
History of Cameroon
Encyclopedia

Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
.
Early history
The earliest inhabitants of CameroonCameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
were probably the Baka (Pygmies). They still inhabit the forests of the south and east provinces. Bantu
Bantu languages
The Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
speakers originating in the Cameroonian highlands were among the first groups to move out before other invaders. The Mandara kingdom
Mandara Kingdom
The Mandara Kingdom was a West African kingdom in the Mandara Mountains of what is today Cameroon. The Mandarawa people are descended from the kingdom's inhabitants.- History :...
in the Mandara Mountains
Mandara Mountains
The Mandara Mountains are a volcanic range extending about 200km along the northern part of the Cameroon-Nigeria border, from the Benue River in the south to the north-west of Maroua in the north . The highest elevation is 1,494 m , the summit of Mount Oupay .The region is densely populated,...
was founded around 1500 and erected magnificent fortified structures, the purpose and exact history of which are still unresolved. The Aro Confederacy
Aro Confederacy
The Aro Confederacy was a political union orchestrated by the Igbo subgroup, the Aro people, centered in Arochukwu in present day Southeastern Nigeria. Their influence and presence was across Eastern Nigeria into parts of the Niger Delta and Southern Igala during the 18th and 19th centuries...
of Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
may have had presence in western (later called British) Cameroon due to migration in the 18th and 19th centuries.
During the late 1770s and the early 19th century, the Fula
Fula people
Fula people or Fulani or Fulbe are an ethnic group spread over many countries, predominantly in West Africa, but found also in Central Africa and Sudanese North Africa...
ni, a pastoral
Pastoralism
Pastoralism or pastoral farming is the branch of agriculture concerned with the raising of livestock. It is animal husbandry: the care, tending and use of animals such as camels, goats, cattle, yaks, llamas, and sheep. It may have a mobile aspect, moving the herds in search of fresh pasture and...
Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
ic people of the western Sahel
Sahel
The Sahel is the ecoclimatic and biogeographic zone of transition between the Sahara desert in the North and the Sudanian Savannas in the south.It stretches across the North African continent between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea....
, conquered most of what is now northern Cameroon, subjugating or displacing its largely non-Muslim inhabitants.
Although the Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
arrived on Cameroon's doorstep in the 16th century, malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
prevented significant European settlement and conquest of the interior until the late 1870s, when large supplies of the malaria suppressant, quinine
Quinine
Quinine is a natural white crystalline alkaloid having antipyretic , antimalarial, analgesic , anti-inflammatory properties and a bitter taste. It is a stereoisomer of quinidine which, unlike quinine, is an anti-arrhythmic...
, became available. The early European presence in Cameroon was primarily devoted to coastal trade and the acquisition of slaves
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
. The northern part of Cameroon was an important part of the Muslim slave trade network. The slave trade was largely suppressed by the mid-19th century. Christian missions
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
established a presence in the late 19th century and continue to play a role in Cameroonian life.
Colonization
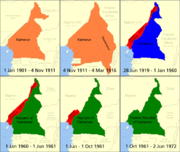

- Further information: German Kamerun, French Cameroun, British Cameroons
Beginning on July 5, 1884, all of present-day Cameroon and parts of several of its neighbours became a German colony
German colonial empire
The German colonial empire was an overseas domain formed in the late 19th century as part of the German Empire. Short-lived colonial efforts by individual German states had occurred in preceding centuries, but Imperial Germany's colonial efforts began in 1884...
, Kamerun
Kamerun
German Cameroon was a West African colony of the German Empire from 1884 to 1916 in the region of today's Republic of Cameroon.-History:-1800s:...
, with a capital first at Buea
Buea
Buea is the capital of the Southwest Region of Cameroon. The town is located on the eastern slopes of Mount Cameroon and has a population of 90,088 . Buea was the colonial capital of the German Kamerun from 1901 to 1919,and the capital of the Southern Cameroons from 1949 until 1961...
and later at Yaoundé
Yaoundé
-Transportation:Yaoundé Nsimalen International Airport is a major civilian hub, while nearby Yaoundé Airport is used by the military. Railway lines run west to the port city of Douala and north to N'Gaoundéré. Many bus companies operate from the city; particularly in the Nsam and Mvan neighborhoods...
.
The Imperial German government made substantial investments in the infrastructure of Cameroon, including the extensive railways, such as the 160-metre single-span railway bridge on the Sanaga South branch. Hospitals were opened all over the colony, including two major hospitals at Douala
Douala
Douala is the largest city in Cameroon and the capital of Cameroon's Littoral Province. Home to Cameroon's largest port and its major international airport, Douala International Airport, it is the commercial capital of the country...
, one of which specialised in tropical diseases (the Germans had discovered the 1912, wrote in an official report in 1919 that the population of Kamerun had increased significantly. However, the indigenous peoples proved reluctant to work on these projects, so the Germans instigated a harsh and unpopular system of forced labour
Unfree labour
Unfree labour includes all forms of slavery as well as all other related institutions .-Payment for unfree labour:If payment occurs, it may be in one or more of the following forms:...
. In fact, Jesko von Puttkamer
Jesko von Puttkamer
Jesko Albert Eugen von Puttkamer was a German colonial military chief, and nine times governor of Kamerun:*13 May 1887 - 4 October 1887*14 August 1890 - 2 December 1890*31 December 1894 - 27 March 1895...
was relieved of duty as governor of the colony due to his untoward actions toward the native Cameroonians. In 1911 at the Treaty of Fez
Treaty of Fez
By the Treaty of Fez , signed March 30, 1912, Sultan Abdelhafid gave up the sovereignty of Morocco to the French, making the country a protectorate, resolving the Agadir Crisis of July 1, 1911....
after the Agadir Crisis
Agadir Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, also called the Second Moroccan Crisis, or the Panthersprung, was the international tension sparked by the deployment of the German gunboat Panther, to the Moroccan port of Agadir on July 1, 1911.-Background:...
, France ceded a nearly 300,000 km² portion of the territory of French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa or the AEF was the federation of French colonial possessions in Middle Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River to the Sahara Desert.-History:...
to Kamerun which became Neukamerun
Neukamerun
Neukamerun was the name of Central African territories ceded by France to Germany in 1911. Upon taking office in 1907, Theodor Seitz, governor of German Kamerun, advocated the acquisition of territories from the French Congo...
, while Germany ceded a smaller area in the north in present day Chad
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
to France.
In World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
the British invaded Cameroon from Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
in 1914 in the West Africa campaign
West Africa Campaign (World War I)
The West Africa Campaign of World War I consisted of two small and fairly short military operations to capture the German colonies in West Africa: Togoland and Kamerun.-Overview:...
, with the last German fort in the country surrendering in February 1916. After the war this colony was partitioned between the United Kingdom and France under a June 28, 1919 League of Nations mandates (Class B). France gained the larger geographical share, transferred Neukamerun back to neighboring French colonies, and ruled the rest from Yaoundé as Cameroun (French Cameroons). Britain's territory, a strip bordering Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
from the sea to Lake Chad
Lake Chad
Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, whose size has varied over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998; yet it also states that "the 2007 ...
, with an equal population was ruled from Lagos
Lagos
Lagos is a port and the most populous conurbation in Nigeria. With a population of 7,937,932, it is currently the third most populous city in Africa after Cairo and Kinshasa, and currently estimated to be the second fastest growing city in Africa...
as Cameroons
Cameroons
British Cameroons was a British Mandate territory in West Africa, now divided between Nigeria and Cameroon.The area of present-day Cameroon was claimed by Germany as a protectorate during the "Scramble for Africa" at the end of the 19th century...
(British Cameroons). German administrators were allowed to once again run the plantations of the southwestern coastal area. A British Parliamentary Publication, Report on the British Sphere of the Cameroons (May 1922, p. 62-8), reports that the German plantations there were "as a whole . . . wonderful examples of industry, based on solid scientific knowledge. The natives have been taught discipline and have come to realise what can be achieved by industry. Large numbers who return to their villages take up cocoa or other cultivation on their own account, thus increasing the general prosperity of the country."
In 1955, the outlawed Union of the Peoples of Cameroon
Union of the Peoples of Cameroon
The Union of the Peoples of Cameroon is a political party in Cameroon.-History:UPC was founded on April 10, 1948, at a meeting in the bar Chez Sierra in Bassa. 12 men assisted the founding meeting, including Charles Assalé, Léonard Bouli, and Guillaume Bagal. The majority of the participants were...
(UPC), based largely among the Bamileke
Bamileke
The Bamileke is a folk whose native ancestral area is in the western highlands of Cameroon's West Province, west of the Noun River and southeast of the Bamboutos Mountains and in the Moungo region of the Littoral, Southwest, and Centre Provinces. They are a part of the Semi-Bantu ethnic groups...
and Bassa ethnic groups, began an armed struggle for independence in French Cameroon. This rebellion continued, with diminishing intensity, even after independence. Estimates of death from this conflict vary from thousands to hundreds of thousands.
Cameroon after independence
French Cameroons achieved independence on January 1, 1960 as the Republic of Cameroon. After Guinea, it was the second of France's colonies in Sub-Saharan Africa to be granted independence. The following year, on October 1, 1961, the largely Muslim northern two-thirds of British Cameroons voted to join Nigeria; the largely Christian southern third, Southern CameroonsSouthern Cameroons
Southern Cameroons was the southern part of the British Mandate territory of Cameroons in West Africa. Since 1961 it is part of the Republic of Cameroon, where it makes up the Northwest Province and Southwest Province...
, voted to join with the Republic of Cameroon to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. The formerly French and British regions each maintained substantial autonomy
Self-governance
Self-governance is an abstract concept that refers to several scales of organization.It may refer to personal conduct or family units but more commonly refers to larger scale activities, i.e., professions, industry bodies, religions and political units , up to and including autonomous regions and...
. Ahmadou Ahidjo
Ahmadou Ahidjo
Ahmadou Babatoura Ahidjo was the first President of Cameroon from 1960 until 1982.-Early life:Ahidjo was born in Garoua, a major river port along the Benue River in northern Cameroun, which was at the time a French mandate territory...
, a French-educated Fulani, was chosen president of the federation in 1961. Ahidjo, relying on a pervasive internal security apparatus, outlawed all political parties but his own in 1966. He successfully suppressed the continuing UPC rebellion, capturing the last important rebel leader in 1970. In 1972, a new constitution replaced the federation with a unitary state called the United Republic of Cameroon.
Although Ahidjo's rule was characterised as authoritarian, he was seen as noticeably lacking in charisma in comparison to many post-colonial African leaders. He didn't follow the anti-western policies pursued by many of these leaders, which helped Cameroon achieve a degree of comparative political stability and economic growth.
Ahidjo resigned as president in 1982 and was constitutionally succeeded by his Prime Minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
, Paul Biya
Paul Biya
Paul Biya is a Cameroonian politician who has been the President of Cameroon since 6 November 1982. A native of Cameroon's south, Biya rose rapidly as a bureaucrat under President Ahmadou Ahidjo in the 1960s, serving as Secretary-General of the Presidency from 1968 to 1975 and then as Prime...
, a career official from the Beti-Pahuin
Beti-Pahuin
The Beti-Pahuin are a group of related peoples who inhabit the rain forest regions of Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe. Though they separate themselves into several individual ethnic groups, they all share a common history and culture. They were...
ethnic group. Ahidjo later regretted his choice of successors, but his supporters failed to overthrow Biya in a 1984 coup
Cameroonian Palace Guard Revolt
An attempted coup d'état occurred in Cameroon in 1984; presidential palace guards unsuccessfully tried to overthrow President Paul Biya, resulting in fighting that began on April 6, 1984 and ended several days later...
. Biya won single-candidate elections in 1983 and 1984 when the country was again named the Republic of Cameroon. Biya has remained in power, winning flawed multiparty elections in 1992, 1997, and 2004. His Cameroon People's Democratic Movement
Cameroon People's Democratic Movement
The Cameroon People's Democratic Movement is the ruling political party in Cameroon.-History:Previously known as the Cameroon National Union, which had dominated Cameroon politics since independence in 1960, it was renamed in 1985...
(CPDM) party holds a sizeable majority in the legislature.
On August 15, 1984, Lake Monoun
Lake Monoun
Lake Monoun is a lake in West Province, Cameroon, that lies in the Oku Volcanic Field . On August 15, 1984, the lake exploded in a limnic eruption, which resulted in the release of a large amount of carbon dioxide that killed 37 people. At first, the cause of the deaths was a mystery, and...
exploded in a limnic eruption
Limnic eruption
A limnic eruption, also referred to as a lake overturn, is a rare type of natural disaster in which carbon dioxide suddenly erupts from deep lake water, suffocating wildlife, livestock and humans. Such an eruption may also cause tsunamis in the lake as the rising CO2 displaces water. Scientists...
that released carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, suffocating
Asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of severely deficient supply of oxygen to the body that arises from being unable to breathe normally. An example of asphyxia is choking. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which primarily affects the tissues and organs...
37 people to death. On August 21, 1986, another limnic eruption at Lake Nyos
Lake Nyos
Lake Nyos is a crater lake in the Northwest Region of Cameroon, located about northwest of Yaoundé. Nyos is a deep lake high on the flank of an inactive volcano in the Oku volcanic plain along the Cameroon line of volcanic activity...
killed as many as 1,800 people and 3,500 livestock. The two disasters are the only recorded instances of limnic eruptions.
Corruption in Cameroon
Despite democratic reform begun in 1990 with the legalization of political parties other than the CPDM, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Biya and a small circle of CPDM members from his own ethnic group. Biya was reelected on October 11, 1992 amid accusations of voting irregularities. Biya reportedly got 39 percent of the vote to 35 percent for John Fru NdiJohn Fru Ndi
Ni John Fru Ndi is the founder and leader of Cameroon's Social Democratic Front .Fru Ndi was born in Baba II, near Bamenda in the Northwest Province of Cameroon. The title of Ni, a marker of respect, was given to him when he was born...
. (Ndi briefly proclaimed himself president before the government released the polling figures.) In contrast, the March 1, 1992 legislative election was considered free and fair by international observers, although many parties boycotted the elections and the CPDM won several constituencies by default. But even though opposition parties were well-represented in the legislature (92 of 180 seats), there were, according to the 1992 constitution
Constitution of Cameroon
The Constitution of Cameroon is the supreme law of the Republic of Cameroon. The document consists of a preamble and 13 Parts, each divided into Articles...
, few legislative or judicial checks on the president.
Following the elections, civil unrest erupted as the population expressed the widespread belief that Ndi had won the presidential elections. By late 1992, Ndi and his supporters were under house arrest and the international community had made clear its displeasure at the antidemocratic and increasingly violent turn the Biya regime was taking.
Biya agreed in May 1993 to hold a so-called Great National Constitutional Debate and in June he began preparing a draft of a new constitution to be adopted either by referendum or by the National Assembly. In 1994, 16 opposition parties formed a loose alliance, dominated by Ndi's Social Democrats, to work for constitutional and electoral reform. In October 1995, the CPDM reelected Biya as its leader. In December of that year the National Assembly adopted a number of amendments to address the power of the president. These reforms included a strengthening of the judiciary, the creation of a partially elected 100-member senate, the creation of regional councils, and the fixing of the presidential term to 7 years, renewable once. Strikes and demonstrations became commonplace as Biya resisted implementation of reforms.
The May 1997 legislative elections were marred by mismanagement, vote-rigging, and fraud, resulting in the Supreme Court's cancellation of results in three constituencies (seven seats). Based on the misconduct of these elections, the opposition boycotted the October 1997 presidential elections, in which Biya claimed victory with 93 percent of the vote. To add further insult, Cameroon topped Transparency International
Transparency International
Transparency International is a non-governmental organization that monitors and publicizes corporate and political corruption in international development. It publishes an annual Corruption Perceptions Index, a comparative listing of corruption worldwide...
's list of the most corrupt countries in the world in 1998, prompting the creation of an anticorruption body.
On June 30, 2002 the country held legislative and municipal elections that again were denounced by the opposition as fraudulent. The Supreme Court cancelled the results of nine constituencies, ordering new elections in these constituencies on September 15. In the end, the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement
Cameroon People's Democratic Movement
The Cameroon People's Democratic Movement is the ruling political party in Cameroon.-History:Previously known as the Cameroon National Union, which had dominated Cameroon politics since independence in 1960, it was renamed in 1985...
(CPDM)/Rassemblement Démocratique du Peuple Camerounais (RDPC) won 149 of 180 seats.
The victory for the ruling party was cemented with the reelection of the 72-year old president Paul Biya in October 2004, thus enhancing the chances of continued domination by the ruling party until the end of his term in 2011. By 2006, appeals were being heard in Biya's home province in favour of a constitutional amendment that would allow him to run for another term when his current term expires. However, against the backdrop of worsening social conditions and high poverty, students protested and conducted strikes for several weeks in April 2005, and clashes with police led to two student deaths. Opposition parties registered their intention to block any attempt to amend the constitution that would allow Biya to run for a third term.
In early 2006 a final resolution to the dispute between Cameroon and Nigeria over the oil-rich Bakassi peninsula was expected. In October 2002, the International Court of Justice had ruled in favour of Cameroon. Nonetheless, a lasting solution would require agreement by both countries’ presidents, parliaments, and by the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
. The peninsula was the site of fighting between the two countries in 1994 and again in June 2005, which led to the death of a Cameroonian soldier.
Football
Cameroon has received some international attention following the relative success of its football teamCameroon national football team
The Cameroon national football team, nicknamed Les Lions Indomptables , is controlled by the Fédération Camerounaise de Football and is Africa's most successful side in FIFA world cup; having qualified for the FIFA World Cup six times – in 1982, 1990, 1994, 1998, 2002 and 2010– more than any...
. It has qualified for the FIFA World Cup on a number of occasions. Its most notable performance was at Italia 90, when the team beat Argentina
Argentina national football team
The Argentina national football team represents Argentina in association football and is controlled by the Argentine Football Association , the governing body for football in Argentina. Argentina's home stadium is Estadio Monumental Antonio Vespucio Liberti and their head coach is Alejandro...
, the then reigning Champions in the opening game; Cameroon eventually lost in extra time in the Quarter Finals to England
England national football team
The England national football team represents England in association football and is controlled by the Football Association, the governing body for football in England. England is the joint oldest national football team in the world, alongside Scotland, whom they played in the world's first...
.
Prominent footballers from Cameroon include:
- Roger MillaRoger MillaRoger Milla is a retired Cameroonian footballer who played as a striker. He was one of the first African players to be a major star on the international stage...
- Samuel Eto'oSamuel Eto'oSamuel Eto'o Fils is a Cameroonian professional footballer who plays as a striker for Russian team Anzhi Makhachkala. He is also the current captain of the Cameroon national team.Eto'o trained at Kadji Sports Academy...
- Rigobert SongRigobert SongRigobert Song Bahanag is a former Cameroonian footballer who is currently a main consultant for the famous sports channel 'Orange sports'. Although receiving many propositions from top clubs, Song declined. Song played for Kosovo super league club KF Drenica, when his contract after season 2010/12...
- Thomas Nkono
See also
- AmbazoniaAmbazoniaThe name Ambazonia or Ambazania refers to two separate entities. One pertains to an advocacy group struggling for the total restoration of the statehood of the Crown Colony formerly known as the British Southern Cameroons...
- History of AfricaHistory of AfricaThe history of Africa begins with the prehistory of Africa and the emergence of Homo sapiens in East Africa, continuing into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. Agriculture began about 10,000 BCE and metallurgy in about 4000 BCE. The history of early...
- Politics of CameroonPolitics of CameroonPolitics of Cameroon takes place in a framework of a unitary presidential republic, whereby the President of Cameroon is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government...
- List of heads of government of Cameroon
- List of heads of state of Cameroon

