1936–1952 era), and the African American
wing, which has steadily grown since the 1960s. Since the 1970s, environmentalism
has been a major new component.
In recent decades, the party has adopted a centrist
economic and socially progressive agenda, with the voter base having shifted considerably. Today, Democrats advocate more social freedoms, affirmative action
, balanced budget
, and a free enterprise
system tempered by government intervention
(mixed economy
). The economic policy adopted by the modern Democratic Party, including the former Clinton administration
, has been referred to as the "Third Way
". The party believes that government should play a role in alleviating poverty and social injustice
and use a system of progressive tax
ation.
The Democratic Party, once dominant in the Southeastern United States
, is now strongest in the Northeast (Mid-Atlantic
and New England
), Great Lakes region
, and the Pacific Coast
(including Hawaii
). The Democrats are also very strong in major cities.
 Social liberals
Social liberals
(modern liberals) and progressives constitute roughly half of the Democratic voter base. Liberals thereby form the largest united typological demographic within the Democratic base. According to the 2008 exit poll results, liberals constituted 22% of the electorate, and 89% of American liberals favored the candidate of the Democratic Party. White-collar
college-educated professionals were mostly Republican until the 1950s; they now compose perhaps the most vital component of the Democratic Party. A large majority of liberals favor universal health care
, with many supporting a single-payer system
. A majority also favor diplomacy
over military action
, stem cell research
, the legalization of same-sex marriage
, secular government, stricter gun control
, and environmental protection laws as well as the preservation of abortion rights
. Immigration and cultural diversity
is deemed positive; liberals favor cultural pluralism
, a system in which immigrants retain their native culture in addition to adopting their new culture. They tend to be divided on free trade
agreements and organizations such as the North American Free Trade Agreement
(NAFTA). Most liberals oppose increased military spending and the display of the Ten Commandments
in public buildings.
This ideological group differs from the traditional organized labor base. According to the Pew Research Center
, a plurality of 41% resided in mass affluent
households and 49% were college graduates, the highest figure of any typographical group. It was also the fastest growing typological group between the late 1990s and early 2000s. Liberals include most of academia and large portions of the professional class.
of Democratic presidential candidate Senator George McGovern
of South Dakota; others were involved in the presidential candidacies of Vermont
Governor Howard Dean
and U.S. Representative Dennis Kucinich
of Ohio
. The Congressional Progressive Caucus
(CPC) is a caucus of progressive Democrats, and is the single largest Democratic caucus in the House of Representatives. Its members have included Dennis Kucinich
of Ohio, John Conyers
of Michigan, Jim McDermott
of Washington, John Lewis
of Georgia, Barbara Lee
of California, the late Senator Paul Wellstone
of Minnesota, and Sherrod Brown
of Ohio, now a Senator. America Votes
and the Leadership Conference on Civil Rights
are liberal umbrella organizations that push for progressive causes.
and separation of church and state
are more closely aligned to their own than the positions of the Republican Party. They oppose gun control, the "War on Drugs
," protectionism
, corporate welfare
, government debt
, and an interventionist
foreign policy. The Democratic Freedom Caucus is an organized group of this faction. Some civil libertarians also support the party because of their support of habeas corpus
for unlawful combatants, opposition to torture
of suspected terrorists, extraordinary rendition, warrantless wiretapping
, indefinite detention
without trial or charge, the Patriot Act, the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base
and what they see as the erosion of the protections of the Bill of Rights
.
has stated that conservative Democrat
s represent 15% of registered voters
and 14% of the general electorate. In the House of Representatives
, the Blue Dog Coalition, a caucus of fiscal and social conservatives and moderates
forms part of the Democratic Party's current faction of conservative Democrat
s. They have acted as a unified voting bloc in the past, giving its forty plus members some ability to change legislation and broker compromises with the Republican Party
's leadership. Historically, southern Democrats were generally much more ideologically conservative. In 1972, the last year that a sizable number of conservatives dominated the southern wing of the Democratic Party, the American Conservative Union gave higher ratings to most southern Democratic Senators and Congressmen than it did to Republicans.
Democrats differ on a variety of issues, they typically foster a mix of political views and ideas. Compared to other Democratic factions, they tend to be supportive of the use of military force, including the war in Iraq, and are more willing to reduce government welfare, as indicated by their support for welfare reform
and tax cut
s. One of the most influential factions is the Democratic Leadership Council
(DLC), a nonprofit organization that advocates centrist
positions for the party. The DLC hails President Bill Clinton
as proof of the viability of "Third Way
" politicians and a DLC success story. Former Representative Harold Ford, Jr.
of Tennessee
is its current chairman. Centrist Democrats form the New Democrat Coalition
in the House of Representatives
and Senate
.
and whose work revolves around the conceptualization of ideas, have supported the Democratic Party by a slight majority since 2000. Between 1988 and 2000, professionals favored Democrats by a 12-percentage point margin. While the professional class was once a stronghold of the Republican Party, it has become increasingly split between the two parties, leaning in favor of the Democratic Party. The increasing support for Democratic candidates among professionals may be traced to the prevalence of social liberal values among this group.
A study on the political attitudes of medical students
, for example, found that "U.S. medical students are considerably more likely to be liberal than conservative and are more likely to be liberal than are other young U.S. adults. Future U.S. physicians may be more receptive to liberal messages than conservative ones, and their political orientation may profoundly affect their health system attitudes." Similar results are found for professors, who are more strongly inclined towards liberalism and the Democratic Party than other occupational groups. The Democratic Party also has strong support among scientist
s, with 55% identifying as Democrats, 32% as Independents, and 6% as Republicans and 52% identifying as liberal, 35% as moderate, and 9% as conservative.
 Academics, intellectuals, and the highly educated
Academics, intellectuals, and the highly educated
overall constitute an important part of the Democratic voter base. Academia
in particular tends to be progressive. In a 2005 survey, nearly 72% of full-time faculty members identified as liberal, while 15% identified as conservative. The social sciences
and humanities
were the most liberal disciplines while business was the most conservative. Male professors at more advanced stages of their careers as well as those at elite institutions tend be the most liberal. Another survey by UCLA conducted in 2001/02, found 47.6% of scholars identifying as liberal, 34.3% as moderate, and 18% as conservative. Percentages of professors who identified as liberal ranged from 49% in business to over 80% in political science
and the humanities. Social scientists, such as Brett O'Bannon of DePauw University
, have claimed that the "liberal" opinions of professors seem to have little, if any, effect on the political orientation of students. Whether or not that is true, some conservatives and Republicans complain they are offended and even threatened by the liberal atmosphere of college campuses. As of July 2008 the Students for Academic Freedom
arm of the David Horowitz Freedom Center
, a conservative organization, posted a list of 440 student complaints, most of which pertain to perceived liberal bias of college professors.
Some attribute the liberal inclination of American professors to the more liberal outlook of the highly educated.
Those with graduate education
, have become increasingly Democratic beginning in the 1992, 1996, 2000, 2004, and 2008 elections. Intellectualism, the tendency to constantly reexamine issues, or in the words of Edwards Shields, the "penetration beyond the screen of immediate concrete experience," has also been named as an explanation why academia is strongly democratic and liberal.
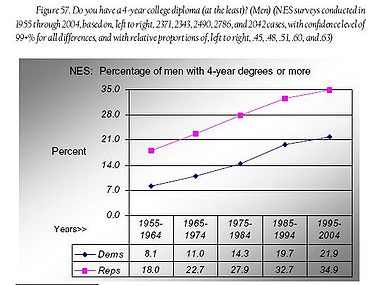
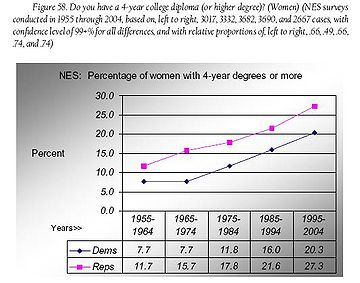
Although Democrats are well-represented at the postgraduate level, self-identified Republicans are more likely to have attained a 4-year college degree. The trends for the years 1955 through 2004 are shown by gender in the graphs above, reproduced with permission from Democrats and Republicans — Rhetoric and Reality, a book published in 2008 by Joseph Fried. These results are based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies, supported by the National Science Foundation.
and George H. W. Bush
, the young have voted in favor of the Democratic presidential candidate in every election since Bill Clinton
in 1992, and are more likely to identify as liberals than the general population. In the 2004 presidential election
, Democratic presidential candidate John Kerry
received 54% of the vote from voters of the age group 18–29, while Republican George W. Bush
received 45% of the vote from the same age group. In the 2006 midterm election
s, the Democrats received 60% of the vote from the same age group. Polls suggest that younger voters tend to be more liberal than the general population and have more liberal views than the public on same-sex marriage and universal healthcare, helping Barack Obama
carry 66% of their votes in 2008. The Young Democrats of America
are an affiliated organization of members of the party younger than 36 that advocates for youth issues and works for youth voter turnout.
. Labor unions supply a great deal of the money, grass roots
political organization
, and voting base of support for the party. Democrats are far more likely to be represented by unions, although union membership has declined, in general, during the last few decades. This trend is depicted in the following graph from the book, Democrats and Republicans — Rhetoric and Reality. It is based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies (NES).
The historic decline in union membership over the past half century has been accompanied by a growing disparity between public sector and private sector union membership percentages. The three most significant labor groupings in the Democratic coalition today are the AFL-CIO
and Change to Win
labor federations
, as well as the National Education Association
, a large, unaffiliated teachers'
union. Both the AFL-CIO and Change to Win have identified their top legislative priority for 2007 as passage of the Employee Free Choice Act
. Other important issues for labor unions include supporting industrial policy
(including protectionism
) that sustains unionized manufacturing
jobs, raising the minimum wage
and promoting broad social programs such as Social Security
and universal health care
.
has lost much of its political strength with the decline of labor unions
, it remains a stronghold of the Democratic Party and continues as an essential part of the Democratic base. Today, roughly a third of the American public is estimated to be working class with around 52% being either members of the working or lower classes
. Yet, as those with lower socioeconomic status are less likely to vote, the working and lower classes are underrepresented in the electorate. The working class is largely distinguished by highly routinized and closely supervised work. It consists mainly of clerical and blue-collar worker
s. Even though most in the working class are able to afford an adequate standard of living
, high economic insecurity and possible personal benefit from an extended social safety net
, make the majority of working class person left-of-center on economic issues. Most working class Democrats differ from most liberals, however, in their more socially conservative views. Working class Democrats tend to be more religious and likely to belong to an ethnic minority. Socially conservative and disadvantaged Democrats are among the least educated and lowest earning ideological demographics. In 2005, only 15% had a college degree, compared to 27% at the national average and 49% of liberals, respectively. Together socially conservative and the financially disadvantaged comprised roughly 54% of the Democratic base. The continued importance of the working class votes manifests itself in recent CNN exit polls, which shows that the majority of those with low incomes
and little education vote for the Democratic Party.
is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that often support Democratic candidates are Emily's List
and the National Organization for Women
.
GSS
surveys of more than 11,000 Democrats and Republicans conducted between 1996 and 2006 came to the result that the differences in fertility rates are not statistically significant between these parties, with the average Democrat having 1.94 children and the average Republican having 1.91 children.
However, there is a significant difference in fertility rates between the two related groups liberals
and conservatives, with liberals reproducing at much lower rate than conservatives.
, gay
, bisexual, and transgender
Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70-77% range, according to national media exit polling. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85-94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16% and 13% for others. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25% with 5% for others, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23% and in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27% with 3% to others. Patrick Egan, a professor of politics at New York University specializing in LGBT voting patterns, calls this a "remarkable continuity." Saying "about three-fourths vote Democratic and one-fourth Republican from year to year." Notable LGBT Democrats include current Representatives Barney Frank
of Massachusetts, Tammy Baldwin
of Wisconsin, Jared Polis
of Colorado and David Cicilline
of Rhode Island. The late activist and San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk
was a Democrat. The National Stonewall Democrats is an LGBT advocacy group associated with the Democratic Party. The LGBT Equality Caucus is a congressional caucus of 76 Democrats and 1 Republican that work and advocate for LGBT rights within the House of Representatives
.
s primarily favored the Republican Party due to its overwhelming political and more tangible efforts in achieving abolition, particularly through President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation
. The south had long been a Democratic stronghold, favoring a state's right to legal slavery. In addition, the ranks of the fledgling Ku Klux Klan
were composed almost entirely of white Democrats angry over poor treatment by northerners and bent on reversing the policies of Reconstruction. However, as years passed and memories waned, African American
s began drifting to the Democratic Party, as Franklin Roosevelt's
New Deal
programs gave economic relief to all minorities, including African Americans and Hispanic
s. Support for the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s by Democratic presidents John F. Kennedy
and Lyndon B. Johnson
helped give the Democrats even larger support among the African American community, which consistently vote between 85-95% Democratic.
Prominent modern-day African-American Democratic politicians include Jim Clyburn
, Ed Towns
, Maxine Waters
, John Lewis, Deval Patrick
, Charles Rangel, John Conyers
, and the current President of the United States, Barack Obama
, who managed to net over 95% of the African American vote in the 2008 election. Despite being unaffiliated, the NAACP often participates in organizing and voter turnout drives and advocates for progressive causes, especially those that affect people of color. Within the House of Representatives
, the Congressional Black Caucus
, consisting of 44 black Democrats, serves to represent the interests of African Americans and advocate on issues that affect them.
population, particularly the large Mexican American
population in the Southwest
and the large Puerto Rican
and Dominican
populations in the Northeast
, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. They commonly favor liberal views on immigration. In the 1996 presidential election
, Democratic President Bill Clinton
received 72% of the Hispanic vote. Since then, however, the Republican Party has gained increasing support from the Hispanic community, especially among Hispanic Protestants and Pentecostals
. Along with Bush's much more liberal views on immigration, President Bush was the first Republican president to gain 40% of the Hispanic vote (he did so in the 2004 presidential election
). Yet, the Republican Party's support among Hispanics eroded in the 2006 midterm elections, dropping from 44 to 30 percent, with the Democrats gaining in the Hispanic vote from 55% in 2004 to 69% in 2006.
Democrats increased their share of the Hispanic vote in the 2008 presidential election
, with Barack Obama
receiving 67%. Cuban American
s still heavily vote Republican, though there has been a noticeable change since the 2008 elections. During the 2008 elections Barack Obama received 47% of the Cuban American vote in Florida. According to Bendixen's exit polls, 84% of Miami-Dade Cuban American voters 65 or older backed McCain, while 55% of those 29 or younger backed Obama. Showing that the younger Cuban-American generation have shifted to becoming more liberal. Unaffiliated Hispanic advocacy groups that often support progressive candidates and causes include the National Council of La Raza
and the League of United Latin American Citizens
. In the House of Representatives
, the Democratic caucus of Hispanic Americans is the Congressional Hispanic Caucus
.
Throughout the decade of the 2000s, 60% or more of Hispanic Roman Catholics registered voters have identified as either Democratic or leaning towards the Party.
population, particularly in Arizona
, New Mexico
, Montana
, North Dakota
, South Dakota
, Washington, Alaska
, Idaho
, Minnesota
, Wisconsin
, and North Carolina
. Though now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African-Americans.
communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party, with more than 70% of Jewish voters having cast their ballots for the Democrats in the 2004 and 2006 elections. Support tends to vary among specific sectarian groups. For example, only 13% of Orthodox Jews supported Barack Obama in 2008 while around 60% of Conservative Jews and Reform Jews did so. A 2010 poll by the Pew Research Center found that 60% of self-described Jews identified as Democratic or leaning towards the party, compared to 33% with those feelings towards Republicans.
Jews as an important Democratic constituency are especially politically active and influential in large cities such as New York City
, Los Angeles
, Boston
, Chicago
and play critical roles in large cities within Presidential Swing States such as Philadelphia, Miami, and Las Vegas
. Many prominent national Democrats in recent decades have been Jewish, including Chuck Schumer, Abraham Ribicoff, Henry Waxman
, Martin Frost
, Joseph Lieberman, Dianne Feinstein
, Barney Frank
, Barbara Boxer
, Paul Wellstone
, Rahm Emanuel
, Russ Feingold
, Herb Kohl
, and Howard Metzenbaum
.
s and Muslim Americans
have leaned Democratic since the Iraq War
. Zogby
found in June 2007 that 39% of Arab Americans identify as Democrats, 26% as Republicans, and 28% as independent
s.
Arab Americans, generally socially conservative but with more diverse economic views, historically voted Republican until recent years, having supported George W. Bush
over Al Gore
in 2000.
argues that the current Democractic Party and President Obama have adopted the same positions held by moderate Republicans
in the early 1990s.
The following views are generally held by most Democrats. Some Democrats take other positions on these issues.
, and more regular increases. The Fair Minimum Wage Act of 2007
was an early component of the Democrats' agenda during the 110th Congress
. In 2006, the Democrats supported six state ballot initiatives to increase the minimum wage; all six initiatives passed.
structure to provide more services and reduce economic inequality
. Currently they have proposed allowing those tax cuts the Bush administration
gave to the wealthiest Americans to expire as written in the original legislation while wishing to keep in place those given to the middle class. Democrats generally support more government spending
on social services while spending less on the military. They oppose the cutting of social services, such as Social Security
, Medicare
, Medicaid
, and various welfare programs, believing it to be harmful to efficiency and social justice
. Democrats believe the benefits of social services, in monetary and non-monetary terms, are a more productive labor
force and cultured population, and believe that the benefits of this are greater than any benefits that could be derived from lower taxes, especially on top earners, or cuts to social services. Furthermore, Democrats see social services as essential towards providing positive freedom
, i.e. freedom derived from economic opportunity. The Democratic-led House of Representatives reinstated the PAYGO
(pay-as-you-go) budget rule at the start of the 110th Congress
. DNC Chairman Howard Dean
has cited Bill Clinton's presidency
as a model for fiscal responsibility.
or universal health care
in a variety of forms to address the rising costs of modern health insurance
. Some Democrats, such as Representatives John Conyers
and John Dingell
, have called for a single-payer program
of Medicare for All. The Progressive Democrats of America
, a group operating inside the Democratic Party, has made single-payer universal health care one of their primary policy goals.
Some Democratic governors have supported purchasing Canadian drugs, citing lower costs and budget restrictions as a primary incentive. Recognizing that unpaid insurance bills increase costs to the service provider, who passes the cost on to health-care consumers, many Democrats advocate expansion of health insurance coverage.
Policies which most Democrats favor include:
Many of these proposals were included in the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
and Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
.
, such as Montana
's state-supported wind farm and "clean coal" programs as well as setting in place a cap and trade policy
in hopes of reducing carbon emissions and creating incentives for clean-energy innovations.
. In more recent years, this stance has had as its emphasis alternative energy generation as the basis for an improved economy, greater national security
, and general environmental benefits.
The Democratic Party also favors expansion of conservation lands and encourages open space and rail travel to relieve highway and airport congestion and improve air quality and economy; it "believe[s] that communities, environmental interests, and government should work together to protect resources while ensuring the vitality of local economies. Once Americans were led to believe they had to make a choice between the economy and the environment. They now know this is a false choice."
The most important environmental concern of the Democratic Party is global warming
. Democrats, most notably former Vice President Al Gore
, have pressed for stern regulation of greenhouse gas
es. On October 15, 2007, he won the Nobel Peace Prize
for his efforts to build greater knowledge about man-made climate change
, and laying the foundations for the measures needed to counteract these changes asserting that "the climate crisis is not a political issue, it is a moral and spiritual challenge to all of humanity."
or college tuition
tax deduction
.
agreements that reflects a diversity of viewpoints in the party. The liberal and cosmopolitan
wing of the party, including the intelligentsia and college-educated professionals overall, tend to favor globalization
, while the organized labor wing of the party opposes it. In the 1990s, the Clinton administration and a number of prominent Democrats pushed through a number of agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement
(NAFTA). Since then, the party's shift away from free trade became evident in the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) vote, with 15 House Democrats voting for the agreement and 187 voting against.
In his 1997 Achieving Our Country, philosopher
Richard Rorty
, professor
at Stanford University
states that economic globalization "invites two responses from the Left. The first is to insist that the inequalities between nations need to be mitigated... The second is to insist that the primary responsibility of each democratic nation-state is to its own least advantaged citizens... the first response suggests that the old democracies should open their borders, whereas the second suggests that they should close them. The first response comes naturally to academic leftists, who have always been internationally minded. The second comes naturally to members of trade unions, and to marginally employed people who can most easily be recruited into right-wing populist movements." (p. 88)
(AMT). The tax was originally designed to tax the rich but now may affect many households, especially those with incomes
ranging from $75,000 to $100,000. The party proposed to re-adjust the tax in such a manner as to restore its initial intention. According to a 2007 Reuters News Report, "House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Charles B. Rangel
has said he will push for permanent AMT relief for those taxpayers who were never meant to pay it."
for all Americans regardless of sex, age, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation
, gender identity
, religion, creed, or national origin. The Party supports affirmative action
programs to further this goal. Democrats also strongly support the Americans with Disabilities Act
to prohibit discrimination against people based on physical or mental disability.
, though support for it has been increasing and most of the support for same-sex marriage in the United States
has come from Democrats. Some members favor civil union
s for same-sex couples, others favor full and equal legalized marriage, and others are opposed to same-sex marriage on religious or ideological grounds. Support for same-sex marriage has increased in the past decade according to ABC News. An April 2009 ABC News/Washington Post public opinion poll put support among Democrats at 62% A June 2008 Newsweek
poll found that 42% of Democrats support same-sex marriage while 23% support civil union
s or domestic partnership
laws and 28% oppose any legal recognition at all. The 2004 Democratic National Platform stated that marriage should be defined at the state level and it repudiated the Federal Marriage Amendment
. Senator
John Kerry
, Democratic presidential candidate in 2004, did not support same-sex marriage. Former President Bill Clinton
and former Vice President Al Gore
said in 2009 that they now support gay marriage.
President Barack Obama
has stated that he considers marriage to be "something sanctified between a man and a woman". He campaigned for the election promising to "give same-sex couples equal legal rights and privileges as married couples" in civil union
s. At the same time, Obama opposed California
's Prop 8, and he has promised to repeal the Defense of Marriage Act
. Obama has stated that generally "decisions about marriage should be left to the states as they always have been." However, when running for the Illinois Senate in 1996, he said that he "unequivocally support(ed) gay marriage" and "favor(ed) legalizing same-sex marriages, and would fight efforts to prohibit such marriages."
A broad majority of Democrats have supported other LGBT related laws such as extending hate crime
statutes, legally preventing discrimination against LGBT people in the workforce
, and repealing Don't ask, don't tell
. A 2006 Pew Research Center
poll of Democrats found that 55% supported gays adopting children with 40% opposed while 70% support gays in the military
with only 23% opposed. Gallup polling from May 2009 stated that 82% of Democrats support open enlistment.
, and support public funding of contraception for poor women. The Democratic Party, in its national platforms from 1992 to 2004, has called for abortion
to be "safe, legal and rare" — namely, keeping it legal by rejecting laws that allow governmental interference in abortion decisions, and reducing the number of abortions by promoting both knowledge of reproduction and contraception, and incentives for adoption. The wording changed in the 2008 platform. When Congress voted on the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act
in 2003, Congressional Democrats were split, with a minority (including current Senate Majority Leader
Harry Reid
) supporting the ban, and the majority of Democrats opposing the legislation.
The Democratic Party opposes attempts to reverse the 1973 Supreme Court decision Roe v. Wade
, which declared abortion covered by the constitutionally protected individual right to privacy under the Ninth Amendment
, and Planned Parenthood v. Casey
, which lays out the legal framework in which government action alleged to violate that right is assessed by courts. As a matter of the right to privacy
and of gender equality
, many Democrats believe all women should have the ability to choose to abort without governmental interference. They believe that each woman, conferring with her conscience, has the right to choose for herself whether abortion is morally correct. Some Democrats also believe that poor women should have a right to publicly funded abortions.
Current Senate Majority Leader
Harry Reid
self-identifies as 'pro-life
', while President Barack Obama
and Speaker of the House
Nancy Pelosi
self-identify as 'pro-choice
'. Groups such as Democrats for Life of America
represent the pro-life faction
of the party, while groups such as EMILY's List
represent the pro-choice faction
. A Newsweek
poll from October 2006 found that 25% of Democrats were pro-life while a 69% majority was pro-choice. Pro-life Democrats themselves state that they represent over 40% of Democrats.
with federal funding. In his 2004 platform, John Kerry
affirmed his support of federally funded embryonic stem cell research "under the strictest ethical guidelines," saying, "We will not walk away from the chance to save lives and reduce human suffering." In 2009, Barack Obama lifted the eight-year running ban on embryonic stem cell research and proposed federal funding to further research.
against "those responsible for the recent attacks launched against the United States" in Afghanistan
in 2001, supporting the NATO coalition invasion of the nation. Most elected Democrats continue to support the Afghanistan conflict, and some, such as a Democratic National Committee
spokesperson, have voiced concerns that the Iraq War shifted too many resources away from the presence in Afghanistan. Since 2006, Democratic candidate Barack Obama
has called for a "surge" of troops into Afghanistan and, since 2008, Republican candidate John McCain
has also called for a "surge".
Speaker of the House
Nancy Pelosi
and Senator Chuck Schumer expressed support for Obama's plan. Pelosi stated in mid-2008, “We need more resources there... We are understaffed there, not only in our military presence, but also in terms of the reconstruction of Afghanistan." After his election as President, Barack Obama sent about 21,000 additional U.S. forces into the country. He has planned to send 68,000 troops by the year's end.
Support for the war among the American people has diminished over time, and many Democrats have changed their opinion and now oppose a continuation of the conflict. In July 2008, Gallup found that 41% of Democrats called the invasion a "mistake" while a 55% majority disagreed; in contrast, Republicans were more supportive of the war. The survey described Democrats as evenly divided about whether or not more troops should be sent— 56% support it if it would mean removing troops from Iraq and only 47% support it otherwise. A CNN
survey in August 2009 stated that a majority of Democrats now oppose the war. CNN polling director Keating Holland said, "Nearly two thirds of Republicans support the war in Afghanistan. Three quarters of Democrats oppose the war." An August 2009 Washington Post poll found similar results, and the paper stated that Obama's policies would anger his closest supporters.
Nancy Pelosi
has said, “When it comes to Israel, Republicans and Democrats speak with one voice.” A 2008 Gallup poll found that 64% say that they have a favorable image of Israel while only 16% say that they have a favorable image of the Palestinian Authority. Within the party, the majority view is held by the Democratic leadership although some members such as John Conyers Jr., George Miller, Nick Rahall
, Dave Obey
, Pete Stark
, Dennis Kucinich
, Jim McDermott
, and Cynthia McKinney
as well as former President Jimmy Carter
are less or not supportive of Israel. The party leadership refers to the other side as a "fringe".
The 2008 Democratic Party Platform acknowledges a "special relationship
with Israel, grounded in shared interests and shared values, and a clear, strong, fundamental commitment to the security of Israel, our strongest ally in the region and its only established democracy." It also included:
A January 2009 Pew Research Center
study found that, when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates and/or independents sided with Israel.
; 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate, 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former Senator John Edwards
, have expressed regret about this decision, and have called it a mistake, while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton
have criticized the conduct of the war but not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, in April 2007 Senate Majority Leader
Harry Reid
declared the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about WMDs in Iraq
. Amongst lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the 2006 mid-term elections.
A March 2003 CBS News
poll taken a few days before the invasion of Iraq
found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations
backing, 51% would support it only with its backing, and 14% would not support it at all. The Los Angeles Times
stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center
stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News
poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution
disapproving of President Bush's decision to send additional troops into Iraq in 2007
. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the president, and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the president after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War
subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007
led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate Barack Obama
advocated a withdrawal of combat troops within Iraq by late 2010 with a residual force of peacekeeping troops left in place. He stated that both the speed of withdrawal and the amount of troops left over would be "entirely conditions-based."
On February 27, 2009, President Obama announced, “As a candidate for president, I made clear my support for a timeline of 16 months to carry out this drawdown, while pledging to consult closely with our military commanders upon taking office to ensure that we preserve the gains we’ve made and protect our troops... Those consultations are now complete, and I have chosen a timeline that will remove our combat brigades over the next 18 months." Around 50,000 non-combat related forces will remain. Obama's plan drew wide bipartisan support, including that of defeated Republican Presidential candidate Senator John McCain
.
, which dictates that the United States should use military force without any assistance from other nations whenever it believes there is a threat to its security or welfare. They believe the United States should act in the international arena in concert with strong alliances and broad international support. This was a major foreign policy issue of John Kerry
's 2004 presidential campaign; his platform attributed rifts with international allies to unilateralism. Barack Obama's 2008 campaign also discussed promoting the image of the United States abroad.
In a general sense, the modern Democratic Party is more closely aligned with the international relations theories
of liberalism
, neoliberalism
, and functionalism
than realism and neorealism, though realism has some influence on the party. Wilsonian idealism
, in which unilateral foreign intervention
is justified to end genocide
or other humanitarian crises, has also played a major role both historically and currently- with its supporters known as 'liberal hawk
s'.
to exercise their right to self-determination. Puerto Rico has been under U.S. sovereignty for over a century and Puerto Ricans have been U.S. citizens since 1917, but the island’s ultimate status still has not been determined and its 3.9 million residents still do not have voting representation in their national government. Also states that U.S. citizens in Puerto Rico should receive treatment under federal programs that is comparable to that of citizens in the States. The following are the appropriate section from the 2000, 2004 and 2008 party platforms:
against individuals apprehended and held prisoner by the U.S. military
, and hold that categorizing such prisoners as unlawful combatant
s does not release the U.S. from its obligations under the Geneva Conventions
. Democrats contend that torture is inhumane, decreases the United States' moral standing in the world, and produces questionable results. Democrats largely spoke out against waterboarding
.
legislation in 2001. The lone nay vote was from Russ Feingold
of Wisconsin
; Mary Landrieu
of Louisiana
did not vote. In the House the Democrats voted for the Act by 145 yea and 62 nay. Democrats split on the renewal in 2006. In the Senate, Democrats voted 34 for the 2006 renewal, and 9 against. In the House, Democrats voted 66 voted for the renewal, and 124 against.
. For example, Democrats have generally opposed the NSA warrantless surveillance of U.S. citizens
.
Some Democratic officeholders have championed consumer protection
laws that limit the sharing of consumer data between corporations. Most Democrats oppose sodomy laws
and believe that government should not regulate consensual noncommercial sexual conduct among adults as a matter of personal privacy.
measures, most notably the Gun Control Act of 1968
, the Brady Bill
of 1993, and Crime Control Act of 1994. However, some Democrats, especially rural, Southern, and Western Democrats, favor fewer restrictions on firearm possession and warned the party was defeated in the 2000 presidential election in rural areas because of the issue. In the national platform for 2008, the only statement explicitly favoring gun control was a plan calling for renewal of the 1994 Assault Weapons Ban
.
. Though most Democrats in Congress have never seriously moved to overturn the rarely used federal death penalty, both Russ Feingold
and Dennis Kucinich
have introduced such bills with little success. Democrats have led efforts to overturn state death penalty laws, particularly in New Jersey and in New Mexico. They have also sought to prevent reinstatement of the death penalty in those states which currently prohibit it, including Massachusetts and New York. During the Clinton administration
, Democrats led the expansion of the federal death penalty. These efforts resulted in the passage of the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996
, Signed into law by President Clinton
, the law heavily limited appeals in death penalty cases.
In 1992, 1993, and 1995, Democratic Texas Congressman Henry González
unsuccessfully introduced the Death Penalty Abolition Amendment which prohibited the use of capital punishment in the United States
. Democratic Missouri Congressman William Lacy Clay, Sr.
cosponsored the amendment in 1993.
During his Illinois Senate career
, now-President
Barack Obama
successfully introduced legislation intended to reduce the likelihood of wrongful conviction
s in capital cases, requiring videotaping of confessions. When campaigning for the presidency
, Obama stated that he supports the limited use of the death penalty, including for people who have been convicted of raping a minor under the age of 12, having opposed the Supreme Court
's ruling in Kennedy v. Louisiana
that the death penalty was unconstitutional in child rape cases. Obama has stated that he thinks the "death penalty does little to deter crime", and that it is used too frequently and too inconsistently.
, with the hope of stigmatizing them as purveyors of democracy or mob rule. By the Jacksonian era, the term "The Democracy" was in use by the party; the name "Democratic Party" was eventually settled upon. Since the 1995s, Republicans have often referred to the Democratic Party using the phrase "Democrat Party" as a political epithet
.
The most common mascot symbol for the party is the donkey
, although the party never officially adopted this symbol. Andrew Jackson's opponents had labeled him a jackass during the intense mudslinging in 1828
. A political cartoon titled "A Modern Balaam and his Ass" depicting Jackson riding and directing a donkey (representing the Democratic Party) was published in 1837. A political cartoon by Thomas Nast
in an 1870 edition of Harper's Weekly
revived the donkey as a symbol for the Democratic Party. Cartoonists followed Nast and used the donkey to represent the Democrats, and the elephant to represent the Republicans.
In the early 20th century, the traditional symbol of the Democratic Party in Midwestern states such as Indiana, Kentucky, Oklahoma and Ohio was the rooster, as opposed to the Republican eagle. This symbol still appears on Oklahoma, Kentucky, Indiana, and West Virginia ballot
s. In New York, the Democratic ballot symbol is a five-pointed star. For the majority of the 20th century, Missouri Democrats used the Statue of Liberty
as their ballot emblem. This meant that when Libertarian
candidates received ballot access
in Missouri in 1976, they could not use the Statue of Liberty, their national symbol, as the ballot emblem. Missouri Libertarians instead used the Liberty Bell
until 1995, when the mule became Missouri's state animal. From 1995 to 2004, there was some confusion among voters, as the Democratic ticket was marked with the Statue of Liberty (used by Libertarians in other states) and the Libertarians' mule was easily mistaken for a Democratic donkey.
Although both major political parties (and many minor ones) use the traditional American red, white, and blue colors in their marketing and representations, since election night 2000
the color blue has become the identified color of the Democratic Party, while the color red has become the identified color of the Republican Party. That night, for the first time, all major broadcast television networks used the same color scheme for the electoral map: blue states for Al Gore
(Democratic nominee) and red states for George W. Bush
(Republican nominee). Since then, the color blue has been widely used by the media to represent the party. This has caused confusion among non-American observers because blue is the traditional color of the right
and red the color of the left
outside of the United States. For example, in Canada red represents the Liberals
, while blue represents the Conservatives
. In the United Kingdom, red denotes the Labour Party
and blue symbolizes the Conservative Party
. Blue has also been used both by party supporters for promotional efforts — ActBlue
, BuyBlue, BlueFund, as examples — and by the party itself in 2006 both for its "Red to Blue Program", created to support Democratic candidates running against Republican incumbents in the midterm elections
that year, and on its official website.
In September, 2010, the Democratic Party unveiled its new logo, which featured a blue D inside a blue circle. It was the party's first official logo, as the donkey logo had been used as a semi-official party logo.
Jefferson-Jackson Day
is the annual fundraising event (dinner) held by Democratic Party organizations across the United States. It is named after Presidents Thomas Jefferson
and Andrew Jackson, whom the party regards as its distinguished early leaders.
The song "Happy Days Are Here Again
" is the unofficial song of the Democratic Party. It was used prominently when Franklin D. Roosevelt
was nominated for president at the 1932 Democratic National Convention
and remains a sentimental favorite for Democrats today. For example, Paul Shaffer
played the theme on the Late Show with David Letterman
after the Democrats won Congress in 2006. More recently, the emotionally similar song "Beautiful Day
" by the band U2
has become a favorite theme song for Democratic candidates. John Kerry
used the song during his 2004 presidential campaign, and several Democratic Congressional candidates used it as a celebratory tune in 2006.
Aaron Copland
's Fanfare for the Common Man
is traditionally performed at the beginning of the Democratic National Convention.
Major party
A major party is a political party that holds substantial influence in a country's politics, standing in contrast to a minor party. It should not be confused with majority party.According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary:...
contemporary political parties in the United States
Political parties in the United States
This article presents the historical development and role of political parties in United States politics, and outlines more extensively the significant modern political parties. Throughout most of its history, American politics have been dominated by a two-party system...
, along with the Republican Party
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
. The party's socially liberal
Social liberalism
Social liberalism is the belief that liberalism should include social justice. It differs from classical liberalism in that it believes the legitimate role of the state includes addressing economic and social issues such as unemployment, health care, and education while simultaneously expanding...
and progressive
Progressivism
Progressivism is an umbrella term for a political ideology advocating or favoring social, political, and economic reform or changes. Progressivism is often viewed by some conservatives, constitutionalists, and libertarians to be in opposition to conservative or reactionary ideologies.The...
platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum
Politics of the United States
The United States is a federal constitutional republic, in which the President of the United States , Congress, and judiciary share powers reserved to the national government, and the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.The executive branch is headed by the President...
. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous operation in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, and is one of the oldest political parties in the world. Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
is the 15th Democrat to hold the office of President of the United States
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
.
As of the 112th Congress following the 2010 elections
United States elections, 2010
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested in this election along with 38 state and territorial...
, the Democratic Party currently holds a minority of seats in the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
, but holds a majority of seats in the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
. It currently holds a minority of state governorships
Governor (United States)
In the United States, the title governor refers to the chief executive of each state or insular territory, not directly subordinate to the federal authorities, but the political and ceremonial head of the state.-Role and powers:...
, as well as a minority of state legislatures.
History
The Democratic Party evolved from Anti-FederalistAnti-Administration Party (United States)
Anti-Administration "Party" was the informal faction comprising the opponents of the policies of Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton in the first term of President George Washington. This was not an organized political party but an unorganized faction...
factions that opposed the fiscal policies
Hamiltonian economic program
The Hamiltonian economic program was the set of measures that were proposed by American Founding Father and 1st Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton in three notable reports and implemented by Congress during George Washington's first administration....
of Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton was a Founding Father, soldier, economist, political philosopher, one of America's first constitutional lawyers and the first United States Secretary of the Treasury...
in the early 1790s. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
and James Madison
James Madison
James Madison, Jr. was an American statesman and political theorist. He was the fourth President of the United States and is hailed as the “Father of the Constitution” for being the primary author of the United States Constitution and at first an opponent of, and then a key author of the United...
organized these factions into the Democratic-Republican Party. The party favored states' rights
States' rights
States' rights in U.S. politics refers to political powers reserved for the U.S. state governments rather than the federal government. It is often considered a loaded term because of its use in opposition to federally mandated racial desegregation...
and strict adherence to the Constitution
Constitution
A constitution is a set of fundamental principles or established precedents according to which a state or other organization is governed. These rules together make up, i.e. constitute, what the entity is...
; it opposed a national bank and wealthy, moneyed interests. The Democratic-Republican Party ascended to power in the election of 1800
United States presidential election, 1800
In the United States Presidential election of 1800, sometimes referred to as the "Revolution of 1800," Vice-President Thomas Jefferson defeated President John Adams. The election was a realigning election that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican Party rule and the eventual demise of...
.
After the War of 1812
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, the party's chief rival, the Federalist Party disbanded. Democratic-Republicans split over the choice of a successor to President James Monroe
James Monroe
James Monroe was the fifth President of the United States . Monroe was the last president who was a Founding Father of the United States, and the last president from the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation...
, and the party faction that supported many of the old Jeffersonian principles, led by Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson was the seventh President of the United States . Based in frontier Tennessee, Jackson was a politician and army general who defeated the Creek Indians at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend , and the British at the Battle of New Orleans...
and Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
, became the Democratic Party. Along with the Whig Party
Whig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
, the Democratic Party was the chief party in the United States until the Civil War. The Whigs were a commercial party, and usually less popular, if better financed. The Whigs divided over the slavery issue
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
after the Mexican–American War
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known as the First American Intervention, the Mexican War, or the U.S.–Mexican War, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848 in the wake of the 1845 U.S...
and faded away. In the 1850s, under the stress of the Fugitive Slave Law
Fugitive slave laws
The fugitive slave laws were laws passed by the United States Congress in 1793 and 1850 to provide for the return of slaves who escaped from one state into another state or territory.-Pre-colonial and Colonial eras:...
and the Kansas–Nebraska Act, anti-slavery
Abolitionism
Abolitionism is a movement to end slavery.In western Europe and the Americas abolitionism was a movement to end the slave trade and set slaves free. At the behest of Dominican priest Bartolomé de las Casas who was shocked at the treatment of natives in the New World, Spain enacted the first...
Democrats left the party. Joining with former members of existing or dwindling parties, the Republican Party
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
emerged.
The Democrats split over the choice of a successor to President James Buchanan
James Buchanan
James Buchanan, Jr. was the 15th President of the United States . He is the only president from Pennsylvania, the only president who remained a lifelong bachelor and the last to be born in the 18th century....
along Northern and Southern lines, while the Republican Party gained ascendancy in the election of 1860
United States presidential election, 1860
The United States presidential election of 1860 was a quadrennial election, held on November 6, 1860, for the office of President of the United States and the immediate impetus for the outbreak of the American Civil War. The nation had been divided throughout the 1850s on questions surrounding the...
. As the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
broke out, Northern Democrats were divided into War Democrats
War Democrats
War Democrats in American politics of the 1860s were adherents of the Democratic Party who rejected the Copperheads/Peace Democrats who controlled the party...
and Peace Democrats
Copperheads (politics)
The Copperheads were a vocal group of Democrats in the Northern United States who opposed the American Civil War, wanting an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates. Republicans started calling anti-war Democrats "Copperheads," likening them to the venomous snake...
. The Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, seeing parties as evils, did not have any. Most War Democrats rallied to Republican President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
and the Republicans' National Union Party
National Union Party (United States)
The National Union Party was the name used by the Republican Party for the national ticket in the 1864 presidential election, held during the Civil War. State Republican parties did not usually change their name....
in 1864, which put Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson was the 17th President of the United States . As Vice-President of the United States in 1865, he succeeded Abraham Lincoln following the latter's assassination. Johnson then presided over the initial and contentious Reconstruction era of the United States following the American...
on the ticket as a Democrat from the South. Johnson replaced Lincoln in 1865 but stayed independent of both parties . The Democrats benefited from white Southerners' resentment of Reconstruction after the war and consequent hostility to the Republican Party. After Redeemers
Redeemers
In United States history, "Redeemers" and "Redemption" were terms used by white Southerners to describe a political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction era which followed the American Civil War...
ended Reconstruction in the 1870s, and the extremely violent disenfranchisement of African Americans took place in the 1890s, the South, voting Democratic, became known as the "Solid South
Solid South
Solid South is the electoral support of the Southern United States for the Democratic Party candidates for nearly a century from 1877, the end of Reconstruction, to 1964, during the middle of the Civil Rights era....
." Though Republicans won all but two presidential elections, the Democrats remained competitive. The party was dominated by pro-business Bourbon Democrat
Bourbon Democrat
Bourbon Democrat was a term used in the United States from 1876 to 1904 to refer to a member of the Democratic Party, conservative or classical liberal, especially one who supported President Grover Cleveland in 1884–1888/1892–1896 and Alton B. Parker in 1904. After 1904, the Bourbons faded away...
s led by Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel Jones Tilden was the Democratic candidate for the U.S. presidency in the disputed election of 1876, one of the most controversial American elections of the 19th century. He was the 25th Governor of New York...
and Grover Cleveland
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States. Cleveland is the only president to serve two non-consecutive terms and therefore is the only individual to be counted twice in the numbering of the presidents...
, who represented mercantile, banking, and railroad interests; opposed imperialism
Imperialism
Imperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
and overseas expansion; fought for the gold standard
Gold standard
The gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed mass of gold. There are distinct kinds of gold standard...
; opposed bimetallism
Bimetallism
In economics, bimetallism is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent both to a certain quantity of gold and to a certain quantity of silver; such a system establishes a fixed rate of exchange between the two metals...
; and crusaded against corruption, high taxes, and tariffs. Cleveland was elected to non-consecutive presidential terms in 1884 and 1892.
Agrarian Democrats demanding Free Silver
Free Silver
Free Silver was an important United States political policy issue in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Its advocates were in favor of an inflationary monetary policy using the "free coinage of silver" as opposed to the less inflationary Gold Standard; its supporters were called...
overthrew the Bourbon Democrats in 1896 and nominated William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States...
for the presidency (a nomination repeated by Democrats in 1900 and 1908). Bryan waged a vigorous campaign attacking Eastern moneyed interests, but he lost to Republican William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
. The Democrats took control of the House in 1910 and elected Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
as president in 1912 and 1916. Wilson effectively led Congress to put to rest the issues of tariffs, money, and antitrust that had dominated politics for 40 years with new progressive laws. The Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
in 1929 that occurred under Republican President Herbert Hoover
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover was the 31st President of the United States . Hoover was originally a professional mining engineer and author. As the United States Secretary of Commerce in the 1920s under Presidents Warren Harding and Calvin Coolidge, he promoted partnerships between government and business...
and the Republican Congress set the stage for a more liberal government; the Democrats controlled the House of Representatives nearly uninterrupted from 1931 until 1995 and won most presidential elections until 1968. Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
, elected to the presidency in 1932, came forth with government programs called the New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
. New Deal liberalism meant the promotion of social welfare, labor unions, civil rights, and regulation of business. The opponents, who stressed long-term growth, support for business, and low taxes, started calling themselves "conservatives."
Issues facing parties and the United States after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
included the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
and the Civil Rights Movement. Republicans attracted conservatives and white Southerners from the Democratic coalition with their resistance to New Deal and Great Society
Great Society
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States promoted by President Lyndon B. Johnson and fellow Democrats in Congress in the 1960s. Two main goals of the Great Society social reforms were the elimination of poverty and racial injustice...
liberalism and the Republicans' use of the Southern strategy
Southern strategy
In American politics, the Southern strategy refers to the Republican Party strategy of winning elections in Southern states by exploiting anti-African American racism and fears of lawlessness among Southern white voters and appealing to fears of growing federal power in social and economic matters...
. African Americans, who traditionally supported the Republican Party, began supporting Democrats following the ascent of the Franklin Roosevelt administration, the New Deal, and the Civil Rights movement. The Democratic Party's main base of support shifted to the Northeast
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States is a region of the United States as defined by the United States Census Bureau.-Composition:The region comprises nine states: the New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont; and the Mid-Atlantic states of New...
, marking a dramatic reversal of history. Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
was elected to the presidency in 1992, governing as a New Democrat
New Democrats
New Democrats, in the politics of the United States, are an ideologically centrist faction within the Democratic Party that emerged after the victory of Republican George H. W. Bush in the 1988 presidential election. They are identified with centrist social/cultural/pluralist positions and...
. The Democratic Party lost control of Congress in the election of 1994
Republican Revolution
The Republican Revolution or Revolution of '94 is what the media dubbed Republican Party success in the 1994 U.S. midterm elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of Representatives, and a pickup of eight seats in the Senate...
to the Republican Party. Re-elected in 1996, Clinton was the first Democratic President since Franklin Roosevelt to be elected to two terms. Following twelve years of Republican rule, the Democratic Party regained majority control of both the House and the Senate in the 2006 elections
United States general elections, 2006
The 2006 United States midterm elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006. All United States House of Representatives seats and one third of the United States Senate seats were contested in this election, as well as 36 state governorships, many state legislatures, four territorial...
. Some of the party's key issues in the early 21st century in their last national platform have included the methods of how to combat terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
, homeland security
Homeland security
Homeland security is an umbrella term for security efforts to protect states against terrorist activity. Specifically, is a concerted national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the U.S., reduce America’s vulnerability to terrorism, and minimize the damage and recover from attacks that do...
, expanding access to health care
Health care
Health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. Health care is delivered by practitioners in medicine, chiropractic, dentistry, nursing, pharmacy, allied health, and other care providers...
, labor rights
Labor rights
Labor rights or workers' rights are a group of legal rights and claimed human rights having to do with labor relations between workers and their employers, usually obtained under labor and employment law. In general, these rights' debates have to do with negotiating workers' pay, benefits, and safe...
, environmentalism, and the preservation of liberal government programs. In the 2010 elections
United States elections, 2010
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested in this election along with 38 state and territorial...
, the Democratic Party lost control of the House, but kept a small majority in the Senate (reduced from the 111th Congress). It also lost its majority in state legislatures and state governorships.
The Democratic Party traces its origins to the inspiration of Democratic-Republican Party, founded by Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, and other influential opponents of the Federalist
Federalist Party (United States)
The Federalist Party was the first American political party, from the early 1790s to 1816, the era of the First Party System, with remnants lasting into the 1820s. The Federalists controlled the federal government until 1801...
s in 1792. That party also inspired the Whigs and modern Republicans. Organizationally, the modern Democratic Party truly arose in the 1830s, with the election of Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson was the seventh President of the United States . Based in frontier Tennessee, Jackson was a politician and army general who defeated the Creek Indians at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend , and the British at the Battle of New Orleans...
. Since the division of the Republican Party in the election of 1912
United States presidential election, 1912
The United States presidential election of 1912 was a rare four-way contest. Incumbent President William Howard Taft was renominated by the Republican Party with the support of its conservative wing. After former President Theodore Roosevelt failed to receive the Republican nomination, he called...
, it has gradually positioned itself to the left
Left-wing politics
In politics, Left, left-wing and leftist generally refer to support for social change to create a more egalitarian society...
of the Republican Party on economic and social issues
Social issues
Social issues are controversial issues which relate to people's personal lives and interactions. Social issues are distinguished from economic issues...
. Until the period following the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Democratic Party was primarily a coalition of two parties divided by region. Southern Democrats were typically given high conservative ratings by the American Conservative Union
American Conservative Union
The American Conservative Union is an American political organization advocating conservative policies, and is the oldest such conservative lobbying organization in the country.-Organization:...
while northern Democrats were typically given very low ratings. Southern Democrats were a core bloc of the bipartisan conservative coalition
Conservative coalition
In the United States, the conservative coalition was an unofficial Congressional coalition bringing together the conservative majority of the Republican Party and the conservative, mostly Southern, wing of the Democratic Party...
which lasted through the Reagan-era. The economically activist philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
, which has strongly influenced American liberalism
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is a broad political philosophy centered on the unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion for all belief systems, and the separation of church and state, right to due process...
, has shaped much of the party's economic agenda since 1932, and served to tie the two regional factions of the party together until the late 1960s. In fact, Roosevelt's New Deal coalition
New Deal coalition
The New Deal Coalition was the alignment of interest groups and voting blocs that supported the New Deal and voted for Democratic presidential candidates from 1932 until the late 1960s. It made the Democratic Party the majority party during that period, losing only to Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1952...
usually controlled the national government until the 1970s.
, Gallup
The Gallup Organization
The Gallup Organization, is primarily a research-based performance-management consulting company. Some of Gallup's key practice areas are - Employee Engagement, Customer Engagement and Well-Being. Gallup has over 40 offices in 27 countries. World headquarters are in Washington, D.C. Operational...
polling found that 31% of Americans identified as Democrats, 29% as Republicans, and 38% as independents. A Pew Research Center survey of registered voters released August 2010 stated that 47% identified as Democrats or leaned towards the party, in comparison to 43% of Republicans.
Current structure and composition
The Democratic National CommitteeDemocratic National Committee
The Democratic National Committee is the principal organization governing the United States Democratic Party on a day to day basis. While it is responsible for overseeing the process of writing a platform every four years, the DNC's central focus is on campaign and political activity in support...
(DNC) is responsible for promoting Democratic campaign activities. While the DNC is responsible for overseeing the process of writing the Democratic Platform, the DNC is more focused on campaign and organizational strategy than public policy
Public policy
Public policy as government action is generally the principled guide to action taken by the administrative or executive branches of the state with regard to a class of issues in a manner consistent with law and institutional customs. In general, the foundation is the pertinent national and...
. In presidential elections, it supervises the Democratic National Convention
Democratic National Convention
The Democratic National Convention is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1832 by the United States Democratic Party. They have been administered by the Democratic National Committee since the 1852 national convention...
. The national convention is, subject to the charter of the party, the ultimate authority within the Democratic Party when it is in session, with the DNC running the party's organization at other times. The DNC is currently chaired by Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
congresswomen Debbie Wasserman Schultz
Debbie Wasserman Schultz
Debbie Wasserman Schultz is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 2005. She is a member of the Democratic Party and the Chairwoman of the Democratic National Committee. She previously served in the Florida House of Representatives and the Florida Senate...
.
The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee
Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee
The Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee is the Democratic Hill committee for the United States House of Representatives, working to elect Democrats to that body. They play a critical role in recruiting candidates, raising funds, and organizing races in districts that are expected to yield...
(DCCC) assists party candidates in House races; its current chairman (selected by the party caucus) is Rep. Steve Israel
Steve Israel
Steve J. Israel is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 2001. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The district is located on Long Island and includes the towns of Huntington, Babylon, Islip, and Smithtown in Suffolk County, part of the town of Oyster Bay in Nassau County, and the...
of New York. Similarly, the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee
Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee
The Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee is the Democratic Hill committee for the United States Senate. It is the only organization solely dedicated to electing Democrats to the United States Senate. The DSCC's current chair is Sen. Patty Murray, who succeeded Sen. Robert Menendez following...
(DSCC), currently headed by Senator Patty Murray
Patty Murray
Patricia Lynn "Patty" Murray is the senior United States Senator from Washington and a member of the Democratic Party. Murray was first elected to the Senate in 1992, becoming Washington's first female senator...
of Washington, raises large sums for Senate races. The Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), currently chaired by Mike Gronstal of Iowa, is a smaller organization with much less funding that focuses on state legislative races. The DNC sponsors the College Democrats of America (CDA), a student-outreach organization with the goal of training and engaging a new generation of Democratic activists. Democrats Abroad
Democrats Abroad
Democrats Abroad is the official organization of the Democratic Party for United States citizens living permanently or temporarily abroad. The organization is given state-level recognition by the Democratic National Committee....
is the organization for Americans living outside the United States; they work to advance the goals of the party and encourage Americans living abroad to support the Democrats. The Young Democrats of America
Young Democrats of America
The Young Democrats of America , founded in 1932, is the official youth arm of the Democratic Party of the United States, although it severed official ties with the Democratic National Committee following passage of the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 and became an independent 527 group...
(YDA) is a youth-led organization that attempts to draw in and mobilize young people for Democratic candidates, but operates outside of the DNC. In addition, the recently created branch of the Young Democrats, the Young Democrats High School Caucus, attempts to raise awareness and activism
Activism
Activism consists of intentional efforts to bring about social, political, economic, or environmental change. Activism can take a wide range of forms from writing letters to newspapers or politicians, political campaigning, economic activism such as boycotts or preferentially patronizing...
amongst teenagers to not only vote and volunteer, but participate in the future as well. The Democratic Governors Association
Democratic Governors Association
The Democratic Governors Association is a Washington, D.C. based 527 organization founded in 1983, consisting of U.S. state and territorial governors affiliated with the Democratic Party. The mission of the organization is to provide party support to the election and re-election of Democratic...
(DGA), chaired by Governor Martin O'Malley
Martin O'Malley
Martin Joseph O'Malley is an American Democratic politician who is currently serving as the 61st Governor of Maryland. Previously, he served as the mayor of Baltimore from 1999 to 2007. He is currently the chairman of the Democratic Governors Association.-Early life, education and career:O'Malley...
of Maryland, is an organization supporting the candidacies of Democratic gubernatorial nominees and incumbents. Likewise, the mayors of the largest cities and urban centers convene as the National Conference of Democratic Mayors
National Conference of Democratic Mayors
The National Conference of Democratic Mayors is the representative body of city mayors in the United States affiliated to the Democratic Party, in the same way that the Democratic Governors Association represents state governors within the party....
.
Each state also has a state committee, made up of elected committee members as well as ex-officio committee members (usually elected officials and representatives of major constituencies), which in turn elects a chair. County, town, city, and ward committees generally are composed of individuals elected at the local level. State and local committees often coordinate campaign activities within their jurisdiction, oversee local conventions and in some cases primaries or caucuses, and may have a role in nominating candidates for elected office under state law. Rarely do they have much funding, but in 2005, DNC Chairman Dean began a program (called the "50 State Strategy") of using DNC national funds to assist all state parties and paying for full-time professional staffers.
Ideology
Since the 1890s, the Democratic Party has favored liberal positions (the term "liberal" in this sense describes social liberalismSocial liberalism
Social liberalism is the belief that liberalism should include social justice. It differs from classical liberalism in that it believes the legitimate role of the state includes addressing economic and social issues such as unemployment, health care, and education while simultaneously expanding...
, not classical liberalism
Classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is the philosophy committed to the ideal of limited government, constitutionalism, rule of law, due process, and liberty of individuals including freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, and free markets....
). In recent exit poll
Exit poll
An election exit poll is a poll of voters taken immediately after they have exited the polling stations. Unlike an opinion poll, which asks whom the voter plans to vote for or some similar formulation, an exit poll asks whom the voter actually voted for. A similar poll conducted before actual...
s, the Democratic Party has had broad appeal across all socio-ethno-economic demographics.
Historically, the party has favored farmers, laborers, labor unions, and religious and ethnic minorities; it has opposed unregulated business and finance, and favored progressive income taxes. In foreign policy, internationalism (including interventionism) was a dominant theme from 1913 to the mid-1960s. In the 1930s, the party began advocating welfare spending programs targeted at the poor. The party had a fiscally conservative, pro-business wing, typified by Grover Cleveland
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States. Cleveland is the only president to serve two non-consecutive terms and therefore is the only individual to be counted twice in the numbering of the presidents...
and Al Smith
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith. , known in private and public life as Al Smith, was an American statesman who was elected the 42nd Governor of New York three times, and was the Democratic U.S. presidential candidate in 1928...
, and a Southern
Southern Democrats
Southern Democrats are members of the U.S. Democratic Party who reside in the American South. In the 19th century, they were the definitive pro-slavery wing of the party, opposed to both the anti-slavery Republicans and the more liberal Northern Democrats.Eventually "Redemption" was finalized in...
conservative wing that shrank after President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States...
supported the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was a landmark piece of legislation in the United States that outlawed major forms of discrimination against African Americans and women, including racial segregation...
. The major influences for liberalism were labor unions (which peaked in the 1936–1952 era), and the African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
wing, which has steadily grown since the 1960s. Since the 1970s, environmentalism
Environmentalism
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology and social movement regarding concerns for environmental conservation and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the concerns of non-human elements...
has been a major new component.
In recent decades, the party has adopted a centrist
Centrism
In politics, centrism is the ideal or the practice of promoting policies that lie different from the standard political left and political right. Most commonly, this is visualized as part of the one-dimensional political spectrum of left-right politics, with centrism landing in the middle between...
economic and socially progressive agenda, with the voter base having shifted considerably. Today, Democrats advocate more social freedoms, affirmative action
Affirmative action
Affirmative action refers to policies that take factors including "race, color, religion, gender, sexual orientation or national origin" into consideration in order to benefit an underrepresented group, usually as a means to counter the effects of a history of discrimination.-Origins:The term...
, balanced budget
Balanced budget
A balanced budget is when there is neither a budget deficit or a budget surplus – when revenues equal expenditure – particularly by a government. More generally, it refers to when there is no deficit, but possibly a surplus...
, and a free enterprise
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
system tempered by government intervention
Public sector
The public sector, sometimes referred to as the state sector, is a part of the state that deals with either the production, delivery and allocation of goods and services by and for the government or its citizens, whether national, regional or local/municipal.Examples of public sector activity range...
(mixed economy
Mixed economy
Mixed economy is an economic system in which both the state and private sector direct the economy, reflecting characteristics of both market economies and planned economies. Most mixed economies can be described as market economies with strong regulatory oversight, in addition to having a variety...
). The economic policy adopted by the modern Democratic Party, including the former Clinton administration
Presidency of Bill Clinton
The United States Presidency of Bill Clinton, also known as the Clinton Administration, was the executive branch of the federal government of the United States from January 20, 1993 to January 20, 2001. Clinton was the first Democratic president since Franklin D. Roosevelt to win a second full term...
, has been referred to as the "Third Way
Third way (centrism)
The Third Way refers to various political positions which try to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of right-wing economic and left-wing social policies. Third Way approaches are commonly viewed from within the first- and second-way perspectives as...
". The party believes that government should play a role in alleviating poverty and social injustice
Social injustice
Social injustice is a concept relating to the claimed unfairness or injustice of a society in its divisions of rewards and burdens and other incidental inequalities...
and use a system of progressive tax
Progressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. "Progressive" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate progresses from low to high, where the average tax rate is less than the marginal tax rate...
ation.
The Democratic Party, once dominant in the Southeastern United States
Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, colloquially referred to as the Southeast, is the eastern portion of the Southern United States. It is one of the most populous regions in the United States of America....
, is now strongest in the Northeast (Mid-Atlantic
Mid-Atlantic States
The Mid-Atlantic states, also called middle Atlantic states or simply the mid Atlantic, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South...
and New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
), Great Lakes region
Great Lakes region (North America)
The Great Lakes region of North America, occasionally known as the Third Coast or the Fresh Coast , includes the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin as well as the Canadian province of Ontario...
, and the Pacific Coast
West Coast of the United States
West Coast or Pacific Coast are terms for the westernmost coastal states of the United States. The term most often refers to the states of California, Oregon, and Washington. Although not part of the contiguous United States, Alaska and Hawaii do border the Pacific Ocean but can't be included in...
(including Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
). The Democrats are also very strong in major cities.
Liberals

Social liberalism
Social liberalism is the belief that liberalism should include social justice. It differs from classical liberalism in that it believes the legitimate role of the state includes addressing economic and social issues such as unemployment, health care, and education while simultaneously expanding...
(modern liberals) and progressives constitute roughly half of the Democratic voter base. Liberals thereby form the largest united typological demographic within the Democratic base. According to the 2008 exit poll results, liberals constituted 22% of the electorate, and 89% of American liberals favored the candidate of the Democratic Party. White-collar
White-collar worker
The term white-collar worker refers to a person who performs professional, managerial, or administrative work, in contrast with a blue-collar worker, whose job requires manual labor...
college-educated professionals were mostly Republican until the 1950s; they now compose perhaps the most vital component of the Democratic Party. A large majority of liberals favor universal health care
Universal health care
Universal health care is a term referring to organized health care systems built around the principle of universal coverage for all members of society, combining mechanisms for health financing and service provision.-History:...
, with many supporting a single-payer system
Single-payer health care
Single-payer health care is medical care funded from a single insurance pool, run by the state. Under a single-payer system, universal health care for an entire population can be financed from a pool to which many parties employees, employers, and the state have contributed...
. A majority also favor diplomacy
Diplomacy
Diplomacy is the art and practice of conducting negotiations between representatives of groups or states...
over military action
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
, stem cell research
Stem cell
This article is about the cell type. For the medical therapy, see Stem Cell TreatmentsStem cells are biological cells found in all multicellular organisms, that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells...
, the legalization of same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage is marriage between two persons of the same biological sex or social gender. Supporters of legal recognition for same-sex marriage typically refer to such recognition as marriage equality....
, secular government, stricter gun control
Gun politics in the United States
Gun politics in the United States refers to an ongoing political and social debate regarding both the restriction and availability of firearms within the United States. It has long been among the most controversial and intractable issues in American politics...
, and environmental protection laws as well as the preservation of abortion rights
Pro-choice
Support for the legalization of abortion is centered around the pro-choice movement, a sociopolitical movement supporting the ethical view that a woman should have the legal right to elective abortion, meaning the right to terminate her pregnancy....
. Immigration and cultural diversity
Cultural diversity
Cultural diversity is having different cultures respect each other's differences. It could also mean the variety of human societies or cultures in a specific region, or in the world as a whole...
is deemed positive; liberals favor cultural pluralism
Cultural pluralism
Cultural pluralism is a term used when smaller groups within a larger society maintain their unique cultural identities, and their values and practices are accepted by the wider culture. Cultural pluralism is often confused with Multiculturalism...
, a system in which immigrants retain their native culture in addition to adopting their new culture. They tend to be divided on free trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
agreements and organizations such as the North American Free Trade Agreement
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
(NAFTA). Most liberals oppose increased military spending and the display of the Ten Commandments
Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments, also known as the Decalogue , are a set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship, which play a fundamental role in Judaism and most forms of Christianity. They include instructions to worship only God and to keep the Sabbath, and prohibitions against idolatry,...
in public buildings.
This ideological group differs from the traditional organized labor base. According to the Pew Research Center
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
, a plurality of 41% resided in mass affluent
Mass affluent
Mass affluent and emerging affluent are marketing terms used to refer to the high end of the mass market. It is most commonly used by the financial services industry to refer to individuals with US$100,000 to US$1,000,000 of liquid financial assets, although the exact definition varies...
households and 49% were college graduates, the highest figure of any typographical group. It was also the fastest growing typological group between the late 1990s and early 2000s. Liberals include most of academia and large portions of the professional class.
Progressives
Many progressive Democrats are descendants of the New LeftNew Left
The New Left was a term used mainly in the United Kingdom and United States in reference to activists, educators, agitators and others in the 1960s and 1970s who sought to implement a broad range of reforms, in contrast to earlier leftist or Marxist movements that had taken a more vanguardist...
of Democratic presidential candidate Senator George McGovern
George McGovern
George Stanley McGovern is an historian, author, and former U.S. Representative, U.S. Senator, and the Democratic Party nominee in the 1972 presidential election....
of South Dakota; others were involved in the presidential candidacies of Vermont
Vermont
Vermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
Governor Howard Dean
Howard Dean
Howard Brush Dean III is an American politician and physician from Vermont. He served six terms as the 79th Governor of Vermont and ran unsuccessfully for the 2004 Democratic presidential nomination. He was chairman of the Democratic National Committee from 2005 to 2009. Although his U.S...
and U.S. Representative Dennis Kucinich
Dennis Kucinich
Dennis John Kucinich is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1997. He was furthermore a candidate for the Democratic nomination for President of the United States in the 2004 and 2008 presidential elections....
of Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
. The Congressional Progressive Caucus
Congressional Progressive Caucus
The Congressional Progressive Caucus is the largest caucus within the Democratic caucus in the United States Congress with 83 declared members, and works to advance progressive issues and positions....
(CPC) is a caucus of progressive Democrats, and is the single largest Democratic caucus in the House of Representatives. Its members have included Dennis Kucinich
Dennis Kucinich
Dennis John Kucinich is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1997. He was furthermore a candidate for the Democratic nomination for President of the United States in the 2004 and 2008 presidential elections....
of Ohio, John Conyers
John Conyers
John Conyers, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1965 . He is a member of the Democratic Party...
of Michigan, Jim McDermott
Jim McDermott
James Adelbert "Jim" McDermott is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1989. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The 7th District includes most of Seattle and Vashon Island, and portions of Shoreline, Lake Forest Park, Tukwila, SeaTac, and Burien.He serves on the House Ways and Means...
of Washington, John Lewis
John Lewis (politician)
John Robert Lewis is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1987. He was a leader in the American Civil Rights Movement and chairman of the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee , playing a key role in the struggle to end segregation...
of Georgia, Barbara Lee
Barbara Lee
Barbara Jean Lee is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1998. She is a member of the Democratic Party. She is the first woman to represent that district. Lee was the Chair of the Congressional Black Caucus and was the Co-Chair of the Congressional Progressive Caucus...
of California, the late Senator Paul Wellstone
Paul Wellstone
Paul David Wellstone was a two-term U.S. Senator from the state of Minnesota and member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which is affiliated with the national Democratic Party. Before being elected to the Senate in 1990, he was a professor of political science at Carleton College...
of Minnesota, and Sherrod Brown
Sherrod Brown
Sherrod Campbell Brown is the senior United States Senator from Ohio and a member of the Democratic Party. Before his election to the U.S. Senate, he was a member of the United States House of Representatives, representing Ohio's 13th congressional district from 1993 to 2007...
of Ohio, now a Senator. America Votes
America Votes
America Votes is an American 527 organization whose mission is to build a permanent progressive campaign infrastructure. America Votes leads national and state-based coalitions to develop shared strategies that advance progressive policies, engage communities and increase voter turnout.America...
and the Leadership Conference on Civil Rights
Leadership Conference on Civil Rights
The Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights , formerly called The Leadership Conference on Civil Rights, is an umbrella group of American civil rights interest groups.-Organizational history:...
are liberal umbrella organizations that push for progressive causes.
Libertarians and civil libertarians
Some libertarians also support the Democratic Party because Democratic positions on such issues as civil rightsCivil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from unwarranted infringement by governments and private organizations, and ensure one's ability to participate in the civil and political life of the state without discrimination or repression.Civil rights include...
and separation of church and state
Separation of church and state
The concept of the separation of church and state refers to the distance in the relationship between organized religion and the nation state....
are more closely aligned to their own than the positions of the Republican Party. They oppose gun control, the "War on Drugs
Prohibition (drugs)
The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent drug use. Prohibition of drugs has existed at various levels of government or other authority from the Middle Ages to the present....
," protectionism
Protectionism
Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations designed to allow "fair competition" between imports and goods and services produced domestically.This...
, corporate welfare
Corporate welfare
Corporate welfare is a pejorative term describing a government's bestowal of money grants, tax breaks, or other special favorable treatment on corporations or selected corporations. The term compares corporate subsidies and welfare payments to the poor, and implies that corporations are much less...
, government debt
Government debt
Government debt is money owed by a central government. In the US, "government debt" may also refer to the debt of a municipal or local government...
, and an interventionist
Interventionism (politics)
Interventionism is a term for a policy of non-defensive activity undertaken by a nation-state, or other geo-political jurisdiction of a lesser or greater nature, to manipulate an economy or society...
foreign policy. The Democratic Freedom Caucus is an organized group of this faction. Some civil libertarians also support the party because of their support of habeas corpus
Habeas corpus in the United States
Habeas corpus , Latin for "you [shall] have the body," is the name of a legal action or writ by means of which detainees can seek relief from unlawful imprisonment...
for unlawful combatants, opposition to torture
Torture and the United States
Torture in the United States includes documented and alleged cases of torture both inside the United States and outside its borders by U.S. government personnel...
of suspected terrorists, extraordinary rendition, warrantless wiretapping
NSA warrantless surveillance controversy
The NSA warrantless surveillance controversy concerns surveillance of persons within the United States during the collection of foreign intelligence by the U.S. National Security Agency as part of the war on terror...
, indefinite detention
Indefinite detention
Indefinite detention is the incarceration of an arrested person by a national government or law enforcement agency without a trial. It is a controversial practice on the part of any government or agency that is in violation of many national and international laws, including human rights laws...
without trial or charge, the Patriot Act, the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base
Guantanamo Bay Naval Base
Guantanamo Bay Naval Base is located on of land and water at Guantánamo Bay, Cuba which the United States leased for use as a coaling station following the Cuban-American Treaty of 1903. The base is located on the shore of Guantánamo Bay at the southeastern end of Cuba. It is the oldest overseas...
and what they see as the erosion of the protections of the Bill of Rights
United States Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the collective name for the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These limitations serve to protect the natural rights of liberty and property. They guarantee a number of personal freedoms, limit the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and...
.
Conservatives
The Pew Research CenterPew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
has stated that conservative Democrat
Conservative Democrat
In American politics, a conservative Democrat is a Democratic Party member with conservative political views, or with views relatively conservative with respect to those of the national party...
s represent 15% of registered voters
Voter registration
Voter registration is the requirement in some democracies for citizens and residents to check in with some central registry specifically for the purpose of being allowed to vote in elections. An effort to get people to register is known as a voter registration drive.-Centralized/compulsory vs...
and 14% of the general electorate. In the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
, the Blue Dog Coalition, a caucus of fiscal and social conservatives and moderates
Centrism
In politics, centrism is the ideal or the practice of promoting policies that lie different from the standard political left and political right. Most commonly, this is visualized as part of the one-dimensional political spectrum of left-right politics, with centrism landing in the middle between...
forms part of the Democratic Party's current faction of conservative Democrat
Conservative Democrat
In American politics, a conservative Democrat is a Democratic Party member with conservative political views, or with views relatively conservative with respect to those of the national party...
s. They have acted as a unified voting bloc in the past, giving its forty plus members some ability to change legislation and broker compromises with the Republican Party
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
's leadership. Historically, southern Democrats were generally much more ideologically conservative. In 1972, the last year that a sizable number of conservatives dominated the southern wing of the Democratic Party, the American Conservative Union gave higher ratings to most southern Democratic Senators and Congressmen than it did to Republicans.
Centrists
Though centristCentrism
In politics, centrism is the ideal or the practice of promoting policies that lie different from the standard political left and political right. Most commonly, this is visualized as part of the one-dimensional political spectrum of left-right politics, with centrism landing in the middle between...
Democrats differ on a variety of issues, they typically foster a mix of political views and ideas. Compared to other Democratic factions, they tend to be supportive of the use of military force, including the war in Iraq, and are more willing to reduce government welfare, as indicated by their support for welfare reform
Welfare reform
Welfare reform refers to the process of reforming the framework of social security and welfare provisions, but what is considered reform is a matter of opinion. The term was used in the United States to support the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Act...
and tax cut
Tax cut
A tax cut is a reduction in taxes. The immediate effects of a tax cut are a decrease in the real income of the government and an increase in the real income of those whose tax rate has been lowered. Due to the perceived benefit in growing real incomes among tax payers politicians have sought to...
s. One of the most influential factions is the Democratic Leadership Council
Democratic Leadership Council
The Democratic Leadership Council was a non-profit 501 corporation that, upon its formation, argued the United States Democratic Party should shift away from the leftward turn it took in the late 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s...
(DLC), a nonprofit organization that advocates centrist
Centrism
In politics, centrism is the ideal or the practice of promoting policies that lie different from the standard political left and political right. Most commonly, this is visualized as part of the one-dimensional political spectrum of left-right politics, with centrism landing in the middle between...
positions for the party. The DLC hails President Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
as proof of the viability of "Third Way
Third way (centrism)
The Third Way refers to various political positions which try to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of right-wing economic and left-wing social policies. Third Way approaches are commonly viewed from within the first- and second-way perspectives as...
" politicians and a DLC success story. Former Representative Harold Ford, Jr.
Harold Ford, Jr.
Harold Eugene Ford, Jr. is an American politician and was the last chairman of the now-defunct Democratic Leadership Council . He was a Democratic Party member of the United States House of Representatives from , centered in Memphis, from 1997 to 2007...
of Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
is its current chairman. Centrist Democrats form the New Democrat Coalition
New Democrat Coalition
The New Democrat Coalition is a Congressional Member Organization within the United States Congress made up of Democrats who support an agenda that the organization describes as moderate and pro-growth. A July 2009 Press release described the organization as "the largest moderate coalition in the U.S...
in the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
and Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
.
Voter base
Professionals
Professionals, those who have a college educationHigher education
Higher, post-secondary, tertiary, or third level education refers to the stage of learning that occurs at universities, academies, colleges, seminaries, and institutes of technology...
and whose work revolves around the conceptualization of ideas, have supported the Democratic Party by a slight majority since 2000. Between 1988 and 2000, professionals favored Democrats by a 12-percentage point margin. While the professional class was once a stronghold of the Republican Party, it has become increasingly split between the two parties, leaning in favor of the Democratic Party. The increasing support for Democratic candidates among professionals may be traced to the prevalence of social liberal values among this group.
A study on the political attitudes of medical students
Medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches medicine. Degree programs offered at medical schools often include Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, Bachelor/Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Philosophy, master's degree, or other post-secondary...
, for example, found that "U.S. medical students are considerably more likely to be liberal than conservative and are more likely to be liberal than are other young U.S. adults. Future U.S. physicians may be more receptive to liberal messages than conservative ones, and their political orientation may profoundly affect their health system attitudes." Similar results are found for professors, who are more strongly inclined towards liberalism and the Democratic Party than other occupational groups. The Democratic Party also has strong support among scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
s, with 55% identifying as Democrats, 32% as Independents, and 6% as Republicans and 52% identifying as liberal, 35% as moderate, and 9% as conservative.
Academia


Educational attainment
Educational attainment is a term commonly used by statisticians to refer to the highest degree of education an individual has completed.The US Census Bureau Glossary defines educational attainment as "the highest level of education completed in terms of the highest degree or the highest level of...
overall constitute an important part of the Democratic voter base. Academia
Academia
Academia is the community of students and scholars engaged in higher education and research.-Etymology:The word comes from the akademeia in ancient Greece. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning...
in particular tends to be progressive. In a 2005 survey, nearly 72% of full-time faculty members identified as liberal, while 15% identified as conservative. The social sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
and humanities
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
were the most liberal disciplines while business was the most conservative. Male professors at more advanced stages of their careers as well as those at elite institutions tend be the most liberal. Another survey by UCLA conducted in 2001/02, found 47.6% of scholars identifying as liberal, 34.3% as moderate, and 18% as conservative. Percentages of professors who identified as liberal ranged from 49% in business to over 80% in political science
Political science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
and the humanities. Social scientists, such as Brett O'Bannon of DePauw University
DePauw University
DePauw University in Greencastle, Indiana, USA, is a private, national liberal arts college with an enrollment of approximately 2,400 students. The school has a Methodist heritage and was originally known as Indiana Asbury University. DePauw is a member of both the Great Lakes Colleges Association...
, have claimed that the "liberal" opinions of professors seem to have little, if any, effect on the political orientation of students. Whether or not that is true, some conservatives and Republicans complain they are offended and even threatened by the liberal atmosphere of college campuses. As of July 2008 the Students for Academic Freedom
Students for Academic Freedom
According to its website, Students for Academic Freedom is "a clearing house and communications center for a national coalition of student organizations whose goal is to end the political abuse of the university and to restore integrity to the academic mission as a disinterested pursuit of...
arm of the David Horowitz Freedom Center
David Horowitz Freedom Center
The David Horowitz Freedom Center is a conservative foundation founded in 1988 by political activist David Horowitz and his long-time collaborator Peter Collier...
, a conservative organization, posted a list of 440 student complaints, most of which pertain to perceived liberal bias of college professors.
Some attribute the liberal inclination of American professors to the more liberal outlook of the highly educated.
Those with graduate education
Postgraduate education
Postgraduate education involves learning and studying for degrees or other qualifications for which a first or Bachelor's degree generally is required, and is normally considered to be part of higher education...
, have become increasingly Democratic beginning in the 1992, 1996, 2000, 2004, and 2008 elections. Intellectualism, the tendency to constantly reexamine issues, or in the words of Edwards Shields, the "penetration beyond the screen of immediate concrete experience," has also been named as an explanation why academia is strongly democratic and liberal.
Although Democrats are well-represented at the postgraduate level, self-identified Republicans are more likely to have attained a 4-year college degree. The trends for the years 1955 through 2004 are shown by gender in the graphs above, reproduced with permission from Democrats and Republicans — Rhetoric and Reality, a book published in 2008 by Joseph Fried. These results are based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies, supported by the National Science Foundation.
Youth
Studies have shown that younger voters tend to vote mostly for Democratic candidates in recent years. Despite supporting Ronald ReaganRonald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
and George H. W. Bush
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 41st President of the United States . He had previously served as the 43rd Vice President of the United States , a congressman, an ambassador, and Director of Central Intelligence.Bush was born in Milton, Massachusetts, to...
, the young have voted in favor of the Democratic presidential candidate in every election since Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
in 1992, and are more likely to identify as liberals than the general population. In the 2004 presidential election
United States presidential election, 2004
The United States presidential election of 2004 was the United States' 55th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. Republican Party candidate and incumbent President George W. Bush defeated Democratic Party candidate John Kerry, the then-junior U.S. Senator...
, Democratic presidential candidate John Kerry
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry is the senior United States Senator from Massachusetts, the 10th most senior U.S. Senator and chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He was the presidential nominee of the Democratic Party in the 2004 presidential election, but lost to former President George W...
received 54% of the vote from voters of the age group 18–29, while Republican George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
received 45% of the vote from the same age group. In the 2006 midterm election
Midterm election
Midterm elections in the United States refer to general elections in the United States that are held two years after the quadrennial elections for the President of the United States...
s, the Democrats received 60% of the vote from the same age group. Polls suggest that younger voters tend to be more liberal than the general population and have more liberal views than the public on same-sex marriage and universal healthcare, helping Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
carry 66% of their votes in 2008. The Young Democrats of America
Young Democrats of America
The Young Democrats of America , founded in 1932, is the official youth arm of the Democratic Party of the United States, although it severed official ties with the Democratic National Committee following passage of the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 and became an independent 527 group...
are an affiliated organization of members of the party younger than 36 that advocates for youth issues and works for youth voter turnout.
Labor
Since the 1930s, a critical component of the Democratic Party coalition has been organized laborLabor unions in the United States
Labor unions in the United States are legally recognized as representatives of workers in many industries. The most prominent unions are among public sector employees such as teachers and police...
. Labor unions supply a great deal of the money, grass roots
Grassroots
A grassroots movement is one driven by the politics of a community. The term implies that the creation of the movement and the group supporting it are natural and spontaneous, highlighting the differences between this and a movement that is orchestrated by traditional power structures...
political organization
Political organisation
A political organization is an organization that involves itself in the political process. In a broader sense, a political organization can also be viewed as a political system, as long as it includes the entire system and body of government...
, and voting base of support for the party. Democrats are far more likely to be represented by unions, although union membership has declined, in general, during the last few decades. This trend is depicted in the following graph from the book, Democrats and Republicans — Rhetoric and Reality. It is based on surveys conducted by the National Election Studies (NES).
The historic decline in union membership over the past half century has been accompanied by a growing disparity between public sector and private sector union membership percentages. The three most significant labor groupings in the Democratic coalition today are the AFL-CIO
AFL-CIO
The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations, commonly AFL–CIO, is a national trade union center, the largest federation of unions in the United States, made up of 56 national and international unions, together representing more than 11 million workers...
and Change to Win
Change to Win Federation
The Change to Win Federation is a coalition of American labor unions originally formed in 2005 as an alternative to the AFL-CIO. The coalition is associated with strong advocacy of the organizing model...
labor federations
National trade union center
A national trade union center is a federation or confederation of trade unions in a single country. Nearly every country in the world has a national trade union center, and many have more than one. When there is more than one national center, it is often because of ideological differences—in some...
, as well as the National Education Association
National Education Association
The National Education Association is the largest professional organization and largest labor union in the United States, representing public school teachers and other support personnel, faculty and staffers at colleges and universities, retired educators, and college students preparing to become...
, a large, unaffiliated teachers'
Teacher
A teacher or schoolteacher is a person who provides education for pupils and students . The role of teacher is often formal and ongoing, carried out at a school or other place of formal education. In many countries, a person who wishes to become a teacher must first obtain specified professional...
union. Both the AFL-CIO and Change to Win have identified their top legislative priority for 2007 as passage of the Employee Free Choice Act
Employee Free Choice Act
The Employee Free Choice Act was a legislative bill that was introduced into both chambers of the U.S. Congress on March 10, 2009. The bill's purpose was to,...
. Other important issues for labor unions include supporting industrial policy
Industrial policy
The Industrial Policy plan of a nation, sometimes shortened IP, "denotes a nation's declared, official, total strategic effort to influence sectoral development and, thus, national industry portfolio." These interventionist measures comprise "policies that stimulate specific activities and promote...
(including protectionism
Protectionism
Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations designed to allow "fair competition" between imports and goods and services produced domestically.This...
) that sustains unionized manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
jobs, raising the minimum wage
Minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest hourly, daily or monthly remuneration that employers may legally pay to workers. Equivalently, it is the lowest wage at which workers may sell their labour. Although minimum wage laws are in effect in a great many jurisdictions, there are differences of opinion about...
and promoting broad social programs such as Social Security
Social Security (United States)
In the United States, Social Security refers to the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance program.The original Social Security Act and the current version of the Act, as amended encompass several social welfare and social insurance programs...
and universal health care
Universal health care
Universal health care is a term referring to organized health care systems built around the principle of universal coverage for all members of society, combining mechanisms for health financing and service provision.-History:...
.
Working class
While the American working classWorking class
Working class is a term used in the social sciences and in ordinary conversation to describe those employed in lower tier jobs , often extending to those in unemployment or otherwise possessing below-average incomes...
has lost much of its political strength with the decline of labor unions
Trade union
A trade union, trades union or labor union is an organization of workers that have banded together to achieve common goals such as better working conditions. The trade union, through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labour contracts with...
, it remains a stronghold of the Democratic Party and continues as an essential part of the Democratic base. Today, roughly a third of the American public is estimated to be working class with around 52% being either members of the working or lower classes
American lower class
The concept of a lower class in the United States is used to describe those at or near the lower end of the socio-economic hierarchy. As with all social classes in the United States, the lower class is loosely defined and its boundaries and definitions subject to debate and ambiguous popular...
. Yet, as those with lower socioeconomic status are less likely to vote, the working and lower classes are underrepresented in the electorate. The working class is largely distinguished by highly routinized and closely supervised work. It consists mainly of clerical and blue-collar worker
Blue-collar worker
A blue-collar worker is a member of the working class who performs manual labor. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled, manufacturing, mining, construction, mechanical, maintenance, technical installation and many other types of physical work...
s. Even though most in the working class are able to afford an adequate standard of living
Standard of living
Standard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
, high economic insecurity and possible personal benefit from an extended social safety net
Social safety net
Social safety nets, or "socioeconomic safety nets", are non-contributory transfer programs seeking to prevent the poor or those vulnerable to shocks and poverty from falling below a certain poverty level. Safety net programs can be provided by the public sector or by the private sector...
, make the majority of working class person left-of-center on economic issues. Most working class Democrats differ from most liberals, however, in their more socially conservative views. Working class Democrats tend to be more religious and likely to belong to an ethnic minority. Socially conservative and disadvantaged Democrats are among the least educated and lowest earning ideological demographics. In 2005, only 15% had a college degree, compared to 27% at the national average and 49% of liberals, respectively. Together socially conservative and the financially disadvantaged comprised roughly 54% of the Democratic base. The continued importance of the working class votes manifests itself in recent CNN exit polls, which shows that the majority of those with low incomes
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
and little education vote for the Democratic Party.
Women
Although the "gender gap" has varied over many years, women of all ages are more likely than men to identify as Democrats. Recent polls have indicated that 41% of women identify as Democrats while only 25% of women identify as Republicans and 26% as independents, while 32% of men identify as Democrats, 28% as Republicans and 34% as independents. Among ethnic minorities, women also are more likely than males to identify as Democrats. Also, American women that identified as single, living with a domestic partner, divorced, separated, or widowed are more likely than men in these categories to vote Democratic, in contrast to married Americans, which split about equally between Democrat and Republican. Again, women in these categories are significantly more likely than males in these categories to vote Democratic. The National Federation of Democratic WomenNational Federation of Democratic Women
The National Federation of Democratic Women was established in 1971 as a means of supporting women’s voices within the Democratic Party. The NFDW hosts national and state-level conferences and activities designed to support the extraordinary group of women who support our goals and ideals.The NFDW...
is an affiliated organization meant to advocate for women's issues. National women's organizations that often support Democratic candidates are Emily's List
EMILY's List
EMILY's List is a political action committee in the United States that aims to help elect female candidates to office. It was founded by Ellen Malcolm in 1984....
and the National Organization for Women
National Organization for Women
The National Organization for Women is the largest feminist organization in the United States. It was founded in 1966 and has a membership of 500,000 contributing members. The organization consists of 550 chapters in all 50 U.S...
.
Relation to marital status and parenthood
Americans that identify as single, living with a domestic partner, divorced, separated, or widowed are more likely to vote Democratic, in contrast to married Americans, which split about equally between Democrat and Republican.GSS
General Social Survey
The General Social Survey is a sociological survey used to collect data on demographic characteristics and attitudes of residents of the United States. The survey is conducted face-to-face with an in-person interview by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago, of a...
surveys of more than 11,000 Democrats and Republicans conducted between 1996 and 2006 came to the result that the differences in fertility rates are not statistically significant between these parties, with the average Democrat having 1.94 children and the average Republican having 1.91 children.
However, there is a significant difference in fertility rates between the two related groups liberals
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is a broad political philosophy centered on the unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion for all belief systems, and the separation of church and state, right to due process...
and conservatives, with liberals reproducing at much lower rate than conservatives.
LGBT Americans
LesbianLesbian
Lesbian is a term most widely used in the English language to describe sexual and romantic desire between females. The word may be used as a noun, to refer to women who identify themselves or who are characterized by others as having the primary attribute of female homosexuality, or as an...
, gay
Gay
Gay is a word that refers to a homosexual person, especially a homosexual male. For homosexual women the specific term is "lesbian"....
, bisexual, and transgender
Transgender
Transgender is a general term applied to a variety of individuals, behaviors, and groups involving tendencies to vary from culturally conventional gender roles....
Americans typically vote Democratic in national elections within the 70-77% range, according to national media exit polling. In heavily gay precincts in large cities across the nation, the average was higher, ranging from 85-94%. This trend has continued since 1996 when Bill Clinton won 71% of the LGBT vote compared to Bob Dole's 16% and 13% for others. In 2000 Al Gore won 70% to George W. Bush's 25% with 5% for others, in 2004 John Kerry won 77% to George W. Bush's 23% and in 2008 Barack Obama won 70% to John McCain's 27% with 3% to others. Patrick Egan, a professor of politics at New York University specializing in LGBT voting patterns, calls this a "remarkable continuity." Saying "about three-fourths vote Democratic and one-fourth Republican from year to year." Notable LGBT Democrats include current Representatives Barney Frank
Barney Frank
Barney Frank is the U.S. Representative for . A member of the Democratic Party, he is the former chairman of the House Financial Services Committee and is considered the most prominent gay politician in the United States.Born and raised in New Jersey, Frank graduated from Harvard College and...
of Massachusetts, Tammy Baldwin
Tammy Baldwin
Tammy Suzanne Green Baldwin is the U.S. Representative for Wisconsin's 2nd congressional district, serving since 1999. She is a member of the Democratic Party. In September 2011, Baldwin announced she would be a candidate in the 2012 U.S...
of Wisconsin, Jared Polis
Jared Polis
Jared Schutz Polis is an American entrepreneur, philanthropist, and U.S. Representative for , serving since 2009. He is a member of the Democratic Party...
of Colorado and David Cicilline
David Cicilline
David Nicola Cicilline is the U.S. Representative for . He is a member of the Democratic Party. He is formerly the Mayor of Providence, Rhode Island, and was the first openly gay mayor of a U.S. state capital.-Early life, education, and career:...
of Rhode Island. The late activist and San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk
Harvey Milk
Harvey Bernard Milk was an American politician who became the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California when he won a seat on the San Francisco Board of Supervisors...
was a Democrat. The National Stonewall Democrats is an LGBT advocacy group associated with the Democratic Party. The LGBT Equality Caucus is a congressional caucus of 76 Democrats and 1 Republican that work and advocate for LGBT rights within the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
.
African Americans
From the end of the Civil War, African AmericanAfrican American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
s primarily favored the Republican Party due to its overwhelming political and more tangible efforts in achieving abolition, particularly through President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation is an executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War using his war powers. It proclaimed the freedom of 3.1 million of the nation's 4 million slaves, and immediately freed 50,000 of them, with nearly...
. The south had long been a Democratic stronghold, favoring a state's right to legal slavery. In addition, the ranks of the fledgling Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan
Ku Klux Klan, often abbreviated KKK and informally known as the Klan, is the name of three distinct past and present far-right organizations in the United States, which have advocated extremist reactionary currents such as white supremacy, white nationalism, and anti-immigration, historically...
were composed almost entirely of white Democrats angry over poor treatment by northerners and bent on reversing the policies of Reconstruction. However, as years passed and memories waned, African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
s began drifting to the Democratic Party, as Franklin Roosevelt's
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
programs gave economic relief to all minorities, including African Americans and Hispanic
Hispanic
Hispanic is a term that originally denoted a relationship to Hispania, which is to say the Iberian Peninsula: Andorra, Gibraltar, Portugal and Spain. During the Modern Era, Hispanic sometimes takes on a more limited meaning, particularly in the United States, where the term means a person of ...
s. Support for the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s by Democratic presidents John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
and Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States...
helped give the Democrats even larger support among the African American community, which consistently vote between 85-95% Democratic.
Prominent modern-day African-American Democratic politicians include Jim Clyburn
Jim Clyburn
James Enos "Jim" Clyburn is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1993, and the Assistant Democratic Leader since 2011. He was previously House Majority Whip, serving in that post from 2007 to 2011. He is a member of the Democratic Party...
, Ed Towns
Ed Towns
Edolphus "Ed" Towns is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1983, and the former Chairman of the House Oversight and Government Reform Committee. He is a member of the Democratic Party...
, Maxine Waters
Maxine Waters
Maxine Waters is the U.S. Representative for , and previously the 29th district, serving since 1991. She is a member of the Democratic Party....
, John Lewis, Deval Patrick
Deval Patrick
Deval Laurdine Patrick is the 71st and current Governor of Massachusetts. A member of the Democratic Party, Patrick served as an Assistant United States Attorney General under President Bill Clinton...
, Charles Rangel, John Conyers
John Conyers
John Conyers, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1965 . He is a member of the Democratic Party...
, and the current President of the United States, Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
, who managed to net over 95% of the African American vote in the 2008 election. Despite being unaffiliated, the NAACP often participates in organizing and voter turnout drives and advocates for progressive causes, especially those that affect people of color. Within the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
, the Congressional Black Caucus
Congressional Black Caucus
The Congressional Black Caucus is an organization representing the black members of the United States Congress. Membership is exclusive to blacks, and its chair in the 112th Congress is Representative Emanuel Cleaver of Missouri.-Aims:...
, consisting of 44 black Democrats, serves to represent the interests of African Americans and advocate on issues that affect them.
Hispanic and Latino Americans
The HispanicHispanic and Latino Americans
Hispanic or Latino Americans are Americans with origins in the Hispanic countries of Latin America or in Spain, and in general all persons in the United States who self-identify as Hispanic or Latino.1990 Census of Population and Housing: A self-designated classification for people whose origins...
population, particularly the large Mexican American
Mexican American
Mexican Americans are Americans of Mexican descent. As of July 2009, Mexican Americans make up 10.3% of the United States' population with over 31,689,000 Americans listed as of Mexican ancestry. Mexican Americans comprise 66% of all Hispanics and Latinos in the United States...
population in the Southwest
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States is a region defined in different ways by different sources. Broad definitions include nearly a quarter of the United States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Utah...
and the large Puerto Rican
Puerto Ricans in the United States
Stateside Puerto Ricans are American citizens of Puerto Rican origin, including those who migrated from Puerto Rico to the United States and those who were born outside of Puerto Rico in the United States...
and Dominican
Dominican American
A Dominican American is any American who has origins in the Dominican Republic.Immigration records of Dominicans in the United States date from the late 19th century, and New York City has had a Dominican community since the 1930s...
populations in the Northeast
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States is a region of the United States as defined by the United States Census Bureau.-Composition:The region comprises nine states: the New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont; and the Mid-Atlantic states of New...
, have been strong supporters of the Democratic Party. They commonly favor liberal views on immigration. In the 1996 presidential election
United States presidential election, 1996
The United States presidential election of 1996 was a contest between the Democratic national ticket of President Bill Clinton of Arkansas and Vice President Al Gore of Tennessee and the Republican national ticket of former Senator Bob Dole of Kansas for President and former Housing Secretary Jack...
, Democratic President Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
received 72% of the Hispanic vote. Since then, however, the Republican Party has gained increasing support from the Hispanic community, especially among Hispanic Protestants and Pentecostals
Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism is a diverse and complex movement within Christianity that places special emphasis on a direct personal experience of God through the baptism in the Holy Spirit, has an eschatological focus, and is an experiential religion. The term Pentecostal is derived from Pentecost, the Greek...
. Along with Bush's much more liberal views on immigration, President Bush was the first Republican president to gain 40% of the Hispanic vote (he did so in the 2004 presidential election
United States presidential election, 2004
The United States presidential election of 2004 was the United States' 55th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. Republican Party candidate and incumbent President George W. Bush defeated Democratic Party candidate John Kerry, the then-junior U.S. Senator...
). Yet, the Republican Party's support among Hispanics eroded in the 2006 midterm elections, dropping from 44 to 30 percent, with the Democrats gaining in the Hispanic vote from 55% in 2004 to 69% in 2006.
Democrats increased their share of the Hispanic vote in the 2008 presidential election
United States presidential election, 2008
The United States presidential election of 2008 was the 56th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 2008. Democrat Barack Obama, then the junior United States Senator from Illinois, defeated Republican John McCain, the senior U.S. Senator from Arizona. Obama received 365...
, with Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
receiving 67%. Cuban American
Cuban American
A Cuban American is a United States citizen who traces his or her "national origin" to Cuba. Cuban Americans are also considered native born Americans with Cuban parents or Cuban-born persons who were raised and educated in US...
s still heavily vote Republican, though there has been a noticeable change since the 2008 elections. During the 2008 elections Barack Obama received 47% of the Cuban American vote in Florida. According to Bendixen's exit polls, 84% of Miami-Dade Cuban American voters 65 or older backed McCain, while 55% of those 29 or younger backed Obama. Showing that the younger Cuban-American generation have shifted to becoming more liberal. Unaffiliated Hispanic advocacy groups that often support progressive candidates and causes include the National Council of La Raza
National Council of La Raza
The National Council of La Raza is a non-profit and non-partisan advocacy group in the United States, focused on improving opportunities for Hispanics. It is sometimes confused with La Raza Unida...
and the League of United Latin American Citizens
League of United Latin American Citizens
The League of United Latin American Citizens was created to combat the discrimination that Hispanics face in the United States. Established February 17, 1929 in Corpus Christi, Texas, LULAC was a consolidation of smaller, like-minded civil rights groups already in existence...
. In the House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
, the Democratic caucus of Hispanic Americans is the Congressional Hispanic Caucus
Congressional Hispanic Caucus
The Congressional Hispanic Caucus comprises 21 Democratic members of the United States Congress most of whom are of Hispanic origin. The Caucus is dedicated to voicing and advancing, through the legislative process, issues affecting Hispanics and Latinos in the United States and Puerto Rico...
.
Throughout the decade of the 2000s, 60% or more of Hispanic Roman Catholics registered voters have identified as either Democratic or leaning towards the Party.
Native Americans
The Democratic Party also has strong support among the Native AmericanNative Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
population, particularly in Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
, New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
, Montana
Montana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
, North Dakota
North Dakota
North Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west. North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S....
, South Dakota
South Dakota
South Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux American Indian tribes. Once a part of Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889. The state has an area of and an estimated population of just over...
, Washington, Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
, Idaho
Idaho
Idaho is a state in the Rocky Mountain area of the United States. The state's largest city and capital is Boise. Residents are called "Idahoans". Idaho was admitted to the Union on July 3, 1890, as the 43rd state....
, Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
, and North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
. Though now a small percentage of the population (virtually non-existent in some regions), most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African-Americans.
Jewish Americans
Jewish AmericanAmerican Jews
American Jews, also known as Jewish Americans, are American citizens of the Jewish faith or Jewish ethnicity. The Jewish community in the United States is composed predominantly of Ashkenazi Jews who emigrated from Central and Eastern Europe, and their U.S.-born descendants...
communities tend to be a stronghold for the Democratic Party, with more than 70% of Jewish voters having cast their ballots for the Democrats in the 2004 and 2006 elections. Support tends to vary among specific sectarian groups. For example, only 13% of Orthodox Jews supported Barack Obama in 2008 while around 60% of Conservative Jews and Reform Jews did so. A 2010 poll by the Pew Research Center found that 60% of self-described Jews identified as Democratic or leaning towards the party, compared to 33% with those feelings towards Republicans.
Jews as an important Democratic constituency are especially politically active and influential in large cities such as New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
, Los Angeles
Los Ángeles
Los Ángeles is the capital of the province of Biobío, in the commune of the same name, in Region VIII , in the center-south of Chile. It is located between the Laja and Biobío rivers. The population is 123,445 inhabitants...
, Boston
Boston
Boston is the capital of and largest city in Massachusetts, and is one of the oldest cities in the United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is regarded as the unofficial "Capital of New England" for its economic and cultural impact on the entire New England region. The city proper had...
, Chicago
Chicago
Chicago is the largest city in the US state of Illinois. With nearly 2.7 million residents, it is the most populous city in the Midwestern United States and the third most populous in the US, after New York City and Los Angeles...
and play critical roles in large cities within Presidential Swing States such as Philadelphia, Miami, and Las Vegas
Las Vegas metropolitan area
The Las Vegas Valley is the heart of the Las Vegas-Paradise, NV MSA also known as the Las Vegas–Paradise–Henderson MSA which includes all of Clark County, Nevada, and is a metropolitan area in the southern part of the U.S. state of Nevada. The Valley is defined by the Las Vegas Valley landform, a ...
. Many prominent national Democrats in recent decades have been Jewish, including Chuck Schumer, Abraham Ribicoff, Henry Waxman
Henry Waxman
Henry Arnold Waxman is the U.S. Representative for , serving in Congress since 1975. He is a member of the Democratic Party. He is considered to be one of the most influential liberal members of Congress...
, Martin Frost
Martin Frost
Jonas Martin Frost III is an American politician, who was the Democratic representative to the U.S. House of Representatives for Texas's 24th congressional district from 1979 to 2005.-Personal life:...
, Joseph Lieberman, Dianne Feinstein
Dianne Feinstein
Dianne Goldman Berman Feinstein is the senior U.S. Senator from California. A member of the Democratic Party, she has served in the Senate since 1992. She also served as 38th Mayor of San Francisco from 1978 to 1988....
, Barney Frank
Barney Frank
Barney Frank is the U.S. Representative for . A member of the Democratic Party, he is the former chairman of the House Financial Services Committee and is considered the most prominent gay politician in the United States.Born and raised in New Jersey, Frank graduated from Harvard College and...
, Barbara Boxer
Barbara Boxer
Barbara Levy Boxer is the junior United States Senator from California . A member of the Democratic Party, she previously served in the U.S. House of Representatives ....
, Paul Wellstone
Paul Wellstone
Paul David Wellstone was a two-term U.S. Senator from the state of Minnesota and member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which is affiliated with the national Democratic Party. Before being elected to the Senate in 1990, he was a professor of political science at Carleton College...
, Rahm Emanuel
Rahm Emanuel
Rahm Israel Emanuel is an American politician and the 55th and current Mayor of Chicago. He was formerly White House Chief of Staff to President Barack Obama...
, Russ Feingold
Russ Feingold
Russell Dana "Russ" Feingold is an American politician from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. He served as a Democratic party member of the U.S. Senate from 1993 to 2011. From 1983 to 1993, Feingold was a Wisconsin State Senator representing the 27th District.He is a recipient of the John F...
, Herb Kohl
Herb Kohl
Herbert H. "Herb" Kohl is the senior U.S. Senator from Wisconsin and a member of the Democratic Party. He is also a philanthropist and the owner of the Milwaukee Bucks National Basketball Association team...
, and Howard Metzenbaum
Howard Metzenbaum
Howard Morton Metzenbaum was an American politician who served for almost 20 years as a Democratic member of the U.S. Senate from Ohio . He also served in the Ohio House of Representatives and Senate from 1943 to 1951.-Early life:Metzenbaum was born in Cleveland, to a poor Jewish family, the son...
.
Arab and Muslim Americans
Arab AmericanArab American
An Arab American is a United States citizen or resident of Arab ethnic, cultural and linguistic heritage or identity, who identifies themselves as Arab. Arab Americans trace ancestry to any of the various waves of immigrants of the countries comprising the Arab World...
s and Muslim Americans
Islam in the United States
From the 1880s to 1914, several thousand Muslims immigrated to the United States from the Ottoman Empire, and from parts of South Asia; they did not form distinctive settlements, and probably most assimilated into the wider society....
have leaned Democratic since the Iraq War
2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq , was the start of the conflict known as the Iraq War, or Operation Iraqi Freedom, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded Iraq and toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 21 days of major combat operations...
. Zogby
Zogby International
IBOPE Zogby International is an international market research, opinion polling firm founded in 1984 by John Zogby. The company polls and consults for a wide spectrum of business media, government, and political groups, and conducts public opinion research in more than 70 countries...
found in June 2007 that 39% of Arab Americans identify as Democrats, 26% as Republicans, and 28% as independent
Independent (voter)
An independent voter, those who register as an unaffiliated voter in the United States, is a voter of a democratic country who does not align him- or herself with a political party...
s.
Arab Americans, generally socially conservative but with more diverse economic views, historically voted Republican until recent years, having supported George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
over Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
in 2000.
Recent issue stances
Columnist Ezra KleinEzra Klein
Ezra Klein is a liberal American blogger and columnist for The Washington Post, columnist for Bloomberg, a columnist for Newsweek, and a contributor to MSNBC...
argues that the current Democractic Party and President Obama have adopted the same positions held by moderate Republicans
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
in the early 1990s.
The following views are generally held by most Democrats. Some Democrats take other positions on these issues.
Minimum wage
Democrats favor a higher minimum wageMinimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest hourly, daily or monthly remuneration that employers may legally pay to workers. Equivalently, it is the lowest wage at which workers may sell their labour. Although minimum wage laws are in effect in a great many jurisdictions, there are differences of opinion about...
, and more regular increases. The Fair Minimum Wage Act of 2007
Fair Minimum Wage Act of 2007
The Fair Minimum Wage Act of 2007 is a US Act of Congress that amended the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 to gradually raise the federal minimum wage from $5.15 per hour to $7.25 per hour. It was signed into law on May 25, 2007 as part of the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina...
was an early component of the Democrats' agenda during the 110th Congress
110th United States Congress
The One Hundred Tenth United States Congress was the meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, between January 3, 2007, and January 3, 2009, during the last two years of the second term of President George W. Bush. It was composed of the Senate and the House of...
. In 2006, the Democrats supported six state ballot initiatives to increase the minimum wage; all six initiatives passed.
Fiscal policy
Democrats generally support a more progressive taxProgressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. "Progressive" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate progresses from low to high, where the average tax rate is less than the marginal tax rate...
structure to provide more services and reduce economic inequality
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
. Currently they have proposed allowing those tax cuts the Bush administration
Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003
The Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003 , was passed by the United States Congress on May 23, 2003 and signed into law by President George W. Bush on May 28, 2003...
gave to the wealthiest Americans to expire as written in the original legislation while wishing to keep in place those given to the middle class. Democrats generally support more government spending
Government spending
Government spending includes all government consumption, investment but excludes transfer payments made by a state. Government acquisition of goods and services for current use to directly satisfy individual or collective needs of the members of the community is classed as government final...
on social services while spending less on the military. They oppose the cutting of social services, such as Social Security
Social Security (United States)
In the United States, Social Security refers to the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance program.The original Social Security Act and the current version of the Act, as amended encompass several social welfare and social insurance programs...
, Medicare
Medicare (United States)
Medicare is a social insurance program administered by the United States government, providing health insurance coverage to people who are aged 65 and over; to those who are under 65 and are permanently physically disabled or who have a congenital physical disability; or to those who meet other...
, Medicaid
Medicaid
Medicaid is the United States health program for certain people and families with low incomes and resources. It is a means-tested program that is jointly funded by the state and federal governments, and is managed by the states. People served by Medicaid are U.S. citizens or legal permanent...
, and various welfare programs, believing it to be harmful to efficiency and social justice
Social justice
Social justice generally refers to the idea of creating a society or institution that is based on the principles of equality and solidarity, that understands and values human rights, and that recognizes the dignity of every human being. The term and modern concept of "social justice" was coined by...
. Democrats believe the benefits of social services, in monetary and non-monetary terms, are a more productive labor
Productive and unproductive labour
Productive and unproductive labour were concepts used in classical political economy mainly in the 18th and 19th century, which survive today to some extent in modern management discussions, economic sociology and Marxist or Marxian economic analysis...
force and cultured population, and believe that the benefits of this are greater than any benefits that could be derived from lower taxes, especially on top earners, or cuts to social services. Furthermore, Democrats see social services as essential towards providing positive freedom
Positive liberty
Positive liberty is defined as having the power and resources to fulfill one's own potential ; as opposed to negative liberty, which is freedom from external restraint...
, i.e. freedom derived from economic opportunity. The Democratic-led House of Representatives reinstated the PAYGO
PAYGO
PAYGO is the practice in the United States of financing expenditures with funds that are currently available rather than borrowed.-Budgeting:The PAYGO compels new spending or tax changes not to add to the federal deficit. Not to be confused with pay-as-you-go financing, which is when a government...
(pay-as-you-go) budget rule at the start of the 110th Congress
110th United States Congress
The One Hundred Tenth United States Congress was the meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, between January 3, 2007, and January 3, 2009, during the last two years of the second term of President George W. Bush. It was composed of the Senate and the House of...
. DNC Chairman Howard Dean
Howard Dean
Howard Brush Dean III is an American politician and physician from Vermont. He served six terms as the 79th Governor of Vermont and ran unsuccessfully for the 2004 Democratic presidential nomination. He was chairman of the Democratic National Committee from 2005 to 2009. Although his U.S...
has cited Bill Clinton's presidency
Presidency of Bill Clinton
The United States Presidency of Bill Clinton, also known as the Clinton Administration, was the executive branch of the federal government of the United States from January 20, 1993 to January 20, 2001. Clinton was the first Democratic president since Franklin D. Roosevelt to win a second full term...
as a model for fiscal responsibility.
Health care reform
Democrats call for "affordable and quality health care," and many advocate an expansion of government intervention in this area. Many Democrats favor national health insuranceNational health insurance
National health insurance is health insurance that insures a national population for the costs of health care and usually is instituted as a program of healthcare reform. It is enforced by law. It may be administered by the public sector, the private sector, or a combination of both...
or universal health care
Universal health care
Universal health care is a term referring to organized health care systems built around the principle of universal coverage for all members of society, combining mechanisms for health financing and service provision.-History:...
in a variety of forms to address the rising costs of modern health insurance
Health insurance
Health insurance is insurance against the risk of incurring medical expenses among individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health care expenses among a targeted group, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to ensure that money is...
. Some Democrats, such as Representatives John Conyers
John Conyers
John Conyers, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1965 . He is a member of the Democratic Party...
and John Dingell
John Dingell
John David Dingell, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1955 . He is a member of the Democratic Party...
, have called for a single-payer program
Single-payer health care
Single-payer health care is medical care funded from a single insurance pool, run by the state. Under a single-payer system, universal health care for an entire population can be financed from a pool to which many parties employees, employers, and the state have contributed...
of Medicare for All. The Progressive Democrats of America
Progressive Democrats of America
The Progressive Democrats of America is a progressive political organization and grassroots political action committee operating inside the United States Democratic Party.-History:...
, a group operating inside the Democratic Party, has made single-payer universal health care one of their primary policy goals.
Some Democratic governors have supported purchasing Canadian drugs, citing lower costs and budget restrictions as a primary incentive. Recognizing that unpaid insurance bills increase costs to the service provider, who passes the cost on to health-care consumers, many Democrats advocate expansion of health insurance coverage.
Policies which most Democrats favor include:
- ending the ability of insurers to drop coverage when people get sick
- ending lifetime caps on benefits and payments insurers provide
- creating a nation-wide insurance exchange across state lines
- dropping the current anti-trust provision for insurance companies
- requiring large businesses to provide employer-based insurance
- mandating coverage for all Americans
- ending insurance companies ability to discriminate based on pre-existing conditions
- expansion of Medicaid
- providing subsidies for low to moderate income families and small businesses
- allowing children to stay on their parents coverage longer
- the expansion of Medicare to those aged 55
- importing Canadian drugs and creating a national public insurance option paid for by premiums and co-pays.
Many of these proposals were included in the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act is a United States federal statute signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. The law is the principal health care reform legislation of the 111th United States Congress...
and Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
The Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 is a law that was enacted by the 111th United States Congress, by means of the reconciliation process, in order to amend the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act...
.
Renewable energy and oil
Democrats have opposed tax cuts and incentives to oil companies, favoring a policy of developing domestic renewable energyRenewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
, such as Montana
Montana
Montana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
's state-supported wind farm and "clean coal" programs as well as setting in place a cap and trade policy
Emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach used to control pollution by providing economic incentives for achieving reductions in the emissions of pollutants....
in hopes of reducing carbon emissions and creating incentives for clean-energy innovations.
Environment
Democrats believe that the government should protect the environment and have a history of environmentalismEnvironmentalism
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology and social movement regarding concerns for environmental conservation and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the concerns of non-human elements...
. In more recent years, this stance has had as its emphasis alternative energy generation as the basis for an improved economy, greater national security
National security
National security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
, and general environmental benefits.
The Democratic Party also favors expansion of conservation lands and encourages open space and rail travel to relieve highway and airport congestion and improve air quality and economy; it "believe[s] that communities, environmental interests, and government should work together to protect resources while ensuring the vitality of local economies. Once Americans were led to believe they had to make a choice between the economy and the environment. They now know this is a false choice."
The most important environmental concern of the Democratic Party is global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
. Democrats, most notably former Vice President Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
, have pressed for stern regulation of greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
es. On October 15, 2007, he won the Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes bequeathed by the Swedish industrialist and inventor Alfred Nobel.-Background:According to Nobel's will, the Peace Prize shall be awarded to the person who...
for his efforts to build greater knowledge about man-made climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
, and laying the foundations for the measures needed to counteract these changes asserting that "the climate crisis is not a political issue, it is a moral and spiritual challenge to all of humanity."
College education
Most Democrats have the long-term aim of having low-cost, publicly funded college education with low tuition fees (like in much of Europe and Canada), which should be available to every eligible American student, or alternatively, with increasing state funding for student financial aid such as the Pell GrantPell Grant
A Pell Grant is money the federal government provides for students who need it to pay for college. Federal Pell Grants are limited to students with financial need, who have not earned their first bachelor's degree or who are not enrolled in certain post-baccalaureate programs, through participating...
or college tuition
College tuition
The term college tuition refers to fees that students have to pay to colleges in the United States. Pay increases in the U.S. have caused chronic controversy since shortly after World War II. Except for its military academies, the U.S. federal government does not directly support higher education...
tax deduction
Tax deduction
Income tax systems generally allow a tax deduction, i.e., a reduction of the income subject to tax, for various items, especially expenses incurred to produce income. Often these deductions are subject to limitations or conditions...
.
Trade agreements
The Democratic Party has a mixed record on international tradeInternational trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product...
agreements that reflects a diversity of viewpoints in the party. The liberal and cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitanism
Cosmopolitanism is the ideology that all human ethnic groups belong to a single community based on a shared morality. This is contrasted with communitarian and particularistic theories, especially the ideas of patriotism and nationalism...
wing of the party, including the intelligentsia and college-educated professionals overall, tend to favor globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
, while the organized labor wing of the party opposes it. In the 1990s, the Clinton administration and a number of prominent Democrats pushed through a number of agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
(NAFTA). Since then, the party's shift away from free trade became evident in the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) vote, with 15 House Democrats voting for the agreement and 187 voting against.
In his 1997 Achieving Our Country, philosopher
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
Richard Rorty
Richard Rorty
Richard McKay Rorty was an American philosopher. He had a long and diverse academic career, including positions as Stuart Professor of Philosophy at Princeton, Kenan Professor of Humanities at the University of Virginia, and Professor of Comparative Literature at Stanford University...
, professor
Professor
A professor is a scholarly teacher; the precise meaning of the term varies by country. Literally, professor derives from Latin as a "person who professes" being usually an expert in arts or sciences; a teacher of high rank...
at Stanford University
Stanford University
The Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University or Stanford, is a private research university on an campus located near Palo Alto, California. It is situated in the northwestern Santa Clara Valley on the San Francisco Peninsula, approximately northwest of San...
states that economic globalization "invites two responses from the Left. The first is to insist that the inequalities between nations need to be mitigated... The second is to insist that the primary responsibility of each democratic nation-state is to its own least advantaged citizens... the first response suggests that the old democracies should open their borders, whereas the second suggests that they should close them. The first response comes naturally to academic leftists, who have always been internationally minded. The second comes naturally to members of trade unions, and to marginally employed people who can most easily be recruited into right-wing populist movements." (p. 88)
Alternative Minimum Tax
While the Democratic Party is in support of a progressive tax structure, it has vowed to adjust the Alternative Minimum TaxAlternative Minimum Tax
The Alternative Minimum Tax is an income tax imposed by the United States federal government on individuals, corporations, estates, and trusts. AMT is imposed at a nearly flat rate on an adjusted amount of taxable income above a certain threshold . This exemption is substantially higher than the...
(AMT). The tax was originally designed to tax the rich but now may affect many households, especially those with incomes
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
ranging from $75,000 to $100,000. The party proposed to re-adjust the tax in such a manner as to restore its initial intention. According to a 2007 Reuters News Report, "House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Charles B. Rangel
Charles B. Rangel
Charles Bernard "Charlie" Rangel is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1971. A member of the Democratic Party, he is the third-longest currently serving member of the House of Representatives. As its most senior member, he is also the Dean of New York's congressional delegation...
has said he will push for permanent AMT relief for those taxpayers who were never meant to pay it."
Discrimination
The Democratic Party supports equal opportunityEqual opportunity
Equal opportunity, or equality of opportunity, is a controversial political concept; and an important informal decision-making standard without a precise definition involving fair choices within the public sphere...
for all Americans regardless of sex, age, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation
Sexual orientation
Sexual orientation describes a pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attractions to the opposite sex, the same sex, both, or neither, and the genders that accompany them. By the convention of organized researchers, these attractions are subsumed under heterosexuality, homosexuality,...
, gender identity
Gender identity
A gender identity is the way in which an individual self-identifies with a gender category, for example, as being either a man or a woman, or in some cases being neither, which can be distinct from biological sex. Basic gender identity is usually formed by age three and is extremely difficult to...
, religion, creed, or national origin. The Party supports affirmative action
Affirmative action
Affirmative action refers to policies that take factors including "race, color, religion, gender, sexual orientation or national origin" into consideration in order to benefit an underrepresented group, usually as a means to counter the effects of a history of discrimination.-Origins:The term...
programs to further this goal. Democrats also strongly support the Americans with Disabilities Act
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 is a law that was enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1990. It was signed into law on July 26, 1990, by President George H. W. Bush, and later amended with changes effective January 1, 2009....
to prohibit discrimination against people based on physical or mental disability.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender rights
The Democratic Party has been divided on the subject of same-sex marriageSame-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage is marriage between two persons of the same biological sex or social gender. Supporters of legal recognition for same-sex marriage typically refer to such recognition as marriage equality....
, though support for it has been increasing and most of the support for same-sex marriage in the United States
Same-sex marriage in the United States
The federal government does not recognize same-sex marriage in the United States, but such marriages are recognized by some individual states. The lack of federal recognition was codified in 1996 by the Defense of Marriage Act, before Massachusetts became the first state to grant marriage licenses...
has come from Democrats. Some members favor civil union
Civil union
A civil union, also referred to as a civil partnership, is a legally recognized form of partnership similar to marriage. Beginning with Denmark in 1989, civil unions under one name or another have been established by law in many developed countries in order to provide same-sex couples rights,...
s for same-sex couples, others favor full and equal legalized marriage, and others are opposed to same-sex marriage on religious or ideological grounds. Support for same-sex marriage has increased in the past decade according to ABC News. An April 2009 ABC News/Washington Post public opinion poll put support among Democrats at 62% A June 2008 Newsweek
Newsweek
Newsweek is an American weekly news magazine published in New York City. It is distributed throughout the United States and internationally. It is the second-largest news weekly magazine in the U.S., having trailed Time in circulation and advertising revenue for most of its existence...
poll found that 42% of Democrats support same-sex marriage while 23% support civil union
Civil union
A civil union, also referred to as a civil partnership, is a legally recognized form of partnership similar to marriage. Beginning with Denmark in 1989, civil unions under one name or another have been established by law in many developed countries in order to provide same-sex couples rights,...
s or domestic partnership
Domestic partnership
A domestic partnership is a legal or personal relationship between two individuals who live together and share a common domestic life but are neither joined by marriage nor a civil union...
laws and 28% oppose any legal recognition at all. The 2004 Democratic National Platform stated that marriage should be defined at the state level and it repudiated the Federal Marriage Amendment
Federal Marriage Amendment
The Federal Marriage Amendment H.J. Res. 56 was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution which would have limited marriage in the United States to unions of one man and one woman...
. Senator
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
John Kerry
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry is the senior United States Senator from Massachusetts, the 10th most senior U.S. Senator and chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He was the presidential nominee of the Democratic Party in the 2004 presidential election, but lost to former President George W...
, Democratic presidential candidate in 2004, did not support same-sex marriage. Former President Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
and former Vice President Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
said in 2009 that they now support gay marriage.
President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
has stated that he considers marriage to be "something sanctified between a man and a woman". He campaigned for the election promising to "give same-sex couples equal legal rights and privileges as married couples" in civil union
Civil union
A civil union, also referred to as a civil partnership, is a legally recognized form of partnership similar to marriage. Beginning with Denmark in 1989, civil unions under one name or another have been established by law in many developed countries in order to provide same-sex couples rights,...
s. At the same time, Obama opposed California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
's Prop 8, and he has promised to repeal the Defense of Marriage Act
Defense of Marriage Act
The Defense of Marriage Act is a United States federal law whereby the federal government defines marriage as a legal union between one man and one woman. Under the law, no U.S. state may be required to recognize as a marriage a same-sex relationship considered a marriage in another state...
. Obama has stated that generally "decisions about marriage should be left to the states as they always have been." However, when running for the Illinois Senate in 1996, he said that he "unequivocally support(ed) gay marriage" and "favor(ed) legalizing same-sex marriages, and would fight efforts to prohibit such marriages."
A broad majority of Democrats have supported other LGBT related laws such as extending hate crime
Hate crime
In crime and law, hate crimes occur when a perpetrator targets a victim because of his or her perceived membership in a certain social group, usually defined by racial group, religion, sexual orientation, disability, class, ethnicity, nationality, age, gender, gender identity, social status or...
statutes, legally preventing discrimination against LGBT people in the workforce
Employment Non-Discrimination Act
The Employment Non-Discrimination Act is a proposed bill in the United States Congress that would prohibit discrimination against employees on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity by civilian, nonreligious employers with at least 15 employees.ENDA has been introduced in every...
, and repealing Don't ask, don't tell
Don't ask, don't tell
"Don't ask, don't tell" was the official United States policy on homosexuals serving in the military from December 21, 1993 to September 20, 2011. The policy prohibited military personnel from discriminating against or harassing closeted homosexual or bisexual service members or applicants, while...
. A 2006 Pew Research Center
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
poll of Democrats found that 55% supported gays adopting children with 40% opposed while 70% support gays in the military
Sexual orientation and military service
The military forces of the world have differing approaches to the enlistment of homosexual and bisexual individuals. The armed forces of most developed countries have now removed policies excluding non-heterosexual individuals...
with only 23% opposed. Gallup polling from May 2009 stated that 82% of Democrats support open enlistment.
Reproductive rights
Most members of the Democratic Party believe that all women should have access to birth controlBirth control
Birth control is an umbrella term for several techniques and methods used to prevent fertilization or to interrupt pregnancy at various stages. Birth control techniques and methods include contraception , contragestion and abortion...
, and support public funding of contraception for poor women. The Democratic Party, in its national platforms from 1992 to 2004, has called for abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
to be "safe, legal and rare" — namely, keeping it legal by rejecting laws that allow governmental interference in abortion decisions, and reducing the number of abortions by promoting both knowledge of reproduction and contraception, and incentives for adoption. The wording changed in the 2008 platform. When Congress voted on the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act
Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act
The Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act of 2003 is a United States law prohibiting a form of late-term abortion that the Act calls "partial-birth abortion", often referred to in medical literature as intact dilation and extraction...
in 2003, Congressional Democrats were split, with a minority (including current Senate Majority Leader
Party leaders of the United States Senate
The Senate Majority and Minority Leaders are two United States Senators who are elected by the party conferences that hold the majority and the minority respectively. These leaders serve as the chief Senate spokespeople for their parties and manage and schedule the legislative and executive...
Harry Reid
Harry Reid
Harry Mason Reid is the senior United States Senator from Nevada, serving since 1987. A member of the Democratic Party, he has been the Senate Majority Leader since January 2007, having previously served as Minority Leader and Minority and Majority Whip.Previously, Reid was a member of the U.S...
) supporting the ban, and the majority of Democrats opposing the legislation.
The Democratic Party opposes attempts to reverse the 1973 Supreme Court decision Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade, , was a controversial landmark decision by the United States Supreme Court on the issue of abortion. The Court decided that a right to privacy under the due process clause in the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution extends to a woman's decision to have an abortion,...
, which declared abortion covered by the constitutionally protected individual right to privacy under the Ninth Amendment
Ninth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Ninth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which is part of the Bill of Rights, addresses rights of the people that are not specifically enumerated in the Constitution.-Text:-Adoption:When the U.S...
, and Planned Parenthood v. Casey
Planned Parenthood v. Casey
Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833 was a case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States in which the constitutionality of several Pennsylvania state regulations regarding abortion were challenged...
, which lays out the legal framework in which government action alleged to violate that right is assessed by courts. As a matter of the right to privacy
Privacy
Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves and thereby reveal themselves selectively...
and of gender equality
Gender equality
Gender equality is the goal of the equality of the genders, stemming from a belief in the injustice of myriad forms of gender inequality.- Concept :...
, many Democrats believe all women should have the ability to choose to abort without governmental interference. They believe that each woman, conferring with her conscience, has the right to choose for herself whether abortion is morally correct. Some Democrats also believe that poor women should have a right to publicly funded abortions.
Current Senate Majority Leader
Party leaders of the United States Senate
The Senate Majority and Minority Leaders are two United States Senators who are elected by the party conferences that hold the majority and the minority respectively. These leaders serve as the chief Senate spokespeople for their parties and manage and schedule the legislative and executive...
Harry Reid
Harry Reid
Harry Mason Reid is the senior United States Senator from Nevada, serving since 1987. A member of the Democratic Party, he has been the Senate Majority Leader since January 2007, having previously served as Minority Leader and Minority and Majority Whip.Previously, Reid was a member of the U.S...
self-identifies as 'pro-life
Pro-life
Opposition to the legalization of abortion is centered around the pro-life, or anti-abortion, movement, a social and political movement opposing elective abortion on moral grounds and supporting its legal prohibition or restriction...
', while President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
and Speaker of the House
Speaker of the United States House of Representatives
The Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, or Speaker of the House, is the presiding officer of the United States House of Representatives...
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia D'Alesandro Pelosi is the Minority Leader of the United States House of Representatives and served as the 60th Speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 2007 to 2011...
self-identify as 'pro-choice
Pro-choice
Support for the legalization of abortion is centered around the pro-choice movement, a sociopolitical movement supporting the ethical view that a woman should have the legal right to elective abortion, meaning the right to terminate her pregnancy....
'. Groups such as Democrats for Life of America
Democrats for Life of America
Democrats for Life of America is an advocacy group in the United States attempting to reshape the political left, primarily the Democratic Party, into taking a pro-life position. Usually this involves political opposition to abortion, but the DFLA also opposes capital punishment and euthanasia...
represent the pro-life faction
Political faction
A political faction is a grouping of individuals, such as a political party, a trade union, or other group with a political purpose. A faction or political party may include fragmented sub-factions, “parties within a party," which may be referred to as power blocs, or voting blocs. The individuals...
of the party, while groups such as EMILY's List
EMILY's List
EMILY's List is a political action committee in the United States that aims to help elect female candidates to office. It was founded by Ellen Malcolm in 1984....
represent the pro-choice faction
Political faction
A political faction is a grouping of individuals, such as a political party, a trade union, or other group with a political purpose. A faction or political party may include fragmented sub-factions, “parties within a party," which may be referred to as power blocs, or voting blocs. The individuals...
. A Newsweek
Newsweek
Newsweek is an American weekly news magazine published in New York City. It is distributed throughout the United States and internationally. It is the second-largest news weekly magazine in the U.S., having trailed Time in circulation and advertising revenue for most of its existence...
poll from October 2006 found that 25% of Democrats were pro-life while a 69% majority was pro-choice. Pro-life Democrats themselves state that they represent over 40% of Democrats.
Embryonic stem cell research
The Democratic Party has voiced strong support for embryonic stem cell researchEmbryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, an early-stage embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells...
with federal funding. In his 2004 platform, John Kerry
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry is the senior United States Senator from Massachusetts, the 10th most senior U.S. Senator and chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He was the presidential nominee of the Democratic Party in the 2004 presidential election, but lost to former President George W...
affirmed his support of federally funded embryonic stem cell research "under the strictest ethical guidelines," saying, "We will not walk away from the chance to save lives and reduce human suffering." In 2009, Barack Obama lifted the eight-year running ban on embryonic stem cell research and proposed federal funding to further research.
Invasion of Afghanistan
Democrats in the House of Representatives and in the Senate near-unanimously voted for the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against TerroristsAuthorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists
The Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Terrorists , one of two resolutions commonly known as "AUMF" , was a joint resolution passed by the United States Congress on September 14, 2001, authorizing the use of United States Armed Forces against those responsible for the attacks on...
against "those responsible for the recent attacks launched against the United States" in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
in 2001, supporting the NATO coalition invasion of the nation. Most elected Democrats continue to support the Afghanistan conflict, and some, such as a Democratic National Committee
Democratic National Committee
The Democratic National Committee is the principal organization governing the United States Democratic Party on a day to day basis. While it is responsible for overseeing the process of writing a platform every four years, the DNC's central focus is on campaign and political activity in support...
spokesperson, have voiced concerns that the Iraq War shifted too many resources away from the presence in Afghanistan. Since 2006, Democratic candidate Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
has called for a "surge" of troops into Afghanistan and, since 2008, Republican candidate John McCain
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election....
has also called for a "surge".
Speaker of the House
Speaker of the United States House of Representatives
The Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, or Speaker of the House, is the presiding officer of the United States House of Representatives...
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia D'Alesandro Pelosi is the Minority Leader of the United States House of Representatives and served as the 60th Speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 2007 to 2011...
and Senator Chuck Schumer expressed support for Obama's plan. Pelosi stated in mid-2008, “We need more resources there... We are understaffed there, not only in our military presence, but also in terms of the reconstruction of Afghanistan." After his election as President, Barack Obama sent about 21,000 additional U.S. forces into the country. He has planned to send 68,000 troops by the year's end.
Support for the war among the American people has diminished over time, and many Democrats have changed their opinion and now oppose a continuation of the conflict. In July 2008, Gallup found that 41% of Democrats called the invasion a "mistake" while a 55% majority disagreed; in contrast, Republicans were more supportive of the war. The survey described Democrats as evenly divided about whether or not more troops should be sent— 56% support it if it would mean removing troops from Iraq and only 47% support it otherwise. A CNN
CNN
Cable News Network is a U.S. cable news channel founded in 1980 by Ted Turner. Upon its launch, CNN was the first channel to provide 24-hour television news coverage, and the first all-news television channel in the United States...
survey in August 2009 stated that a majority of Democrats now oppose the war. CNN polling director Keating Holland said, "Nearly two thirds of Republicans support the war in Afghanistan. Three quarters of Democrats oppose the war." An August 2009 Washington Post poll found similar results, and the paper stated that Obama's policies would anger his closest supporters.
Israel
The Democratic Party has both recently and historically supported Israel. House SpeakerSpeaker of the United States House of Representatives
The Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, or Speaker of the House, is the presiding officer of the United States House of Representatives...
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia D'Alesandro Pelosi is the Minority Leader of the United States House of Representatives and served as the 60th Speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 2007 to 2011...
has said, “When it comes to Israel, Republicans and Democrats speak with one voice.” A 2008 Gallup poll found that 64% say that they have a favorable image of Israel while only 16% say that they have a favorable image of the Palestinian Authority. Within the party, the majority view is held by the Democratic leadership although some members such as John Conyers Jr., George Miller, Nick Rahall
Nick Rahall
Nick Joe Rahall II is the U.S. Representative for West Virginia's 3rd congressional district, serving since 1977. Rahall is currently Ranking Member of the House Resources Committee. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The district includes much of the southern portion of the state, including...
, Dave Obey
Dave Obey
David Ross "Dave" Obey is the former U.S. Representative for , serving 21 consecutive terms from 1969 until 2011. The district includes much of the northwestern portion of the state, including Wausau and Superior...
, Pete Stark
Pete Stark
Fortney Hillman "Pete" Stark, Jr. is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1973. He is a member of the Democratic Party. Currently he is the 5th most senior Representative, as well as 6th most senior member of Congress overall...
, Dennis Kucinich
Dennis Kucinich
Dennis John Kucinich is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1997. He was furthermore a candidate for the Democratic nomination for President of the United States in the 2004 and 2008 presidential elections....
, Jim McDermott
Jim McDermott
James Adelbert "Jim" McDermott is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1989. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The 7th District includes most of Seattle and Vashon Island, and portions of Shoreline, Lake Forest Park, Tukwila, SeaTac, and Burien.He serves on the House Ways and Means...
, and Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia McKinney
Cynthia Ann McKinney is a former US Congresswoman and a member of the Green Party since 2007. As a member of the Democratic Party, she served six terms as a member of the United States House of Representatives. In 2008, the Green Party nominated McKinney for President of the United States...
as well as former President Jimmy Carter
Jimmy Carter
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office...
are less or not supportive of Israel. The party leadership refers to the other side as a "fringe".
The 2008 Democratic Party Platform acknowledges a "special relationship
Special relationship
The Special Relationship is a phrase used to describe the exceptionally close political, diplomatic, cultural, economic, military and historical relations between the United Kingdom and the United States, following its use in a 1946 speech by British statesman Winston Churchill...
with Israel, grounded in shared interests and shared values, and a clear, strong, fundamental commitment to the security of Israel, our strongest ally in the region and its only established democracy." It also included:
It is in the best interests of all parties, including the United States, that we take an active role to
help secure a lasting settlement of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict with a democratic, viable
Palestinian state dedicated to living in peace and security side by side with the Jewish State of
Israel. To do so, we must help Israel identify and strengthen those partners who are truly
committed to peace, while isolating those who seek conflict and instability, and stand with Israel
against those who seek its destruction. The United States and its Quartet partners should
continue to isolate Hamas until it renounces terrorism, recognizes Israel’s right to exist, and
abides by past agreements. Sustained American leadership for peace and security will require
patient efforts and the personal commitment of the President of the United States. The creation
of a Palestinian state through final status negotiations, together with an international
compensation mechanism, should resolve the issue of Palestinian refugees by allowing them to
settle there, rather than in Israel. All understand that it is unrealistic to expect the outcome of
final status negotiations to be a full and complete return to the armistice lines of 1949. Jerusalem
is and will remain the capital of Israel. The parties have agreed that Jerusalem is a matter for
final status negotiations. It should remain an undivided city accessible to people of all faiths.
A January 2009 Pew Research Center
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
study found that, when asked "which side do you sympathize with more", 42% of Democrats and 33% of liberals (a plurality in both groups) sympathize most with the Israelis. Around half of all political moderates and/or independents sided with Israel.
Iraq War
In 2002, Congressional Democrats were divided on the Authorization for Use of Military Force Against IraqIraq Resolution
The Iraq Resolution or the Iraq War Resolution is a joint resolution passed by the United States Congress in October 2002 as Public Law No: 107-243, authorizing military action against Iraq.-Contents:The resolution cited many factors to justify the use of military force against...
; 147 voted against it (21 in the Senate and 126 in the House) and 110 voted for it (29 in the Senate, 81 in the House). Since then, many prominent Democrats, such as former Senator John Edwards
John Edwards
Johnny Reid "John" Edwards is an American politician, who served as a U.S. Senator from North Carolina. He was the Democratic nominee for Vice President in 2004, and was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 2004 and 2008.He defeated incumbent Republican Lauch Faircloth in...
, have expressed regret about this decision, and have called it a mistake, while others, such as Senator Hillary Clinton
Hillary Rodham Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is the 67th United States Secretary of State, serving in the administration of President Barack Obama. She was a United States Senator for New York from 2001 to 2009. As the wife of the 42nd President of the United States, Bill Clinton, she was the First Lady of the...
have criticized the conduct of the war but not repudiated their initial vote for it (though Clinton later went on to repudiate her stance during the 2008 primaries). Referring to Iraq, in April 2007 Senate Majority Leader
Party leaders of the United States Senate
The Senate Majority and Minority Leaders are two United States Senators who are elected by the party conferences that hold the majority and the minority respectively. These leaders serve as the chief Senate spokespeople for their parties and manage and schedule the legislative and executive...
Harry Reid
Harry Reid
Harry Mason Reid is the senior United States Senator from Nevada, serving since 1987. A member of the Democratic Party, he has been the Senate Majority Leader since January 2007, having previously served as Minority Leader and Minority and Majority Whip.Previously, Reid was a member of the U.S...
declared the war to be "lost" while other Democrats (especially during the 2004 presidential election cycle) accused the President of lying to the public about WMDs in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. Amongst lawmakers, Democrats are the most vocal opponents of Operation Iraqi Freedom and campaigned on a platform of withdrawal ahead of the 2006 mid-term elections.
A March 2003 CBS News
CBS News
CBS News is the news division of American television and radio network CBS. The current chairman is Jeff Fager who is also the executive producer of 60 Minutes, while the current president of CBS News is David Rhodes. CBS News' flagship program is the CBS Evening News, hosted by the network's main...
poll taken a few days before the invasion of Iraq
2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq , was the start of the conflict known as the Iraq War, or Operation Iraqi Freedom, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded Iraq and toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 21 days of major combat operations...
found that 34% of Democrats nationwide would support it without United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
backing, 51% would support it only with its backing, and 14% would not support it at all. The Los Angeles Times
Los Angeles Times
The Los Angeles Times is a daily newspaper published in Los Angeles, California, since 1881. It was the second-largest metropolitan newspaper in circulation in the United States in 2008 and the fourth most widely distributed newspaper in the country....
stated in early April 2003 that 70% of Democrats supported the decision to invade while 27% opposed it. The Pew Research Center
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is an American think tank organization based in Washington, D.C. that provides information on issues, attitudes and trends shaping the United States and the world. The Center and its projects receive funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts. In 1990, Donald S...
stated in August 2007 that opposition increased from 37% during the initial invasion to 74%. In April 2008, a CBS News
CBS News
CBS News is the news division of American television and radio network CBS. The current chairman is Jeff Fager who is also the executive producer of 60 Minutes, while the current president of CBS News is David Rhodes. CBS News' flagship program is the CBS Evening News, hosted by the network's main...
poll found that about 90% of Democrats disapprove of the Bush administration's conduct and want to end the war within the next year.
Democrats in the House of Representatives near-unanimously supported a non-binding resolution
Non-binding resolution
A non-binding resolution is a written motion adopted by a deliberative body that cannot progress into a law. The substance of the resolution can be anything that can normally be proposed as a motion....
disapproving of President Bush's decision to send additional troops into Iraq in 2007
Iraq War troop surge of 2007
In the context of the Iraq War, the surge refers to United States President George W. Bush's 2007 increase in the number of American troops in order to provide security to Baghdad and Al Anbar Province....
. Congressional Democrats overwhelmingly supported military funding legislation that included a provision that set "a timeline for the withdrawal of all US combat troops from Iraq" by March 31, 2008, but also would leave combat forces in Iraq for purposes such as targeted counter-terrorism operations. After a veto from the president, and a failed attempt in Congress to override the veto, the U.S. Troop Readiness, Veterans' Care, Katrina Recovery, and Iraq Accountability Appropriations Act, 2007 was passed by Congress and signed by the president after the timetable was dropped. Criticism of the Iraq War
Criticism of the Iraq War
The U.S. rationale for the Iraq War has faced heavy criticism from an array of popular and official sources both inside and outside the United States. Putting this controversy aside, both proponents and opponents of the invasion have also criticised the prosecution of the war effort along a number...
subsided after the Iraq War troop surge of 2007
Iraq War troop surge of 2007
In the context of the Iraq War, the surge refers to United States President George W. Bush's 2007 increase in the number of American troops in order to provide security to Baghdad and Al Anbar Province....
led to a dramatic decrease in Iraqi violence. The Democratic-controlled 110th Congress continued to fund efforts in both Iraq and Afghanistan. Presidential candidate Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
advocated a withdrawal of combat troops within Iraq by late 2010 with a residual force of peacekeeping troops left in place. He stated that both the speed of withdrawal and the amount of troops left over would be "entirely conditions-based."
On February 27, 2009, President Obama announced, “As a candidate for president, I made clear my support for a timeline of 16 months to carry out this drawdown, while pledging to consult closely with our military commanders upon taking office to ensure that we preserve the gains we’ve made and protect our troops... Those consultations are now complete, and I have chosen a timeline that will remove our combat brigades over the next 18 months." Around 50,000 non-combat related forces will remain. Obama's plan drew wide bipartisan support, including that of defeated Republican Presidential candidate Senator John McCain
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III is the senior United States Senator from Arizona. He was the Republican nominee for president in the 2008 United States election....
.
Unilateralism
Democrats usually oppose the doctrine of unilateralismUnilateralism
Unilateralism is any doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action. Such action may be in disregard for other parties, or as an expression of a commitment toward a direction which other parties may find agreeable...
, which dictates that the United States should use military force without any assistance from other nations whenever it believes there is a threat to its security or welfare. They believe the United States should act in the international arena in concert with strong alliances and broad international support. This was a major foreign policy issue of John Kerry
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry is the senior United States Senator from Massachusetts, the 10th most senior U.S. Senator and chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He was the presidential nominee of the Democratic Party in the 2004 presidential election, but lost to former President George W...
's 2004 presidential campaign; his platform attributed rifts with international allies to unilateralism. Barack Obama's 2008 campaign also discussed promoting the image of the United States abroad.
In a general sense, the modern Democratic Party is more closely aligned with the international relations theories
International relations theory
International relations theory is the study of international relations from a theoretical perspective; it attempts to provide a conceptual framework upon which international relations can be analyzed. Ole Holsti describes international relations theories act as a pair of coloured sunglasses,...
of liberalism
Liberal international relations theory
Unlike realism where the state is seen as a unitary actor, liberalism allows for plurality in state actors. Thus, preferences will vary from state to state, depending on factors such as culture, economic system or government type...
, neoliberalism
Neoliberalism in international relations
In the study of international relations, neoliberalism refers to a school of thought which believes that nation-states are, or at least should be, concerned first and foremost with absolute gains rather than relative gains to other nation-states...
, and functionalism
Functionalism in international relations
Functionalism is a theory of international relations that arose during the inter-War period principally from the strong concern about the obsolescence of the State as a form of social organization...
than realism and neorealism, though realism has some influence on the party. Wilsonian idealism
Wilsonian
Wilsonianism or Wilsonian are words used to describe a certain type of ideological perspectives on foreign policy. The term comes from the ideology of United States President Woodrow Wilson and his famous Fourteen Points that he believed would help create world peace if implemented.Common...
, in which unilateral foreign intervention
Humanitarian intervention
Humanitarian intervention "refers to a state using military force against another state when the chief publicly declared aim of that military action is ending human-rights violations being perpetrated by the state against which it is directed."...
is justified to end genocide
Genocide
Genocide is defined as "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group", though what constitutes enough of a "part" to qualify as genocide has been subject to much debate by legal scholars...
or other humanitarian crises, has also played a major role both historically and currently- with its supporters known as 'liberal hawk
Liberal Hawk
The term liberal hawk refers to a politically liberal individual who supports a hawkish, interventionist foreign policy. Past U.S. presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry S. Truman, John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson have been described as liberal hawks for their roles in bringing about...
s'.
Political status of Puerto Rico
The Democratic Party has expressed its support for the U.S. Citizens of Puerto RicoPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
to exercise their right to self-determination. Puerto Rico has been under U.S. sovereignty for over a century and Puerto Ricans have been U.S. citizens since 1917, but the island’s ultimate status still has not been determined and its 3.9 million residents still do not have voting representation in their national government. Also states that U.S. citizens in Puerto Rico should receive treatment under federal programs that is comparable to that of citizens in the States. The following are the appropriate section from the 2000, 2004 and 2008 party platforms:
Torture
Many Democrats are opposed to the use of tortureTorture
Torture is the act of inflicting severe pain as a means of punishment, revenge, forcing information or a confession, or simply as an act of cruelty. Throughout history, torture has often been used as a method of political re-education, interrogation, punishment, and coercion...
against individuals apprehended and held prisoner by the U.S. military
United States armed forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard.The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military...
, and hold that categorizing such prisoners as unlawful combatant
Unlawful combatant
An unlawful combatant or unprivileged combatant/belligerent is a civilian who directly engages in armed conflict in violation of the laws of war. An unlawful combatant may be detained or prosecuted under the domestic law of the detaining state for such action.The Geneva Conventions apply in wars...
s does not release the U.S. from its obligations under the Geneva Conventions
Geneva Conventions
The Geneva Conventions comprise four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish the standards of international law for the humanitarian treatment of the victims of war...
. Democrats contend that torture is inhumane, decreases the United States' moral standing in the world, and produces questionable results. Democrats largely spoke out against waterboarding
Waterboarding
Waterboarding is a form of torture in which water is poured over the face of an immobilized captive, thus causing the individual to experience the sensation of drowning...
.
USA PATRIOT Act
All but two Democrats in the U.S. Senate voted for the original USA PATRIOT ActUSA PATRIOT Act
The USA PATRIOT Act is an Act of the U.S. Congress that was signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 26, 2001...
legislation in 2001. The lone nay vote was from Russ Feingold
Russ Feingold
Russell Dana "Russ" Feingold is an American politician from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. He served as a Democratic party member of the U.S. Senate from 1993 to 2011. From 1983 to 1993, Feingold was a Wisconsin State Senator representing the 27th District.He is a recipient of the John F...
of Wisconsin
Wisconsin
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is...
; Mary Landrieu
Mary Landrieu
Mary Loretta Landrieu is the senior United States Senator from the State of Louisiana and a member of the Democratic Party.Born in Arlington, Virginia, Landrieu was raised in New Orleans, Louisiana...
of Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
did not vote. In the House the Democrats voted for the Act by 145 yea and 62 nay. Democrats split on the renewal in 2006. In the Senate, Democrats voted 34 for the 2006 renewal, and 9 against. In the House, Democrats voted 66 voted for the renewal, and 124 against.
Right to privacy
The Democratic Party believes that individuals should have a right to privacyPrivacy law
Privacy law refers to the laws which deal with the regulation of personal information about individuals which can be collected by governments and other public as well as private organizations and its storage and use....
. For example, Democrats have generally opposed the NSA warrantless surveillance of U.S. citizens
NSA warrantless surveillance controversy
The NSA warrantless surveillance controversy concerns surveillance of persons within the United States during the collection of foreign intelligence by the U.S. National Security Agency as part of the war on terror...
.
Some Democratic officeholders have championed consumer protection
Consumer protection
Consumer protection laws designed to ensure fair trade competition and the free flow of truthful information in the marketplace. The laws are designed to prevent businesses that engage in fraud or specified unfair practices from gaining an advantage over competitors and may provide additional...
laws that limit the sharing of consumer data between corporations. Most Democrats oppose sodomy laws
Sodomy laws in the United States
Sodomy laws in the United States, which outlawed a variety of sexual acts, were historically universal. While they often targeted sexual acts between persons of the same sex, many statutes employed definitions broad enough to outlaw certain sexual acts between persons of different sexes as well,...
and believe that government should not regulate consensual noncommercial sexual conduct among adults as a matter of personal privacy.
Gun control
With a stated goal of reducing crime and homicide, the Democratic Party has introduced various gun controlGun politics in the United States
Gun politics in the United States refers to an ongoing political and social debate regarding both the restriction and availability of firearms within the United States. It has long been among the most controversial and intractable issues in American politics...
measures, most notably the Gun Control Act of 1968
Gun Control Act of 1968
The Gun Control Act of 1968 , by president Lyndon Johnson, is a federal law in the United States that broadly regulates the firearms industry and firearms owners...
, the Brady Bill
Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act
The Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act is an Act of the United States Congress that, for the first time, instituted federal background checks on firearm purchasers in the United States....
of 1993, and Crime Control Act of 1994. However, some Democrats, especially rural, Southern, and Western Democrats, favor fewer restrictions on firearm possession and warned the party was defeated in the 2000 presidential election in rural areas because of the issue. In the national platform for 2008, the only statement explicitly favoring gun control was a plan calling for renewal of the 1994 Assault Weapons Ban
Federal assault weapons ban
The Federal Assault Weapons Ban was a subtitle of the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act of 1994, a federal law in the United States that included a prohibition on the manufacture for civilian use of certain semi-automatic firearms, so called "assault weapons"...
.
Death penalty
The Democratic Party supports the death penalty far less than the Republican PartyRepublican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
. Though most Democrats in Congress have never seriously moved to overturn the rarely used federal death penalty, both Russ Feingold
Russ Feingold
Russell Dana "Russ" Feingold is an American politician from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. He served as a Democratic party member of the U.S. Senate from 1993 to 2011. From 1983 to 1993, Feingold was a Wisconsin State Senator representing the 27th District.He is a recipient of the John F...
and Dennis Kucinich
Dennis Kucinich
Dennis John Kucinich is the U.S. Representative for , serving since 1997. He was furthermore a candidate for the Democratic nomination for President of the United States in the 2004 and 2008 presidential elections....
have introduced such bills with little success. Democrats have led efforts to overturn state death penalty laws, particularly in New Jersey and in New Mexico. They have also sought to prevent reinstatement of the death penalty in those states which currently prohibit it, including Massachusetts and New York. During the Clinton administration
Presidency of Bill Clinton
The United States Presidency of Bill Clinton, also known as the Clinton Administration, was the executive branch of the federal government of the United States from January 20, 1993 to January 20, 2001. Clinton was the first Democratic president since Franklin D. Roosevelt to win a second full term...
, Democrats led the expansion of the federal death penalty. These efforts resulted in the passage of the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996
Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996
The Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996, Pub. L. No. 104-132, 110 Stat. 1214, is an act of Congress signed into law on April 24, 1996...
, Signed into law by President Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
, the law heavily limited appeals in death penalty cases.
In 1992, 1993, and 1995, Democratic Texas Congressman Henry González
Henry B. Gonzalez
Henry Barbosa González was a Democratic politician from the state of Texas. He represented Texas's 20th congressional district from 1961 to 1999.-Background:...
unsuccessfully introduced the Death Penalty Abolition Amendment which prohibited the use of capital punishment in the United States
Capital punishment in the United States
Capital punishment in the United States, in practice, applies only for aggravated murder and more rarely for felony murder. Capital punishment was a penalty at common law, for many felonies, and was enforced in all of the American colonies prior to the Declaration of Independence...
. Democratic Missouri Congressman William Lacy Clay, Sr.
Bill Clay
William Lacy "Bill" Clay, Sr. is a politician from the state of Missouri. As Congressman from Missouri's First District, he represented portions of St. Louis in the U.S. House of Representatives for 32 years....
cosponsored the amendment in 1993.
During his Illinois Senate career
Illinois Senate career of Barack Obama
The Illinois Senate career of Barack Obama began in with the 1997 swearing in of Barack Obama to his first term in the Illinois Senate and ended in 2004 with his election to the United States Senate...
, now-President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
successfully introduced legislation intended to reduce the likelihood of wrongful conviction
Miscarriage of justice
A miscarriage of justice primarily is the conviction and punishment of a person for a crime they did not commit. The term can also apply to errors in the other direction—"errors of impunity", and to civil cases. Most criminal justice systems have some means to overturn, or "quash", a wrongful...
s in capital cases, requiring videotaping of confessions. When campaigning for the presidency
Barack Obama presidential campaign, 2008
Barack Obama, then junior United States Senator from Illinois, announced his candidacy for the presidency of the United States in Springfield, Illinois, on February 10, 2007. On August 27, 2008, he was declared nominee of the Democratic Party for the 2008 presidential election...
, Obama stated that he supports the limited use of the death penalty, including for people who have been convicted of raping a minor under the age of 12, having opposed the Supreme Court
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all state and federal courts, and original jurisdiction over a small range of cases...
's ruling in Kennedy v. Louisiana
Kennedy v. Louisiana
Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 U.S. 407 was a landmark decision by the Supreme Court of the United States that held that the Eighth Amendment's Cruel and Unusual Punishment Clause did not permit a state to punish the crime of rape of a child with the death penalty; more broadly, the power of the state...
that the death penalty was unconstitutional in child rape cases. Obama has stated that he thinks the "death penalty does little to deter crime", and that it is used too frequently and too inconsistently.
Name and symbols
Initially calling itself the "Republican Party," Jeffersonians were labeled "Democratic" by the opposition FederalistsFederalist Party (United States)
The Federalist Party was the first American political party, from the early 1790s to 1816, the era of the First Party System, with remnants lasting into the 1820s. The Federalists controlled the federal government until 1801...
, with the hope of stigmatizing them as purveyors of democracy or mob rule. By the Jacksonian era, the term "The Democracy" was in use by the party; the name "Democratic Party" was eventually settled upon. Since the 1995s, Republicans have often referred to the Democratic Party using the phrase "Democrat Party" as a political epithet
Epithet
An epithet or byname is a descriptive term accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, divinities, objects, and binomial nomenclature. It is also a descriptive title...
.
The most common mascot symbol for the party is the donkey
Donkey
The donkey or ass, Equus africanus asinus, is a domesticated member of the Equidae or horse family. The wild ancestor of the donkey is the African Wild Ass, E...
, although the party never officially adopted this symbol. Andrew Jackson's opponents had labeled him a jackass during the intense mudslinging in 1828
United States presidential election, 1828
The United States presidential election of 1828 featured a rematch between John Quincy Adams, now incumbent President, and Andrew Jackson, the runner-up in the 1824 election. With no other major candidates, Jackson and his chief ally Martin Van Buren consolidated their bases in the South and New...
. A political cartoon titled "A Modern Balaam and his Ass" depicting Jackson riding and directing a donkey (representing the Democratic Party) was published in 1837. A political cartoon by Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast was a German-born American caricaturist and editorial cartoonist who is considered to be the "Father of the American Cartoon". He was the scourge of Boss Tweed and the Tammany Hall machine...
in an 1870 edition of Harper's Weekly
Harper's Magazine
Harper's Magazine is a monthly magazine of literature, politics, culture, finance, and the arts, with a generally left-wing perspective. It is the second-oldest continuously published monthly magazine in the U.S. . The current editor is Ellen Rosenbush, who replaced Roger Hodge in January 2010...
revived the donkey as a symbol for the Democratic Party. Cartoonists followed Nast and used the donkey to represent the Democrats, and the elephant to represent the Republicans.
In the early 20th century, the traditional symbol of the Democratic Party in Midwestern states such as Indiana, Kentucky, Oklahoma and Ohio was the rooster, as opposed to the Republican eagle. This symbol still appears on Oklahoma, Kentucky, Indiana, and West Virginia ballot
Ballot
A ballot is a device used to record choices made by voters. Each voter uses one ballot, and ballots are not shared. In the simplest elections, a ballot may be a simple scrap of paper on which each voter writes in the name of a candidate, but governmental elections use pre-printed to protect the...
s. In New York, the Democratic ballot symbol is a five-pointed star. For the majority of the 20th century, Missouri Democrats used the Statue of Liberty
Statue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor, designed by Frédéric Bartholdi and dedicated on October 28, 1886...
as their ballot emblem. This meant that when Libertarian
Libertarian Party (United States)
The Libertarian Party is the third largest and fastest growing political party in the United States. The political platform of the Libertarian Party reflects its brand of libertarianism, favoring minimally regulated, laissez-faire markets, strong civil liberties, minimally regulated migration...
candidates received ballot access
Ballot access
Ballot access rules, called nomination rules outside the United States, regulate the conditions under which a candidate or political party is either entitled to stand for election or to appear on voters' ballots...
in Missouri in 1976, they could not use the Statue of Liberty, their national symbol, as the ballot emblem. Missouri Libertarians instead used the Liberty Bell
Liberty Bell
The Liberty Bell is an iconic symbol of American Independence, located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Formerly placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House , the bell was commissioned from the London firm of Lester and Pack in 1752, and was cast with the lettering "Proclaim LIBERTY...
until 1995, when the mule became Missouri's state animal. From 1995 to 2004, there was some confusion among voters, as the Democratic ticket was marked with the Statue of Liberty (used by Libertarians in other states) and the Libertarians' mule was easily mistaken for a Democratic donkey.
Although both major political parties (and many minor ones) use the traditional American red, white, and blue colors in their marketing and representations, since election night 2000
United States presidential election, 2000
The United States presidential election of 2000 was a contest between Republican candidate George W. Bush, then-governor of Texas and son of former president George H. W. Bush , and Democratic candidate Al Gore, then-Vice President....
the color blue has become the identified color of the Democratic Party, while the color red has become the identified color of the Republican Party. That night, for the first time, all major broadcast television networks used the same color scheme for the electoral map: blue states for Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
(Democratic nominee) and red states for George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
(Republican nominee). Since then, the color blue has been widely used by the media to represent the party. This has caused confusion among non-American observers because blue is the traditional color of the right
Right-wing politics
In politics, Right, right-wing and rightist generally refer to support for a hierarchical society justified on the basis of an appeal to natural law or tradition. To varying degrees, the Right rejects the egalitarian objectives of left-wing politics, claiming that the imposition of equality is...
and red the color of the left
Left-wing politics
In politics, Left, left-wing and leftist generally refer to support for social change to create a more egalitarian society...
outside of the United States. For example, in Canada red represents the Liberals
Liberal Party of Canada
The Liberal Party of Canada , colloquially known as the Grits, is the oldest federally registered party in Canada. In the conventional political spectrum, the party sits between the centre and the centre-left. Historically the Liberal Party has positioned itself to the left of the Conservative...
, while blue represents the Conservatives
Conservative Party of Canada
The Conservative Party of Canada , is a political party in Canada which was formed by the merger of the Canadian Alliance and the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada in 2003. It is positioned on the right of the Canadian political spectrum...
. In the United Kingdom, red denotes the Labour Party
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a centre-left democratic socialist party in the United Kingdom. It surpassed the Liberal Party in general elections during the early 1920s, forming minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in 1924 and 1929-1931. The party was in a wartime coalition from 1940 to 1945, after...
and blue symbolizes the Conservative Party
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, formally the Conservative and Unionist Party, is a centre-right political party in the United Kingdom that adheres to the philosophies of conservatism and British unionism. It is the largest political party in the UK, and is currently the largest single party in the House...
. Blue has also been used both by party supporters for promotional efforts — ActBlue
ActBlue
ActBlue is a United States political committee established in June 2004 that enables anyone to fundraise on the Internet for the Democratic Party candidates of their choice....
, BuyBlue, BlueFund, as examples — and by the party itself in 2006 both for its "Red to Blue Program", created to support Democratic candidates running against Republican incumbents in the midterm elections
United States general elections, 2006
The 2006 United States midterm elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006. All United States House of Representatives seats and one third of the United States Senate seats were contested in this election, as well as 36 state governorships, many state legislatures, four territorial...
that year, and on its official website.
In September, 2010, the Democratic Party unveiled its new logo, which featured a blue D inside a blue circle. It was the party's first official logo, as the donkey logo had been used as a semi-official party logo.
Jefferson-Jackson Day
Jefferson-Jackson Day
Jefferson-Jackson Day is the most common name given to the annual fundraising celebration held by Democratic Party organizations in the United States. It is named for Presidents Thomas Jefferson and Andrew Jackson...
is the annual fundraising event (dinner) held by Democratic Party organizations across the United States. It is named after Presidents Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
and Andrew Jackson, whom the party regards as its distinguished early leaders.
The song "Happy Days Are Here Again
Happy Days Are Here Again
"Happy Days Are Here Again" is a song copyrighted in 1929 by Milton Ager and Jack Yellen and published by EMI Robbins Catalog, Inc./Advanced Music Corp...
" is the unofficial song of the Democratic Party. It was used prominently when Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
was nominated for president at the 1932 Democratic National Convention
1932 Democratic National Convention
The 1932 Democratic National Convention was held in Chicago, Illinois from June 27 - July 2, 1932. The convention resulted in the nomination of Governor Franklin Roosevelt of New York for President and Speaker of the House John Nance Garner of Texas for Vice-President...
and remains a sentimental favorite for Democrats today. For example, Paul Shaffer
Paul Shaffer
Paul Allen Wood Shaffer, CM is a Canadian musician, actor, voice actor, author, comedian, and composer who has been David Letterman's sidekick since 1982.-Early years:...
played the theme on the Late Show with David Letterman
Late Show with David Letterman
Late Show with David Letterman is a U.S. late-night talk show hosted by David Letterman on CBS. The show debuted on August 30, 1993, and is produced by Letterman's production company, Worldwide Pants Incorporated. The show's music director and band-leader of the house band, the CBS Orchestra, is...
after the Democrats won Congress in 2006. More recently, the emotionally similar song "Beautiful Day
Beautiful Day
"Beautiful Day" is a song by the rock band U2. It is the first track from their 2000 album, All That You Can't Leave Behind, and it was released as the album's lead single. It was a commercial success, helping launch the album to multi-platinum status, and is one of U2's biggest hits to date...
" by the band U2
U2
U2 are an Irish rock band from Dublin. Formed in 1976, the group consists of Bono , The Edge , Adam Clayton , and Larry Mullen, Jr. . U2's early sound was rooted in post-punk but eventually grew to incorporate influences from many genres of popular music...
has become a favorite theme song for Democratic candidates. John Kerry
John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry is the senior United States Senator from Massachusetts, the 10th most senior U.S. Senator and chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He was the presidential nominee of the Democratic Party in the 2004 presidential election, but lost to former President George W...
used the song during his 2004 presidential campaign, and several Democratic Congressional candidates used it as a celebratory tune in 2006.
Aaron Copland
Aaron Copland
Aaron Copland was an American composer, composition teacher, writer, and later in his career a conductor of his own and other American music. He was instrumental in forging a distinctly American style of composition, and is often referred to as "the Dean of American Composers"...
's Fanfare for the Common Man
Fanfare for the Common Man
Fanfare for the Common Man is a 20th-century American classical music work by American composer Aaron Copland. The piece was written in 1942 for the Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra under conductor Eugene Goossens. It was inspired in part by a famous speech made earlier in the same year where vice...
is traditionally performed at the beginning of the Democratic National Convention.
State and territorial parties
- Alabama Democratic PartyAlabama Democratic PartyThe Alabama Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the state of Alabama. It is chaired by Judge Mark Kennedy. The Executive Director is Bradley Davidson....
(Site) - Alaska Democratic PartyAlaska Democratic Party-Introduction:The Alaska Democratic Party is the primary Democratic Party political organization in the state of Alaska, headquartered in Anchorage....
(Site) - Arizona Democratic PartyArizona Democratic PartyThe Arizona Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in Arizona. Its headquarters is in Phoenix.-Party organization:The Arizona Democratic Party is organized into three parts, the state committee, the executive committee, and the executive board.-State Committee:The state committee...
(Site) - Democratic Party of ArkansasDemocratic Party of ArkansasThe Democratic Party of Arkansas is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Arkansas. It is responsible for promoting the ideologies and core values of the national Democratic Party in Arkansas.-History:...
(Site) - California Democratic PartyCalifornia Democratic PartyThe California Democratic Party is the state branch of the Democratic Party in the state of California, headquartered in Sacramento. It is chaired by veteran Democratic politician and former United States Representative John L. Burton, who succeeded Art Torres in April 2009. It is the majority...
(Site) - Colorado Democratic PartyColorado Democratic PartyThe Colorado Democratic Party is the state affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Colorado. Its chair is Rick Palacio, and its executive director is Alec Garnett.The remaining officers are:...
(Site) - Democratic State Central Committee of ConnecticutDemocratic State Central Committee of ConnecticutThe Democratic State Central Committee of Connecticut is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Connecticut. The state chair of the party is Nancy DiNardo, and the Vice Chair is State Representative Steve Fontana...
(Site) - Delaware Democratic PartyDelaware Democratic PartyThe Delaware Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the US State of Delaware, headquartered in unincorporated New Castle County. John D. Daniello is the state Chair.-Federal executive:...
(Site) - District of Columbia Democratic State CommitteeDistrict of Columbia Democratic State CommitteeThe District of Columbia Democratic State Committee is the local branch of the Democratic Party in Washington, D.C.Democrats make up 75 percent of the registered voters in the District of Columbia, while 7 percent are registered with the Republican Party , 1 percent with the D.C...
(Site) - Florida Democratic PartyFlorida Democratic PartyThe Florida Democratic Party is the official organization for Democrats in the state of Florida.-History:The Florida Democratic Party has historically dominated dodo Florida's state and local politics. Florida's Governor's Mansion was closed to Republicans from 1877 until 1967, when Claude R...
(Site) - Democratic Party of GeorgiaDemocratic Party of GeorgiaThe Democratic Party of Georgia is one of the two major political parties in the U.S. state of Georgia. It is affiliated with the United States Democratic Party.-Leadership:...
(Site) - Democratic Party of HawaiiDemocratic Party of HawaiiThe Democratic Party of Hawaii is an arm of the Democratic Party of the United States based in Honolulu, Hawaii. The party is a centralized organization established to promote the party platform as drafted in convention biennially...
(Site) - Idaho Democratic PartyIdaho Democratic PartyThe Idaho Democratic Party is an Idaho political party affiliated with the United States Democratic Party. Although the party has been in the minority for most of the state's history, it has produced several notable public figures, including the late U.S...
(Site) - Democratic Party of IllinoisDemocratic Party of IllinoisThe Democratic Party of Illinois is a political party and affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in Illinois. It is the oldest still-existing state party in Illinois and, along with the Green and Republican Parties, one of just three legally established parties in the state.-History:The...
(Site) - Indiana Democratic PartyIndiana Democratic PartyThe Democratic Party of Indiana is a political party and affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in Indiana. The Indiana Democratic Party also hold three of Indiana's nine Congressional seats...
(Site) - Iowa Democratic PartyIowa Democratic PartyThe Iowa Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the state of Iowa.-Current elected officials:Iowa Democrats are in control of the Iowa Senate, one of the state's United States Senate seats, and three out of the state's five United States House of Representatives seats. ...
(Site) - Kansas Democratic PartyKansas Democratic PartyThe Kansas Democratic Party is the state affiliate political party of the United States Democratic Party headquartered in Topeka, Kansas. The State Party Chairman is Joan Wagnon-Overview:...
(Site) - Kentucky Democratic PartyKentucky Democratic PartyThe Kentucky Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the Commonwealth of Kentucky, USA. The party Chairman is Daniel Logsdon, Jr., Party Vice-Chair is Susie Watkins, and David Tandy is Treasurer...
(Site) - Louisiana Democratic PartyLouisiana Democratic PartyThe Louisiana Democratic Party is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Louisiana. The party historically has been prominent in politics since before the American Civil War, but consolidated this power after Reconstruction as a result of the rise of the Solid South...
(Site) - Maine Democratic PartyMaine Democratic PartyThe Maine Democratic Party is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Maine.-Current Democratic officeholders:The Maine Democratic Party is the minority party in both the Maine Senate and Maine House of Representatives. The party, however, holds both of the state's U.S...
(Site) - Maryland Democratic PartyMaryland Democratic PartyThe Maryland Democratic Party is the state affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in the U.S. State of Maryland, headquartered in Annapolis. The current state party chair is Yvette Lewis.-History:...
(Site) - Massachusetts Democratic PartyMassachusetts Democratic PartyThe Massachusetts Democratic Party is the state affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in the U.S. Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The state party chairman is John E...
(Site) - Michigan Democratic PartyMichigan Democratic PartyThe Michigan Democratic Party is the state-level party of the United States Democratic Party in Michigan. It is based in Lansing. Mark Brewer is the current Party Chair.-Current officeholders:...
(Site) - Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor PartyMinnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor PartyThe Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party is a major political party in the state of Minnesota and the state affiliate of the Democratic Party. It was created on April 15, 1944, with the merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the Farmer–Labor Party...
(Site) - Democratic Party of the State of MississippiDemocratic Party of the State of MississippiThe Democratic Party of the State of Mississippi is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Mississippi. Its headquarters is located in Jackson which is also the state capitol....
(Site) - Missouri Democratic PartyMissouri Democratic PartyThe Missouri Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the state of Missouri. The party Chairwoman is Susan Montee, a former state auditor, who was given the position in December 2010.-Past political strength:...
(Site)
- Montana Democratic PartyMontana Democratic PartyThe Montana Democratic Party is the Montana party affiliate of the Democratic Party. The Montana Democratic Party is also one of the two major political parties in the U.S. state of Montana. The party is led by Chairman Jim Elliot and Vice Chair Nancy Anderson...
(Site) - Nebraska Democratic PartyNebraska Democratic PartyThe Nebraska Democratic Party is the official arm of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Nebraska. As of 2009, the only statewide elected official in the party is United States Senator Ben Nelson.-Historically prominent Nebraska Democrats:...
(Site) - Nevada Democratic PartyNevada Democratic PartyThe Nevada Democratic Party is the state affiliate of the United States Democratic Party in Nevada. Its chair is Roberta Lange, and its Executive Director is Zach Zaragoza .-History:...
(Site) - New Hampshire Democratic PartyNew Hampshire Democratic PartyThe New Hampshire Democratic Party is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of New Hampshire. The chair is Raymond Buckley. The vice chairs are Martha Fuller Clark and Jane Clemmons.-Current elected officials:...
( Site) - New Jersey Democratic State CommitteeNew Jersey Democratic State CommitteeThe New Jersey Democratic State Committee is the New Jersey state affiliate of the United States Democratic Party.New Jersey Assemblyman John S. Wisniewski is the Chairman and Camden Mayor Dana Redd is the Vice-Chairwoman. They were elected on January 27, 2010.-Party structure:The NJDSC is the...
(Site) - Democratic Party of New MexicoDemocratic Party of New MexicoThe Democratic Party of New Mexico is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of New Mexico, headquartered in Albuquerque. The party is led by Chairman Javier Gonzales and Vice-Chair Annadelle Sanchez.-Historical development:...
(Site) - New York State Democratic CommitteeNew York State Democratic CommitteeThe New York State Democratic Committee runs the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of New York. Its headquarters are in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, and it has an office in Albany.-List of chairpersons:...
(Site) - North Carolina Democratic PartyNorth Carolina Democratic PartyThe North Carolina Democratic Party is the North Carolina affiliate of the national Democratic Party in the United States. It is headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina. They are located in the historic Goodwin house which is located in the downtown area of Raleigh at 220 Hillsborough Street...
( Site) - North Dakota Democratic-NPL Party (Site)
- Ohio Democratic PartyOhio Democratic PartyThe Ohio Democratic Party is the Ohio affiliate to the United States Democratic Party. Former Ohio House Minority Leader Chris Redfern is the Ohio Democratic Party chairman. Redfern was elected to office in December 2005...
(Site) - Oklahoma Democratic PartyOklahoma Democratic PartyThe Oklahoma Democratic Party is an Oklahoma political party affiliated with the United States Democratic Party. Along with the Oklahoma Republican Party, it one of the two major parties in Oklahoma politics....
(Site) - Democratic Party of OregonDemocratic Party of OregonThe Democratic Party of Oregon, based in Portland, is the official Oregon affiliate of the United States Democratic Party. It is recognized by the state of Oregon as a major political party, along with the Oregon Republican Party...
(Site) - Pennsylvania Democratic PartyPennsylvania Democratic PartyThe Pennsylvania Democratic Party is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Pennsylvania. The party has had strong support in the Pittsburgh and Philadelphia area for a long time, having controlled the mayoral office in Philadelphia since 1952, and the Pittsburgh...
(Site) - Puerto Rico Democratic PartyPuerto Rico Democratic PartyThe Puerto Rico Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. The party is divided between supporters of the current Commonwealth status and those who favor statehood for Puerto Rico....
(Site) - Rhode Island Democratic CommitteeRhode Island Democratic CommitteeThe Rhode Island Democratic Committee is the local branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Rhode Island. Edwin R. Pacheco is the chairman of the Party.-Democratic Party dominance in Rhode Island:...
(Site) - South Carolina Democratic PartySouth Carolina Democratic PartyThe South Carolina Democratic Party is the South Carolina affiliate of the United States Democratic Party. The Democratic party thrived during the Second Party System between 1832 and the mid-1850s and was one of the causes of the collapse of the Whig Party....
(Site) - South Dakota Democratic PartySouth Dakota Democratic PartyThe South Dakota Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the state of South Dakota. Jack Billion recently resigned as party chair. Cheryl Chapman is currently serving as interim chair and will be running for the position in April...
(Site) - Tennessee Democratic PartyTennessee Democratic PartyThe Tennessee Democratic Party is the organized coalition of Democrats in Tennessee founded in 1826, tracing its philosophical roots to President Andrew Jackson. Andrew Jackson was born in 1767 in the Carolinas. After fighting in the Revolutionary War he moved to Tennessee in search of opportunity....
(Site) - Texas Democratic PartyTexas Democratic PartyThe Texas Democratic Party is one of the two major political parties in Texas and the local branch of the United States Democratic Party. It is headquartered in Downtown Austin within close proximity to the Texas State Capitol.-19th century:...
(Site) - Utah Democratic PartyUtah Democratic PartyThe Utah State Democratic Party works to elect Democrats to office in the state of Utah. The Utah Democratic Party, like other national, state, and county parties, maintains a party platform that lists general principles or issues of importance to members of the Utah Democratic Party and maintains...
(Site) - Vermont Democratic PartyVermont Democratic PartyThe Vermont Democratic Party is the affiliate branch of the United States Democratic Party in the state of Vermont. The party advocates progressivism, American liberalism and social democracy in the Vermont government. It holds the governorship and the majority in both houses of the state legislature...
(Site) - Democratic Party of VirginiaDemocratic Party of VirginiaThe Democratic Party of Virginia is based in Richmond in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is affiliated with the national Democratic Party of the United States. The organization is governed by a State Party Plan, which guarantees an open and fair candidate selection process...
(Site) - Washington State Democratic PartyWashington State Democratic PartyThe Washington State Democratic Party is the local Democratic Party branch in the State of Washington, headquartered in the Broderick Building in Downtown Seattle. It is also commonly referred to as the Washington State Democrats and the Washington Democratic Party.-Washington State Democratic...
(Site) - West Virginia Democratic PartyWest Virginia Democratic PartyThe West Virginia Democratic Party is the state level chapter of the United States Democratic Party in the state of West Virginia.-History:The state of West Virginia granted itself statehood after its people, through a state constitutional convention, became a free state and broke away from the...
(Site) - Democratic Party of WisconsinDemocratic Party of WisconsinThe Democratic Party of Wisconsin is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in Wisconsin. As of 2009, it is headed by state party chairman Mike Tate, who is the youngest chairman of a state party...
(Site) - Wyoming Democratic PartyWyoming Democratic PartyThe Wyoming Democratic Party is the local branch of the Democratic Party in the state of Wyoming. The party is led by State Party Chair Chuck Herz.-Legislative leaders:*Senate Minority Leader: John Hastert*House Minority Leader: W. Patrick Goggles...
(Site)
See also
- List of United States Democratic Party presidential tickets
- Democratic organizationsDemocratic organizationsThis is an incomplete list of official and unofficial organizations associated with the United States Democratic Party.* 21st Century Democrats* America Votes* Blue Dog Democrats* Center for American Progress* College Democrats* Democracy for America...
- Factions in the Democratic Party (United States)Factions in the Democratic Party (United States)The Democratic Party of the United States is composed of various factions, with some overlap and enough agreement between them to coexist with each other within the party.-Progressive Democrats:...
- Politics of the United States - Organization of American political parties
- Political party strength in U.S. statesPolitical party strength in U.S. statesThroughout most of the 20th century, although the Republican and Democratic parties alternated in power at a national level, some states were so overwhelmingly dominated by one party that nomination was usually tantamount to election...
- 2008 Democratic National Convention2008 Democratic National ConventionThe United States 2008 Democratic National Convention was a quadrennial presidential nominating convention of the Democratic Party where it adopted its national platform and officially nominated its candidates for President and Vice President of the United States. The convention was held in Denver,...
- Atari DemocratAtari DemocratAtari Democrat, a phrase first popularized during the early 1980s, references both the video game brand Atari and Democratic legislators who suggested that the support and development of high tech and related businesses would stimulate the economy and create jobs.-Definition:The definition of an...
- National Jewish Democratic CouncilNational Jewish Democratic CouncilThe National Jewish Democratic Council works as lobbying organization for the country of Israel in the United States of America and the Democratic Party and its mission is to promote pro-Israeli policies within the Party, and to promote the Democratic Party within the jewish community.The NJDC is...
Organizations
- Democrats.org — Official website of the Democratic National Committee
- Democratic Senate Caucus
- Democratic House Caucus
- Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee
- Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee
- Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee
- Democratic Governors Association
- Democratic Attorneys General Association
- National Conference of Democratic Mayors
- National Federation of Democratic Women
- College Democrats of America
- Young Democrats of America
- Democrats Abroad
- Progressive Democrats of America
- Democrats.com — "Aggressive Progressive" Democrats, not to be confused with the official Democratic Party site Democrats.org

