
Aramaic alphabet
Encyclopedia
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet
and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonant
s, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowel
s.
The Aramaic alphabet
is historically significant, since virtually all modern Middle East
ern writing systems use a script
that can be traced back to it, as well as numerous Altaic
writing systems of Central and East Asia. This is primarily due to the widespread usage of the Aramaic language as both a lingua franca
and the official language of the Neo-Assyrian, and its successor, the Achaemenid Empire
. Among the scripts in modern use, the Hebrew alphabet
bears the closest relation to the Imperial Aramaic script
of the 5th century BC, with an identical letter inventory and, for the most part, nearly identical letter shapes.
Writing systems that indicate consonants but do not indicate most vowels (like the Aramaic one) or indicate them with added diacritical signs, have been called abjad
s by Peter T. Daniels
to distinguish them from later alphabets, such as Greek, that represent vowels more systematically. This is to avoid the notion that a writing system that represents sounds must be either a syllabary or an alphabet, which implies that a system like Aramaic must be either a syllabary (as argued by Gelb) or an incomplete or deficient alphabet (as most other writers have said); rather, it is a different type.
use the Phoenician alphabet
. Over time, the alphabet developed into the form shown below. Aramaic gradually became the lingua franca throughout the Middle East, with the script at first complementing and then displacing Assyrian cuneiform as the predominant writing system.
conquest of Mesopotamia under Darius I
, Old Aramaic was adopted by the conquerors as the "vehicle for written communication between the different regions of the vast empire with its different peoples and languages. The use of a single official language, which modern scholarship has dubbed Official Aramaic or Imperial Aramaic, can be assumed to have greatly contributed to the astonishing success of the Achaemenids in holding their far-flung empire together for as long as they did."
Imperial Aramaic was highly standardised; its orthography was based more on historical roots than any spoken dialect and was inevitably influenced by Old Persian.
For centuries after the fall of the Achaemenid Empire in 331 BC, Imperial Aramaic—or near enough for it to be recognisable—would remain an influence on the various native Iranian languages
. The Aramaic script would survive as the essential characteristics of the Pahlavi writing system
.
A group of thirty Aramaic documents from Bactria
have been recently discovered. An analysis was published in November 2006. The texts, which were rendered on leather, reflect the use of Aramaic in the 4th century BC. Achaemenid administration of Bactria and Sogdiana
.
Its widespread usage led to the gradual adoption of the Aramaic alphabet for writing the Hebrew language
. Formerly, Hebrew had been written using an alphabet closer in form to that of Phoenician (the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet
).
After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, the unity of the Imperial Aramaic script was lost, diversifying into a number of descendant cursives.
The Hebrew
and Nabataean alphabets, as they stood by the Roman era, were little changed in style from the Imperial Aramaic alphabet.
A Cursive Hebrew variant developed from the early centuries AD, but it remained restricted to the status of a variant used alongside the non-cursive. By contrast, the cursive developed out of the Nabataean alphabet in the same period soon became the standard for writing Arabic, evolving into the Arabic alphabet
as it stood by the time of the early spread of Islam.
The development of cursive versions of Aramaic also led to the creation of the Syriac
, Palmyrenean and Mandaic alphabet
s. These scripts formed the basis of the historical scripts of Central Asia, such as the Sogdian
and Mongolian
alphabets.
The Old Turkic script evident in epigraphy from the 8th century likely also has its origins in the Aramaic script.
, Jewish Neo-Aramaic dialects and the Aramaic language of the Talmud
are written in the Hebrew alphabet. Syriac
and Christian Neo-Aramaic dialects are written in the Syriac alphabet
. Mandaic
is written in the Mandaic alphabet
.
Due to the near-identity of the Aramaic and the classical Hebrew alphabets, Aramaic text is mostly typeset in standard Hebrew script in scholarly literature.
Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Imperial Aramaic is U+10840–U+1085F:
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s.
The Aramaic alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
is historically significant, since virtually all modern Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
ern writing systems use a script
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
that can be traced back to it, as well as numerous Altaic
Altaic languages
Altaic is a proposed language family that includes the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, and Japonic language families and the Korean language isolate. These languages are spoken in a wide arc stretching from northeast Asia through Central Asia to Anatolia and eastern Europe...
writing systems of Central and East Asia. This is primarily due to the widespread usage of the Aramaic language as both a lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
and the official language of the Neo-Assyrian, and its successor, the Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
. Among the scripts in modern use, the Hebrew alphabet
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
bears the closest relation to the Imperial Aramaic script
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
of the 5th century BC, with an identical letter inventory and, for the most part, nearly identical letter shapes.
Writing systems that indicate consonants but do not indicate most vowels (like the Aramaic one) or indicate them with added diacritical signs, have been called abjad
Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
s by Peter T. Daniels
Peter T. Daniels
Peter T. Daniels is a scholar of writing systems, specializing in typology. He was co-editor of the book The World's Writing Systems , and he introduced the terms abjad and abugida as modern linguistic terms...
to distinguish them from later alphabets, such as Greek, that represent vowels more systematically. This is to avoid the notion that a writing system that represents sounds must be either a syllabary or an alphabet, which implies that a system like Aramaic must be either a syllabary (as argued by Gelb) or an incomplete or deficient alphabet (as most other writers have said); rather, it is a different type.
Origins
The earliest inscriptions in the Aramaic languageAramaic language
Aramaic is a group of languages belonging to the Afroasiatic language phylum. The name of the language is based on the name of Aram, an ancient region in central Syria. Within this family, Aramaic belongs to the Semitic family, and more specifically, is a part of the Northwest Semitic subfamily,...
use the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
. Over time, the alphabet developed into the form shown below. Aramaic gradually became the lingua franca throughout the Middle East, with the script at first complementing and then displacing Assyrian cuneiform as the predominant writing system.
Achaemenid period
Around 500 BC, following the AchaemenidAchaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
conquest of Mesopotamia under Darius I
Darius I of Persia
Darius I , also known as Darius the Great, was the third king of kings of the Achaemenid Empire...
, Old Aramaic was adopted by the conquerors as the "vehicle for written communication between the different regions of the vast empire with its different peoples and languages. The use of a single official language, which modern scholarship has dubbed Official Aramaic or Imperial Aramaic, can be assumed to have greatly contributed to the astonishing success of the Achaemenids in holding their far-flung empire together for as long as they did."
Imperial Aramaic was highly standardised; its orthography was based more on historical roots than any spoken dialect and was inevitably influenced by Old Persian.
For centuries after the fall of the Achaemenid Empire in 331 BC, Imperial Aramaic—or near enough for it to be recognisable—would remain an influence on the various native Iranian languages
Iranian languages
The Iranian languages form a subfamily of the Indo-Iranian languages which in turn is a subgroup of Indo-European language family. They have been and are spoken by Iranian peoples....
. The Aramaic script would survive as the essential characteristics of the Pahlavi writing system
Pahlavi scripts
Pahlavi or Pahlevi denotes a particular and exclusively written form of various Middle Iranian languages. The essential characteristics of Pahlavi are*the use of a specific Aramaic-derived script, the Pahlavi script;...
.
A group of thirty Aramaic documents from Bactria
Bactria
Bactria and also appears in the Zend Avesta as Bukhdi. It is the ancient name of a historical region located between south of the Amu Darya and west of the Indus River...
have been recently discovered. An analysis was published in November 2006. The texts, which were rendered on leather, reflect the use of Aramaic in the 4th century BC. Achaemenid administration of Bactria and Sogdiana
Sogdiana
Sogdiana or Sogdia was the ancient civilization of an Iranian people and a province of the Achaemenid Empire, eighteenth in the list on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great . Sogdiana is "listed" as the second of the "good lands and countries" that Ahura Mazda created...
.
Its widespread usage led to the gradual adoption of the Aramaic alphabet for writing the Hebrew language
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
. Formerly, Hebrew had been written using an alphabet closer in form to that of Phoenician (the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet
Paleo-Hebrew alphabet
The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet , is an abjad offshoot of the ancient Semitic alphabet, identical to the Phoenician alphabet. At the very least it dates to the 10th century BCE...
).
Aramaic-derived scripts
Since the evolution of the Aramaic alphabet out of the Phoenician one was a gradual process, the division of the world's alphabets into those derived from the Phoenician one directly and those derived from Phoenician via Aramaic is somewhat artificial. In general, the alphabets of the Mediterranean region (Anatolia, Greece, Italy) are classified as Phoenician-derived, adapted from around the 8th century BC, while those of the East (the Levant, Persia, Central Asia and India) are considered Aramaic-derived, adapted from around the 6th century BC from the Imperial Aramaic script of the Achaemenid Empire.After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, the unity of the Imperial Aramaic script was lost, diversifying into a number of descendant cursives.
The Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
and Nabataean alphabets, as they stood by the Roman era, were little changed in style from the Imperial Aramaic alphabet.
A Cursive Hebrew variant developed from the early centuries AD, but it remained restricted to the status of a variant used alongside the non-cursive. By contrast, the cursive developed out of the Nabataean alphabet in the same period soon became the standard for writing Arabic, evolving into the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
as it stood by the time of the early spread of Islam.
The development of cursive versions of Aramaic also led to the creation of the Syriac
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
, Palmyrenean and Mandaic alphabet
Mandaic alphabet
The Mandaic alphabet is based on the Aramaic alphabet, and is used for writing the Mandaic language.The Mandaic name for the script is Abagada or Abaga, after the first letters of the alphabet...
s. These scripts formed the basis of the historical scripts of Central Asia, such as the Sogdian
Sogdian alphabet
The Sogdian alphabet was originally used for the Sogdian language, a language in the Iranian family used by the people of Sogdiana. The alphabet is derived from Syriac, the descendant script of the Aramaic alphabet. The Sogdian alphabet is one of three scripts used to write the Sogdian language,...
and Mongolian
Mongolian script
The classical Mongolian script , also known as Uyghurjin, was the first writing system created specifically for the Mongolian language, and was the most successful until the introduction of Cyrillic in 1946...
alphabets.
The Old Turkic script evident in epigraphy from the 8th century likely also has its origins in the Aramaic script.
Modern
Today, Biblical AramaicBiblical Aramaic
Biblical Aramaic is the form of the Aramaic language that is used in the books of Daniel, Ezra and a few other places in the Hebrew Bible and should not be confused with the Aramaic translations of the Hebrew Bible known as targumim....
, Jewish Neo-Aramaic dialects and the Aramaic language of the Talmud
Talmud
The Talmud is a central text of mainstream Judaism. It takes the form of a record of rabbinic discussions pertaining to Jewish law, ethics, philosophy, customs and history....
are written in the Hebrew alphabet. Syriac
Syriac language
Syriac is a dialect of Middle Aramaic that was once spoken across much of the Fertile Crescent. Having first appeared as a script in the 1st century AD after being spoken as an unwritten language for five centuries, Classical Syriac became a major literary language throughout the Middle East from...
and Christian Neo-Aramaic dialects are written in the Syriac alphabet
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
. Mandaic
Mandaic language
The Mandaic language is the language of the Mandaean religion. Classical Mandaic is used by a section of the Mandaean community in liturgical rites....
is written in the Mandaic alphabet
Mandaic alphabet
The Mandaic alphabet is based on the Aramaic alphabet, and is used for writing the Mandaic language.The Mandaic name for the script is Abagada or Abaga, after the first letters of the alphabet...
.
Due to the near-identity of the Aramaic and the classical Hebrew alphabets, Aramaic text is mostly typeset in standard Hebrew script in scholarly literature.
Imperial Aramaic alphabet
Redrawn from A Grammar of Biblical Aramaic, Franz Rosenthal; forms are as used in Egypt, 5th century BC. Names are as in Biblical Aramaic.| Letter name | Letter form | Letter | Equivalent Hebrew | Equivalent Arabic | Equivalent Syriac | Sound value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ālaph Aleph * Aleph or Alef is the first letter of the Semitic abjads descended from Proto-Canaanite, Arabic alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Syriac alphabet-People:*Aleph , an Italo disco artist and alias of Dave Rodgers... |
 |
𐡀 | א | أ | ܐ | /ʔ/; /aː/, /eː/ |
| Bēth Bet (letter) Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac... |
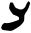 |
𐡁 | ב | ب | ܒ | /b/, /v/ |
| Gāmal Gimel (letter) Gimel is the third letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew , Syriac and Arabic... |
 |
𐡂 | ג | ج | ܓ | /ɡ/, /ɣ/ |
| Dālath Dalet Dalet is the fourth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew , Syriac and Arabic... |
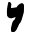 |
𐡃 | ד | د | ܕ | /d/, /ð/ |
| Hē He (letter) He is the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician , Aramaic, Hebrew , Syriac and Arabic . Its sound value is a voiceless glottal fricative .... |
 |
𐡄 | ה | ﻫ | ܗ | /h/ |
| Waw Waw (letter) Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic .... |
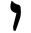 |
𐡅 | ו | و | ܘ | /w/; /oː/, /uː/ |
| Zain Zayin Zayin is the seventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic , Hebrew , Syriac and Perso-Arabic alphabet... |
 |
𐡆 | ז | ز | ܙ | /z/ |
| Ḥēth Heth (letter) ' or ' is the reconstructed name of the eighth letter of the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, continued in descended Semitic alphabets as Phoenician , Syriac , Hebrew ḥēth , Arabic , and Berber .Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or... |
 |
𐡇 | ח | خ,ح | ܚ | /ħ/ |
| Ṭēth Teth ' is the ninth letter of many Semitic abjads , including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Tet , Syriac and Arabic ; it is 9th in abjadi order and 16th in modern Arabic order.... |
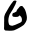 |
𐡈 | ט | ط | ܛ | emphatic Emphatic consonant Emphatic consonant is a term widely used in Semitic linguistics to describe one of a series of obstruent consonants which originally contrasted with series of both voiced and voiceless obstruents. In specific Semitic languages, the members of this series may be realized as pharyngealized,... /tˤ/ |
| Yudh Yodh Yodh is the tenth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Yud , Syriac and Arabic... |
 |
𐡉 | י | ي | ܝ | /j/; /iː/, /eː/ |
| Kāph Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... |
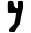 |
𐡊 | כ ך | ك | ܟܟ | /k/, /x/ |
| Lāmadh Lamedh Lamed or Lamedh is the twelfth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Lamed and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is .The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Lambda , Latin L, and Cyrillic Л.-Origins:... |
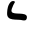 |
𐡋 | ל | ل | ܠ | /l/ |
| Mim Mem Mem is the thirteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic... |
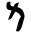 |
𐡌 | מ ם | م | ܡܡ | /m/ |
| Nun Nun (letter) Nun is the fourteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . It is the third letter in Thaana , pronounced as "noonu"... |
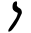 |
𐡍 | נ ן | ن | ܢܢ ܢ | /n/ |
| Semkath Samekh Samekh or Simketh is the fifteenth letter in many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Hebrew, and Aramaic, representing . The Arabic alphabet, however, uses a letter based on Phoenician šin to represent ; however, that glyph takes Samekh's place in the traditional Abjadi order of the Arabic... |
 |
𐡎 | ס | س | ܣ | /s/ |
| ‘Ē Ayin ' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet... |
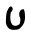 |
𐡏 | ע | غ,ع | ܥ | /ʕ/ |
| Pē Pe (letter) Pe is the seventeenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Pei and Persian, Arabic .... |
 |
𐡐 | פ ף | ف | ܦ | /p/, /f/ |
| Ṣādhē Tsade ' is the eighteenth letter in many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew ' and Arabic ' . Its oldest sound value is probably , although there is a variety of pronunciation in different modern Semitic languages and their dialects... |
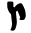 , , 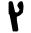 |
𐡑 | צ ץ | ص | ܨ | emphatic /sˤ/ |
| Qoph Qoph Qoph or Qop is the nineteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Syriac, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is an emphatic or . The OHED gives the letter Qoph a transliteration value of Q or a K and a final transliteration value as a ck... |
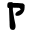 |
𐡒 | ק | ق | ܩ | /q/ |
| Rēsh Resh Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew.... |
 |
𐡓 | ר | ر | ܪ | /r/ |
| Shin Shin (letter) Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic .... |
 |
𐡔 | ש | ش,س | ܫ | /ʃ/ |
| Tau Taw (letter) Taw, Tav or Taf is the twenty-second and last letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Taw and Arabic alphabet .Its original sound value is .... |
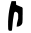 |
𐡕 | ת | ت,ث | ܬ | /t/, /θ/ |
* Arabic س sīn derives only its position in the traditional abjadi orderAbjad numeralsThe Abjad numerals are a decimal numeral system in which the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet are assigned numerical values. They have been used in the Arabic-speaking world since before the 8th century Arabic numerals...
in the Arabic alphabet from samekh; its shape is derived from shīn as a function of a sound changeSound changeSound change includes any processes of language change that affect pronunciation or sound system structures...
from Proto-West or Central SemiticProto-Semitic languageProto-Semitic is the hypothetical proto-language ancestral to historical Semitic languages of the Middle East. Locations which have been proposed for its origination include northern Mesopotamia, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Levant with a 2009 study proposing that it may have originated around...
to ArabicArabic languageArabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
.
Matres lectionis
The letters Waw and Yudh, put following the consonants that were followed by the vowels u and i (and often also o and e), are used to indicate the long vowels û and î respectively (often also ô and ê respectively). These letters, which stand for both consonant and vowel sounds, are known as matres lectionis. The letter Alaph, likewise, had some of the characteristics of a mater lectionis: in initial positions, it indicated a specific consonant called glottal stop (followed by a vowel), and, in the middle of the word and word finally, it often also stood for the long vowels â or ê. Among Jews, influence of Hebrew spelling often led to the use of He instead of Alaph in word final positions. The practice of using certain letters to hold vowel values spread to child writing systems of Aramaic, such as Hebrew and Arabic, where they are still used today.Unicode
The Aramaic alphabet was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Imperial Aramaic is U+10840–U+1085F:

