
Hata Model for Suburban Areas
Encyclopedia
The Hata Model for Suburban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model
, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in city outskirts and other rural areas. This model incorporates the graphical information from Okumura model and develops it further to better suite the need. This model also has two more varieties for transmission in Urban Areas
and Open Areas
.
Hata Model predicts the total path loss
along a link of terrestrial microwave
or other type of cellular communications. And is a function of transmission frequency and the average path loss in urban areas.
This model is suited for both point-to-point and broadcast
transmissions.
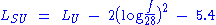
Where,
LSU = Path loss in suburban areas. Unit: decibel
(dB)
LU = Average Path loss in urban areas
. Unit: decibel (dB)
f = Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz (MHz).
Okumura Model
The Okumura model for Urban Areas is a Radio propagation model that was built using the data collected in the city of Tokyo, Japan. The model is ideal for using in cities with many urban structures but not many tall blocking structures. The model served as a base for the Hata Model.Okumura model...
, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in city outskirts and other rural areas. This model incorporates the graphical information from Okumura model and develops it further to better suite the need. This model also has two more varieties for transmission in Urban Areas
Hata Model for Urban Areas
In wireless communication, the Hata Model for Urban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used radio frequency propagation model for predicting the behaviour of cellular transmissions in built up areas...
and Open Areas
Hata Model for Open Areas
The Hata Model for Open Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in open areas. This model incorporates the graphical information...
.
Hata Model predicts the total path loss
Path loss
Path loss is the reduction in power density of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system....
along a link of terrestrial microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
or other type of cellular communications. And is a function of transmission frequency and the average path loss in urban areas.
Applicable to/under conditions
This particular version of Hata model is applicable to the transmissions just out of the cities and on rural areas where man-made structures are there but not so high and dense as in the cities. To be more precise, this model is suitable where buildings exist, but the mobile station does not have a significant variation of its height.This model is suited for both point-to-point and broadcast
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience via any audio visual medium. Receiving parties may include the general public or a relatively large subset of thereof...
transmissions.
Mathematical Formulation
Hata Model for Suburban Areas is formulated as,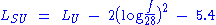
Where,
LSU = Path loss in suburban areas. Unit: decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
(dB)
LU = Average Path loss in urban areas
Hata Model for Urban Areas
In wireless communication, the Hata Model for Urban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used radio frequency propagation model for predicting the behaviour of cellular transmissions in built up areas...
. Unit: decibel (dB)
f = Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz (MHz).
Points to note
This model is based on Hata Model for Urban Areas and uses the median path loss from urban areas.See also
- Hata Model for Urban AreasHata Model for Urban AreasIn wireless communication, the Hata Model for Urban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used radio frequency propagation model for predicting the behaviour of cellular transmissions in built up areas...
- Hata Model for Open AreasHata Model for Open AreasThe Hata Model for Open Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in open areas. This model incorporates the graphical information...
- Okumura ModelOkumura ModelThe Okumura model for Urban Areas is a Radio propagation model that was built using the data collected in the city of Tokyo, Japan. The model is ideal for using in cities with many urban structures but not many tall blocking structures. The model served as a base for the Hata Model.Okumura model...
- COST 231 ModelCost 231 ModelThe COST-Hata-Model is the most often cited of the COST 231 models. Also called the Hata Model PCS Extension, it is a radio propagation model that extends the Hata Model to cover a more elaborated range of frequencies...
- Radio propagation modelRadio propagation modelA radio propagation model, also known as the Radio Wave Propagation Model or the Radio Frequency Propagation Model, is an empirical mathematical formulation for the characterization of radio wave propagation as a function of frequency, distance and other conditions...

