HIPPS
Encyclopedia
A High Integrity Pressure Protection System (HIPPS) is a type of safety instrumented system
(SIS) designed to prevent over-pressurization of a plant, such as a chemical plant
or oil refinery
. The HIPPS will shut off the source of the high pressure before the design pressure of the system is exceeded, thus preventing loss of containment through rupture (explosion
) of a line or vessel. Therefore, a HIPPS is considered as a barrier between a high-pressure and a low-pressure section of an installation.
. A relief system will open an alternative outlet for the fluids in the system once a set pressure is exceeded, to avoid further build-up of pressure in the protected system. This alternative outlet generally leads to a flare
or venting system to safely dispose the excess fluids. A relief system aims at removing any excess inflow of fluids for safe disposal, where a HIPPS aims at stopping the inflow of excess fluids and containing them in the system.
Conventional relief systems have disadvantages such as release of (flammable and toxic) process fluids or their combustion products in the environment and often a large footprint of the installation. With the increasing environmental awareness, relief systems are not always an acceptable solution. However, because of their simplicity, relatively low cost and wide availability, conventional relief systems are still often applied.
HIPPS is an instrumented safety system that is designed and built in accordance with the IEC 61508
and IEC 61511
standards.
The international standards IEC 61508 and 61511 refer to safety functions and Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) when discussing a device to protect equipment, personnel and environment. Older standards use terms like safety shut-down systems, emergency shut-down systems or last layers of defence.
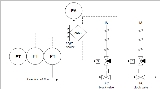
 The scheme above presents 3 pressure transmitters (PT) connected to a logic solver. The solver will decide based on 2-out-of-3 (2oo3) voting whether or not to activate the final element. The final elements consist here of two block valves that stop flow to the downstream facilities (right) to prevent them from exceeding a maximum pressure. The operator of the plant is warned through a pressure alarm (PA) that the HIPPS was activated.
The scheme above presents 3 pressure transmitters (PT) connected to a logic solver. The solver will decide based on 2-out-of-3 (2oo3) voting whether or not to activate the final element. The final elements consist here of two block valves that stop flow to the downstream facilities (right) to prevent them from exceeding a maximum pressure. The operator of the plant is warned through a pressure alarm (PA) that the HIPPS was activated.
This system has a high degree of redundancy:
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has introduced the IEC 61508
and the IEC 61511
standards in 1998 and 2003. These are performance based, non-prescriptive, standards which provide a detailed framework and a life-cycle approach for the design, implementation and management of safety systems applicable to a variety of sectors with different levels of risk definition. These standards also apply to HIPPS.
The IEC 61508 mainly focuses on Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Safety-related systems. However it also provides a framework for safety-related systems based on other technologies including mechanical systems. The IEC 61511 is added by the IEC specifically for designers, integrators and users of safety instrumented systems and covers the other parts of the safety loop (sensors and final elements) more in detail.
The basis for the design of your safety instrumented system is the required Safety Integrity Level
(SIL). The SIL is obtained during the risk analysis of a plant or process and represents the required risk reduction. The SIS shall meet the requirements of the applicable SIL which ranges from 1 to 4. The IEC standards define the requirements for each SIL for the lifecycle of the equipment, including design and maintenance. The SIL also defines a required probability of failure on demand (PFD) for the complete loop and architectural constraints for the loop and its different elements.
The requirements of the HIPPS should not be simplified to a PFD level only, the qualitative requirements and architectural constraints form an integral part of the requirements to an instrumented protection system such as HIPPS.
The European standard EN12186 (formerly the DIN
G491) and more specific the EN14382 (formerly DIN 3381) has been used for the past decades in (mechanically) instrumented overpressure protection systems. These standards prescribe the requirements for the over-pressure protection systems, and their components, in gas plants. Not only the response time and accuracy of the loop but also safety factors for over-sizing of the actuator of the final element are dictated by these standards. Independent design verification and testing to prove compliance to the EN14382 standard is mandatory. Therefore the users often refer to this standard for HIPPS design.
Safety instrumented system
A Safety Instrumented System is a form of process control usually implemented in industrial processes, such as those of a factory or an oil refinery. The SIS performs specified functions to achieve or maintain a safe state of the process when unacceptable or dangerous process conditions are detected...
(SIS) designed to prevent over-pressurization of a plant, such as a chemical plant
Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use special equipment,...
or oil refinery
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
. The HIPPS will shut off the source of the high pressure before the design pressure of the system is exceeded, thus preventing loss of containment through rupture (explosion
Explosion
An explosion is a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner, usually with the generation of high temperatures and the release of gases. An explosion creates a shock wave. If the shock wave is a supersonic detonation, then the source of the blast is called a "high explosive"...
) of a line or vessel. Therefore, a HIPPS is considered as a barrier between a high-pressure and a low-pressure section of an installation.
Traditional systems
In traditional systems over-pressure is dealt with through relief systemsRelief valve
The relief valve is a type of valve used to control or limit the pressure in a system or vessel which can build up by a process upset, instrument or equipment failure, or fire....
. A relief system will open an alternative outlet for the fluids in the system once a set pressure is exceeded, to avoid further build-up of pressure in the protected system. This alternative outlet generally leads to a flare
Gas flare
A gas flare, alternatively known as a flare stack, is an elevated vertical conveyance found accompanying the presence of oil wells, gas wells, rigs, refineries, chemical plants, natural gas plants, and landfills....
or venting system to safely dispose the excess fluids. A relief system aims at removing any excess inflow of fluids for safe disposal, where a HIPPS aims at stopping the inflow of excess fluids and containing them in the system.
Conventional relief systems have disadvantages such as release of (flammable and toxic) process fluids or their combustion products in the environment and often a large footprint of the installation. With the increasing environmental awareness, relief systems are not always an acceptable solution. However, because of their simplicity, relatively low cost and wide availability, conventional relief systems are still often applied.
Advantages of HIPPS
HIPPS provides a solution to protect equipment in cases where:- high-pressures and / or flow rates are processed
- the environment is to be protected
- the economic viability of a development needs improvement
- the risk profile of the plant must be reduced
HIPPS is an instrumented safety system that is designed and built in accordance with the IEC 61508
IEC 61508
IEC 61508 is an international standard of rules applied in industry. It is titled "Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems"....
and IEC 61511
IEC 61511
IEC 61511 is a technical standard which sets out practices in the engineering of systems that ensure the safety of an industrial process through the use of instrumentation. Such systems are referred to as Safety Instrumented Systems...
standards.
The international standards IEC 61508 and 61511 refer to safety functions and Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) when discussing a device to protect equipment, personnel and environment. Older standards use terms like safety shut-down systems, emergency shut-down systems or last layers of defence.
Components of HIPPS
A system that closes the source of over-pressure within 2 seconds with at least the same reliability as a safety relief valve is usually called a HIPPS. Such a High Integrity Pressure Protection System is a complete functional loop consisting of:- sensors, (or initiators) that detect the high pressure
- a logic solver, which processes the input from the sensors to an output to the final element
- final elements, that actually perform the corrective action in the field by bringing the process to a safe state. In case of a HIPPS this means shutting-off the source of overpressure. The final element consists of a valve, actuator and solenoids.
Diagram

This system has a high degree of redundancy:
- failure of one of the 3 pressure transmitters will not compromise the HIPPS functionality, as two readings of high pressure are needed for activation.
- failure of one of the 2 block valves will not compromise the HIPPS functionality, as the other valve will close on activation of the HIPPS.
Standards and design practices
The ever-increasing flow rates in combination with the environmental constraints initiated the widespread and rapid acceptance in the last decades of HIPPS as the ultimate protection system.The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has introduced the IEC 61508
IEC 61508
IEC 61508 is an international standard of rules applied in industry. It is titled "Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems"....
and the IEC 61511
IEC 61511
IEC 61511 is a technical standard which sets out practices in the engineering of systems that ensure the safety of an industrial process through the use of instrumentation. Such systems are referred to as Safety Instrumented Systems...
standards in 1998 and 2003. These are performance based, non-prescriptive, standards which provide a detailed framework and a life-cycle approach for the design, implementation and management of safety systems applicable to a variety of sectors with different levels of risk definition. These standards also apply to HIPPS.
The IEC 61508 mainly focuses on Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Safety-related systems. However it also provides a framework for safety-related systems based on other technologies including mechanical systems. The IEC 61511 is added by the IEC specifically for designers, integrators and users of safety instrumented systems and covers the other parts of the safety loop (sensors and final elements) more in detail.
The basis for the design of your safety instrumented system is the required Safety Integrity Level
Safety Integrity Level
Safety Integrity Level is defined as a relative level of risk-reduction provided by a safety function, or to specify a target level of risk reduction. In simple terms, SIL is a measurement of performance required for a Safety Instrumented Function ....
(SIL). The SIL is obtained during the risk analysis of a plant or process and represents the required risk reduction. The SIS shall meet the requirements of the applicable SIL which ranges from 1 to 4. The IEC standards define the requirements for each SIL for the lifecycle of the equipment, including design and maintenance. The SIL also defines a required probability of failure on demand (PFD) for the complete loop and architectural constraints for the loop and its different elements.
The requirements of the HIPPS should not be simplified to a PFD level only, the qualitative requirements and architectural constraints form an integral part of the requirements to an instrumented protection system such as HIPPS.
The European standard EN12186 (formerly the DIN
Din
DIN or Din or din can have several meanings:* A din is a loud noise.* Dīn, an Arabic term meaning "religion" or "way of life".* Din is one of the ten aspects of the Ein Sof in Kabbalah ....
G491) and more specific the EN14382 (formerly DIN 3381) has been used for the past decades in (mechanically) instrumented overpressure protection systems. These standards prescribe the requirements for the over-pressure protection systems, and their components, in gas plants. Not only the response time and accuracy of the loop but also safety factors for over-sizing of the actuator of the final element are dictated by these standards. Independent design verification and testing to prove compliance to the EN14382 standard is mandatory. Therefore the users often refer to this standard for HIPPS design.

