
Hata Model for Urban Areas
Encyclopedia
In wireless communication, the Hata Model for Urban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model
, is the most widely used radio frequency propagation model for predicting the behaviour of cellular transmissions in built up areas. This model incorporates the graphical information from Okumura model and develops it further to realize the effects of diffraction, reflection and scattering caused by city structures. This model also has two more varieties for transmission in Suburban Areas
and Open Areas
.
Hata Model predicts the total path loss
along a link of terrestrial microwave
or other type of cellular communications.
This model is suited for both point-to-point and broadcast
transmissions and it is based on extensive empirical measurements taken.
PCS is another extension of the Hata model. The Walfisch and Bertoni Model is further advanced.
: 150 MHz to 1500 MHz
Mobile Station
Antenna
Height: between 1 m and 10 m
Base station
Antenna
Height: between 30 m and 200 m
Link distance: between 1 km and 20 km.
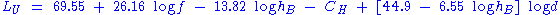
For small or medium sized city,
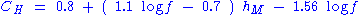
and for large cities,
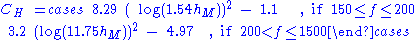
Where,
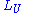 = Path loss in Urban Areas. Unit: decibel
= Path loss in Urban Areas. Unit: decibel
(dB)
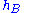 = Height of base station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of base station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
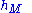 = Height of mobile station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of mobile station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
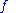 = Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz(MHz).
= Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz(MHz).
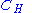 = Antenna
= Antenna
height correction factor
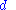 = Distance between the base and mobile stations. Unit: kilometer (km).
= Distance between the base and mobile stations. Unit: kilometer (km).
rooftops and building height by using diffraction to predict average signal
strength at street level. The model considers the path loss, S, to be a product of
three factors.
S = Po Q2 P1
where P0 represents free space path loss between isotropic antennas given by
Po = (lambda / 4 pai R)2 (whole square)
The factor Q2 gives the reduction in the rooftop signal due to the row of
buildings which immediately shadow the receiver at street level. The P1 term is
based upon diffraction and determines the signal loss from the rooftop to the
street.
In dB, the path loss is given by
S(dB) =Lo+Lrts+Lms
where L0 represents free space loss, Lrts represents the "rooftop-to-street diffraction
and scatter loss", and Lms denotes multiscreen thffiaction loss due to
the rows of buildings [X1a92]. This model is being considered for use
by ITU-R in the IMT-2000 standards activities.
THIS PARAGRAPH IS FROM THE BOOK: Wireless Communications by Theodore S. Rappaport, p157, ch 4.11
Okumura Model
The Okumura model for Urban Areas is a Radio propagation model that was built using the data collected in the city of Tokyo, Japan. The model is ideal for using in cities with many urban structures but not many tall blocking structures. The model served as a base for the Hata Model.Okumura model...
, is the most widely used radio frequency propagation model for predicting the behaviour of cellular transmissions in built up areas. This model incorporates the graphical information from Okumura model and develops it further to realize the effects of diffraction, reflection and scattering caused by city structures. This model also has two more varieties for transmission in Suburban Areas
Hata Model for Suburban Areas
The Hata Model for Suburban Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in city outskirts and other rural areas...
and Open Areas
Hata Model for Open Areas
The Hata Model for Open Areas, also known as the Okumura-Hata model for being a developed version of the Okumura Model, is the most widely used model in radio frequency propagation for predicting the behavior of cellular transmissions in open areas. This model incorporates the graphical information...
.
Hata Model predicts the total path loss
Path loss
Path loss is the reduction in power density of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system....
along a link of terrestrial microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
or other type of cellular communications.
Applicable to/under conditions
This particular version of the Hata model is applicable to the radio propagation within urban areas.This model is suited for both point-to-point and broadcast
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience via any audio visual medium. Receiving parties may include the general public or a relatively large subset of thereof...
transmissions and it is based on extensive empirical measurements taken.
PCS is another extension of the Hata model. The Walfisch and Bertoni Model is further advanced.
Coverage
FrequencyFrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
: 150 MHz to 1500 MHz
Mobile Station
Mobile Station
The mobile station comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network.The mobile station refers to global system connected to the mobile network, i.e. mobile phone or mobile computer connected using a mobile broadband adapter. This is the terminology of 2G...
Antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
Height: between 1 m and 10 m
Base station
Base station
The term base station can be used in the context of land surveying and wireless communications.- Land surveying :In the context of external land surveying, a base station is a GPS receiver at an accurately-known fixed location which is used to derive correction information for nearby portable GPS...
Antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
Height: between 30 m and 200 m
Link distance: between 1 km and 20 km.
Mathematical formulation
Hata Model for Urban Areas is formulated as: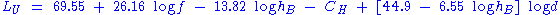
For small or medium sized city,
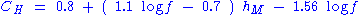
and for large cities,
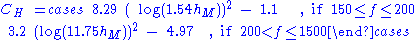
Where,
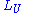 = Path loss in Urban Areas. Unit: decibel
= Path loss in Urban Areas. Unit: decibelDecibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
(dB)
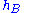 = Height of base station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of base station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)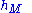 = Height of mobile station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of mobile station Antenna. Unit: meter (m)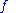 = Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz(MHz).
= Frequency of Transmission. Unit: megahertz(MHz).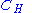 = Antenna
= AntennaAntenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
height correction factor
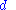 = Distance between the base and mobile stations. Unit: kilometer (km).
= Distance between the base and mobile stations. Unit: kilometer (km).Points to note Walfisch and bertoni model
A model developed by Walfisch and Bertoni [Wa]88] considers the impact ofrooftops and building height by using diffraction to predict average signal
strength at street level. The model considers the path loss, S, to be a product of
three factors.
S = Po Q2 P1
where P0 represents free space path loss between isotropic antennas given by
Po = (lambda / 4 pai R)2 (whole square)
The factor Q2 gives the reduction in the rooftop signal due to the row of
buildings which immediately shadow the receiver at street level. The P1 term is
based upon diffraction and determines the signal loss from the rooftop to the
street.
In dB, the path loss is given by
S(dB) =Lo+Lrts+Lms
where L0 represents free space loss, Lrts represents the "rooftop-to-street diffraction
and scatter loss", and Lms denotes multiscreen thffiaction loss due to
the rows of buildings [X1a92]. This model is being considered for use
by ITU-R in the IMT-2000 standards activities.
THIS PARAGRAPH IS FROM THE BOOK: Wireless Communications by Theodore S. Rappaport, p157, ch 4.11
Limitations
Though based on the Okumura Model, the Hata model does not provide coverage to the whole range of frequencies covered by Okumura Model. Hata model does not go beyond 1500 MHz while Okumura provides support for up to 1920 MHz.External links
- "On the use of the universal Okumura-Hata propagation predictionmodel in rural areas" IEEE Explore Retrieved on April 12, 2009
- VOLCANO advanced radio propagation model including both direct-path and multi-path ray-tracingRay tracing (physics)In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces,...
models
See also
- Cost 231 ModelCost 231 ModelThe COST-Hata-Model is the most often cited of the COST 231 models. Also called the Hata Model PCS Extension, it is a radio propagation model that extends the Hata Model to cover a more elaborated range of frequencies...
- Radio propagation modelRadio propagation modelA radio propagation model, also known as the Radio Wave Propagation Model or the Radio Frequency Propagation Model, is an empirical mathematical formulation for the characterization of radio wave propagation as a function of frequency, distance and other conditions...
- Ray tracing (physics)Ray tracing (physics)In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces,...

