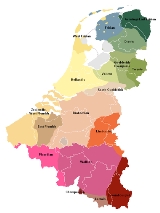
Hollandic
Encyclopedia
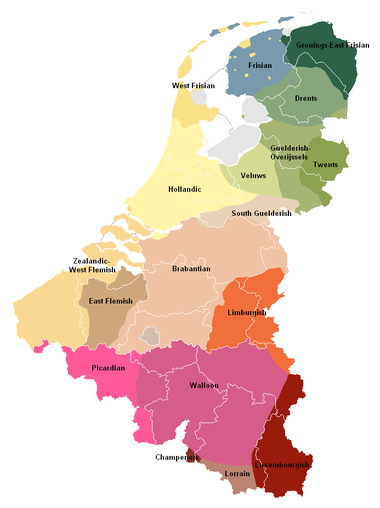
Brabantian
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic , is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant, as well as the institutional Region of...
, the most frequently used dialect of the Dutch language
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
. Other important Low Franconian
Low Franconian languages
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, or Istvaeonic, is a group of several West Germanic languages spoken in the Netherlands, northern Belgium , in the northern department of France, in western Germany , as well as in Suriname, South Africa and Namibia that originally descended from Old Frankish.- The...
language varieties spoken in the same area are Zeelandic
Zeelandic
Zeelandic is a regional language spoken in the Dutch province of Zeeland and on the South Holland island of Goeree-Overflakkee...
, East Flemish
East Flemish
East Flemish is a group of dialects of the Dutch language, which is a Low Franconian language. It is spoken in the province of East Flanders in Belgium, but also spoken in Zeeuws-Vlaanderen in the Netherlands.-Brabantic Expansion:...
, West Flemish
West Flemish
West Flemish , , , Fransch vlaemsch in French Flemish) is a group of dialects or regional language related to Dutch spoken in parts of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France....
and Limburgish.
Development
Originally in the later county of Holland, Old FrisianOld Frisian
Old Frisian is a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries in the area between the Rhine and Weser on the European North Sea coast. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland also spoke Old Frisian but no medieval texts of this area are known...
was spoken. Low Franconian settlers only came in the 12th century and 13th century when Flemish
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
settlers (Frankish speaking) played an important part in draining the swamp
Swamp
A swamp is a wetland with some flooding of large areas of land by shallow bodies of water. A swamp generally has a large number of hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodical inundation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp...
lands between the coast of Holland and Utrecht
Utrecht (city)
Utrecht city and municipality is the capital and most populous city of the Dutch province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, and is the fourth largest city of the Netherlands with a population of 312,634 on 1 Jan 2011.Utrecht's ancient city centre features...
. They mixed with the original inhabitants and a Hollandic dialect was created that was partly Franconian, partly Frisian.
In the 16th century the Dutch language was standardized, the Brabantian Dutch of Antwerp being the most influential. In that time the written language of the county of Holland, then the most urbanised province in Europe, imitated this Brabantish
Brabantian
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic , is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant, as well as the institutional Region of...
standard. During the Eighty Years' War and especially after 1585, the sack of Antwerp
Sack of Antwerp
The sack of Antwerp or the Spanish Fury at Antwerp was an episode of the Eighty Years' War.On 4 November 1576, Spanish tercios began the sack of Antwerp, leading to three days of horror among the population of the city, which was the cultural, economic and financial center of the Netherlands. The...
, and the successes of the Duke of Parma in the 1580s between 100,000 and 200,000 of Brabantish and Flemish Calvinist
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
(and other) refugees and emigrants settled in the cities of Holland proper, which had the result of creating a mixture of their Dutch with the Dutch of the residents before this immigration. This new language perhaps locally destroyed most of the original Hollandic dialects, further diluting the Frisian influences on the Dutch language, and certainly slowed linguistic change through the influence on spoken language of the very conservative written standard.
Distance to standard language
As a result the colloquial Dutch in Holland proper (i.e. the area of the old county), spoken in the urban dialects, is today closer to the standard than any Dutch spoken elsewhere. Traditionally, the Dutch of the city of HaarlemHaarlem
Haarlem is a municipality and a city in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland, the northern half of Holland, which at one time was the most powerful of the seven provinces of the Dutch Republic...
is seen as closest to Standard Dutch. The Dutch in Belgium has diverged more during the last centuries, which is partly because the Dutch standard language had no official status between the 17th and 20th centuries there; the language of administration being French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
.
Shades of other dialects
In FrieslandFriesland
Friesland is a province in the north of the Netherlands and part of the ancient region of Frisia.Until the end of 1996, the province bore Friesland as its official name. In 1997 this Dutch name lost its official status to the Frisian Fryslân...
there are areas and cities where Hollandic is spoken, strongly influenced by Frisian. In the north of North Holland
North Holland
North Holland |West Frisian]]: Noard-Holland) is a province situated on the North Sea in the northwest part of the Netherlands. The provincial capital is Haarlem and its largest city is Amsterdam.-Geography:...
province (especially in the region of West Friesland
West Friesland (historical region)
West Friesland is a historical region in the northern part of the Netherlands. It was located in parts of what now is Noord-Holland and the Waddenzee. The region was bordered by the rivers Vlie and IJ...
), Scheveningen, Katwijk
Katwijk
Katwijk is a coastal municipality and town in the province of South Holland in the western Netherlands. It has a population of 61,292.-Location:...
and other coastal places the original Frisian substratum
Substratum
In linguistics, a stratum or strate is a language that influences, or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum is a language which has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum is the language that has higher power or prestige. Both substratum and superstratum...
of the Hollandic dialect is still an important part of the local West Frisian dialect group.
In the region Zaanstreek ( middle of the province North-Holland) which is an old and traditional region, the old Hollandic dialect can also still be found. This is called: Zaans
Zaans
Zaans is a dialect of Dutch spoken in the Zaan district, which lies north of Amsterdam, in the Dutch province of North-Holland. Zaans is one of the oldest dialects in the country...
. This dialect is without large Frisian influence. Some words are similar due to a little influence of migrating westfrisian farmers in the 13th to 15th century. The subdialect "Zaans" can be seen as one of the few (together with Westfries) and oldest original Hollandic dialects. It is also still spoken today. This also goes for the old "Waterlands" dialect, which is still spoken today as well. The town of Volendam is an example of where they still speak their old dialect "Waterlands". Both Zaans and Waterlands are dialects that when they are spoken fluently, they are not understandable for someone who does not come from the that region in North-Holland. However, people who speak Zaans, Westfrisian and Waterlands are able to understand each other better than outsiders. This is because all three dialects use words and sentences that are similar to each other.
On the South Holland
South Holland
South Holland is a province situated on the North Sea in the western part of the Netherlands. The provincial capital is The Hague and its largest city is Rotterdam.South Holland is one of the most densely populated and industrialised areas in the world...
province island of Goeree-Overflakkee
Goeree-Overflakkee
Goeree-Overflakkee is the southernmost delta island of the province of South Holland, Netherlands. It is separated from Voorne-Putten and Hoeksche Waard by the Haringvliet, from the mainland of North Brabant by the Volkerak, and from Schouwen-Duiveland by Lake Grevelingen.From west to east, it...
West Flemish
West Flemish
West Flemish , , , Fransch vlaemsch in French Flemish) is a group of dialects or regional language related to Dutch spoken in parts of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France....
is spoken. In the east and south the Hollandic dialects graduate into more Brabantian forms like the South Guelderish
South Guelderish
South Guelderish refers to a group of dialects of the Dutch language which are spoken along the Nederrijn in the Netherlands and around the city of Cleves in Germany...
. Utrechts-Alblasserwaards, spoken in the area immediately east of the coastal districts, is variously considered a subdialect of Hollandic or a separate dialect.
List of the subdialects
- Amsterdams
- Bildts, Midslands, Stadsfries, and Amelands
- Kennemerlands
- South Hollandic
- Utrechts-Alblasserwards
- Westhoeks
- Westlands
- West FrisianWest Frisian (dialect)The West Frisian dialect is a Dutch dialect spoken in the contemporary West Friesland region , Wieringen, Wieringermeer, the coastal area from Den Helder to Castricum, and the island of Texel. It is a Hollandic Dutch dialect but has affinities to the Frisian language...
- Waterlands and Volendams
- ZaansZaansZaans is a dialect of Dutch spoken in the Zaan district, which lies north of Amsterdam, in the Dutch province of North-Holland. Zaans is one of the oldest dialects in the country...
- Huizers

