
Hausman test
Encyclopedia
The Hausman test or Hausman specification test is a statistical
test in econometrics
named after Jerry A. Hausman
. The test evaluates the significance of an estimator
versus an alternative estimator
. It helps one evaluate if a statistical model corresponds to the data.
and X is vector of regressors, b is a vector of coefficients and e is the error term. We have two estimators for b: b0 and b1. Under the null hypothesis
, both of these estimators are consistent
, but b1 is efficient
(has the smallest asymptotic variance), at least in the class of estimators containing b0. Under the alternative hypothesis, b0 is consistent, whereas b1 isn’t.
Then the Hausman statistic
is:
where † denotes the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse. This statistic has asymptotically the chi-squared distribution with the number of degrees of freedom equal to the rank of matrix .
If we reject the null hypothesis, one or both of the estimators is inconsistent. This test can be used to check for the endogeneity
of a variable (by comparing instrumental variable
(IV) estimates to ordinary least squares
(OLS) estimates). It can also be used to check the validity of extra instruments
by comparing IV estimates using a full set of instruments Z to IV estimates that use a proper subset of Z. Note that in order for the test to work in the latter case, we must be certain of the validity of the subset of Z and that subset must have enough instruments to identify the parameters of the equation.
Hausman also showed that the covariance between an efficient estimator and the difference of an efficient and inefficient estimator is zero.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
test in econometrics
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
named after Jerry A. Hausman
Jerry A. Hausman
Jerry A. Hausman is the John and Jennie S. MacDonald Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a famous econometrician. He has also published numerous papers in applied microeconomics...
. The test evaluates the significance of an estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
versus an alternative estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
. It helps one evaluate if a statistical model corresponds to the data.
Details
Consider the linear model y = bX + e, where y is univariateUnivariate
In mathematics, univariate refers to an expression, equation, function or polynomial of only one variable. Objects of any of these types but involving more than one variable may be called multivariate...
and X is vector of regressors, b is a vector of coefficients and e is the error term. We have two estimators for b: b0 and b1. Under the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
, both of these estimators are consistent
Consistent estimator
In statistics, a sequence of estimators for parameter θ0 is said to be consistent if this sequence converges in probability to θ0...
, but b1 is efficient
Efficiency (statistics)
In statistics, an efficient estimator is an estimator that estimates the quantity of interest in some “best possible” manner. The notion of “best possible” relies upon the choice of a particular loss function — the function which quantifies the relative degree of undesirability of estimation errors...
(has the smallest asymptotic variance), at least in the class of estimators containing b0. Under the alternative hypothesis, b0 is consistent, whereas b1 isn’t.
Then the Hausman statistic
Statistic
A statistic is a single measure of some attribute of a sample . It is calculated by applying a function to the values of the items comprising the sample which are known together as a set of data.More formally, statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function...
is:
-
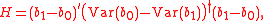
- (reference: Greene Econometrics Text)
where † denotes the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse. This statistic has asymptotically the chi-squared distribution with the number of degrees of freedom equal to the rank of matrix .
If we reject the null hypothesis, one or both of the estimators is inconsistent. This test can be used to check for the endogeneity
Endogeneity (economics)
In an econometric model, a parameter or variable is said to be endogenous when there is a correlation between the parameter or variable and the error term. Endogeneity can arise as a result of measurement error, autoregression with autocorrelated errors, simultaneity, omitted variables, and sample...
of a variable (by comparing instrumental variable
Instrumental variable
In statistics, econometrics, epidemiology and related disciplines, the method of instrumental variables is used to estimate causal relationships when controlled experiments are not feasible....
(IV) estimates to ordinary least squares
Ordinary least squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares or linear least squares is a method for estimating the unknown parameters in a linear regression model. This method minimizes the sum of squared vertical distances between the observed responses in the dataset and the responses predicted by the linear...
(OLS) estimates). It can also be used to check the validity of extra instruments
Instrumental variable
In statistics, econometrics, epidemiology and related disciplines, the method of instrumental variables is used to estimate causal relationships when controlled experiments are not feasible....
by comparing IV estimates using a full set of instruments Z to IV estimates that use a proper subset of Z. Note that in order for the test to work in the latter case, we must be certain of the validity of the subset of Z and that subset must have enough instruments to identify the parameters of the equation.
Hausman also showed that the covariance between an efficient estimator and the difference of an efficient and inefficient estimator is zero.

