
He (letter)
Encyclopedia
He is the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician
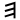 , Aramaic
, Aramaic
, Hebrew
, Syriac
and Arabic
. Its sound value is a voiceless glottal fricative
([h]).
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
Epsilon
, Etruscan , Latin
E
and Cyrillic
Е
. He, like all Phoenician letters, represented a consonant
, but the Latin, Greek and Cyrillic equivalents have all come to represent vowel
sounds.
V28 "thread
",
A28 "jubilation", compare South Arabian
 ,
,  ,
,  , Ge'ez
, Ge'ez
ሀ, ሐ, ኀ, andO6 "court
". In the Phoenician alphabet
, and are merged into Heth
"fence", while is replaced by He "window
".
Hebrew spelling:
, the letter represents a voiceless glottal fricative
. /h/ may also be dropped, although this pronunciation is seen as substandard.
Also, in many variant Hebrew pronunciations the letter may represent a glottal stop. In word-final position, He is used to indicate an a-vowel, usually that of qamatz (ָ ), and in this sense functions like Aleph
, Vav
, and Yud
as a mater lectionis
, indicating the presence of a long vowel.
Hei, along with Aleph, Ayin
, Resh
, and Heth
, cannot receive a dagesh. Nonetheless, it does receive a marking identical to the dagesh, to form Hei-mappiq (הּ). Although indistinguishable for most modern speakers or readers of Hebrew, the mapiq is placed in a word-final Hei to indicate that the letter is not merely a mater lectionis, but that the consonant should be aspirated in that position. It is generally used in Hebrew to indicate the third-person feminine singular genitive marker. Today such a pronunciation only occurs in religious contexts, and then often only by careful readers of the scriptures.
, Hei symbolizes the number five, and when used at the beginning of Hebrew years
, it means 5000 (i.e. התשנ״ד in numbers
would be the date
5754).
Attached to words, Hei may have three possible meanings:
in modern hebrew the frequency of the usage of he, out of all the letters, is 8.18%.
Hei, representing five in gematria, is often found on amulets, symbolizing the five fingers of a hand, a very common talismanic symbol
.
: ה׳.
In the Syriac alphabet
, the fifth letter is — Heh . It is pronounced as an[ h
] . At the end of a word with a point above it, it represents the third-person
feminine
singular
suffix
. Without the point, it stands for the masculine equivalent. Standing alone with a horizontal line above it, it is the abbreviation
for either hānoh , meaning 'this is' or 'that is', or halelûya
. As a numeral, He represents the number five.
is used as a suffix (with the harakat
dictated by ) indicating possession
, indicating that the noun marked with the suffix belongs to a specific masculine
possessor; for example, كتاب ("book") becomes كتابه ("his book") with the addition of final ; the possessor is implied in the suffix. A longer example, هو يقرأ كتابه, (huwa yaqraʼu kitābahu, "he reads his book") more clearly indicates the possessor.
The suffix appended to a verb represents a masculine object
(e.g. يقرأه, , "he reads it").
The feminine form of this construction is in both cases ـها .
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
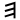
Aramaic alphabet
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....
, Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
, Syriac
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
and Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
. Its sound value is a voiceless glottal fricative
Voiceless glottal fricative
The voiceless glottal transition, commonly called a "fricative", is a type of sound used in some spoken languages which patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant...
([h]).
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
Epsilon
Epsilon
Epsilon is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a close-mid front unrounded vowel . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 5. It was derived from the Phoenician letter He...
, Etruscan , Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
E
E
E is the fifth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is the most commonly used letter in the Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Hungarian, Latin, Norwegian, Spanish, and Swedish languages.-History:...
and Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
Е
Ye (Cyrillic)
Ye is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. In some languages this letter is called E.It commonly represents the vowel or , like the pronunciation of ⟨e⟩ in "yes".Ye is romanized using the Latin letter E....
. He, like all Phoenician letters, represented a consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
, but the Latin, Greek and Cyrillic equivalents have all come to represent vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
sounds.
Origins
In Proto-Northwest Semitic there were still three voiceless fricatives: uvular , glottal , and pharyngeal . In the Wadi el-Hol script, these appear to be expressed by derivatives ofYarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery and ropemaking. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or...
",
South Arabian alphabet
The ancient Yemeni alphabet branched from the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet in about the 9th century BC. It was used for writing the Yemeni Old South Arabic languages of the Sabaean, Qatabanian, Hadramautic, Minaean, Himyarite, and proto-Ge'ez in Dʿmt...
 ,
,  ,
,  , Ge'ez
, Ge'ezGe'ez alphabet
Ge'ez , also called Ethiopic, is a script used as an abugida for several languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea but originated in an abjad used to write Ge'ez, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian and Eritrean Orthodox Church...
ሀ, ሐ, ኀ, and
Court
A court is a form of tribunal, often a governmental institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law...
". In the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, and are merged into Heth
Heth (letter)
' or ' is the reconstructed name of the eighth letter of the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, continued in descended Semitic alphabets as Phoenician , Syriac , Hebrew ḥēth , Arabic , and Berber .Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or...
"fence", while is replaced by He "window
Window
A window is a transparent or translucent opening in a wall or door that allows the passage of light and, if not closed or sealed, air and sound. Windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material like float glass. Windows are held in place by frames, which...
".
Hebrew Hei
| Orthographic Orthography The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography... variants |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various Print Fonts | Cursive Hebrew |
Rashi Script Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
||
| Serif | Sans-serif Sans-serif In typography, a sans-serif, sans serif or san serif typeface is one that does not have the small projecting features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. The term comes from the French word sans, meaning "without".... | Monospaced | ||
| ה | ה | ה |  |
 |
Hebrew spelling:
Pronunciation
In modern HebrewHebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, the letter represents a voiceless glottal fricative
Voiceless glottal fricative
The voiceless glottal transition, commonly called a "fricative", is a type of sound used in some spoken languages which patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant...
. /h/ may also be dropped, although this pronunciation is seen as substandard.
Also, in many variant Hebrew pronunciations the letter may represent a glottal stop. In word-final position, He is used to indicate an a-vowel, usually that of qamatz (ָ ), and in this sense functions like Aleph
Aleph
* Aleph or Alef is the first letter of the Semitic abjads descended from Proto-Canaanite, Arabic alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Syriac alphabet-People:*Aleph , an Italo disco artist and alias of Dave Rodgers...
, Vav
Vav
VAV as a three-letter abbreviation may refer to* A Volcanic Ash Victim meaning someone who has been left stranded by a volcanic ash cloud that is hindering air travel.* A variable air volume device, used in HVAC systems to control the flow of air...
, and Yud
Yodh
Yodh is the tenth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Yud , Syriac and Arabic...
as a mater lectionis
Mater lectionis
In the spelling of Hebrew and some other Semitic languages, matres lectionis , refers to the use of certain consonants to indicate a vowel. The letters that do this in Hebrew are aleph, he, waw and yod...
, indicating the presence of a long vowel.
Hei, along with Aleph, Ayin
Ayin
' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet...
, Resh
Resh
Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew....
, and Heth
Heth (letter)
' or ' is the reconstructed name of the eighth letter of the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, continued in descended Semitic alphabets as Phoenician , Syriac , Hebrew ḥēth , Arabic , and Berber .Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or...
, cannot receive a dagesh. Nonetheless, it does receive a marking identical to the dagesh, to form Hei-mappiq (הּ). Although indistinguishable for most modern speakers or readers of Hebrew, the mapiq is placed in a word-final Hei to indicate that the letter is not merely a mater lectionis, but that the consonant should be aspirated in that position. It is generally used in Hebrew to indicate the third-person feminine singular genitive marker. Today such a pronunciation only occurs in religious contexts, and then often only by careful readers of the scriptures.
Significance of Hei
In gematriaGematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
, Hei symbolizes the number five, and when used at the beginning of Hebrew years
Hebrew calendar
The Hebrew calendar , or Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today predominantly for Jewish religious observances. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate public reading of Torah portions, yahrzeits , and daily Psalm reading, among many ceremonial uses...
, it means 5000 (i.e. התשנ״ד in numbers
Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
would be the date
Calendar date
A date in a calendar is a reference to a particular day represented within a calendar system. The calendar date allows the specific day to be identified. The number of days between two dates may be calculated. For example, "24 " is ten days after "14 " in the Gregorian calendar. The date of a...
5754).
Attached to words, Hei may have three possible meanings:
- A preposition meaning "the", "that", or "who" (as in "a boy who reads"). For example, yeled, a boy; hayeled, the boy.
- A prefix indicating that the sentence is a question. (For example, Yadata, You knew; Hayadata?, Did you know?)
- A suffix after place names indicating movement towards the given noun. (For example, Yerushalayim, Jerusalem; Yerushalaymah, towards Jerusalem.)
in modern hebrew the frequency of the usage of he, out of all the letters, is 8.18%.
Hei, representing five in gematria, is often found on amulets, symbolizing the five fingers of a hand, a very common talismanic symbol
Hamsa
Hamsa or Khamsa can refer to:*Arabic "five, quintet"** Ḫamsa, a Near Eastern symbol often used as a protective amulet** a commonly used alternative name for the Panj Ganj or Quinary, ie quintet of Nizami's first five great epics*Sanskrit ...
.
In Judaism
Hei is often used to represent the name of God, as He stands for Hashem, which means The Name and is a way of saying God without actually saying the name of God. In print, Hashem is usually written as Hei with a gereshGeresh
Geresh is a sign in Hebrew writing. It has two meanings.#An apostrophe-like sign placed after a letter :...
: ה׳.
Syriac Heh
| Heh |
|---|
| Madnḫaya Heh |
| Serṭo Heh |
| Esṭrangela Heh |
In the Syriac alphabet
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
, the fifth letter is — Heh . It is pronounced as an
Voiceless glottal fricative
The voiceless glottal transition, commonly called a "fricative", is a type of sound used in some spoken languages which patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant...
Grammatical person
Grammatical person, in linguistics, is deictic reference to a participant in an event; such as the speaker, the addressee, or others. Grammatical person typically defines a language's set of personal pronouns...
feminine
Grammatical gender
Grammatical gender is defined linguistically as a system of classes of nouns which trigger specific types of inflections in associated words, such as adjectives, verbs and others. For a system of noun classes to be a gender system, every noun must belong to one of the classes and there should be...
singular
Grammatical number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, and adjective and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions ....
suffix
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs...
. Without the point, it stands for the masculine equivalent. Standing alone with a horizontal line above it, it is the abbreviation
Abbreviation
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. Usually, but not always, it consists of a letter or group of letters taken from the word or phrase...
for either hānoh , meaning 'this is' or 'that is', or halelûya
Hallelujah
Hallelujah, Halleluyah, and the Latin form Alleluia are transliterations of the Hebrew word meaning "Praise Yah". The last syllable is from the first two letters of the name of God, YHWH, written JHVH in Latin). Hallelujah is found primarily in the book of Psalms...
. As a numeral, He represents the number five.
Arabic hāʾ
The letter is named . Commonly known in Egypt as he. It is written in several ways depending on its position in the word:is used as a suffix (with the harakat
Harakat
The Arabic script has numerous diacritics, including ijam ⟨⟩ , and tashkil ⟨⟩...
dictated by ) indicating possession
Possession (linguistics)
Possession, in the context of linguistics, is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which possesses the referent of the other ....
, indicating that the noun marked with the suffix belongs to a specific masculine
Grammatical gender
Grammatical gender is defined linguistically as a system of classes of nouns which trigger specific types of inflections in associated words, such as adjectives, verbs and others. For a system of noun classes to be a gender system, every noun must belong to one of the classes and there should be...
possessor; for example, كتاب ("book") becomes كتابه ("his book") with the addition of final ; the possessor is implied in the suffix. A longer example, هو يقرأ كتابه, (huwa yaqraʼu kitābahu, "he reads his book") more clearly indicates the possessor.
The suffix appended to a verb represents a masculine object
Object (grammar)
An object in grammar is part of a sentence, and often part of the predicate. It denotes somebody or something involved in the subject's "performance" of the verb. Basically, it is what or whom the verb is acting upon...
(e.g. يقرأه, , "he reads it").
The feminine form of this construction is in both cases ـها .

