
Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
Encyclopedia
The Gibbs–Helmholtz equation is a thermodynamic
equation
useful for calculating changes in the Gibbs energy of a system as a function of temperature
. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs
and Hermann von Helmholtz
:
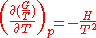
With:
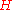 the enthalpy
the enthalpy
 the absolute temperature
the absolute temperature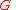 the Gibbs free energy
the Gibbs free energy
at constant pressure
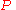 . The equation states that the change in the G/T ratio at constant pressure as a result of an infinitesimally small change in temperature is a factor (H/T2).
. The equation states that the change in the G/T ratio at constant pressure as a result of an infinitesimally small change in temperature is a factor (H/T2).
For a chemical reaction
the equation reads:
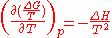
with as the change in Gibbs energy and
as the change in Gibbs energy and  as the enthalpy change (which is considered independent of temperature).
as the enthalpy change (which is considered independent of temperature).
which can rearrange to:
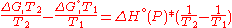
This equation quickly enables the calculation of the Gibbs free energy change for a chemical reaction at any temperature T2 with knowledge of just the Standard Gibbs free energy change of formation and the Standard enthalpy change of formation
for the individual components at 25°C and 1 bar.
Through:
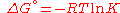
which relates Gibbs energy to an equilibrium constant, the van 't Hoff equation is derived.
for a closed system
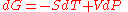
at constant pressure
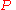 (dP = 0) reduces to
(dP = 0) reduces to
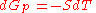
or
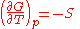
The dependence of the G/T ratio
on T is found with the aid of the quotient rule:
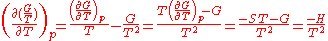
Sometimes it can be found like this:
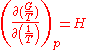
Here, the chain rule
has been used with a bit of rearrangement. If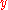 and
and  are functions of
are functions of  , the chain rule says that
, the chain rule says that  . Dividing both sides through by
. Dividing both sides through by 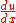 gives
gives 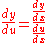 . In the equation above,
. In the equation above, 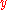 is
is  ,
,  is
is  , and u is
, and u is 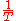 . Thus,
. Thus, 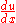 is
is 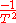 .
.
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
useful for calculating changes in the Gibbs energy of a system as a function of temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs was an American theoretical physicist, chemist, and mathematician. He devised much of the theoretical foundation for chemical thermodynamics as well as physical chemistry. As a mathematician, he invented vector analysis . Yale University awarded Gibbs the first American Ph.D...
and Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz was a German physician and physicist who made significant contributions to several widely varied areas of modern science...
:
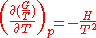
With:
 the enthalpy
the enthalpyEnthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
 the absolute temperature
the absolute temperature the Gibbs free energy
the Gibbs free energyGibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
at constant pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
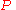 . The equation states that the change in the G/T ratio at constant pressure as a result of an infinitesimally small change in temperature is a factor (H/T2).
. The equation states that the change in the G/T ratio at constant pressure as a result of an infinitesimally small change in temperature is a factor (H/T2).For a chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
the equation reads:
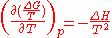
with
 as the change in Gibbs energy and
as the change in Gibbs energy and  as the enthalpy change (which is considered independent of temperature).
as the enthalpy change (which is considered independent of temperature).which can rearrange to:

This equation quickly enables the calculation of the Gibbs free energy change for a chemical reaction at any temperature T2 with knowledge of just the Standard Gibbs free energy change of formation and the Standard enthalpy change of formation
Standard enthalpy change of formation
The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states...
for the individual components at 25°C and 1 bar.
Through:

which relates Gibbs energy to an equilibrium constant, the van 't Hoff equation is derived.
Proof
The Gibbs free energyGibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
for a closed system
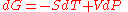
at constant pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
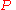 (dP = 0) reduces to
(dP = 0) reduces to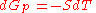
or
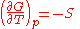
The dependence of the G/T ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
on T is found with the aid of the quotient rule:
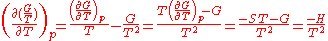
Sometimes it can be found like this:
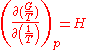
Here, the chain rule
Chain rule
In calculus, the chain rule is a formula for computing the derivative of the composition of two or more functions. That is, if f is a function and g is a function, then the chain rule expresses the derivative of the composite function in terms of the derivatives of f and g.In integration, the...
has been used with a bit of rearrangement. If
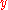 and
and  are functions of
are functions of  , the chain rule says that
, the chain rule says that  . Dividing both sides through by
. Dividing both sides through by 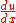 gives
gives 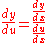 . In the equation above,
. In the equation above, 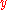 is
is  ,
,  is
is  , and u is
, and u is  . Thus,
. Thus, 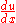 is
is 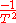 .
.
