Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Encyclopedia
Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition which has a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrium
, ovary
, stomach
, small intestine
, hepatobiliary tract
, upper urinary tract, brain
, and skin
. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair
.
Other sources reserve the term "Lynch syndrome" when there is a known DNA mismatch repair
defect, and use the term "Familial colorectal cancer type X" when the Amsterdam criteria
are met but there is no known DNA mismatch repair defect. The putative "type X" families appear to have a lower overall incidence of cancer and lower risk for non-colorectal cancers than families with documented DNA mismatch repair deficiency. About 35% of patients meeting Amsterdam criteria do not have a DNA-mismatch-repair gene mutation.
Complicating matters is the presence of an alternative set of criteria, known as the "Bethesda Guidelines".
, MicroSatellite Instability
) cancers can be recognized by histopathological criteria:
. The mean age of colorectal cancer
diagnosis is 44 for members of families that meet the Amsterdam criteria. Also, women with HNPCC have a 80% lifetime risk of endometrial cancer. The average age of diagnosis of endometrial cancer is about 46 years. Among women with HNPCC who have both colon and endometrial cancer, about half present first with endometrial cancer
. In HNPCC, the mean age of diagnosis of gastric cancer is 56 years of age with intestinal-type adenocarcinoma
being the most commonly reported pathology. HNPCC-associated ovarian cancers have an average age of diagnosis of 42.5 years-old; approximately 30% are diagnosed before age 40 years. Other HNPCC-related cancers have been reported with specific features: the urinary tract cancers are transitional carcinoma
of the ureter and renal pelvis
; small bowel cancers occur most commonly in the duodenum
and jejunum
; the central nervous system
tumor most often seen is glioblastoma.
 HNPCC defects in DNA mismatch repair
HNPCC defects in DNA mismatch repair
lead to microsatellite instability
, also known as MSI-H, which is a hallmark of HNPCC. MSI is identifiable in cancer
specimens in the pathology
laboratory. Most cases result in changes in the lengths of dinucleotide repeats of the nucleobase
s cytosine and adenine (sequence: CACACACACA...).
HNPCC is known to be associated with mutations in gene
s involved in the DNA mismatch repair
pathway
Patients with MSH6 mutations are more likely to be Amsterdam criteria II-negative. The presentation with MSH6 is slightly different than with MLH1 and MSH2, and the term "MSH6 syndrome" has been used to describe this condition. In one study, the Bethesda guidelines were more sensitive than the Amsterdam Criteria in detecting it.
Up to 39% of families with mutations in an HNPCC gene do not meet the Amsterdam criteria
. Therefore, families found to have a deleterious mutation in an HNPCC gene should be considered to have HNPCC regardless of the extent of the family history. This also means that the Amsterdam criteria fail to identify many patients at risk for Lynch syndrome. Improving the criteria for screening is an active area of research, as detailed in the Screening Strategies section of this article.
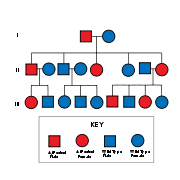
HNPCC is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Most people with HNPCC inherit the condition from a parent. However, due to incomplete penetrance, variable age of cancer diagnosis, cancer risk reduction, or early death, not all patients with an HNPCC gene mutation have a parent who had cancer. Some patients develop HNPCC de-novo in a new generation, without inheriting the gene. These patients are often only identified after developing an early-life colon cancer. Parents with HNPCC have a 50% chance to pass the gene on to each child. However each person is different therefore there is no way to accurately tell who will develop the disorder.
for mutations in DNA mismatch repair
genes is expensive and time-consuming, so researchers have proposed techniques for identifying cancer patients who are most likely to be HNPCC carriers as ideal candidates for genetic testing
. The Amsterdam Criteria
(see below) are useful, but do not identify up to 30% of potential Lynch syndrome carriers. In colon cancer patients, pathologists can measure microsatellite instability
in colon tumor specimens, which is a surrogate marker for DNA mismatch repair
gene dysfunction. If there is microsatellite instability
identified, there is a higher likelihood for a Lynch syndrome diagnosis. Recently, researchers combined microsatellite instability
(MSI) profiling and immunohistochemistry
testing for DNA mismatch repair
gene expression and identified an extra 32% of Lynch syndrome carriers who would have been missed on MSI profiling alone. Currently, this combined immunohistochemistry
and MSI profiling strategy is the most advanced way of identifying candidates for genetic testing
for the Lynch syndrome.
Genetic counseling
and genetic testing
are recommended for families that meet the Amsterdam criteria
, preferably before the onset of colon cancer.
Amsterdam Criteria:
Amsterdam Criteria II:
, and genetic testing
can make a diagnosis of Lynch syndrome. Genetic testing is commercially available and consists of a blood test.
After reporting a null finding from their randomized controlled trial of aspirin (ASA) to prevent against the colorectal neoplasia of Lynch Syndrome, Burn and colleagues have recently reported new data, representing a longer follow-up period than reported in the initial NEJM paper. These new data demonstrate a reduced incidence in Lynch Syndrome patients who were exposed to at least four years of high-dose aspirin, with a satisfactory risk profile. These results have been widely covered in the media; future studies will look at modifying (lowering) the dose (to reduce risk associated with the high dosage of ASA. Individuals with Lynch Syndrome may wish to discuss the application of these results with their medical care team.
are diagnosed each year. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer is responsible for approximately 2 percent to 7 percent of all diagnosed cases of colorectal cancer
. The average age of diagnosis of cancer in patients with this syndrome is 44 years old, as compared to 64 years old in people without the syndrome.
Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer refers to several types of malignancies that arise from the endometrium, or lining, of the uterus. Endometrial cancers are the most common gynecologic cancers in the United States, with over 35,000 women diagnosed each year. The incidence is on a slow rise secondary to the...
, ovary
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
, stomach
Stomach cancer
Gastric cancer, commonly referred to as stomach cancer, can develop in any part of the stomach and may spread throughout the stomach and to other organs; particularly the esophagus, lungs, lymph nodes, and the liver...
, small intestine
Gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, bowels, and anus. The symptoms relate to the organ affected, and can include obstruction , abnormal bleeding, or other associated problems...
, hepatobiliary tract
Gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a relatively uncommon cancer. It has peculiar geographical distribution being common in central and South America, central and eastern Europe, Japan and northern India; it is also common in certain ethnic groups e.g. Native American Indians and Hispanics. If it is diagnosed...
, upper urinary tract, brain
Brain tumor
A brain tumor is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor within the brain or the central spinal canal.Brain tumors include all tumors inside the cranium or in the central spinal canal...
, and skin
Skin cancer
Skin neoplasms are skin growths with differing causes and varying degrees of malignancy. The three most common malignant skin cancers are basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer, and melanoma, each of which is named after the type of skin cell from which it arises...
. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
.
Terminology
Henry T. Lynch (professor of medicine at Creighton University Medical Center), characterized the syndrome in 1966. In his earlier work, he described the disease entity as "cancer family syndrome." The term "Lynch syndrome" was coined in 1984 by other authors, and Lynch himself coined the term HNPCC in 1985. Since then, the two terms have being used interchangeably, until more recent advances in the understanding of the genetics of the disease led to the term HNPCC falling out of favour.Other sources reserve the term "Lynch syndrome" when there is a known DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
defect, and use the term "Familial colorectal cancer type X" when the Amsterdam criteria
Amsterdam criteria
The Amsterdam criteria are a set of diagnostic criteria used by doctors to help identify families which are likely to have Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer ....
are met but there is no known DNA mismatch repair defect. The putative "type X" families appear to have a lower overall incidence of cancer and lower risk for non-colorectal cancers than families with documented DNA mismatch repair deficiency. About 35% of patients meeting Amsterdam criteria do not have a DNA-mismatch-repair gene mutation.
Complicating matters is the presence of an alternative set of criteria, known as the "Bethesda Guidelines".
Classification
Three major groups of MSI-H (MSIMicrosatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
, MicroSatellite Instability
Microsatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
) cancers can be recognized by histopathological criteria:
- (1) right-sided poorly differentiated cancers
- (2) right-sided mucinous cancers
- (3) adenocarcinomas in any location showing any measurable level of intraepithelial lymphocyteIntraepithelial lymphocyteIntraepithelial lymphocytes are lymphocytes found in the epithelial layer of mammalian mucosal linings, such as the gastrointestinal tract and reproductive tract. However, unlike other T cells, IELs do not need priming. Upon encountering antigens, they immediately release cytokines and cause...
(TIL)
Risk of colon cancer
Individuals with HNPCC have about an 80% lifetime risk for colon cancer. Two-thirds of these cancers occur in the proximal colonColon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
. The mean age of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
diagnosis is 44 for members of families that meet the Amsterdam criteria. Also, women with HNPCC have a 80% lifetime risk of endometrial cancer. The average age of diagnosis of endometrial cancer is about 46 years. Among women with HNPCC who have both colon and endometrial cancer, about half present first with endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer refers to several types of malignancies that arise from the endometrium, or lining, of the uterus. Endometrial cancers are the most common gynecologic cancers in the United States, with over 35,000 women diagnosed each year. The incidence is on a slow rise secondary to the...
. In HNPCC, the mean age of diagnosis of gastric cancer is 56 years of age with intestinal-type adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is a cancer of an epithelium that originates in glandular tissue. Epithelial tissue includes, but is not limited to, the surface layer of skin, glands and a variety of other tissue that lines the cavities and organs of the body. Epithelium can be derived embryologically from...
being the most commonly reported pathology. HNPCC-associated ovarian cancers have an average age of diagnosis of 42.5 years-old; approximately 30% are diagnosed before age 40 years. Other HNPCC-related cancers have been reported with specific features: the urinary tract cancers are transitional carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
of the ureter and renal pelvis
Renal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pyelum is the funnel-like dilated proximal part of the ureter in the kidney.In humans, the renal pelvis is the point of convergence of two or three major calyces...
; small bowel cancers occur most commonly in the duodenum
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum...
and jejunum
Jejunum
The jejunum is the middle section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms middle intestine or mid-gut may be used instead of jejunum.The jejunum lies between the duodenum...
; the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
tumor most often seen is glioblastoma.
Genetics

DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
lead to microsatellite instability
Microsatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
, also known as MSI-H, which is a hallmark of HNPCC. MSI is identifiable in cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
specimens in the pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
laboratory. Most cases result in changes in the lengths of dinucleotide repeats of the nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
s cytosine and adenine (sequence: CACACACACA...).
HNPCC is known to be associated with mutations in gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s involved in the DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
pathway
| OMIM name | Genes implicated in HNPCC | Frequency of mutations in HNPCC families | Locus | First publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNPCC1 | MSH2 MSH2 MSH2 is a gene commonly associated with Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.-Interactions:MSH2 has been shown to interact with Exonuclease 1, MSH3, MSH6, CHEK2, MAX, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related and BRCA1.-Further reading:... |
approximately 60% | 2p22 | Fishel et al., 1993 |
| HNPCC2 | MLH1 MLH1 MutL homolog 1, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 2 , also known as MLH1, is a human gene located on Chromosome 3. It is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.It can also be associated with Turcot syndrome.... |
approximately 30% | 3p21 | Papadopoulos et al., 1994 |
| HNPCC5 | MSH6 MSH6 MSH6 is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.-Function:MSH6 contributes to ADP and ATP binding. It also contributes to ATPase activity... |
7-10% | 2p16 | |
| HNPCC4 | PMS2 PMS2 Mismatch repair endonuclease PMS2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PMS2 gene.-Further reading:-External links:* from the National Institute of Health*... |
relatively infrequent, <5% | 7p22 | |
| HNPCC3 | PMS1 PMS1 PMS1 protein homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PMS1 gene.-Further reading:... |
case report | 2q31-q33 | |
| HNPCC6 | TGFBR2 | case report | 3p22 | |
| HNPCC7 | MLH3 MLH3 DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MLH3 gene.-Further reading:... |
disputed | 14q24.3 | |
Patients with MSH6 mutations are more likely to be Amsterdam criteria II-negative. The presentation with MSH6 is slightly different than with MLH1 and MSH2, and the term "MSH6 syndrome" has been used to describe this condition. In one study, the Bethesda guidelines were more sensitive than the Amsterdam Criteria in detecting it.
Up to 39% of families with mutations in an HNPCC gene do not meet the Amsterdam criteria
Amsterdam criteria
The Amsterdam criteria are a set of diagnostic criteria used by doctors to help identify families which are likely to have Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer ....
. Therefore, families found to have a deleterious mutation in an HNPCC gene should be considered to have HNPCC regardless of the extent of the family history. This also means that the Amsterdam criteria fail to identify many patients at risk for Lynch syndrome. Improving the criteria for screening is an active area of research, as detailed in the Screening Strategies section of this article.
HNPCC is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Most people with HNPCC inherit the condition from a parent. However, due to incomplete penetrance, variable age of cancer diagnosis, cancer risk reduction, or early death, not all patients with an HNPCC gene mutation have a parent who had cancer. Some patients develop HNPCC de-novo in a new generation, without inheriting the gene. These patients are often only identified after developing an early-life colon cancer. Parents with HNPCC have a 50% chance to pass the gene on to each child. However each person is different therefore there is no way to accurately tell who will develop the disorder.
Screening
Genetic testingGenetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
for mutations in DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
genes is expensive and time-consuming, so researchers have proposed techniques for identifying cancer patients who are most likely to be HNPCC carriers as ideal candidates for genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
. The Amsterdam Criteria
Amsterdam criteria
The Amsterdam criteria are a set of diagnostic criteria used by doctors to help identify families which are likely to have Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer ....
(see below) are useful, but do not identify up to 30% of potential Lynch syndrome carriers. In colon cancer patients, pathologists can measure microsatellite instability
Microsatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
in colon tumor specimens, which is a surrogate marker for DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
gene dysfunction. If there is microsatellite instability
Microsatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
identified, there is a higher likelihood for a Lynch syndrome diagnosis. Recently, researchers combined microsatellite instability
Microsatellite instability
Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. Although the length of these microsatellites is highly variable from person to person, each individual has microsatellites of a set length. These repeated sequences are common, and normal...
(MSI) profiling and immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry or IHC refers to the process of detecting antigens in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno," in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and...
testing for DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage....
gene expression and identified an extra 32% of Lynch syndrome carriers who would have been missed on MSI profiling alone. Currently, this combined immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry or IHC refers to the process of detecting antigens in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno," in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and...
and MSI profiling strategy is the most advanced way of identifying candidates for genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
for the Lynch syndrome.
Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling or traveling is the process by which patients or relatives, at risk of an inherited disorder, are advised of the consequences and nature of the disorder, the probability of developing or transmitting it, and the options open to them in management and family planning...
and genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
are recommended for families that meet the Amsterdam criteria
Amsterdam criteria
The Amsterdam criteria are a set of diagnostic criteria used by doctors to help identify families which are likely to have Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer ....
, preferably before the onset of colon cancer.
Amsterdam criteria
The following are the Amsterdam criteria in identifying high-risk candidates for molecular genetic testing:Amsterdam Criteria:
- Three or more family members with a confirmed diagnosis of colorectal cancer, one of whom is a first degree (parent, child, sibling) relative of the other two
- Two successive affected generations
- One or more colon cancers diagnosed under age 50 years
- Familial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
(FAP) has been excluded
Amsterdam Criteria II:
- Three or more family members with HNPCC-related cancers, one of whom is a first degree relative of the other two
- Two successive affected generations
- One or more of the HNPCC-related cancers diagnosed under age 50 years
- Familial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
(FAP) has been excluded
Diagnosis
The Amsterdam clinical criteria identifies candidates for genetic testingGenetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
, and genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
can make a diagnosis of Lynch syndrome. Genetic testing is commercially available and consists of a blood test.
Management
Surgery remains the front-line therapists for HNPCC. There is an ongoing controversy over the benefit of 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapies for HNPCC-related colorectal tumours, particularly those in stages I and II.After reporting a null finding from their randomized controlled trial of aspirin (ASA) to prevent against the colorectal neoplasia of Lynch Syndrome, Burn and colleagues have recently reported new data, representing a longer follow-up period than reported in the initial NEJM paper. These new data demonstrate a reduced incidence in Lynch Syndrome patients who were exposed to at least four years of high-dose aspirin, with a satisfactory risk profile. These results have been widely covered in the media; future studies will look at modifying (lowering) the dose (to reduce risk associated with the high dosage of ASA. Individuals with Lynch Syndrome may wish to discuss the application of these results with their medical care team.
Epidemiology
In the United States, about 160,000 new cases of colorectal cancerColorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
are diagnosed each year. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer is responsible for approximately 2 percent to 7 percent of all diagnosed cases of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
. The average age of diagnosis of cancer in patients with this syndrome is 44 years old, as compared to 64 years old in people without the syndrome.
External links
- FAQs on HNPCC from the National Institute of Health
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Lynch syndrome
- National Cancer Institute: Genetics of Colorectal Cancer information summary

