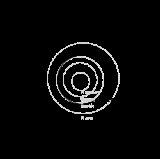
HD 108874
Encyclopedia
HD 108874 is a yellow dwarf
star
(spectral type G5 V) in the constellation
of Coma Berenices
. It is 223 light years from Earth and has two extrasolar planet
s that are possibly in a 4:1 orbital resonance
.
. The star has a temperature of 5407 K and luminosity 1.14 solar. Its metallicity
is 1.38 times solar, meaning it has greater iron
abundance relative to hydrogen
and helium
. It has about the same mass as the Sun, but the radius is 22% greater.
was discovered by the US-based team Paul Butler
, Geoffrey Marcy
, Steven Vogt, and Debra Fischer
. This planet receives the amount of insolation
closest to Earth
of any extrasolar planet
. In 2005, further observations revealed this star has another jovian planet orbiting further out, designated as HD 108874 c
. Those two planets are in a 4:1 orbital resonance. This means if HD 108874 b orbits the star four times, then HD 108874 c orbits only once, because the orbital period
for planet c is four times longer than planet b.
Yellow dwarf
A G-type main-sequence star , often called a yellow dwarf, is a main-sequence star of spectral type G and luminosity class V. Such a star has about 0.8 to 1.2 solar masses and surface temperature of between 5,300 and 6,000 K., Tables VII, VIII...
star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
(spectral type G5 V) in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of Coma Berenices
Coma Berenices
Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole...
. It is 223 light years from Earth and has two extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
s that are possibly in a 4:1 orbital resonance
Orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, an orbital resonance occurs when two orbiting bodies exert a regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually due to their orbital periods being related by a ratio of two small integers. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of...
.
Star
HD 108874 is 2.7 billion years older than our SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. The star has a temperature of 5407 K and luminosity 1.14 solar. Its metallicity
Metallicity
In astronomy and physical cosmology, the metallicity of an object is the proportion of its matter made up of chemical elements other than hydrogen and helium...
is 1.38 times solar, meaning it has greater iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
abundance relative to hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
. It has about the same mass as the Sun, but the radius is 22% greater.
Planetary system
In 2003, the jovian planet HD 108874 bHD 108874 b
HD 108874 b is a gas giant announced in 2003. The orbit lies in the star's habitable zone. It is expected that any moons orbiting this planet are enriched in carbon, and are thus quite different from the silicate-rich bodies in our Solar System....
was discovered by the US-based team Paul Butler
R. Paul Butler
R. Paul Butler is an astronomer who searches for extrasolar planets.He received a BA and an MS from San Francisco State University, completing a Master's thesis with Geoffrey Marcy, and then completed his doctoral studies at the University of Maryland, College Park in 1993...
, Geoffrey Marcy
Geoffrey Marcy
Geoffrey W. Marcy is an American astronomer, who is currently Professor of Astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, famous for discovering more extrasolar planets than anyone else, 70 out of the first 100 to be discovered, along with R...
, Steven Vogt, and Debra Fischer
Debra Fischer
Debra A. Fischer is a professor of astronomy at Yale University. Fischer has co-authored over 100 papers on dwarf and sub-stellar mass objects in the galactic neighborhood, including many on extrasolar planets. She is a principal investigator with the N2K Consortium searching for exoplanets...
. This planet receives the amount of insolation
Insolation
Insolation is a measure of solar radiation energy received on a given surface area in a given time. It is commonly expressed as average irradiance in watts per square meter or kilowatt-hours per square meter per day...
closest to Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
of any extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
. In 2005, further observations revealed this star has another jovian planet orbiting further out, designated as HD 108874 c
HD 108874 c
HD 108874 c is a gas giant discovered in 2005 which orbits beyond the star's habitable zone, and receives insolation 15.9% that of Earth. It has minimum mass similar to Jupiter, although since inclination of the orbit is not known. The true mass of this planet will probably be much greater.This...
. Those two planets are in a 4:1 orbital resonance. This means if HD 108874 b orbits the star four times, then HD 108874 c orbits only once, because the orbital period
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
for planet c is four times longer than planet b.
External links
- Extrasolar Planet Interactions by Rory Barnes & Richard Greenberg, Lunar and Planetary Lab, University of Arizona

