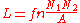Luminosity
Encyclopedia
Luminosity is a measurement
of brightness
.
, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance
, which is the density of luminous intensity
in a given direction. The SI
unit for luminance is candela
per square metre
.
The luminosity function
a.k.a. luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. There are two luminosity functions in common use. For everyday light levels, the photopic luminosity function best approximates the response of the human eye. For low light levels, the response of the human eye changes, and the scotopic curve applies.
's imaging operations, luminosity is the term used incorrectly to refer to the luma
component of a color image signal; that is, a weighted sum of the nonlinear red, green, and blue signals. It seems to be calculated with the Rec. 601 luma co-efficients (Rec. 601: Luma (Y’) = 0.299 R’ + 0.587 G’ + 0.114 B’).
The "L" in HSL color space
is sometimes said incorrectly to stand for luminosity. "L" in this case is calculated as 1/2 (MAX + MIN), where MAX and MIN refer to the highest and lowest of the R'G'B' components to be converted into HSL color space.
, luminosity is the amount of electromagnetic energy
a body radiates per unit of time. The word "luminosity" may also refer to spectral
luminosity, measured either in W/Hz or W/nm.
The luminosity of stars is measured in two forms: apparent (visible light only) and bolometric (total radiant energy). (A bolometer
is an instrument that measures radiant energy
over a wide band by absorption and measurement of heating.) When not qualified, "luminosity" means bolometric luminosity, which is measured either in the SI
units, watt
s; or in terms of solar luminosities,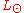 , that is, how many times as much energy the object radiates as the Sun
, that is, how many times as much energy the object radiates as the Sun
, whose luminosity is 3.846×1026 W.
Luminosity is an intrinsic measurable property independent of distance, and is appraised as absolute magnitude
, corresponding to the apparent luminosity in visible light of a star as seen at the interstellar distance of 10 parsec
s, or bolometric magnitude corresponding to bolometric luminosity. In contrast, apparent brightness is related to the distance by an inverse square law. In addition to this brightness decrease from increased distance there is an extra linear decrease of brightness for interstellar "extinction"
from intervening interstellar dust. Visible brightness is usually measured by apparent magnitude
. Both absolute and apparent magnitudes are on an inverse logarithmic scale, where 5 magnitudes increase counterparts a 100th part decrease in nonlogarithmic luminosity.
By measuring the width of certain absorption lines in the stellar spectrum
, it is often possible to assign a certain luminosity class to a star without knowing its distance. Thus a fair measure of its absolute magnitude can be determined without knowing its distance nor the interstellar extinction, and instead the distance and extinction can be determined without measuring it directly through the yearly parallax
. Since the stellar parallax
is usually too small to be measured for many far away stars, this is a common method of determining distances.
In measuring star brightnesses, visible luminosity (not total luminosity at all wave lengths), apparent magnitude
(visible brightness), and distance
are interrelated parameters. If you know two, you can determine the third. Since the sun's luminosity is the standard, comparing these parameters with the sun's apparent magnitude and distance is the easiest way to remember how to convert between them.
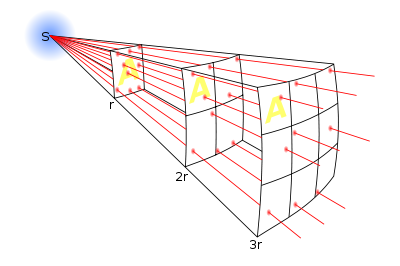 Imagine a point source of light of luminosity
Imagine a point source of light of luminosity 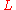 that radiates equally in all directions. A hollow sphere
that radiates equally in all directions. A hollow sphere
centered on the point would have its entire interior surface illuminated. As the radius increases, the surface area will also increase, and the constant luminosity has more surface area to illuminate, leading to a decrease in observed brightness.
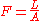
where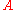 is the area of the illuminated surface.
is the area of the illuminated surface.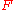 is the flux density
is the flux density
of the illuminated surface.
The surface area of a sphere with radius r is , so for stars and other point sources of light
, so for stars and other point sources of light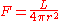
where is the distance from the observer to the light source.
is the distance from the observer to the light source.
It has been shown that the luminosity of a star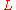 (assuming the star is a black body
(assuming the star is a black body
, which is a good approximation) is also related to temperature and radius
and radius 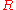 of the star by the equation:
of the star by the equation: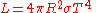
where
Dividing by the luminosity of the sun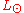 and cancelling constants, we obtain the relationship
and cancelling constants, we obtain the relationship
 .
.
For stars on the main sequence
, luminosity is also related to mass: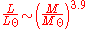
The magnitude of a star is a logarithmic scale of observed visible brightness. The apparent magnitude
is the observed visible brightness from Earth
, and the absolute magnitude
is the apparent magnitude
at a distance of 10 parsecs.
Given a visible luminosity (not total luminosity), one can calculate the apparent magnitude
of a star from a given distance:
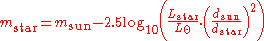
where
Or simplified, given msun = −26.73, distsun = 1.58 × 10−5 lyr:
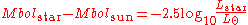
which makes by inversion:
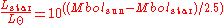
where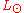 is the sun's (sol) luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
is the sun's (sol) luminosity (bolometric luminosity)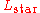 is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)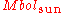 is the bolometric magnitude of the sun
is the bolometric magnitude of the sun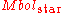 is the bolometric magnitude of the star
is the bolometric magnitude of the star
and accelerator
physics, luminosity is the number of particles per unit area
per unit time
times the opacity
of the target, usually expressed in either the cgs units cm
−2 s
−1 or b
−1 s−1. The integrated luminosity is the integral
of the luminosity with respect to time. The luminosity is an important value to characterize the performance of an accelerator.
where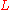 is the (instantaneous) luminosity.
is the (instantaneous) luminosity.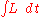 is the integrated luminosity.
is the integrated luminosity.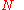 is the number of interactions.
is the number of interactions. is the number density of a particle beam.
is the number density of a particle beam. is the total cross section
is the total cross section
. is the differential
is the differential
solid angle
.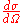 is the differential cross section
is the differential cross section
.
For an intersecting storage ring collider:
where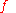 is the revolution frequency
is the revolution frequency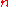 is the number of bunches in one beam in the storage ring.
is the number of bunches in one beam in the storage ring.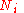 is the number of particles in each bunch
is the number of particles in each bunch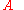 is the cross section of the beam.
is the cross section of the beam.
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
of brightness
Brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target...
.
In photometry and color imaging
In photometryPhotometry (optics)
Photometry is the science of the measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is distinct from radiometry, which is the science of measurement of radiant energy in terms of absolute power; rather, in photometry, the radiant power at each wavelength is weighted by...
, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
, which is the density of luminous intensity
Luminous intensity
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye...
in a given direction. The SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
unit for luminance is candela
Candela
The candela is the SI base unit of luminous intensity; that is, power emitted by a light source in a particular direction, weighted by the luminosity function . A common candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela...
per square metre
Square metre
The square metre or square meter is the SI derived unit of area, with symbol m2 . It is defined as the area of a square whose sides measure exactly one metre...
.
The luminosity function
Luminosity function
The luminosity function or luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. It should not be considered perfectly accurate in every case, but it is a very good representation of visual sensitivity of the human eye and it is...
a.k.a. luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. There are two luminosity functions in common use. For everyday light levels, the photopic luminosity function best approximates the response of the human eye. For low light levels, the response of the human eye changes, and the scotopic curve applies.
In graphics and video
In Adobe PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a graphics editing program developed and published by Adobe Systems Incorporated.Adobe's 2003 "Creative Suite" rebranding led to Adobe Photoshop 8's renaming to Adobe Photoshop CS. Thus, Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the 12th major release of Adobe Photoshop...
's imaging operations, luminosity is the term used incorrectly to refer to the luma
Luma (video)
In video, luma, sometimes called luminance, represents the brightness in an image . Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image without any color, while the chroma components represent the color information...
component of a color image signal; that is, a weighted sum of the nonlinear red, green, and blue signals. It seems to be calculated with the Rec. 601 luma co-efficients (Rec. 601: Luma (Y’) = 0.299 R’ + 0.587 G’ + 0.114 B’).
The "L" in HSL color space
HSL color space
HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model, which rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and perceptually relevant than the cartesian representation...
is sometimes said incorrectly to stand for luminosity. "L" in this case is calculated as 1/2 (MAX + MIN), where MAX and MIN refer to the highest and lowest of the R'G'B' components to be converted into HSL color space.
In astronomy
In astronomyAstronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, luminosity is the amount of electromagnetic energy
Radiant energy
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux with respect to time and, like all forms of energy, its SI unit is the joule. The term is used particularly when radiation is emitted by a source into the...
a body radiates per unit of time. The word "luminosity" may also refer to spectral
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
luminosity, measured either in W/Hz or W/nm.
The luminosity of stars is measured in two forms: apparent (visible light only) and bolometric (total radiant energy). (A bolometer
Bolometer
A bolometer is a device for measuring the power of incident electromagnetic radiation via the heating of a material with a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley...
is an instrument that measures radiant energy
Radiant energy
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux with respect to time and, like all forms of energy, its SI unit is the joule. The term is used particularly when radiation is emitted by a source into the...
over a wide band by absorption and measurement of heating.) When not qualified, "luminosity" means bolometric luminosity, which is measured either in the SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units, watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s; or in terms of solar luminosities,
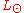 , that is, how many times as much energy the object radiates as the Sun
, that is, how many times as much energy the object radiates as the SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, whose luminosity is 3.846×1026 W.
Luminosity is an intrinsic measurable property independent of distance, and is appraised as absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
, corresponding to the apparent luminosity in visible light of a star as seen at the interstellar distance of 10 parsec
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s, or bolometric magnitude corresponding to bolometric luminosity. In contrast, apparent brightness is related to the distance by an inverse square law. In addition to this brightness decrease from increased distance there is an extra linear decrease of brightness for interstellar "extinction"
Extinction (astronomy)
Extinction is a term used in astronomy to describe the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by matter between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction—also called Galactic extinction, when it occurs in the Milky Way—was first...
from intervening interstellar dust. Visible brightness is usually measured by apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
. Both absolute and apparent magnitudes are on an inverse logarithmic scale, where 5 magnitudes increase counterparts a 100th part decrease in nonlogarithmic luminosity.
By measuring the width of certain absorption lines in the stellar spectrum
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
, it is often possible to assign a certain luminosity class to a star without knowing its distance. Thus a fair measure of its absolute magnitude can be determined without knowing its distance nor the interstellar extinction, and instead the distance and extinction can be determined without measuring it directly through the yearly parallax
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. The term is derived from the Greek παράλλαξις , meaning "alteration"...
. Since the stellar parallax
Stellar parallax
Stellar parallax is the effect of parallax on distant stars in astronomy. It is parallax on an interstellar scale, and it can be used to determine the distance of Earth to another star directly with accurate astrometry...
is usually too small to be measured for many far away stars, this is a common method of determining distances.
In measuring star brightnesses, visible luminosity (not total luminosity at all wave lengths), apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
(visible brightness), and distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
are interrelated parameters. If you know two, you can determine the third. Since the sun's luminosity is the standard, comparing these parameters with the sun's apparent magnitude and distance is the easiest way to remember how to convert between them.
Computing between brightness and luminosity

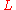 that radiates equally in all directions. A hollow sphere
that radiates equally in all directions. A hollow sphereSphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
centered on the point would have its entire interior surface illuminated. As the radius increases, the surface area will also increase, and the constant luminosity has more surface area to illuminate, leading to a decrease in observed brightness.
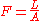
where
 is the area of the illuminated surface.
is the area of the illuminated surface. is the flux density
is the flux densityFlux density
-Formal Statement:The flux density is simply defined as the amount of flux passing through a unit-area. -Mathematical Statement:The flux density would essentially be the number of field lines passing through a defined unit-area...
of the illuminated surface.
The surface area of a sphere with radius r is
 , so for stars and other point sources of light
, so for stars and other point sources of light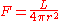
where
 is the distance from the observer to the light source.
is the distance from the observer to the light source.It has been shown that the luminosity of a star
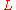 (assuming the star is a black body
(assuming the star is a black bodyBlack body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
, which is a good approximation) is also related to temperature
 and radius
and radius  of the star by the equation:
of the star by the equation:
where
- σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constantStefan-Boltzmann constantThe Stefan–Boltzmann constant , a physical constant denoted by the Greek letter σ, is the constant of proportionality in the Stefan–Boltzmann law: the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body in unit time is proportional to the fourth power of the thermodynamic temperature.The...
5.67 WWattThe watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
·m-2·K-4
Dividing by the luminosity of the sun
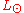 and cancelling constants, we obtain the relationship
and cancelling constants, we obtain the relationship .
.For stars on the main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
, luminosity is also related to mass:
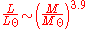
The magnitude of a star is a logarithmic scale of observed visible brightness. The apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
is the observed visible brightness from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, and the absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
is the apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
at a distance of 10 parsecs.
Given a visible luminosity (not total luminosity), one can calculate the apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of a star from a given distance:
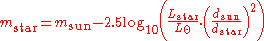
where
- mstar is the apparent magnitude of the star (a pure number)
- msun is the apparent magnitude of the sun (also a pure number)
- Lstar is the visible luminosity of the star
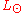 is the solar visible luminosity
is the solar visible luminosity - dstar is the distance to the star
- dsun is the distance to the sun
Or simplified, given msun = −26.73, distsun = 1.58 × 10−5 lyr:
- mstar = − 2.72 − 2.5 · log(Lstar/diststar2)
Computing between luminosity and bolometric magnitude
The difference in bolometric magnitude is related to the luminosity ratio according to: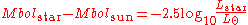
which makes by inversion:
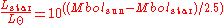
where
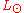 is the sun's (sol) luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
is the sun's (sol) luminosity (bolometric luminosity)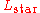 is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)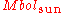 is the bolometric magnitude of the sun
is the bolometric magnitude of the sun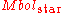 is the bolometric magnitude of the star
is the bolometric magnitude of the starIn scattering theory and accelerator physics
In scattering theoryScattering theory
In mathematics and physics, scattering theory is a framework for studying and understanding the scattering of waves and particles. Prosaically, wave scattering corresponds to the collision and scattering of a wave with some material object, for instance sunlight scattered by rain drops to form a...
and accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
physics, luminosity is the number of particles per unit area
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
per unit time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
times the opacity
Opacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a medium, such as a plasma, dielectric, shielding material, glass, etc...
of the target, usually expressed in either the cgs units cm
Centimetre
A centimetre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one hundredth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. Centi is the SI prefix for a factor of . Hence a centimetre can be written as or — meaning or respectively...
−2 s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
−1 or b
Barn (unit)
A barn is a unit of area. Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is used in all fields of high energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the...
−1 s−1. The integrated luminosity is the integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
of the luminosity with respect to time. The luminosity is an important value to characterize the performance of an accelerator.
Elementary relations for luminosity
The following relations hold-
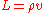 (if the target is perfectly opaque)
(if the target is perfectly opaque) -
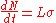
-
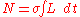
-
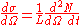
where
 is the (instantaneous) luminosity.
is the (instantaneous) luminosity.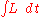 is the integrated luminosity.
is the integrated luminosity.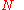 is the number of interactions.
is the number of interactions. is the number density of a particle beam.
is the number density of a particle beam. is the total cross section
is the total cross sectionCross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
.
 is the differential
is the differentialDifferential of a function
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ with respect to changes in the independent variable. The differential dy is defined bydy = f'\,dx,...
solid angle
Solid angle
The solid angle, Ω, is the two-dimensional angle in three-dimensional space that an object subtends at a point. It is a measure of how large that object appears to an observer looking from that point...
.
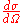 is the differential cross section
is the differential cross sectionCross section (physics)
A cross section is the effective area which governs the probability of some scattering or absorption event. Together with particle density and path length, it can be used to predict the total scattering probability via the Beer-Lambert law....
.
For an intersecting storage ring collider:
where
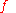 is the revolution frequency
is the revolution frequency is the number of bunches in one beam in the storage ring.
is the number of bunches in one beam in the storage ring.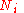 is the number of particles in each bunch
is the number of particles in each bunch is the cross section of the beam.
is the cross section of the beam.