
Solar luminosity
Encyclopedia
The solar luminosity, 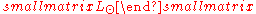 , is a unit of luminosity
, is a unit of luminosity
or radiant power (power
emitted in the form of photon
s) conventionally used by astronomer
s to give the luminosities of star
s. One solar luminosity is equal to the current accepted luminosity of the Sun
, which is 3.839 W
, or 3.839 erg
/s. The value is slightly higher, 3.939 W (equivalent to 4.382 kg/s or 1.9 M☉/d) if the solar neutrino
radiation is included as well as electromagnetic radiation
. The Sun is a weakly variable star
and its luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle
(sunspot cycle), which causes a periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Any other variation over the last 200–300 years is thought to be much smaller than this.
measured at the Earth or by satellites in Earth orbit. The mean irradiance at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is sometimes known as the solar constant
, . Irradiance is defined as power per unit area, so the solar luminosity (total power emitted by the Sun) is the irradiance received at the Earth (solar constant) multiplied by the area of the sphere whose radius is the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun:
. Irradiance is defined as power per unit area, so the solar luminosity (total power emitted by the Sun) is the irradiance received at the Earth (solar constant) multiplied by the area of the sphere whose radius is the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun:
where A is the unit distance
(the value of the astronomical unit
in metre
s) and k is a constant (whose value is very close to one) that reflects the fact that the mean distance from the Earth to the Sun is not exactly one astronomical unit.
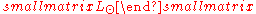 , is a unit of luminosity
, is a unit of luminosityLuminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
or radiant power (power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
emitted in the form of photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s) conventionally used by astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
s to give the luminosities of star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s. One solar luminosity is equal to the current accepted luminosity of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, which is 3.839 W
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
, or 3.839 erg
Erg
An erg is the unit of energy and mechanical work in the centimetre-gram-second system of units, symbol "erg". Its name is derived from the Greek ergon, meaning "work"....
/s. The value is slightly higher, 3.939 W (equivalent to 4.382 kg/s or 1.9 M☉/d) if the solar neutrino
Solar neutrino
Electron neutrinos are produced in the Sun as a product of nuclear fusion. By far the largest fraction of neutrinos passing through the Earth are Solar neutrinos....
radiation is included as well as electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
. The Sun is a weakly variable star
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
and its luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle
Solar cycle
The solar cycle, or the solar magnetic activity cycle, is a periodic change in the amount of irradiation from the Sun that is experienced on Earth. It has a period of about 11 years, and is one component of solar variation, the other being aperiodic fluctuations. Solar variation causes changes in...
(sunspot cycle), which causes a periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Any other variation over the last 200–300 years is thought to be much smaller than this.
Determination
The solar luminosity is related to the solar irradianceIrradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter , while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter...
measured at the Earth or by satellites in Earth orbit. The mean irradiance at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is sometimes known as the solar constant
Solar constant
The solar constant, a measure of flux density, is the amount of incoming solar electromagnetic radiation per unit area that would be incident on a plane perpendicular to the rays, at a distance of one astronomical unit...
,
 . Irradiance is defined as power per unit area, so the solar luminosity (total power emitted by the Sun) is the irradiance received at the Earth (solar constant) multiplied by the area of the sphere whose radius is the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun:
. Irradiance is defined as power per unit area, so the solar luminosity (total power emitted by the Sun) is the irradiance received at the Earth (solar constant) multiplied by the area of the sphere whose radius is the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun:
where A is the unit distance
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
(the value of the astronomical unit
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
in metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
s) and k is a constant (whose value is very close to one) that reflects the fact that the mean distance from the Earth to the Sun is not exactly one astronomical unit.

