
Hydrocodone
Encyclopedia
Hydrocodone or dihydrocodeinone is a semi-synthetic opioid
derived from either of two naturally occurring opiate
s: codeine
and thebaine
. It is an orally active narcotic
analgesic
(pain reliever) and antitussive
(cough suppressant). It is commonly available in tablet, capsule, and syrup form, and is often compounded with other, generally less effective non-opioid compounds such as paracetamol
(also known as acetaminophen) or ibuprofen
, both often added to discourage recreational use (as paracetamol can cause potentially fatal liver toxicity at high doses), and to provide a possible synergy of analgesic effects between hydrocodone and the non-opioid compounds present. The particular niche in which hydrocodone is most commonly used is as an intermediate centrally acting analgesic. Abrupt discontinuation of hydrocodone (Vicodin, Vicodin ES, and Norco) may result in withdrawal symptoms.
and Helene Löwenheim and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on 23 March 1943 for sale in the United States and approved by Health Canada
for sale in Canada under the brand name Hycodan.
Hydrocodone and compounds containing it are marketed, in varying forms, under a number of trademarks, including Vicodin
, Hydrococet, Symtan, Anexsia, Biocodone, Damason-P, Dicodid, Hycodan (or generically Hydromet), Hycomine, Hycet, Lorcet, Lortab, Norco, Novahistex, Hydrovo, Duodin, Kolikodol, Orthoxycol, Panacet, Zydone, Mercodinone, Synkonin, Norgan, Xodol and Hydrokon. Hycodan was the original trade name. The trade name Dicodid was chosen because hydrocodone is the codeine analogue of hydromorphone
(Dilaudid and the naming scheme extended to related drugs like Dihydrin (dihydrocodeine) and Dinarkon (oxycodone). The trade name Vicodin refers to hydrocodone being six times stronger than codeine by mouth, as in the Roman numeral VIcitation needed.
and as an antitussive to treat cough
.
s in the brain
and spinal cord
. It can be taken with or without food as desired. When taken with alcohol, it can intensify drowsiness. It may interact with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, as well as other drugs that cause drowsiness. It is in FDA
pregnancy category
C. Animal reproduction studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus, and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in humans, but potential benefits may warrant use of the drug in pregnant women despite potential risks. In addition, a newborn of a mother taking the medication may exhibit breathing problems or withdrawal symptoms.
Studies have shown hydrocodone is stronger than codeine
but only one-tenth as potent as morphine
at binding to receptors and reported to be only 59% as potent as morphine in analgesic properties. However, in tests conducted on rhesus monkeys, the analgesic potency of hydrocodone was actually found to be higher than that of morphine. Per os hydrocodone has a MEDD factor of .4, meaning that 1 mg of hydrocodone is equivalent to .4 mg of intravenous morphine. However, because of morphine's low oral bioavailability, there is a 1:1 correspondence between orally administered morphine and orally administered hydrocodone.
Hydrocodone can be habit-forming, which leads to physical and psychological dependence, but the potential for addiction varies from individual to individual depending on unique biological differences. Sales and production of this drug have increased significantly in recent years, as have diversion and illicit use. In the U.S., formulations containing more than 15 mg per dosage unit are considered Schedule II drugs, as would any formulation consisting of just hydrocodone alone. Those containing less than or equal to 15 mg per dosage unit in combination with paracetamol or another non-controlled drug are called hydrocodone compounds and are considered Schedule III drugs. Hydrocodone is typically found in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol, aspirin
, ibuprofen
and homatropine methylbromide
. The purpose of the non-controlled drugs in combination is often twofold: 1) To provide increased analgesia via drug synergy. 2) To limit the intake of hydrocodone by causing unpleasant and often unsafe side effects at higher-than-prescribed doses. In the UK, it is listed as a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
. Hydrocodone is not available in pure form in the United States due to a separate regulation, and is always sold with an NSAID
, paracetamol, antihistamine, expectorant, or homatropine. The cough preparation Codiclear DH is the purest US hydrocodone item, containing guaifenesin and small amounts of ethanol
as active ingredients. In Germany and elsewhere, hydrocodone is available as single-active-ingredient tablets as Dicodid (by analogy to the original manufacturer's other products Dilaudid and Dinarkon and others) available in 5- and 10-mg strengths.
As with many other opioids, it is quite possible to reduce the amount of hydrocodone needed to stop a certain level of pain by having the patient take the hydrocodone along with one of the medications with analgesic-sparing properties, also known as potentiators. The most common, one of the most effective with hydrocodone, and safest is hydroxyzine
(often marketed under the brand name Vistaril). Orphenadrine
, nefopam
, carisoprodol
, and antihistamines also potentiate most opioids. Especially in the case of carisoprodol, it is imperative that the titration and addition of the potentiator be done under strict supervision of a physician.
Hydrocodone also interacts relatively well with most adjuvant and atypical analgesics used for severe and neuropathic pain such as first-generation anti-depressants, anticholinergics, anticonvulsants, centrally acting stimulants, NMDA antagonists, etc. Hydrocodone can usually be successfully used with duloxetine
(Cymbalta) for neuropathic pain, especially that from diabetic neuropathy, provided that the patient has normal relative and absolute levels of Cytochrome P450-related liver enzymes.
 When sold commercially in the United States, hydrocodone is always combined with another medication. Those combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) are known by various trademark names, such as Vicodin
When sold commercially in the United States, hydrocodone is always combined with another medication. Those combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) are known by various trademark names, such as Vicodin
and Lortab. Hydrocodone also can be combined with aspirin
(e.g., Lortab ASA) and ibuprofen
(e.g., Vicoprofen).
Combining an opioid such as hydrocodone with another analgesic
can increase the effectiveness of the drug without increasing opioid-related side effects (e.g., nausea, constipation, sedation). Another argument for combining hydrocodone with paracetemol (acetaminophen) is that it limits the potential for misuse. As with other opioid analgesics, with a few exceptions, there is no ceiling dose for hydrocodone in users tolerant to its effects; however the hepatotoxicity of the paracetamol it is often combined with begins to manifest itself with doses of around 4,000 mg/day.
converts it into hydromorphone
, a more potent opioid.
, by the cytochrome 450 CYP2D6. In the population, there are a group of patients that are less responsive to hydrocodone opioid (~10% of the Caucasian population). Genotyping this group showed that they have inherited polymorphisms in their CYP2D6
allele. These patients are regarded to be poor or intermediate metabolizers of opioid medications and would need higher concentrations of opioids to experience the same therapeutic benefits as a person without the polymorphism. Therefore, these patients are more likely to encounter adverse drug reactions. On the other hand, ultra-rapid metabolizers (up to 7% of Caucasians and up to 30% of Asian and African populations) may have increased toxicity due to rapid conversion.
, cocaine
, amphetamines, methylphenidate
, benzodiazapines, barbiturates, and a number of other medications can have severe adverse reactions including but not limited to heart failure, heart attack, respiratory distress, pulmonary failure, liver or kidney failure, jaundice, amnesia, seizures, blackouts, and coma. Also, hydrocodone can cause false indications on blood and urinalysis testing for morphine, codeine, hydromorphone and cocaine depending on usage and dosing. Generally this effect is only present when doses are taken for long periods of time, and the effect ceases after cessation of use. It isn't a false positive if the test is designed to detect opiates.
Alcohol
There are serious health risks posed by concurrently consuming alcohol with hydrocodone compounds.
The most common medication compounded with hydrocodone is paracetamol (acetaminophen), which is metabolized solely by the liver. Therefore the risk of fatal overdose due to hepatotoxicity
can occur with significantly lower levels of paracetamol when mixed with ethanol. Also the mixture can potentially cause serious damage to the liver, kidneys, and stomach wall. Paracetamol may increase the potential for coma, respiratory problems, and can damage the CNS.
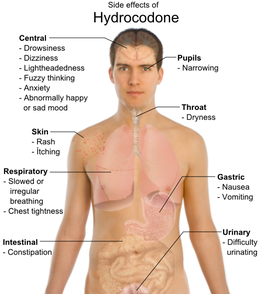 Common side effects
Common side effects
include dizziness
, itching, lightheadedness
, nausea
, sweating
, drowsiness
, constipation
, vomiting, and euphoria
. Vomiting in some patients is so severe that hospitalization is required, although this can be due to alcohol consumption before taking the medication. Some less common side effects are allergic reaction
, blood
disorders, changes in mood, racing heartbeat, mental fogginess, anxiety
, lethargy, difficulty urinating
, spasm
of the ureter
, irregular or depressed respiration
, and rash
.
Hydrocodone in particular, and the -codone family of opioids in general, have been shown to have a liability to cause long term hearing loss over periods of use, though these actual findings are quite rare.
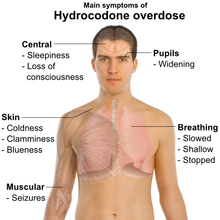 Symptoms of hydrocodone overdose
Symptoms of hydrocodone overdose
include respiratory depression; extreme somnolence
; blue, clammy, or cold skin; narrowed or widened pupils; bradycardia
; coma; seizures; cardiac arrest
; and death.
Daily consumption of hydrocodone should not exceed 40 milligrams in patients not tolerant to opiates. The 2006 Physicians Desk Reference states that Norco 10, containing 10 milligrams of hydrocodone and 325 mg of paracetamol can be taken at a dosage of up to twelve tablets per day (120 mg of hydrocodone). This restriction is only limited by the fact that twelve tablets, each containing 325 mg of paracetamol, puts the patient right below the 24-hour FDA maximum of 4,000 mg of paracetamol. Some specially compounded products are routinely given to chronic pain patients in doses of up to 180 mg of hydrocodone per day.
Some of the effects of hydrocodone come from the fact that a fraction of it is changed to hydromorphone
in the liver, as is the case with all codeine-based analgesics (codeine
into morphine, dihydrocodeine
into dihydromorphine
, nicocodeine
into nicomorphine
etc.). The percentage can vary based on both other medications taken and inherited metabolic quirks involving the Cytochrome P450 metabolic pathways—some cannot process it at all, whereas a smaller percentage can get even more strength from it than usual. These factors can also cause hydrocodone and related drugs to have a threshold effect, cause significant lengthening or shortening of the duration of effects in the absence of tolerance, and increase or decrease the de facto conversion ratio between hydrocodone and other drugs like morphine, hydromorphone, and synthetics like levorphanol
and methadone
.
s including euphoria
, sedation
and somnolence
. Hydrocodone is one of the most common recreational prescription drugs in America, along with oxycodone
. Recreational hydrocodone use is particularly prevalent among teenagers and young adults because of the drug's widespread availability.
Many users of hydrocodone report a sense of satisfaction, especially at higher doses. A number of users also report a warm or pleasant numbing sensation throughout the body, one of the most well known effects of narcotics. Withdrawal effects may include, but are not limited to; severe pain, pins and needles sensation throughout body, sweating, extreme anxiety and restlessness, sneezing, watery eyes, fever, depression, and extreme drug cravings, among others. The presence of paracetamol in hydrocodone-containing products allegedly deters many users, at least in theory, from taking excessive amounts. However, some users will bypass this danger by using cold water extraction
to extract and dispose of a portion of the paracetamol, taking advantage of the water-soluble element of the drug. It is common for users to have liver problems from consuming excessive amounts of paracetamol over a long period of time; taking 10,000 to 15,000 milligrams (10 to 15 grams) of paracetamol in a period of 24 hours typically results in paracetamol overdose and severe hepatotoxicity
; doses in the range of 15,000–20,000 milligrams a day have been reported as fatal. It is this factor that leads many recreational users to use only single-entity opioids such as oxycodone
. One of the major problems today with the illicit use of hydrocodone, especially in younger populations, is that users may not be aware that hydrocodone pills contain paracetamol.
In Belgium, hydrocodone is no longer available for medical use.
Luxembourg
In Luxembourg, hydrocodone is available by prescription under name Biocodone. Prescriptions are more commonly given for use as a cough suppressant (antitussive) rather than for pain relief (analgesic).
Germany
In Germany, hydrocodone is available as single-active-ingredient tablets as Dicodid (by analogy to the original manufacturer's other products Dilaudid and Dinarkon and others) available in 5- and 10-mg strengths. Hydrocodone is listed under the Betäubungsmittelgesetz
as a Suchtgift in the same category as morphine.
Austria
Hydrocodone is regulated in the same fashion as in Germany under the Austrian Suchtmittelgesetz
; since 2002 it has been available in the form of German products and those produced elsewhere in the European Union under Article 76 of the Schengen Treaty—prior to this, no Austrian companies produced hydrocodone products, with dihydrocodeine
and nicomorphine
being more commonly used for the same levels of pain and the former for coughing.
The Netherlands
In the Netherlands, hydrocodone is not available for medical use and is classified as a List 1 drug under the Opium Law
.
United Kingdom
In the UK, hydrocodone is not available for medical use and is listed as a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
. Various formulations of dihydrocodeine
, a weaker opioid, are frequently used as an alternative for the aforementioned indications of hydrocodone use.
United States
Under the Controlled Substances Act
(CSA) hydrocodone is listed as both a Schedule II and Schedule III substance depending on the formulation.
Hydrocodone was until recently the active antitussive in more than 200 formulations of cough syrups and tablets sold in the United States. In late 2006, the FDA began forcing the recall of many of these formulations due to reports of deaths in infants and children under the age of six. The legal status of drug formulations originally sold between 1938 and 1962—before FDA approval was required—was ambiguous. As a result of FDA enforcement action, 88% of the hydrocodone-containing medications have been removed from the market.
At the present time, doctors, pharmacists, and codeine-sensitive or allergic patients or sensitive to the amounts of histamine released by its metabolites must choose among rapidly dwindling supplies of the Hycodan-Codiclear-Hydromet type syrups, Tussionex—an extended-release suspension similar to the European products Codipertussin (codeine hydrochloride), Paracodin suspension (dihydrocodeine
hydroiodide), Tusscodin (nicocodeine
hydrochloride) and others—and a handful of weak dihydrocodeine
syrups. The low sales volume and Schedule II status of Dilaudid cough syrup predictably leads to under-utilisation of the drug. There are several conflicting views concerning the US availability of cough preparations containing ethylmorphine
(also called dionine or codethyline)—Feco Syrup and its equivalents were first marketed circa 1895 and still in common use in the 1940s and 1950s, and the main ingredient is treated like codeine under the Controlled Substances Act
of 1970.
C-III and higher prescriptions are generally valid for 6 months (including any refills).
In the U.S., hydrocodone is always found in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol
, aspirin
, ibuprofen
and homatropine methylbromide
due to compounding regulations. These combinations are considered C-III substances. The purpose of the non-controlled drugs in combination is often twofold: 1) To provide increased analgesia via drug synergy. 2) To limit the intake of hydrocodone by causing unpleasant and often unsafe side effects at higher-than-prescribed doses (See Below). As stated above, hydrocodone is not available in pure form in the United States due to a separate regulation, and is always sold with an NSAID
, paracetamol, antihistamine, expectorant, or homatropine. The cough preparation Codiclear DH is the purest US hydrocodone item, containing guaifenesin and small amounts of ethanol
as active ingredients.
As of July 2010, the FDA is considering banning some hydrocodone and oxycodone fixed-combination proprietary prescription drugs—based on the paracetamol content and the widespread occurrence of liver problems. FDA action on this suggestion would ostensibly also affect codeine
, dihydrocodeine
, and propoxyphene products such as the Tylenol With Codeine and Panlor series of drugs and Darvocet. An extended-release hydrocodone-only product is apparently close to final approval for marketing in the United States, and single-ingredient tablets of oxycodone and codeine are currently marketed. Mixtures of these drugs with other drugs such as Vicoprofen (hydrocodone & ibuprofen), Combunox (ibuprofen and oxycodone), Synalgos DC (aspirin and dihydrocodeine), and the Empirin With Codeine series are also currently available. Presently it is the most prescribed drug in the USA. In 2010 131.2 million prescriptions of Hydrocodone (combined with acetaminophen) were made.
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
derived from either of two naturally occurring opiate
Opiate
In medicine, the term opiate describes any of the narcotic opioid alkaloids found as natural products in the opium poppy plant.-Overview:Opiates are so named because they are constituents or derivatives of constituents found in opium, which is processed from the latex sap of the opium poppy,...
s: codeine
Codeine
Codeine or 3-methylmorphine is an opiate used for its analgesic, antitussive, and antidiarrheal properties...
and thebaine
Thebaine
Thebaine , its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai, an ancient city in Upper Egypt, is an opiate alkaloid. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects, causing convulsions similar to strychnine...
. It is an orally active narcotic
Narcotic
The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with any sleep-inducing properties. In the United States of America it has since become associated with opioids, commonly morphine and heroin and their derivatives, such as hydrocodone. The term is, today, imprecisely...
analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
(pain reliever) and antitussive
Cough medicine
A cough medicine is a medicinal drug used in an attempt to treat coughing and related conditions. For dry coughs, treatment with cough suppressants may be attempted to suppress the body's urge to cough...
(cough suppressant). It is commonly available in tablet, capsule, and syrup form, and is often compounded with other, generally less effective non-opioid compounds such as paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
(also known as acetaminophen) or ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
, both often added to discourage recreational use (as paracetamol can cause potentially fatal liver toxicity at high doses), and to provide a possible synergy of analgesic effects between hydrocodone and the non-opioid compounds present. The particular niche in which hydrocodone is most commonly used is as an intermediate centrally acting analgesic. Abrupt discontinuation of hydrocodone (Vicodin, Vicodin ES, and Norco) may result in withdrawal symptoms.
History
Hydrocodone was first synthesized in Germany in 1920 by Carl MannichCarl Mannich
Carl Ulrich Franz Mannich was a German Chemist. From 1927 to 1943 he was Professor for pharmaceutical chemistry at the University of Berlin...
and Helene Löwenheim and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on 23 March 1943 for sale in the United States and approved by Health Canada
Health Canada
Health Canada is the department of the government of Canada with responsibility for national public health.The current Minister of Health is Leona Aglukkaq, a Conservative Member of Parliament appointed to the position by Prime Minister Stephen Harper.-Branches, regions and agencies:Health Canada...
for sale in Canada under the brand name Hycodan.
Hydrocodone and compounds containing it are marketed, in varying forms, under a number of trademarks, including Vicodin
Vicodin
Hydrocodone/paracetamol is a combination of two analgesic products hydrocodone and paracetamol used to relieve moderate to severe pain...
, Hydrococet, Symtan, Anexsia, Biocodone, Damason-P, Dicodid, Hycodan (or generically Hydromet), Hycomine, Hycet, Lorcet, Lortab, Norco, Novahistex, Hydrovo, Duodin, Kolikodol, Orthoxycol, Panacet, Zydone, Mercodinone, Synkonin, Norgan, Xodol and Hydrokon. Hycodan was the original trade name. The trade name Dicodid was chosen because hydrocodone is the codeine analogue of hydromorphone
Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, a more common synonym for dihydromorphinone, commonly a hydrochloride is a very potent centrally-acting analgesic drug of the opioid class. It is a derivative of morphine, to be specific, a hydrogenated ketone thereof and, therefore, a semi-synthetic drug...
(Dilaudid and the naming scheme extended to related drugs like Dihydrin (dihydrocodeine) and Dinarkon (oxycodone). The trade name Vicodin refers to hydrocodone being six times stronger than codeine by mouth, as in the Roman numeral VIcitation needed.
Medical uses
Hydrocodone is used to treat moderate to severe painPain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
and as an antitussive to treat cough
Cough
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
.
Pharmacology
As a narcotic, hydrocodone relieves pain by binding to opioid receptorOpioid receptor
Opioid receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors...
s in the brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
and spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
. It can be taken with or without food as desired. When taken with alcohol, it can intensify drowsiness. It may interact with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, as well as other drugs that cause drowsiness. It is in FDA
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
pregnancy category
Pregnancy category
The pregnancy category of a pharmaceutical agent is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does not include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites that are present in breast...
C. Animal reproduction studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus, and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in humans, but potential benefits may warrant use of the drug in pregnant women despite potential risks. In addition, a newborn of a mother taking the medication may exhibit breathing problems or withdrawal symptoms.
Studies have shown hydrocodone is stronger than codeine
Codeine
Codeine or 3-methylmorphine is an opiate used for its analgesic, antitussive, and antidiarrheal properties...
but only one-tenth as potent as morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
at binding to receptors and reported to be only 59% as potent as morphine in analgesic properties. However, in tests conducted on rhesus monkeys, the analgesic potency of hydrocodone was actually found to be higher than that of morphine. Per os hydrocodone has a MEDD factor of .4, meaning that 1 mg of hydrocodone is equivalent to .4 mg of intravenous morphine. However, because of morphine's low oral bioavailability, there is a 1:1 correspondence between orally administered morphine and orally administered hydrocodone.
Hydrocodone can be habit-forming, which leads to physical and psychological dependence, but the potential for addiction varies from individual to individual depending on unique biological differences. Sales and production of this drug have increased significantly in recent years, as have diversion and illicit use. In the U.S., formulations containing more than 15 mg per dosage unit are considered Schedule II drugs, as would any formulation consisting of just hydrocodone alone. Those containing less than or equal to 15 mg per dosage unit in combination with paracetamol or another non-controlled drug are called hydrocodone compounds and are considered Schedule III drugs. Hydrocodone is typically found in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol, aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
, ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
and homatropine methylbromide
Homatropine
Homatropine is an anticholinergic medication that inhibits muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and thus the parasympathetic nervous system...
. The purpose of the non-controlled drugs in combination is often twofold: 1) To provide increased analgesia via drug synergy. 2) To limit the intake of hydrocodone by causing unpleasant and often unsafe side effects at higher-than-prescribed doses. In the UK, it is listed as a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of Parliament which represents UK action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic...
. Hydrocodone is not available in pure form in the United States due to a separate regulation, and is always sold with an NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
, paracetamol, antihistamine, expectorant, or homatropine. The cough preparation Codiclear DH is the purest US hydrocodone item, containing guaifenesin and small amounts of ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
as active ingredients. In Germany and elsewhere, hydrocodone is available as single-active-ingredient tablets as Dicodid (by analogy to the original manufacturer's other products Dilaudid and Dinarkon and others) available in 5- and 10-mg strengths.
As with many other opioids, it is quite possible to reduce the amount of hydrocodone needed to stop a certain level of pain by having the patient take the hydrocodone along with one of the medications with analgesic-sparing properties, also known as potentiators. The most common, one of the most effective with hydrocodone, and safest is hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine is a first-generation antihistamine of the diphenylmethane and piperazine classes. It was first synthesized by Union Chimique Belge in 1956 and was marketed by Pfizer in the United States later the same year, and is still in widespread use today....
(often marketed under the brand name Vistaril). Orphenadrine
Orphenadrine
Orphenadrine is an anticholinergic drug of the ethanolamine antihistamine class with prominent CNS and peripheral actions used to treat painful muscle spasms, other similar conditions, as well as the treatment...
, nefopam
Nefopam
Nefopam is a centrally-acting but non-opioid analgesic drug of the benzoxazocine chemical class which was developed by Riker Laboratories in the 1960s. It is widely used, mainly in European countries, for the relief of moderate to severe pain as an alternative to opioid analgesic drugs...
, carisoprodol
Carisoprodol
Carisoprodol is a centrally-acting skeletal muscle relaxant. Carisoprodol is slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol, chloroform and acetone. The drug's solubility is practically independent of pH. Carisoprodol is manufactured and marketed in the United States by Meda Pharmaceuticals...
, and antihistamines also potentiate most opioids. Especially in the case of carisoprodol, it is imperative that the titration and addition of the potentiator be done under strict supervision of a physician.
Hydrocodone also interacts relatively well with most adjuvant and atypical analgesics used for severe and neuropathic pain such as first-generation anti-depressants, anticholinergics, anticonvulsants, centrally acting stimulants, NMDA antagonists, etc. Hydrocodone can usually be successfully used with duloxetine
Duloxetine
Duloxetine is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor manufactured and marketed by Eli Lilly. It is effective for major depressive disorder and has been shown to be as effective as venlafaxine for generalized anxiety disorder...
(Cymbalta) for neuropathic pain, especially that from diabetic neuropathy, provided that the patient has normal relative and absolute levels of Cytochrome P450-related liver enzymes.
Compounds

Vicodin
Hydrocodone/paracetamol is a combination of two analgesic products hydrocodone and paracetamol used to relieve moderate to severe pain...
and Lortab. Hydrocodone also can be combined with aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
(e.g., Lortab ASA) and ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
(e.g., Vicoprofen).
Combining an opioid such as hydrocodone with another analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
can increase the effectiveness of the drug without increasing opioid-related side effects (e.g., nausea, constipation, sedation). Another argument for combining hydrocodone with paracetemol (acetaminophen) is that it limits the potential for misuse. As with other opioid analgesics, with a few exceptions, there is no ceiling dose for hydrocodone in users tolerant to its effects; however the hepatotoxicity of the paracetamol it is often combined with begins to manifest itself with doses of around 4,000 mg/day.
Pharmacokinetics
Hydrocodone is biotransformed by the liver into several metabolites, and has a serum half-life that averages 3.8 hours. The hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2D6CYP2D6
Cytochrome P450 2D6 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. Also, many substances are bioactivated by CYP2D6 to form their active compounds...
converts it into hydromorphone
Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, a more common synonym for dihydromorphinone, commonly a hydrochloride is a very potent centrally-acting analgesic drug of the opioid class. It is a derivative of morphine, to be specific, a hydrogenated ketone thereof and, therefore, a semi-synthetic drug...
, a more potent opioid.
Pharmacogenomics
Analgesic effect by hydrocodone is highly dependent on metabolism to O-demethylated morphine, hydromorphoneHydromorphone
Hydromorphone, a more common synonym for dihydromorphinone, commonly a hydrochloride is a very potent centrally-acting analgesic drug of the opioid class. It is a derivative of morphine, to be specific, a hydrogenated ketone thereof and, therefore, a semi-synthetic drug...
, by the cytochrome 450 CYP2D6. In the population, there are a group of patients that are less responsive to hydrocodone opioid (~10% of the Caucasian population). Genotyping this group showed that they have inherited polymorphisms in their CYP2D6
CYP2D6
Cytochrome P450 2D6 , a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. Also, many substances are bioactivated by CYP2D6 to form their active compounds...
allele. These patients are regarded to be poor or intermediate metabolizers of opioid medications and would need higher concentrations of opioids to experience the same therapeutic benefits as a person without the polymorphism. Therefore, these patients are more likely to encounter adverse drug reactions. On the other hand, ultra-rapid metabolizers (up to 7% of Caucasians and up to 30% of Asian and African populations) may have increased toxicity due to rapid conversion.
Contraindications and interactions
Mixing hydrocodone with alcoholAlcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
, cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
, amphetamines, methylphenidate
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is a psychostimulant drug approved for treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and narcolepsy. It may also be prescribed for off-label use in treatment-resistant cases of lethargy, depression, neural insult and obesity...
, benzodiazapines, barbiturates, and a number of other medications can have severe adverse reactions including but not limited to heart failure, heart attack, respiratory distress, pulmonary failure, liver or kidney failure, jaundice, amnesia, seizures, blackouts, and coma. Also, hydrocodone can cause false indications on blood and urinalysis testing for morphine, codeine, hydromorphone and cocaine depending on usage and dosing. Generally this effect is only present when doses are taken for long periods of time, and the effect ceases after cessation of use. It isn't a false positive if the test is designed to detect opiates.
Alcohol
There are serious health risks posed by concurrently consuming alcohol with hydrocodone compounds.
The most common medication compounded with hydrocodone is paracetamol (acetaminophen), which is metabolized solely by the liver. Therefore the risk of fatal overdose due to hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure...
can occur with significantly lower levels of paracetamol when mixed with ethanol. Also the mixture can potentially cause serious damage to the liver, kidneys, and stomach wall. Paracetamol may increase the potential for coma, respiratory problems, and can damage the CNS.
Adverse effects

Adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
include dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness refers to an impairment in spatial perception and stability. The term is somewhat imprecise. It can be used to mean vertigo, presyncope, disequilibrium, or a non-specific feeling such as giddiness or foolishness....
, itching, lightheadedness
Lightheadedness
Light-headedness is a common and often unpleasant sensation of dizziness and/or feeling that one may be about to faint, which may be transient, recurrent, or occasionally chronic. In some cases, the individual may feel as though his or her head is weightless. The individual may also feel as...
, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, sweating
Sweating
Perspiration is the production of a fluid consisting primarily of water as well as various dissolved solids , that is excreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals...
, drowsiness
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
, constipation
Constipation
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
, vomiting, and euphoria
Euphoria (emotion)
Euphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of well-being, elation, happiness, ecstasy, excitement and joy...
. Vomiting in some patients is so severe that hospitalization is required, although this can be due to alcohol consumption before taking the medication. Some less common side effects are allergic reaction
Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
, blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
disorders, changes in mood, racing heartbeat, mental fogginess, anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, lethargy, difficulty urinating
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, voiding, peeing, weeing, pissing, and more rarely, emiction, is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. In healthy humans the process of urination is under voluntary control...
, spasm
Spasm
In medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
of the ureter
Ureter
In human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually long and ~3-4 mm in diameter....
, irregular or depressed respiration
Respiration (physiology)
'In physiology, respiration is defined as the transport of oxygen from the outside air to the cells within tissues, and the transport of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction...
, and rash
Rash
A rash is a change of the skin which affects its color, appearance or texture. A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracked or blistered, swell and may be painful. The causes, and...
.
Hydrocodone in particular, and the -codone family of opioids in general, have been shown to have a liability to cause long term hearing loss over periods of use, though these actual findings are quite rare.

Drug overdose
The term drug overdose describes the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced...
include respiratory depression; extreme somnolence
Somnolence
Somnolence is a state of near-sleep, a strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods . It has two distinct meanings, referring both to the usual state preceding falling asleep, and the chronic condition referring to being in that state independent of a circadian rhythm...
; blue, clammy, or cold skin; narrowed or widened pupils; bradycardia
Bradycardia
Bradycardia , in the context of adult medicine, is the resting heart rate of under 60 beats per minute, though it is seldom symptomatic until the rate drops below 50 beat/min. It may cause cardiac arrest in some patients, because those with bradycardia may not be pumping enough oxygen to their heart...
; coma; seizures; cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest, is the cessation of normal circulation of the blood due to failure of the heart to contract effectively...
; and death.
Daily consumption of hydrocodone should not exceed 40 milligrams in patients not tolerant to opiates. The 2006 Physicians Desk Reference states that Norco 10, containing 10 milligrams of hydrocodone and 325 mg of paracetamol can be taken at a dosage of up to twelve tablets per day (120 mg of hydrocodone). This restriction is only limited by the fact that twelve tablets, each containing 325 mg of paracetamol, puts the patient right below the 24-hour FDA maximum of 4,000 mg of paracetamol. Some specially compounded products are routinely given to chronic pain patients in doses of up to 180 mg of hydrocodone per day.
Some of the effects of hydrocodone come from the fact that a fraction of it is changed to hydromorphone
Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, a more common synonym for dihydromorphinone, commonly a hydrochloride is a very potent centrally-acting analgesic drug of the opioid class. It is a derivative of morphine, to be specific, a hydrogenated ketone thereof and, therefore, a semi-synthetic drug...
in the liver, as is the case with all codeine-based analgesics (codeine
Codeine
Codeine or 3-methylmorphine is an opiate used for its analgesic, antitussive, and antidiarrheal properties...
into morphine, dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
into dihydromorphine
Dihydromorphine
Dihydromorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid invented in Germany in 1900. In structure, it is very similar to morphine, the only difference being the reduction of the double bond between positions 7 and 8 in morphine to a single bond...
, nicocodeine
Nicocodeine
Nicocodeine is an opiate derivative, closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine developed as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in the...
into nicomorphine
Nicomorphine
Nicomorphine is the 3,6-dinicotinate ester of morphine. It is a strong opioid agonist analgesic two to three times as potent as morphine with a side effect profile similar to that of dihydromorphine, morphine, and diamorphine. Nicomorphine was patented as Vilan by Lannacher Heilmittel Ges. m.b.H...
etc.). The percentage can vary based on both other medications taken and inherited metabolic quirks involving the Cytochrome P450 metabolic pathways—some cannot process it at all, whereas a smaller percentage can get even more strength from it than usual. These factors can also cause hydrocodone and related drugs to have a threshold effect, cause significant lengthening or shortening of the duration of effects in the absence of tolerance, and increase or decrease the de facto conversion ratio between hydrocodone and other drugs like morphine, hydromorphone, and synthetics like levorphanol
Levorphanol
Levorphanol is an opioid medication used to treat severe pain. It is the levorotatory stereoisomer of the synthetic morphinan and a pure opioid agonist, first described in Germany in 1948 as an orally active morphine-like analgesic...
and methadone
Methadone
Methadone is a synthetic opioid, used medically as an analgesic and a maintenance anti-addictive for use in patients with opioid dependency. It was developed in Germany in 1937...
.
Testosterone
Hydrocodone, along with most other opioids, may also severely decrease testosterone levels in men and may cause menstrual irregularities in women. Short-term use of opioids will usually result in a decrease in testosterone with a subsequent rebound post-cessation. However, chronic use is much more dangerous. In a study on cancer survivors using opioids for chronic pain relief, 90% of the subjects had hypogonadal levels of testosterone. This may occur due to both a negative feedback at both the hypothalamus-pituitary and at the gonadal (testicular) level. This is known as "central hypogonadism". Patients using opioid therapy should be screened for such endocrinological problems periodically through blood tests and inquiry of symptoms, which include loss of libido, erectile dysfunction, anxiety, fatigue, loss of muscle mass, and infertility. Treatment should first consist of opioid rotation. If that does not work, then testosterone replacement should commence.Recreational use
Hydrocodone presents much of the same side-effects as other opioidOpioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
s including euphoria
Euphoria
Euphoria is an emotional and mental state defined as a sense of great elation and well being.Euphoria may also refer to:* Euphoria , a genus of scarab beetles* Euphoria, a genus name previously used for the longan and other trees...
, sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
and somnolence
Somnolence
Somnolence is a state of near-sleep, a strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods . It has two distinct meanings, referring both to the usual state preceding falling asleep, and the chronic condition referring to being in that state independent of a circadian rhythm...
. Hydrocodone is one of the most common recreational prescription drugs in America, along with oxycodone
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic medication synthesized from opium-derived thebaine. It was developed in 1916 in Germany, as one of several new semi-synthetic opioids in an attempt to improve on the existing opioids: morphine, diacetylmorphine , and codeine.Oxycodone oral medications are generally...
. Recreational hydrocodone use is particularly prevalent among teenagers and young adults because of the drug's widespread availability.
Many users of hydrocodone report a sense of satisfaction, especially at higher doses. A number of users also report a warm or pleasant numbing sensation throughout the body, one of the most well known effects of narcotics. Withdrawal effects may include, but are not limited to; severe pain, pins and needles sensation throughout body, sweating, extreme anxiety and restlessness, sneezing, watery eyes, fever, depression, and extreme drug cravings, among others. The presence of paracetamol in hydrocodone-containing products allegedly deters many users, at least in theory, from taking excessive amounts. However, some users will bypass this danger by using cold water extraction
Cold water extraction
Cold water extraction is the process whereby a substance is extracted from a mixture via cold water. It is a type of fractional crystallization....
to extract and dispose of a portion of the paracetamol, taking advantage of the water-soluble element of the drug. It is common for users to have liver problems from consuming excessive amounts of paracetamol over a long period of time; taking 10,000 to 15,000 milligrams (10 to 15 grams) of paracetamol in a period of 24 hours typically results in paracetamol overdose and severe hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure...
; doses in the range of 15,000–20,000 milligrams a day have been reported as fatal. It is this factor that leads many recreational users to use only single-entity opioids such as oxycodone
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic medication synthesized from opium-derived thebaine. It was developed in 1916 in Germany, as one of several new semi-synthetic opioids in an attempt to improve on the existing opioids: morphine, diacetylmorphine , and codeine.Oxycodone oral medications are generally...
. One of the major problems today with the illicit use of hydrocodone, especially in younger populations, is that users may not be aware that hydrocodone pills contain paracetamol.
Detection in body fluids
Hydrocodone may be quantitated in blood, plasma or urine to monitor for misuse, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning or assist in a medicolegal death investigation. Many commercial opiate screening tests cross-react appreciably with hydrocodone and its metabolites, but chromatographic techniques can easily distinguish hydrocodone from other opiates. Blood or plasma hydrocodone concentrations are typically in the 5-30 µg/L range in persons taking the drug therapeutically, 100-200 µg/L in abusers and 0.1-2.0 mg/L in cases of acute fatal overdosage.Regulation
BelgiumIn Belgium, hydrocodone is no longer available for medical use.
Luxembourg
In Luxembourg, hydrocodone is available by prescription under name Biocodone. Prescriptions are more commonly given for use as a cough suppressant (antitussive) rather than for pain relief (analgesic).
Germany
In Germany, hydrocodone is available as single-active-ingredient tablets as Dicodid (by analogy to the original manufacturer's other products Dilaudid and Dinarkon and others) available in 5- and 10-mg strengths. Hydrocodone is listed under the Betäubungsmittelgesetz
Betäubungsmittelgesetz
The Betäubungsmittelgesetz , generally meaning Narcotics Law, is the controlled-substances law of Germany. In common with the Misuse of Drugs Act of 1971 of the United Kingdom and Controlled Substances Acts of the US and Canada, it is a consolidation of prior regulation and an implementation of...
as a Suchtgift in the same category as morphine.
Austria
Hydrocodone is regulated in the same fashion as in Germany under the Austrian Suchtmittelgesetz
Suchtmittelgesetz
The Suchtmittelgesetz is the controlled-substances law of Austria, being passed in its current form after the accession of the country to the European Union...
; since 2002 it has been available in the form of German products and those produced elsewhere in the European Union under Article 76 of the Schengen Treaty—prior to this, no Austrian companies produced hydrocodone products, with dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
and nicomorphine
Nicomorphine
Nicomorphine is the 3,6-dinicotinate ester of morphine. It is a strong opioid agonist analgesic two to three times as potent as morphine with a side effect profile similar to that of dihydromorphine, morphine, and diamorphine. Nicomorphine was patented as Vilan by Lannacher Heilmittel Ges. m.b.H...
being more commonly used for the same levels of pain and the former for coughing.
The Netherlands
In the Netherlands, hydrocodone is not available for medical use and is classified as a List 1 drug under the Opium Law
Opium Law
The Opium Law is the section of the Dutch law which covers nearly all psychotropic drugs. All non-psychotropic, but prescription-only drugs are covered by the Medicine Act.- Origin and history :...
.
United Kingdom
In the UK, hydrocodone is not available for medical use and is listed as a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of Parliament which represents UK action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic...
. Various formulations of dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
, a weaker opioid, are frequently used as an alternative for the aforementioned indications of hydrocodone use.
United States
Under the Controlled Substances Act
Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act was enacted into law by the Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970. The CSA is the federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use and distribution of certain...
(CSA) hydrocodone is listed as both a Schedule II and Schedule III substance depending on the formulation.
- Schedule II lists hydrocodone in pure form and any formulations of combination products containing more than 15 mg hydrocodone per dosage unit.
- Schedule III lists hydrocodone in formulations of combination products containing up to 15 mg hydrocodone per dosage unit.
Hydrocodone was until recently the active antitussive in more than 200 formulations of cough syrups and tablets sold in the United States. In late 2006, the FDA began forcing the recall of many of these formulations due to reports of deaths in infants and children under the age of six. The legal status of drug formulations originally sold between 1938 and 1962—before FDA approval was required—was ambiguous. As a result of FDA enforcement action, 88% of the hydrocodone-containing medications have been removed from the market.
At the present time, doctors, pharmacists, and codeine-sensitive or allergic patients or sensitive to the amounts of histamine released by its metabolites must choose among rapidly dwindling supplies of the Hycodan-Codiclear-Hydromet type syrups, Tussionex—an extended-release suspension similar to the European products Codipertussin (codeine hydrochloride), Paracodin suspension (dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
hydroiodide), Tusscodin (nicocodeine
Nicocodeine
Nicocodeine is an opiate derivative, closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine developed as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in the...
hydrochloride) and others—and a handful of weak dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
syrups. The low sales volume and Schedule II status of Dilaudid cough syrup predictably leads to under-utilisation of the drug. There are several conflicting views concerning the US availability of cough preparations containing ethylmorphine
Ethylmorphine
Ethylmorphine is an opiate narcotic analgesic .Ethylmorphine was invented in Germany at Merck in 1884 and was used as a weaker alternative to heroin for all indications. Chemically, ethylmorphine is a morphine molecule with a -25 group substituted for the aromatic 3- group...
(also called dionine or codethyline)—Feco Syrup and its equivalents were first marketed circa 1895 and still in common use in the 1940s and 1950s, and the main ingredient is treated like codeine under the Controlled Substances Act
Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act was enacted into law by the Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970. The CSA is the federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use and distribution of certain...
of 1970.
C-III and higher prescriptions are generally valid for 6 months (including any refills).
In the U.S., hydrocodone is always found in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
, aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
, ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
and homatropine methylbromide
Homatropine
Homatropine is an anticholinergic medication that inhibits muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and thus the parasympathetic nervous system...
due to compounding regulations. These combinations are considered C-III substances. The purpose of the non-controlled drugs in combination is often twofold: 1) To provide increased analgesia via drug synergy. 2) To limit the intake of hydrocodone by causing unpleasant and often unsafe side effects at higher-than-prescribed doses (See Below). As stated above, hydrocodone is not available in pure form in the United States due to a separate regulation, and is always sold with an NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
, paracetamol, antihistamine, expectorant, or homatropine. The cough preparation Codiclear DH is the purest US hydrocodone item, containing guaifenesin and small amounts of ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
as active ingredients.
As of July 2010, the FDA is considering banning some hydrocodone and oxycodone fixed-combination proprietary prescription drugs—based on the paracetamol content and the widespread occurrence of liver problems. FDA action on this suggestion would ostensibly also affect codeine
Codeine
Codeine or 3-methylmorphine is an opiate used for its analgesic, antitussive, and antidiarrheal properties...
, dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine, also called DHC, Drocode, Paracodeine and Parzone and known by the brand names of Synalgos DC, Panlor DC, Panlor SS, Contugesic, New Bron Solution-ACE, Huscode, Drocode, Paracodin, Codidol, Didor Continus, Dicogesic, Codhydrine, Dekacodin, DH-Codeine,...
, and propoxyphene products such as the Tylenol With Codeine and Panlor series of drugs and Darvocet. An extended-release hydrocodone-only product is apparently close to final approval for marketing in the United States, and single-ingredient tablets of oxycodone and codeine are currently marketed. Mixtures of these drugs with other drugs such as Vicoprofen (hydrocodone & ibuprofen), Combunox (ibuprofen and oxycodone), Synalgos DC (aspirin and dihydrocodeine), and the Empirin With Codeine series are also currently available. Presently it is the most prescribed drug in the USA. In 2010 131.2 million prescriptions of Hydrocodone (combined with acetaminophen) were made.

