.gif)
History of video game consoles (fourth generation)
Encyclopedia
In the history of computer and video games
, the fourth generation (more commonly referred to as the 16 bit era) began on October 30, 1987 with the Japan
ese release of Nippon Electric Company's (NEC) PC Engine
(known as the TurboGrafx-16
in North America
). Although NEC released the first fourth generation console, this era was dominated by the rivalry between Nintendo
and Sega
's consoles: the Super Nintendo Entertainment System
(the Super Famicom in Japan) and the Mega Drive (named the Sega Genesis in North America due to trademark issues). Nintendo was able to capitalize on its previous success in the third generation and won a dominant market share in the fourth generation as well. Sega was also successful in this generation and began a new franchise, Sonic the Hedgehog, to compete with Nintendo's Mario
series of games. Several other companies released consoles in this generation, but, with the exception of the Neo Geo
from SNK
, none of them were widely successful. Nevertheless, several other companies started to take notice of the maturing video game industry and began making plans to release consoles of their own in the future.
and NEC
and launched in Japan on October 30, 1987. It launched in North America
during August 1989, under the name TurboGrafx-16.
Initially, the PC Engine was quite successful in Japan, partly due to titles available on the then-new CD-ROM
format. NEC released a CD add-on in 1990 and by 1992 had released a combination TurboGrafx and CD-ROM system known as the Turbo Duo.
In the USA, NEC used Bonk
, a head-banging caveman, as their mascot and featured him in most of the TurboGrafx advertising from 1990 to 1994. The platform was well received initially, especially in larger markets, but failed to make inroads into the smaller metropolitan areas where NEC did not have as many store representatives or as focused in-store promotion.
The PC Engine failed to maintain its sales momentum or to make a strong impact in North America. The TurboGrafx-16 and its CD combination system, the Turbo Duo, ceased manufacturing in North America by 1994, though a small amount of software continued to trickle out for the platform.
In Japan, a number of more adult titles were also available for the PC-Engine, such as a variety of strip mahjong games (such as the Super Real Mahjong series), which set it apart from its competitors.
and Los Angeles
on August 14, 1989 under the name Sega Genesis, and in the rest of North America later that year. The Mega Drive was launched in Europe and Australia on November 30, 1990.
Sega initially had a hard time overcoming Nintendo's ubiquitous presence in the American consumer's home. That changed in late 1990, as Sega built their marketing campaign around their new mascot Sonic the Hedgehog
, pushing the Genesis as the "cooler" alternative to Nintendo's console and inventing the term "Blast Processing" to suggest that the Genesis was capable of handling games with faster motion than the SNES. Their advertising was often directly adversarial, leading to commercials such as "Genesis does what Nintendon't" and the "'SEGA!' scream".
When the arcade game Mortal Kombat
was ported for home release on the Mega Drive and Super Nintendo Entertainment System, Nintendo decided to censor the game's gore, but Sega kept the content in the game, via a code entered at the start screen (A,B,A,C,A,B,B). Sega's gamble paid off, as its version of Mortal Kombat received generally higher and more favorable reviews in the gaming press and outsold the SNES version three to one. This violence also led to Congressional hearings to investigate the marketing of violent video games to children, and to the creation of the Interactive Digital Software Association
and the Entertainment Software Rating Board
. With the new ESRB rating system in place, Nintendo reconsidered its position for the release of Mortal Kombat II
, and this time became the preferred version among reviewers. Sega, however, ran into a minor roadblock with the popularity of fighting games with advanced controls, because its controller only featured three action buttons. In response to the upcoming Street Fighter 2 Special Champion Edition and Mortal Kombat, Sega introduced a 6-button controller. Most new games could still be played with the original 3-button controller however, but the company suggested its gamers buy and adopt the new 6-button model.
Despite the Genesis' success in North America and the Mega Drive's in Europe, the Mega Drive was never popular in Japan, being regularly outsold by the PC Engine. By late 1995, Sega was supporting five different consoles and two add-ons, and Sega of Japan chose to discontinue the Mega Drive in Japan to concentrate on the new Sega Saturn
. While this made perfect sense for the Japanese market, it was disastrous in North America: the market for Genesis games was much larger than for the Saturn, but Sega was left without the inventory or software to meet demand.
(called Nintendo Entertainment System outside Japan). Nintendo's fourth-generation console, the Super Famicom, was released in Japan on November 21, 1990; Nintendo's initial shipment of 300,000 units sold out within hours. The machine reached North America on August 23, 1991, and Europe and Australia in April 1992.
Despite stiff competition from Sega's Mega Drive console, the Super NES eventually took the top selling position, selling 49.10 million units worldwide, and would even remain popular well into the 32-bit generation. Nintendo's market position was defined by their machine's increased video and sound capabilities.
in 1990, the Neo Geo was a home console version of the major arcade platform. Compared to its console competition, the Neo Geo had much better graphics and sound, but the prohibitively expensive launch price of $649.99 USD made the console only accessible to a niche market. A less expensive version, retailing for $399.99, did not include a memory card, pack-in game
or extra joystick.
s for their consoles in this generation. NEC was the first with the release of the TurboGrafx CD system in 1990. Retailing for $499.99 at release, the CD add-on was not a popular purchase, but was largely responsible for the platform's success in Japan. Sega made two attempts: the Sega Mega-CD
(renamed Sega-CD in North America) and the Sega 32X
. The Mega CD was plagued by a high price tag ($300 at its release) and a limited library of games. The 32X faced a number of problems, primarily technical and commercial: the peripheral would occasionally not work with some consoles, and some retailers were not able to meet the initial demand for the add-on, leading to shortages. A unique add-on for the Sega console was Sega Channel
, a subscription based service hosted by local television providers. It required hardware that plugged into a cable line and the 32X.
Nintendo made an attempt with their successful Satellaview
and Super Game Boy
. The former was a satellite service released only on the Japan
ese market and the latter an adapter for the Super Nintendo that allowed Game Boy games to be displayed on a TV in color. Nintendo, working along with Sony
, also had plans to create a CD-ROM drive for the Super NES, but eventually decided not to go through with that project, opting to team up with Philips
in the development of the add-on instead (contrary to popular belief, the CD-i
was largely unrelated to the project). Sony decided to go ahead with the CD-ROM development and used the name "PlayStation
" for their own standalone CD-based console, overseen by former SNES
sound-chip engineer, Ken Kutaragi
.
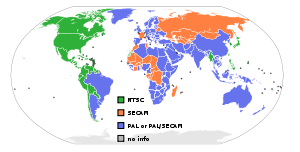 The fourth generation was also the era when the act of buying imported US games became more established in Europe, and regular stores began to carry them. This was perhaps because the PAL
The fourth generation was also the era when the act of buying imported US games became more established in Europe, and regular stores began to carry them. This was perhaps because the PAL
region has a refresh rate of 50 Hz (compared with 60 Hz for NTSC
) and a vertical resolution of 625 interlaced lines (576
effective), compared with 525/480 for NTSC. This means that a game designed for the NTSC standard without any modification would run 17% slower and have black bars at the top and bottom when played on a PAL television. Developers often had a hard time converting games designed for the American and Japanese NTSC standard to the European and Australian PAL standard. Companies such as Konami
, with large budgets and a healthy following in Europe and Australia, readily optimized several games (such as the International Superstar Soccer
series) for this audience, while most smaller developers did not.
Also, few RPGs were released in Europe because they would have needed to be translated into many different languages. RPGs tend to contain much more text than other genres, so one of the biggest problems was simply fitting all of the full translations into one cartridge. The cost of creating multiple full translations was also prohibitive. Only the UK
and Australia
saw any number of RPG releases, and even then the number was a fraction of what was being released in Japan. For the Mega Drive, there were numerous PAL releases of RPGs. Examples include Phantasy Star II, III and IV, Shining in the Darkness and its sequels Shining Force I and II, Sword of Vermilion, Super Hydlide, Landstalker, Story of Thor, Soleil and Light Crusader. A few of them received French and German translations.
Popular US games imported at this time included Final Fantasy IV
(known in the USA as Final Fantasy II), Final Fantasy VI
(known in the USA as Final Fantasy III), Secret of Mana
, Street Fighter II
, Chrono Trigger
, and Super Mario RPG. Secret of Mana and Street Fighter II would eventually receive official release in Europe.
released in the fourth generation was the Game Boy
, on April 21, 1989. It went on to dominate handheld sales by an extremely large margin, despite featuring a monochrome screen while all three of its leading competitors had color. Three major franchises made their debut on the Game Boy: Tetris, the Game Boy's killer application
; Pokémon
; and Kirby
.
The Atari Lynx, included color graphics, a backlight, and networking capabilities, but its comparatively short battery life, high price, and weak games library made it one of the worst-selling handheld game systems of all time, with less than 500,000 units sold.
The third major handheld of the fourth generation was the Sega Game Gear
. It featured graphics capabilities comparable to the Master System, but it also inherited the same shortcomings as the Lynx. While it sold more than ten times as many units as the Lynx, its bulky design and low battery life caused it to be pushed to the sidelines.
Other handheld consoles released during the fourth generation included the TurboExpress
, a handheld version of the TurboGrafx-16 released by NEC in 1990, and the Game Boy Pocket, an improved model of the Game Boy released about two years before the debut of the Game Boy Color
. While the TurboExpress was another early pioneer of color handheld gaming technology and had the added benefit of using the same game cartridges or 'HuCards' as the TurboGrafx16, it had even lower battery life than the Lynx and Game Gear - about three hours on six AA batteries - selling only 1.5 million units.
, Zelda
, Star Fox, Kirby
, Dragon Quest
, Final Fantasy
, Seiken Densetsu
(Secret of Mana
), Sonic the Hedgehog
, Donkey Kong, Street Fighter, Mortal Kombat
, Mega Man X
, and many others had either their first releases or some of their most popular titles during the 16-bit era.
Sonic the Hedgehog
was Sega
's bid to compete head-to head with Nintendo's Mario franchise. Debuting in 1991, Sega's marketing of the Sonic franchise was key to Sega's success in the video game market during the early years of this generation. Though a critical and commercial success, Sonic the Hedgehog and its sequels were never able to surpass Mario in popularity.
Metroid II was released for the Game Boy and Super Metroid
was released in 1994 on a comparatively large 24 megabit
cartridge for the SNES. Super Metroid still is regarded by many gaming organizations as one of the "best games of all time."
The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past
, courted popularity that was larger than that of its predecessors on the NES. It was one of the few action-adventures to be released early in the SNES's lifecycle. Zelda II
on the NES had been mostly action-based and was side-scrolling, while A Link to the Past drew more inspiration from the original Zelda game with its top-down adventure format.
Dragon Quest V
and VI
were released on the Japanese Super Famicom, as well as remakes of the first three games originally released for the NES and a dungeon crawler spin-off: Torneko's Great Adventure, which started Chun Soft's popular Fushigi no Dungeon
series.
Star Fox was the first SNES game to feature the Super FX
chip.
Final Fantasy V
was released only in Japan, while Final Fantasy IV
and Final Fantasy VI
were released in North America with their original numeration shifted. While the series was very successful in Japan
early on, it was not until the release of Final Fantasy VII
on the PlayStation that it reached blockbuster status outside Japan.
Secret of Mana
reintroduced the Seiken Densetsu series, originally conceived as a Final Fantasy spin-off
, to Europe and North America.
Street Fighter II
, a port of the arcade original to the SNES, was the second game in the series to produce a lasting fanbase and set many of the trends seen in fighting games today, most notably its colorful selection of playable fighters from different countries across the globe. As of 2008, it is Capcom
's best-selling consumer game of all time.
Phantasy Star
is Sega's RPG franchise that was established 1987 on the Sega Master System. It was the first console RPG to reach Europe; almost a decade before Final Fantasy VII
. Three sequels were released to the Mega Drive. With its sci-fi theme, the franchise was different from the fantasy-themed Dragon Quest
.
Thunder Force II
, III
and IV
were all released for the Mega Drive, but the third never reached Europe and the fourth was called Lightening Force: Quest for the Darkstar (sic) in the US.
Seeking to follow the example of the above titles, several more franchises were born during this era. While game sequels were far from uncommon during the 8-bit era and even before, it was at this time that the potential for continuing series games was realized.
Notable CD-i releases included the well-received Burn:Cycle
, Escape from Cyber City (made using re-dubbed clips from Galaxy Express 999
), and a port of The 7th Guest
that was bundled with the system at one time.
History of computer and video games
The history of video games goes as far back as the 1940s, when in 1947 Thomas T. Goldsmith, Jr. and Estle Ray Mann filed a United States patent request for an invention they described as a "cathode ray tube amusement device." Video gaming would not reach mainstream popularity until the 1970s and...
, the fourth generation (more commonly referred to as the 16 bit era) began on October 30, 1987 with the Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese release of Nippon Electric Company's (NEC) PC Engine
TurboGrafx-16
TurboGrafx-16, fully titled as TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem and known in Japan as the , is a video game console developed by Hudson Soft and NEC, released in Japan on October 30, 1987, and in North America on August 29, 1989....
(known as the TurboGrafx-16
TurboGrafx-16
TurboGrafx-16, fully titled as TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem and known in Japan as the , is a video game console developed by Hudson Soft and NEC, released in Japan on October 30, 1987, and in North America on August 29, 1989....
in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
). Although NEC released the first fourth generation console, this era was dominated by the rivalry between Nintendo
Nintendo
is a multinational corporation located in Kyoto, Japan. Founded on September 23, 1889 by Fusajiro Yamauchi, it produced handmade hanafuda cards. By 1963, the company had tried several small niche businesses, such as a cab company and a love hotel....
and Sega
Sega
, usually styled as SEGA, is a multinational video game software developer and an arcade software and hardware development company headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo, Japan, with various offices around the world...
's consoles: the Super Nintendo Entertainment System
Super Nintendo Entertainment System
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System is a 16-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America, Europe, Australasia , and South America between 1990 and 1993. In Japan and Southeast Asia, the system is called the , or SFC for short...
(the Super Famicom in Japan) and the Mega Drive (named the Sega Genesis in North America due to trademark issues). Nintendo was able to capitalize on its previous success in the third generation and won a dominant market share in the fourth generation as well. Sega was also successful in this generation and began a new franchise, Sonic the Hedgehog, to compete with Nintendo's Mario
Mario
is a fictional character in his video game series, created by Japanese video game designer Shigeru Miyamoto. Serving as Nintendo's mascot and the main protagonist of the series, Mario has appeared in over 200 video games since his creation...
series of games. Several other companies released consoles in this generation, but, with the exception of the Neo Geo
Neo Geo (console)
The is a cartridge-based arcade and home video game system released on July 1, 1991 by Japanese game company SNK. Being in the Fourth generation of Gaming, it was the first console in the former Neo Geo family, which only lived through the 1990s...
from SNK
SNK Playmore
SNK Playmore Corporation is a Japanese video game hardware and software company. SNK is an acronym of , which was SNK's original name. The company's legal and trading name became SNK in 1986....
, none of them were widely successful. Nevertheless, several other companies started to take notice of the maturing video game industry and began making plans to release consoles of their own in the future.
PC Engine/TurboGrafx-16/TurboGrafx
The PC Engine was the result of a collaboration between Hudson SoftHudson Soft
, formally known as , is a majority-owned subsidiary of Konami Corporation is a Japanese electronic entertainment publisher headquartered in the Midtown Tower in Tokyo Midtown, Akasaka, Minato, Tokyo, Japan, with an additional office in the Hudson Building in Sapporo. It was founded on May 18, 1973...
and NEC
NEC
, a Japanese multinational IT company, has its headquarters in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. NEC, part of the Sumitomo Group, provides information technology and network solutions to business enterprises, communications services providers and government....
and launched in Japan on October 30, 1987. It launched in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
during August 1989, under the name TurboGrafx-16.
Initially, the PC Engine was quite successful in Japan, partly due to titles available on the then-new CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
format. NEC released a CD add-on in 1990 and by 1992 had released a combination TurboGrafx and CD-ROM system known as the Turbo Duo.
In the USA, NEC used Bonk
Bonk (video game)
Bonk is a video game character from NEC's TurboGrafx-16 console. Known in Japan as "PC-Genjin" and as "BC Kid" in PAL territories, Bonk was a mascot for NEC's console, though some Bonk games eventually saw releases on other consoles as well. A large-headed, bald caveman, his favored form of attack...
, a head-banging caveman, as their mascot and featured him in most of the TurboGrafx advertising from 1990 to 1994. The platform was well received initially, especially in larger markets, but failed to make inroads into the smaller metropolitan areas where NEC did not have as many store representatives or as focused in-store promotion.
The PC Engine failed to maintain its sales momentum or to make a strong impact in North America. The TurboGrafx-16 and its CD combination system, the Turbo Duo, ceased manufacturing in North America by 1994, though a small amount of software continued to trickle out for the platform.
In Japan, a number of more adult titles were also available for the PC-Engine, such as a variety of strip mahjong games (such as the Super Real Mahjong series), which set it apart from its competitors.
Sega Genesis/Mega Drive
The Sega Mega Drive was released in Japan on October 29, 1988. The console was released in New York CityNew York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
and Los Angeles
Los Ángeles
Los Ángeles is the capital of the province of Biobío, in the commune of the same name, in Region VIII , in the center-south of Chile. It is located between the Laja and Biobío rivers. The population is 123,445 inhabitants...
on August 14, 1989 under the name Sega Genesis, and in the rest of North America later that year. The Mega Drive was launched in Europe and Australia on November 30, 1990.
Sega initially had a hard time overcoming Nintendo's ubiquitous presence in the American consumer's home. That changed in late 1990, as Sega built their marketing campaign around their new mascot Sonic the Hedgehog
Sonic the Hedgehog (character)
, trademarked Sonic The Hedgehog, is a video game character and the main protagonist of the Sonic video game series released by Sega, as well as in numerous spin-off comics, cartoons, and a feature film. The first game was released on June 23, 1991, to provide Sega with a mascot to rival Nintendo's...
, pushing the Genesis as the "cooler" alternative to Nintendo's console and inventing the term "Blast Processing" to suggest that the Genesis was capable of handling games with faster motion than the SNES. Their advertising was often directly adversarial, leading to commercials such as "Genesis does what Nintendon't" and the "'SEGA!' scream".
When the arcade game Mortal Kombat
Mortal Kombat (video game)
Mortal Kombat is a 1992 fighting-game developed and published by Midway for arcades. In 1993, home versions were released by Acclaim Entertainment. Released in the Fall of 1994, the Microsoft Windows 3.1x version was released by Activision Interactive. It is the first title in the Mortal Kombat...
was ported for home release on the Mega Drive and Super Nintendo Entertainment System, Nintendo decided to censor the game's gore, but Sega kept the content in the game, via a code entered at the start screen (A,B,A,C,A,B,B). Sega's gamble paid off, as its version of Mortal Kombat received generally higher and more favorable reviews in the gaming press and outsold the SNES version three to one. This violence also led to Congressional hearings to investigate the marketing of violent video games to children, and to the creation of the Interactive Digital Software Association
Entertainment Software Association
The Entertainment Software Association is the trade association of the video game industry in the United States. It was formed in April 1994 as the Interactive Digital Software Association and renamed on July 16, 2003...
and the Entertainment Software Rating Board
Entertainment Software Rating Board
The Entertainment Software Rating Board is a self-regulatory organization that assigns age and content ratings, enforces industry-adopted advertising guidelines, and ensures responsible online privacy principles for computer and video games as well as entertainment software in Canada, Mexico and...
. With the new ESRB rating system in place, Nintendo reconsidered its position for the release of Mortal Kombat II
Mortal Kombat II
Mortal Kombat II is a competitive fighting game originally produced by Midway Games for the arcades in . It is the second game in the Mortal Kombat series. Like its predecessor, various home versions were produced...
, and this time became the preferred version among reviewers. Sega, however, ran into a minor roadblock with the popularity of fighting games with advanced controls, because its controller only featured three action buttons. In response to the upcoming Street Fighter 2 Special Champion Edition and Mortal Kombat, Sega introduced a 6-button controller. Most new games could still be played with the original 3-button controller however, but the company suggested its gamers buy and adopt the new 6-button model.
Despite the Genesis' success in North America and the Mega Drive's in Europe, the Mega Drive was never popular in Japan, being regularly outsold by the PC Engine. By late 1995, Sega was supporting five different consoles and two add-ons, and Sega of Japan chose to discontinue the Mega Drive in Japan to concentrate on the new Sega Saturn
Sega Saturn
The is a 32-bit fifth-generation video game console that was first released by Sega on November 22, 1994 in Japan, May 11, 1995 in North America, and July 8, 1995 in Europe...
. While this made perfect sense for the Japanese market, it was disastrous in North America: the market for Genesis games was much larger than for the Saturn, but Sega was left without the inventory or software to meet demand.
Super Nintendo Entertainment System
Nintendo executives were initially reluctant to design a new system, but as the market transitioned to the newer hardware, Nintendo saw the erosion of the commanding market share it had built up with the FamicomNintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System is an 8-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America during 1985, in Europe during 1986 and Australia in 1987...
(called Nintendo Entertainment System outside Japan). Nintendo's fourth-generation console, the Super Famicom, was released in Japan on November 21, 1990; Nintendo's initial shipment of 300,000 units sold out within hours. The machine reached North America on August 23, 1991, and Europe and Australia in April 1992.
Despite stiff competition from Sega's Mega Drive console, the Super NES eventually took the top selling position, selling 49.10 million units worldwide, and would even remain popular well into the 32-bit generation. Nintendo's market position was defined by their machine's increased video and sound capabilities.
Neo Geo
Released by SNKSNK
SNK is a former name of SNK Playmore, a Japanese video game company . This may also refer to:* SNK European Democrats* SNK Union of Independents* Southeast Airlines ICAO code...
in 1990, the Neo Geo was a home console version of the major arcade platform. Compared to its console competition, the Neo Geo had much better graphics and sound, but the prohibitively expensive launch price of $649.99 USD made the console only accessible to a niche market. A less expensive version, retailing for $399.99, did not include a memory card, pack-in game
Pack-in game
- Characteristics :Pack-in games are intended to be system-selling games that make good use of the positive features of a given system. Sometimes a pack-in game will be changed to a more popular game, or another game will be added, along with the original pack-in, if it is perceived that a newer...
or extra joystick.
Add-ons
Nintendo, NEC and Sega also competed with hardware peripheralPeripheral
A peripheral is a device attached to a host computer, but not part of it, and is more or less dependent on the host. It expands the host's capabilities, but does not form part of the core computer architecture....
s for their consoles in this generation. NEC was the first with the release of the TurboGrafx CD system in 1990. Retailing for $499.99 at release, the CD add-on was not a popular purchase, but was largely responsible for the platform's success in Japan. Sega made two attempts: the Sega Mega-CD
Sega Mega-CD
The is an add-on device for the Mega Drive video game console, designed and produced by Sega and released in Japan, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. The device was also released in North America under the name Sega CD, for the Sega Genesis...
(renamed Sega-CD in North America) and the Sega 32X
Sega 32X
The Sega 32X, codenamed Project Mars, is an add-on for the Mega Drive/Genesis video game console by Sega. Its aim was to increase the lifespan of the aging Mega Drive/Genesis system, which was facing stiff competition from the SNES...
. The Mega CD was plagued by a high price tag ($300 at its release) and a limited library of games. The 32X faced a number of problems, primarily technical and commercial: the peripheral would occasionally not work with some consoles, and some retailers were not able to meet the initial demand for the add-on, leading to shortages. A unique add-on for the Sega console was Sega Channel
Sega Channel
Sega Channel was a project developed by Sega for the 16-bit Sega Mega Drive/Genesis console. Starting in December 1994, Sega Channel service was provided to the public by Time Warner Cable and TCI, which later was acquired by AT&T during its cable acquisition spree that formed AT&T...
, a subscription based service hosted by local television providers. It required hardware that plugged into a cable line and the 32X.
Nintendo made an attempt with their successful Satellaview
Satellaview
The is a satellite modem add-on for Nintendo's Super Famicom system that was released in Japan in 1995. Available for pre-release orders as early as February 13, 1995, the Satellaview retailed for between ¥14,000 and 18,000 and came bundled with the BS-X Game Pak and an 8M Memory Pak.The...
and Super Game Boy
Super Game Boy
The is a 16-bit adapter cartridge for Nintendo's Super Nintendo Entertainment System, as well as the Super Famicom in Japan. The Super Game Boy allows game cartridges designed for use on the Game Boy to be played on a TV display using the SNES/Super Famicom controllers. When it was released in...
. The former was a satellite service released only on the Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese market and the latter an adapter for the Super Nintendo that allowed Game Boy games to be displayed on a TV in color. Nintendo, working along with Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
, also had plans to create a CD-ROM drive for the Super NES, but eventually decided not to go through with that project, opting to team up with Philips
Philips
Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company....
in the development of the add-on instead (contrary to popular belief, the CD-i
CD-i
CD-i, or Compact Disc Interactive, is the name of an interactive multimedia CD player developed and marketed by Royal Philips Electronics N.V. CD-i also refers to the multimedia Compact Disc standard used by the CD-i console, also known as Green Book, which was developed by Philips and Sony...
was largely unrelated to the project). Sony decided to go ahead with the CD-ROM development and used the name "PlayStation
PlayStation
The is a 32-bit fifth-generation video game console first released by Sony Computer Entertainment in Japan on December 3, .The PlayStation was the first of the PlayStation series of consoles and handheld game devices. The PlayStation 2 was the console's successor in 2000...
" for their own standalone CD-based console, overseen by former SNES
Super Nintendo Entertainment System
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System is a 16-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America, Europe, Australasia , and South America between 1990 and 1993. In Japan and Southeast Asia, the system is called the , or SFC for short...
sound-chip engineer, Ken Kutaragi
Ken Kutaragi
is the former Chairman and chief executive officer of Sony Computer Entertainment , the video game division of Sony Corporation. He is known as "The Father of the PlayStation", and its successors and spinoffs, including the PlayStation 2, PlayStation Portable, and the PlayStation 3.Before this...
.
European and Australian importing

PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
region has a refresh rate of 50 Hz (compared with 60 Hz for NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
) and a vertical resolution of 625 interlaced lines (576
576i
576i is a standard-definition video mode used in PAL and SECAM countries. In digital applications it is usually referred to as "576i", in analogue contexts it is often quoted as "625 lines"...
effective), compared with 525/480 for NTSC. This means that a game designed for the NTSC standard without any modification would run 17% slower and have black bars at the top and bottom when played on a PAL television. Developers often had a hard time converting games designed for the American and Japanese NTSC standard to the European and Australian PAL standard. Companies such as Konami
Konami
is a Japanese leading developer and publisher of numerous popular and strong-selling toys, trading cards, anime, tokusatsu, slot machines, arcade cabinets and video games...
, with large budgets and a healthy following in Europe and Australia, readily optimized several games (such as the International Superstar Soccer
International Superstar Soccer
International Superstar Soccer is the name of a series of football video games developed by Japanese company Konami, mostly by their Osaka branch, Konami Computer Entertainment Osaka . It should not be confused with Konami Computer Entertainment Tokyo's Pro Evolution Soccer series , which was...
series) for this audience, while most smaller developers did not.
Also, few RPGs were released in Europe because they would have needed to be translated into many different languages. RPGs tend to contain much more text than other genres, so one of the biggest problems was simply fitting all of the full translations into one cartridge. The cost of creating multiple full translations was also prohibitive. Only the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
saw any number of RPG releases, and even then the number was a fraction of what was being released in Japan. For the Mega Drive, there were numerous PAL releases of RPGs. Examples include Phantasy Star II, III and IV, Shining in the Darkness and its sequels Shining Force I and II, Sword of Vermilion, Super Hydlide, Landstalker, Story of Thor, Soleil and Light Crusader. A few of them received French and German translations.
Popular US games imported at this time included Final Fantasy IV
Final Fantasy IV
is a role-playing video game developed and published by Square in 1991 as a part of the Final Fantasy series. The game was originally released for the Super Famicom in Japan and has since then been rereleased for many other platforms with varying modifications. An enhanced remake with 3D graphics...
(known in the USA as Final Fantasy II), Final Fantasy VI
Final Fantasy VI
is a role-playing video game developed and published by Square , released in 1994 for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System as a part of the Final Fantasy series. Set in a fantasy world with a technology level equivalent to that of the Second Industrial Revolution, the game's story focuses on a...
(known in the USA as Final Fantasy III), Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana is an action role-playing game for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System developed and published by Square in 1993. The game was re-released for the Wii's Virtual Console in 2008, and was ported to Japanese mobile phones in 2009...
, Street Fighter II
Street Fighter II
is a competitive fighting game originally released for the arcades in . It is the arcade sequel to the original Street Fighter released in and was Capcom's fourteenth title that ran on the CP System arcade hardware...
, Chrono Trigger
Chrono Trigger
is a role-playing video game developed and published by Square for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System in 1995. Chrono Triggers development team included three designers that Square dubbed the "Dream Team": Hironobu Sakaguchi, the creator of Square's Final Fantasy series; Yuji Horii, a...
, and Super Mario RPG. Secret of Mana and Street Fighter II would eventually receive official release in Europe.
Comparison
| Name | PC-Engine/TurboGrafx-16 TurboGrafx-16 TurboGrafx-16, fully titled as TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem and known in Japan as the , is a video game console developed by Hudson Soft and NEC, released in Japan on October 30, 1987, and in North America on August 29, 1989.... |
Mega Drive/Genesis | Neo Geo Neo Geo (console) The is a cartridge-based arcade and home video game system released on July 1, 1991 by Japanese game company SNK. Being in the Fourth generation of Gaming, it was the first console in the former Neo Geo family, which only lived through the 1990s... |
Super Famicom/Super Nintendo Entertainment System Super Nintendo Entertainment System The Super Nintendo Entertainment System is a 16-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America, Europe, Australasia , and South America between 1990 and 1993. In Japan and Southeast Asia, the system is called the , or SFC for short... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Hudson Soft Hudson Soft , formally known as , is a majority-owned subsidiary of Konami Corporation is a Japanese electronic entertainment publisher headquartered in the Midtown Tower in Tokyo Midtown, Akasaka, Minato, Tokyo, Japan, with an additional office in the Hudson Building in Sapporo. It was founded on May 18, 1973... /NEC NEC , a Japanese multinational IT company, has its headquarters in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. NEC, part of the Sumitomo Group, provides information technology and network solutions to business enterprises, communications services providers and government.... |
Sega Sega , usually styled as SEGA, is a multinational video game software developer and an arcade software and hardware development company headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo, Japan, with various offices around the world... |
SNK SNK SNK is a former name of SNK Playmore, a Japanese video game company . This may also refer to:* SNK European Democrats* SNK Union of Independents* Southeast Airlines ICAO code... |
Nintendo Nintendo is a multinational corporation located in Kyoto, Japan. Founded on September 23, 1889 by Fusajiro Yamauchi, it produced handmade hanafuda cards. By 1963, the company had tried several small niche businesses, such as a cab company and a love hotel.... |
| Console |  |
|||
| Launch prices (USD) | US$249.99 | US$190.00 | US$649.99 (Gold version) US$399.99 (Silver version) |
US$199.99 |
| Release date | ||||
| Media | HuCard HuCard A HuCard is a memory card developed by Hudson Soft. It is the size of a credit card and is used with the NEC PC Engine and SuperGrafx video game consoles. HuCards contain an integrated circuit that is placed close to the connectors and protected by a thin plastic shield... (card-shaped cartridge) CD-ROM (add-on) |
Cartridge CD-ROM (Mega-CD add-on) Data card (Power Base Converter add-on) |
Cartridge CD-Rom (Neo Geo CD Neo Geo CD is a game console from SNK that was released in 1994, four years after its cartridge-based equivalent, in an effort to reduce manufacturing costs. It is the second console of the Neo Geo family. The system was originally priced at US$300 new. The unit's 1X CD-ROM drive was slow, making loading... - was released as a separate system) Data card (Europe/Japan) |
Cartridge Magnetic disc (Japan only) CD-ROM (Aborted add-on) Floptical Floptical Floptical refers to a type of disk drive that combines magnetic and optical technologies to store large amounts of data on media similar to 3½-inch floppy disks. The name is a portmanteau of the words 'floppy' and 'optical'... (Japan only) |
| Best-selling games | Bonk's Adventure Bonk's Adventure Bonk's Adventure is a 2D platform video game developed by Red Company and Atlus and released in 1990 for the TurboGrafx-16. In Japan it was released as PC Genjin in 1989, a play on the Japanese name for the system, 'PC Engine'. The game was re-released for the TurboGrafx-16 in the U.S. in 1992 on... |
Sonic the Hedgehog (15 million) | Samurai Shodown Samurai Shodown Samurai Shodown, known as in Japan, is a competitive fighting game produced by SNK for their Neo Geo arcade and home platform. In contrast to other fighting games at the time which were set in modern times and focused primarily on hand-to-hand combat, Samurai Shodown is set in feudal-era Japan ... |
Super Mario World Super Mario World , subtitled Super Mario Bros. 4 for its original Japanese release, is a platform video game developed and published by Nintendo as a pack-in launch title for the Super Famicom/Super Nintendo Entertainment System , and is the fourth game in the Super Mario series... , 20 million (as of June 25, 2007) |
| Backward compatibility Backward compatibility In the context of telecommunications and computing, a device or technology is said to be backward or downward compatible if it can work with input generated by an older device... |
None | Sega Master System Sega Master System The is a third-generation video game console that was manufactured and released by Sega in 1985 in Japan , 1986 in North America and 1987 in Europe.... (using Power Base Converter) |
None | Game Boy Game Boy The , is an 8-bit handheld video game device developed and manufactured by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on , in North America in , and in Europe on... (using Super Game Boy Super Game Boy The is a 16-bit adapter cartridge for Nintendo's Super Nintendo Entertainment System, as well as the Super Famicom in Japan. The Super Game Boy allows game cartridges designed for use on the Game Boy to be played on a TV display using the SNES/Super Famicom controllers. When it was released in... ) |
| Accessories (retail) |
|
Sega Mega-CD The is an add-on device for the Mega Drive video game console, designed and produced by Sega and released in Japan, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. The device was also released in North America under the name Sega CD, for the Sega Genesis... Sega 32X The Sega 32X, codenamed Project Mars, is an add-on for the Mega Drive/Genesis video game console by Sega. Its aim was to increase the lifespan of the aging Mega Drive/Genesis system, which was facing stiff competition from the SNES... Mouse (computing) In computing, a mouse is a pointing device that functions by detecting two-dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface. Physically, a mouse consists of an object held under one of the user's hands, with one or more buttons... Menacer The Menacer is a lightgun created by Sega for the Mega Drive video game console in 1992, as a response to the Super Scope by Nintendo.The Menacer is made up of three sections which can be disassembled... Multitap A multitap is a video game console peripheral that increases the number of controller ports available to the player, allowing additional controllers to be used in play... |
Neo Geo CD is a game console from SNK that was released in 1994, four years after its cartridge-based equivalent, in an effort to reduce manufacturing costs. It is the second console of the Neo Geo family. The system was originally priced at US$300 new. The unit's 1X CD-ROM drive was slow, making loading... |
Super Scope The Super Scope, or Nintendo Scope in Europe and Australia, is the official Super Nintendo light gun. It was released in the European and North American markets, with a limited release in Japan due to a lack of consumer demand... Multitap A multitap is a video game console peripheral that increases the number of controller ports available to the player, allowing additional controllers to be used in play... Super Game Boy The is a 16-bit adapter cartridge for Nintendo's Super Nintendo Entertainment System, as well as the Super Famicom in Japan. The Super Game Boy allows game cartridges designed for use on the Game Boy to be played on a TV display using the SNES/Super Famicom controllers. When it was released in... SNES Mouse The Super NES Mouse is a peripheral released by Nintendo in 1992 for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System . Originally designed for use with the game Mario Paint, the SNES Mouse was sold in a bundle with the game and included a plastic mouse pad... Super Advantage The SNES Advantage is a large joystick produced by Asciiware, sold for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System. The device is meant to rest at a comfortable level on a flat surface—such as a tabletop or the floor—while the player sits behind it, but it can also used while resting on a players lap... |
| CPU | HuC6280A Hudson Soft HuC6280 The HuC6280 8-bit microprocessor is Japanese company Hudson Soft's improved version of the WDC 65C02 CPU. The most notable product using the HuC6280 is NEC's TurboGrafx 16 video game console.-Description:... (modified 65SC02) 1.79 or 7.16 MHz |
Motorola 68000 Motorola 68000 The Motorola 68000 is a 16/32-bit CISC microprocessor core designed and marketed by Freescale Semiconductor... 7.67 MHz (7.61 MHz PAL) Zilog Z80 Zilog Z80 The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog and sold from July 1976 onwards. It was widely used both in desktop and embedded computer designs as well as for military purposes... 3.58 MHz |
Motorola 68000 Motorola 68000 The Motorola 68000 is a 16/32-bit CISC microprocessor core designed and marketed by Freescale Semiconductor... 12 MHz Zilog Z80 Zilog Z80 The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog and sold from July 1976 onwards. It was widely used both in desktop and embedded computer designs as well as for military purposes... 4 MHz |
Nintendo-custom 5A22 Ricoh 5A22 The Ricoh 5A22 is a microprocessor produced by Ricoh for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game console. The 5A22 is based around the 16-bit CMD/GTE 65c816, itself a version of the WDC 65C816 .... (based on 65C816) 3.58 MHz (3.55 MHz PAL) |
| Memory | 8 KiB work RAM 64 KiB video RAM |
64 KiB main RAM 64 KiB video RAM 8 KiB audio RAM |
64 KiB main RAM 74 KiB video RAM 2 KiB audio RAM |
128 KiB main RAM 64 KiB video RAM 64 KiB audio RAM |
Worldwide sales standings
| Console | Units sold |
|---|---|
| Super Famicom/Super Nintendo Entertainment System Super Nintendo Entertainment System The Super Nintendo Entertainment System is a 16-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America, Europe, Australasia , and South America between 1990 and 1993. In Japan and Southeast Asia, the system is called the , or SFC for short... |
49.10 million |
| Sega Mega Drive/Genesis | 40 million |
| PC Engine/TurboGrafx-16 TurboGrafx-16 TurboGrafx-16, fully titled as TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem and known in Japan as the , is a video game console developed by Hudson Soft and NEC, released in Japan on October 30, 1987, and in North America on August 29, 1989.... |
10 million |
| Mega-CD Sega Mega-CD The is an add-on device for the Mega Drive video game console, designed and produced by Sega and released in Japan, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. The device was also released in North America under the name Sega CD, for the Sega Genesis... (Mega Drive/Genesis add-on) |
6 million |
| Sega 32X Sega 32X The Sega 32X, codenamed Project Mars, is an add-on for the Mega Drive/Genesis video game console by Sega. Its aim was to increase the lifespan of the aging Mega Drive/Genesis system, which was facing stiff competition from the SNES... (Mega Drive/Genesis add-on) |
665,000 (as of 1994) |
| CD-i CD-i CD-i, or Compact Disc Interactive, is the name of an interactive multimedia CD player developed and marketed by Royal Philips Electronics N.V. CD-i also refers to the multimedia Compact Disc standard used by the CD-i console, also known as Green Book, which was developed by Philips and Sony... |
570,000 |
Handheld systems
The first handheld game consoleHandheld game console
A handheld game console is a lightweight, portable electronic device with a built-in screen, game controls and speakers. Handheld game consoles are run on machines of small size allowing people to carry them and play them at any time or place...
released in the fourth generation was the Game Boy
Game Boy
The , is an 8-bit handheld video game device developed and manufactured by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on , in North America in , and in Europe on...
, on April 21, 1989. It went on to dominate handheld sales by an extremely large margin, despite featuring a monochrome screen while all three of its leading competitors had color. Three major franchises made their debut on the Game Boy: Tetris, the Game Boy's killer application
Killer application
A killer application , in the jargon of marketing teams, has been used to refer to any computer program that is so necessary or desirable that it proves the core value of some larger technology, such as computer hardware, gaming console, software, or an operating system...
; Pokémon
Pokémon
is a media franchise published and owned by the video game company Nintendo and created by Satoshi Tajiri in 1996. Originally released as a pair of interlinkable Game Boy role-playing video games developed by Game Freak, Pokémon has since become the second most successful and lucrative video...
; and Kirby
Kirby (series)
The series is a fantasy video game series developed by HAL Laboratory and Nintendo, and produced by Nintendo. The gameplay of a majority of the games in the series consists mainly of action, platform and puzzle-solving elements...
.
The Atari Lynx, included color graphics, a backlight, and networking capabilities, but its comparatively short battery life, high price, and weak games library made it one of the worst-selling handheld game systems of all time, with less than 500,000 units sold.
The third major handheld of the fourth generation was the Sega Game Gear
Sega Game Gear
The was Sega's first handheld game console. It was the third commercially available color handheld console, after the Atari Lynx and the TurboExpress....
. It featured graphics capabilities comparable to the Master System, but it also inherited the same shortcomings as the Lynx. While it sold more than ten times as many units as the Lynx, its bulky design and low battery life caused it to be pushed to the sidelines.
Other handheld consoles released during the fourth generation included the TurboExpress
TurboExpress
The TurboExpress or PC Engine GT in Japan was a portable version of the TurboGrafx-16/PC Engine , released by NEC in 1990 for $249.99 .It was the most advanced handheld of its time and could play all the TurboGrafx-16's games The TurboExpress or PC Engine GT (Game Tank) in Japan was a portable...
, a handheld version of the TurboGrafx-16 released by NEC in 1990, and the Game Boy Pocket, an improved model of the Game Boy released about two years before the debut of the Game Boy Color
Game Boy Color
The is Nintendo's successor to the 8-bit Game Boy handheld game console, and was released on October 21, 1998 in Japan, November 19, 1998 in North America, November 23, 1998 in Europe and November 27, 1998 in the United Kingdom. It features a color screen and is slightly thicker and taller than...
. While the TurboExpress was another early pioneer of color handheld gaming technology and had the added benefit of using the same game cartridges or 'HuCards' as the TurboGrafx16, it had even lower battery life than the Lynx and Game Gear - about three hours on six AA batteries - selling only 1.5 million units.
Comparison
| Console | Game Boy Game Boy The , is an 8-bit handheld video game device developed and manufactured by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on , in North America in , and in Europe on... |
Atari Lynx | Sega Game Gear Sega Game Gear The was Sega's first handheld game console. It was the third commercially available color handheld console, after the Atari Lynx and the TurboExpress.... |
TurboExpress TurboExpress The TurboExpress or PC Engine GT in Japan was a portable version of the TurboGrafx-16/PC Engine , released by NEC in 1990 for $249.99 .It was the most advanced handheld of its time and could play all the TurboGrafx-16's games The TurboExpress or PC Engine GT (Game Tank) in Japan was a portable... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |
|||
| Launch price | ¥12,500 US$89.95 |
US$189.99 | ¥14,500 US$149.99 AUD $155 |
US$299.99 |
| Release date |  April 21, 1989 April 21, 1989 August, 1989 August, 1989 1990 1990 |
 September 1989 September 1989 1990 1990 |
 October 6, 1990 October 6, 1990  1991 1991 1992 1992 |
 November 16, 1990 November 16, 1990 1991 1991 |
| Units sold | 118.69 million (as of December 31, 2009), including Game Boy Color Game Boy Color The is Nintendo's successor to the 8-bit Game Boy handheld game console, and was released on October 21, 1998 in Japan, November 19, 1998 in North America, November 23, 1998 in Europe and November 27, 1998 in the United Kingdom. It features a color screen and is slightly thicker and taller than... units |
less than 500,000 (as of July 30, 2007) | 11 million (as of July 30, 2007) | 1.5 million |
| Media | Cartridge | Cartridge | Cartridge | Datacard |
| Best-selling games | Tetris Tetris (Game Boy) Tetris is a puzzle video game that was included as a pack-in title with the Game Boy at the handheld's release in 1989. It is a portable version of Alexey Pajitnov's Tetris. It was the first game compatible with the Game Boy Game Link Cable, a pack-in accessory that allowed two Game Boys to link... , 35 million (pack-in Pack-in game - Characteristics :Pack-in games are intended to be system-selling games that make good use of the positive features of a given system. Sometimes a pack-in game will be changed to a more popular game, or another game will be added, along with the original pack-in, if it is perceived that a newer... / separately). Pokémon Red, Blue, and Green Pokémon Red and Blue Pokémon Red Version and Blue Version, originally released in Japan as , are role-playing games developed by Game Freak and published by Nintendo for the Game Boy. They are the first installments to the Pokémon series. They were first released in Japan in 1996 as Red and Green, with Blue being... , approximately 20.08 million combined (in Japan and the US) (details). |
Unknown | Sonic the Hedgehog 2 Sonic the Hedgehog 2 (8-bit) Sonic the Hedgehog 2 is a 8-bit 1992 side-scrolling platform handheld console video game developed by Aspect Co., Ltd. and released by Sega for their Master System and Game Gear formats. The Master System version was released in Europe on October 16, 1992... |
Bonk's Adventure |
| Backward compatibility Backward compatibility In the context of telecommunications and computing, a device or technology is said to be backward or downward compatible if it can work with input generated by an older device... |
Original Cartridges compatible with later models | None | Sega Master System Sega Master System The is a third-generation video game console that was manufactured and released by Sega in 1985 in Japan , 1986 in North America and 1987 in Europe.... (using Cartridge Adapter) |
None |
Software
While many of them originated in the 8-bit era, many of the major franchise titles came of age and solidified their grip on the market in the 16-bit era. MetroidMetroid
is an action-adventure video game, and the first entry in the Metroid series. It was co-developed by Nintendo's Research and Development 1 division and Intelligent Systems, and was released in Japan in August 1986, in North America in August 1987, and in Europe in January 1988...
, Zelda
The Legend of Zelda series
, occasionally called Legend of Zelda or simply Zelda, is a high fantasy action-adventure video game series created by Japanese game designers Shigeru Miyamoto and Takashi Tezuka. It is developed and published by Nintendo, with some portable installments outsourced to Flagship/Capcom, Vanpool, and...
, Star Fox, Kirby
Kirby (series)
The series is a fantasy video game series developed by HAL Laboratory and Nintendo, and produced by Nintendo. The gameplay of a majority of the games in the series consists mainly of action, platform and puzzle-solving elements...
, Dragon Quest
Dragon Quest
, published as Dragon Warrior in North America until 2005,Due to the inconsistent usage by sources since Square Enix obtained the naming rights to Dragon Quest in North America. Dragon Quest has been used by sources to refer to games released solely under the Dragon Warrior titles...
, Final Fantasy
Final Fantasy
is a media franchise created by Hironobu Sakaguchi, and is developed and owned by Square Enix . The franchise centers on a series of fantasy and science-fantasy role-playing video games , but includes motion pictures, anime, printed media, and other merchandise...
, Seiken Densetsu
Seiken Densetsu
The Mana series, known in Japan as , is a medieval-fantasy action role-playing game series from Square Enix, created by Koichi Ishii. The series began as a handheld side story to Square's flagship franchise Final Fantasy, though most Final Fantasy-inspired elements were subsequently dropped,...
(Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana is an action role-playing game for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System developed and published by Square in 1993. The game was re-released for the Wii's Virtual Console in 2008, and was ported to Japanese mobile phones in 2009...
), Sonic the Hedgehog
Sonic the Hedgehog (16-bit)
is a seminal 16-bit 1991 platform video game developed in Japan by Sega and published for the Sega Genesis. It is the first installment in Sega's flagship Sonic the Hedgehog video game series and the first title developed by Sonic Team. The game was released in 1991 in North America, Europe, and...
, Donkey Kong, Street Fighter, Mortal Kombat
Mortal Kombat (series)
Mortal Kombat, commonly abbreviated MK, is a science fantasy series of fighting games created by Ed Boon and John Tobias. The first four renditions and their updates were developed by Midway Games and initially released on arcade machines. The arcade titles were later picked up by Acclaim...
, Mega Man X
Mega Man X series
The Mega Man X series is the second Mega Man franchise released by Capcom. It debuted December 17, 1993 in Japan on the Super NES/Super Famicom and spawned sequels on several systems, with the PC platform notably having the most releases within the series...
, and many others had either their first releases or some of their most popular titles during the 16-bit era.
Sonic the Hedgehog
Sonic the Hedgehog (16-bit)
is a seminal 16-bit 1991 platform video game developed in Japan by Sega and published for the Sega Genesis. It is the first installment in Sega's flagship Sonic the Hedgehog video game series and the first title developed by Sonic Team. The game was released in 1991 in North America, Europe, and...
was Sega
Sega
, usually styled as SEGA, is a multinational video game software developer and an arcade software and hardware development company headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo, Japan, with various offices around the world...
's bid to compete head-to head with Nintendo's Mario franchise. Debuting in 1991, Sega's marketing of the Sonic franchise was key to Sega's success in the video game market during the early years of this generation. Though a critical and commercial success, Sonic the Hedgehog and its sequels were never able to surpass Mario in popularity.
Metroid II was released for the Game Boy and Super Metroid
Super Metroid
, also known as Metroid 3, is an action-adventure video game and the third game in the Metroid series. It was designed by Nintendo Research & Development 1, programmed by Intelligent Systems, and published by Nintendo for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game console...
was released in 1994 on a comparatively large 24 megabit
Megabit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix mega is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 106 , and therefore...
cartridge for the SNES. Super Metroid still is regarded by many gaming organizations as one of the "best games of all time."
The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past
The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past
The Legend of Zelda: A Link to the Past, known as in Japan, is an action-adventure video game developed and published by Nintendo for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game console, and the third installment in The Legend of Zelda series. It was first released in Japan in 1991, and was...
, courted popularity that was larger than that of its predecessors on the NES. It was one of the few action-adventures to be released early in the SNES's lifecycle. Zelda II
Zelda II: The Adventure of Link
Zelda II: The Adventure of Link, released as in Japan and often mistakenly called The Adventures of Link, is an action role-playing video game with platforming elements. The second installment in The Legend of Zelda series, it was developed and published by Nintendo for the Nintendo Entertainment...
on the NES had been mostly action-based and was side-scrolling, while A Link to the Past drew more inspiration from the original Zelda game with its top-down adventure format.
Dragon Quest V
Dragon Quest V
, known as Dragon Quest: The Hand of the Heavenly Bride in Europe, is a console role-playing game and the fifth installment in the Dragon Quest video game series...
and VI
Dragon Quest VI
, Dragon Quest VI: Realms of Reverie in Europe, is a console role-playing game developed by Heartbeat and published by Enix for the Super Famicom as a part of the Dragon Quest series. It is the last Dragon Quest game in the Zenithia trilogy. It was released on December 9, 1995 in Japan...
were released on the Japanese Super Famicom, as well as remakes of the first three games originally released for the NES and a dungeon crawler spin-off: Torneko's Great Adventure, which started Chun Soft's popular Fushigi no Dungeon
Fushigi no Dungeon
is a series of roguelike video games, most of which were developed by Chunsoft, but with select titles in the series developed by other companies with permission from Chunsoft to use the name...
series.
Star Fox was the first SNES game to feature the Super FX
Super FX
The Super FX is a coprocessor chip used in select Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game cartridges. This custom-made RISC processor was typically programmed to act like a graphics accelerator chip that would draw polygons to a frame buffer in the RAM that sat adjacent to it...
chip.
Final Fantasy V
Final Fantasy V
is a medieval-fantasy role-playing video game developed and published by Square in 1992 as a part of the Final Fantasy series. The game first appeared only in Japan on Nintendo's Super Famicom . It has been ported with minor differences to Sony's PlayStation and Nintendo's Game Boy Advance...
was released only in Japan, while Final Fantasy IV
Final Fantasy IV
is a role-playing video game developed and published by Square in 1991 as a part of the Final Fantasy series. The game was originally released for the Super Famicom in Japan and has since then been rereleased for many other platforms with varying modifications. An enhanced remake with 3D graphics...
and Final Fantasy VI
Final Fantasy VI
is a role-playing video game developed and published by Square , released in 1994 for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System as a part of the Final Fantasy series. Set in a fantasy world with a technology level equivalent to that of the Second Industrial Revolution, the game's story focuses on a...
were released in North America with their original numeration shifted. While the series was very successful in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
early on, it was not until the release of Final Fantasy VII
Final Fantasy VII
is a role-playing video game developed by Square and published by Sony Computer Entertainment as the seventh installment in the Final Fantasy series. It was originally released in 1997 for the Sony PlayStation and was re-released in 1998 for Microsoft Windows-based personal computers and in 2009...
on the PlayStation that it reached blockbuster status outside Japan.
Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana
Secret of Mana is an action role-playing game for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System developed and published by Square in 1993. The game was re-released for the Wii's Virtual Console in 2008, and was ported to Japanese mobile phones in 2009...
reintroduced the Seiken Densetsu series, originally conceived as a Final Fantasy spin-off
Spin-off (media)
In media, a spin-off is a radio program, television program, video game, or any narrative work, derived from one or more already existing works, that focuses, in particular, in more detail on one aspect of that original work...
, to Europe and North America.
Street Fighter II
Street Fighter II
is a competitive fighting game originally released for the arcades in . It is the arcade sequel to the original Street Fighter released in and was Capcom's fourteenth title that ran on the CP System arcade hardware...
, a port of the arcade original to the SNES, was the second game in the series to produce a lasting fanbase and set many of the trends seen in fighting games today, most notably its colorful selection of playable fighters from different countries across the globe. As of 2008, it is Capcom
Capcom
is a Japanese developer and publisher of video games, known for creating multi-million-selling franchises such as Devil May Cry, Chaos Legion, Street Fighter, Mega Man and Resident Evil. Capcom developed and published Bionic Commando, Lost Planet and Dark Void too, but they are less known. Its...
's best-selling consumer game of all time.
Phantasy Star
Phantasy Star
is the first installment in Sega's renowned series of the same name. It was released for the Sega Master System in Japan on December 20, 1987, and then in North America and Europe in 1988. It is considered one of the pioneers amongst console role-playing games, both for its advanced graphics...
is Sega's RPG franchise that was established 1987 on the Sega Master System. It was the first console RPG to reach Europe; almost a decade before Final Fantasy VII
Final Fantasy VII
is a role-playing video game developed by Square and published by Sony Computer Entertainment as the seventh installment in the Final Fantasy series. It was originally released in 1997 for the Sony PlayStation and was re-released in 1998 for Microsoft Windows-based personal computers and in 2009...
. Three sequels were released to the Mega Drive. With its sci-fi theme, the franchise was different from the fantasy-themed Dragon Quest
Dragon Quest
, published as Dragon Warrior in North America until 2005,Due to the inconsistent usage by sources since Square Enix obtained the naming rights to Dragon Quest in North America. Dragon Quest has been used by sources to refer to games released solely under the Dragon Warrior titles...
.
Thunder Force II
Thunder Force II
Thunder Force II is a scrolling shooter developed by Technosoft. It was first released in Japan in 1988 for the Sharp X68000 computer. A year later, it was ported to the Sega Mega Drive/Genesis game console and released in Japan , Europe, and the United States...
, III
Thunder Force III
Thunder Force III is a scrolling shooter game developed by Technosoft. It is the third chapter in the Thunder Force series. It was released in 1990 in Japan, Europe and the United States for the Mega Drive/Genesis game console. During the same year, it was retooled into an arcade game named Thunder...
and IV
Thunder Force IV
Thunder Force IV is a side-scrolling shoot 'em up video game developed by Technosoft as the fourth installment of the Thunder Force series. It was released respectively in July and September 1992 for the Sega Mega Drive/Genesis console in Japan and the United States, and in December of the same...
were all released for the Mega Drive, but the third never reached Europe and the fourth was called Lightening Force: Quest for the Darkstar (sic) in the US.
Seeking to follow the example of the above titles, several more franchises were born during this era. While game sequels were far from uncommon during the 8-bit era and even before, it was at this time that the potential for continuing series games was realized.
Notable CD-i releases included the well-received Burn:Cycle
Burn:Cycle
Burn:Cycle is a 1994 CD-i title that encompasses puzzle play and 3D graphics with live action footage. The game's star, Sol Cutter, is a small-time data thief whose latest steal at the beginning of the game comes with a nasty sting. The Burn:Cycle virus has been implanted in his head and has given...
, Escape from Cyber City (made using re-dubbed clips from Galaxy Express 999
Galaxy Express 999
is a manga written and drawn by Leiji Matsumoto, as well as various anime films and TV series based on it. It is set in a space-faring, high-tech future in which humans have learned how to transfer their minds into mechanical bodies, thus achieving practical immortality.The manga won the...
), and a port of The 7th Guest
The 7th Guest
The 7th Guest, produced by Trilobyte and released by Virgin Games in 1993, is an FMV-based puzzle video game. It was one of the first computer video games to be released only on CD-ROM. The 7th Guest is a horror story told from the unfolding perspective of the player, as an amnesiac...
that was bundled with the system at one time.

